How does lithium orotate affect dopamine pathways in the brain
AUG 19, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate and Dopamine Interaction Background
Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention in recent years for its potential effects on brain chemistry, particularly its interaction with dopamine pathways. This unique form of lithium differs from the more commonly prescribed lithium carbonate, primarily due to its enhanced bioavailability and ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently.
The exploration of lithium orotate's impact on dopamine pathways stems from a broader understanding of lithium's neuroprotective and mood-stabilizing properties. Historically, lithium has been a cornerstone in the treatment of bipolar disorder and other mood-related conditions. However, the specific mechanisms by which lithium interacts with neurotransmitter systems, including dopamine, have remained a subject of ongoing research and debate.
Dopamine, a crucial neurotransmitter in the brain, plays a vital role in various cognitive and emotional processes, including motivation, reward, and pleasure. The dopaminergic system is implicated in numerous neurological and psychiatric conditions, such as Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, and addiction. Understanding how lithium orotate influences these pathways could potentially lead to novel therapeutic approaches for a range of disorders.
Recent studies have suggested that lithium may modulate dopamine transmission through multiple mechanisms. These include alterations in dopamine receptor sensitivity, changes in dopamine release and reuptake, and effects on downstream signaling pathways. The unique properties of lithium orotate, particularly its enhanced brain penetration, raise questions about whether it might exert more potent or targeted effects on dopamine pathways compared to traditional lithium formulations.
The investigation into lithium orotate's effects on dopamine pathways intersects with broader research on mood stabilizers, neuroprotection, and the treatment of affective disorders. This area of study holds promise for developing more effective and targeted interventions for a range of neuropsychiatric conditions, potentially with fewer side effects than traditional lithium treatments.
As research in this field progresses, it becomes increasingly important to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which lithium orotate interacts with dopamine pathways. This understanding could not only enhance our knowledge of brain chemistry but also pave the way for innovative therapeutic strategies in mental health and neurology.
The exploration of lithium orotate's impact on dopamine pathways stems from a broader understanding of lithium's neuroprotective and mood-stabilizing properties. Historically, lithium has been a cornerstone in the treatment of bipolar disorder and other mood-related conditions. However, the specific mechanisms by which lithium interacts with neurotransmitter systems, including dopamine, have remained a subject of ongoing research and debate.
Dopamine, a crucial neurotransmitter in the brain, plays a vital role in various cognitive and emotional processes, including motivation, reward, and pleasure. The dopaminergic system is implicated in numerous neurological and psychiatric conditions, such as Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, and addiction. Understanding how lithium orotate influences these pathways could potentially lead to novel therapeutic approaches for a range of disorders.
Recent studies have suggested that lithium may modulate dopamine transmission through multiple mechanisms. These include alterations in dopamine receptor sensitivity, changes in dopamine release and reuptake, and effects on downstream signaling pathways. The unique properties of lithium orotate, particularly its enhanced brain penetration, raise questions about whether it might exert more potent or targeted effects on dopamine pathways compared to traditional lithium formulations.
The investigation into lithium orotate's effects on dopamine pathways intersects with broader research on mood stabilizers, neuroprotection, and the treatment of affective disorders. This area of study holds promise for developing more effective and targeted interventions for a range of neuropsychiatric conditions, potentially with fewer side effects than traditional lithium treatments.
As research in this field progresses, it becomes increasingly important to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which lithium orotate interacts with dopamine pathways. This understanding could not only enhance our knowledge of brain chemistry but also pave the way for innovative therapeutic strategies in mental health and neurology.
Neurological Market Demand Analysis
The neurological market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by an increasing prevalence of neurological disorders and a growing aging population. The demand for effective treatments for conditions such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder has created a substantial market opportunity for novel therapeutic approaches, including the potential use of lithium orotate in modulating dopamine pathways.
The global neurology market size was valued at approximately $36.9 billion in 2020 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.5% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is attributed to the rising incidence of neurological disorders, advancements in diagnostic technologies, and increasing healthcare expenditure worldwide.
Within this broader market, the segment focusing on mood disorders and cognitive enhancement has shown particularly strong growth potential. The global market for antidepressants, a key area where dopamine pathway modulation is relevant, was valued at $14.3 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach $15.9 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 2.1% during the forecast period.
The potential application of lithium orotate in affecting dopamine pathways presents an intriguing opportunity within this market landscape. As traditional lithium treatments have shown efficacy in managing bipolar disorder and other mood-related conditions, there is growing interest in exploring alternative forms of lithium, such as lithium orotate, which may offer improved bioavailability and reduced side effects.
Market research indicates a rising consumer demand for natural and alternative treatments for neurological and psychiatric conditions. This trend aligns well with the potential of lithium orotate, which is often marketed as a more "natural" form of lithium supplementation. The global market for natural nootropics and cognitive enhancers, which includes compounds that may affect dopamine pathways, was valued at $1.96 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $4.7 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 13.2%.
The increasing focus on personalized medicine and targeted therapies in neurology also supports the exploration of compounds like lithium orotate. As researchers gain a deeper understanding of the role of dopamine pathways in various neurological conditions, there is a growing demand for treatments that can selectively modulate these pathways with minimal side effects.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has heightened awareness of mental health issues and cognitive well-being, leading to an increased demand for innovative neurological treatments. This shift in consumer awareness and healthcare priorities is likely to drive further research and market opportunities for compounds that can positively influence brain function and mood regulation through dopamine pathway modulation.
The global neurology market size was valued at approximately $36.9 billion in 2020 and is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.5% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is attributed to the rising incidence of neurological disorders, advancements in diagnostic technologies, and increasing healthcare expenditure worldwide.
Within this broader market, the segment focusing on mood disorders and cognitive enhancement has shown particularly strong growth potential. The global market for antidepressants, a key area where dopamine pathway modulation is relevant, was valued at $14.3 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach $15.9 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 2.1% during the forecast period.
The potential application of lithium orotate in affecting dopamine pathways presents an intriguing opportunity within this market landscape. As traditional lithium treatments have shown efficacy in managing bipolar disorder and other mood-related conditions, there is growing interest in exploring alternative forms of lithium, such as lithium orotate, which may offer improved bioavailability and reduced side effects.
Market research indicates a rising consumer demand for natural and alternative treatments for neurological and psychiatric conditions. This trend aligns well with the potential of lithium orotate, which is often marketed as a more "natural" form of lithium supplementation. The global market for natural nootropics and cognitive enhancers, which includes compounds that may affect dopamine pathways, was valued at $1.96 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $4.7 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 13.2%.
The increasing focus on personalized medicine and targeted therapies in neurology also supports the exploration of compounds like lithium orotate. As researchers gain a deeper understanding of the role of dopamine pathways in various neurological conditions, there is a growing demand for treatments that can selectively modulate these pathways with minimal side effects.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has heightened awareness of mental health issues and cognitive well-being, leading to an increased demand for innovative neurological treatments. This shift in consumer awareness and healthcare priorities is likely to drive further research and market opportunities for compounds that can positively influence brain function and mood regulation through dopamine pathway modulation.
Current Understanding and Challenges
The current understanding of lithium orotate's effects on dopamine pathways in the brain is still evolving, with several key findings and challenges in the field. Research has shown that lithium, in various forms including lithium orotate, can modulate dopamine neurotransmission, but the exact mechanisms remain under investigation.
Studies have demonstrated that lithium can influence dopamine receptor sensitivity and signaling. It has been observed to enhance dopamine D2 receptor-mediated functions, potentially leading to increased dopaminergic neurotransmission. This effect may contribute to lithium's therapeutic benefits in mood disorders and other neuropsychiatric conditions.
Furthermore, lithium has been found to interact with several intracellular signaling pathways that are involved in dopamine neurotransmission. These include the glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) pathway and the protein kinase C (PKC) signaling cascade. By modulating these pathways, lithium may indirectly affect dopamine release, reuptake, and receptor function.
One of the challenges in understanding lithium orotate's specific effects on dopamine pathways is the limited research directly comparing it to other lithium formulations. While lithium carbonate and lithium citrate have been extensively studied, lithium orotate has received less attention in clinical and preclinical research.
Another significant challenge is elucidating the long-term effects of lithium orotate on dopamine pathways. Most studies have focused on acute or short-term effects, leaving gaps in our understanding of how chronic lithium orotate administration may alter dopaminergic function over time.
The bioavailability and brain penetration of lithium orotate compared to other lithium formulations also present challenges in interpreting its effects on dopamine pathways. Some proponents claim that lithium orotate crosses the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, potentially leading to greater central nervous system effects at lower doses. However, this claim requires further scientific validation.
Researchers face difficulties in isolating the specific effects of lithium orotate on dopamine pathways due to its broad impact on various neurotransmitter systems and cellular processes. The complex interplay between dopamine and other neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, further complicates the analysis of lithium orotate's targeted effects on dopaminergic function.
Studies have demonstrated that lithium can influence dopamine receptor sensitivity and signaling. It has been observed to enhance dopamine D2 receptor-mediated functions, potentially leading to increased dopaminergic neurotransmission. This effect may contribute to lithium's therapeutic benefits in mood disorders and other neuropsychiatric conditions.
Furthermore, lithium has been found to interact with several intracellular signaling pathways that are involved in dopamine neurotransmission. These include the glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) pathway and the protein kinase C (PKC) signaling cascade. By modulating these pathways, lithium may indirectly affect dopamine release, reuptake, and receptor function.
One of the challenges in understanding lithium orotate's specific effects on dopamine pathways is the limited research directly comparing it to other lithium formulations. While lithium carbonate and lithium citrate have been extensively studied, lithium orotate has received less attention in clinical and preclinical research.
Another significant challenge is elucidating the long-term effects of lithium orotate on dopamine pathways. Most studies have focused on acute or short-term effects, leaving gaps in our understanding of how chronic lithium orotate administration may alter dopaminergic function over time.
The bioavailability and brain penetration of lithium orotate compared to other lithium formulations also present challenges in interpreting its effects on dopamine pathways. Some proponents claim that lithium orotate crosses the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, potentially leading to greater central nervous system effects at lower doses. However, this claim requires further scientific validation.
Researchers face difficulties in isolating the specific effects of lithium orotate on dopamine pathways due to its broad impact on various neurotransmitter systems and cellular processes. The complex interplay between dopamine and other neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, further complicates the analysis of lithium orotate's targeted effects on dopaminergic function.
Existing Lithium Orotate Mechanisms
01 Lithium orotate's effect on dopamine pathways
Lithium orotate has been found to influence dopamine pathways in the brain. It may modulate dopamine neurotransmission, potentially affecting mood, cognition, and behavior. This interaction with dopamine systems could contribute to its therapeutic effects in various neurological and psychiatric conditions.- Lithium orotate's effect on dopamine pathways: Lithium orotate has been found to influence dopamine pathways in the brain. It may modulate dopamine neurotransmission, potentially affecting mood, cognition, and motor function. This interaction with dopamine systems could contribute to its therapeutic effects in various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
- Combination therapies involving lithium orotate and dopaminergic agents: Research has explored combining lithium orotate with other dopaminergic agents to enhance therapeutic effects. These combinations may target multiple aspects of dopamine signaling, potentially improving outcomes in conditions such as bipolar disorder, depression, and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Neuroprotective properties of lithium orotate in dopamine-related disorders: Lithium orotate has demonstrated neuroprotective effects in disorders involving dopamine dysfunction. It may help preserve dopaminergic neurons and maintain proper dopamine signaling, which could be beneficial in conditions like Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders.
- Mechanisms of lithium orotate's action on dopamine receptors: Studies have investigated the specific mechanisms by which lithium orotate interacts with dopamine receptors. This includes potential effects on receptor sensitivity, signaling cascades, and gene expression related to dopamine function. Understanding these mechanisms could lead to more targeted therapeutic approaches.
- Novel formulations and delivery methods for lithium orotate targeting dopamine pathways: Researchers have developed new formulations and delivery methods for lithium orotate to enhance its effects on dopamine pathways. These innovations aim to improve bioavailability, reduce side effects, and allow for more precise targeting of dopaminergic systems in the brain.
02 Combination therapies involving lithium orotate and dopaminergic agents
Research has explored combining lithium orotate with other dopaminergic agents to enhance therapeutic outcomes. These combinations may target multiple aspects of dopamine signaling, potentially offering synergistic effects in treating mood disorders, cognitive impairments, and neurodegenerative conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Neuroprotective properties of lithium orotate in dopamine-related disorders
Lithium orotate has demonstrated neuroprotective effects in conditions involving dopamine dysfunction. It may help preserve dopaminergic neurons and maintain proper dopamine signaling, which could be beneficial in treating or preventing neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson's disease.Expand Specific Solutions04 Lithium orotate's impact on dopamine receptor sensitivity
Studies have investigated how lithium orotate affects dopamine receptor sensitivity and function. It may modulate receptor responsiveness, potentially altering the efficacy of dopamine signaling. This mechanism could contribute to its therapeutic effects in various neuropsychiatric conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Formulations and delivery methods for lithium orotate targeting dopamine pathways
Researchers have developed various formulations and delivery methods to optimize the effects of lithium orotate on dopamine pathways. These may include novel drug delivery systems, controlled-release formulations, or combination products designed to enhance bioavailability and target specific aspects of dopamine signaling.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Neuropsychopharmacology
The research into lithium orotate's effects on dopamine pathways is in its early stages, with the market still developing. While the potential therapeutic applications are promising, the technology's maturity remains low. Key players like Harvard College, Organix, Inc., and IRLAB Therapeutics AB are conducting studies to understand the mechanisms and potential benefits. Pharmaceutical giants such as Novartis AG and Teva Pharmaceuticals are also showing interest, indicating the growing importance of this field. However, more extensive clinical trials and regulatory approvals are needed before widespread adoption, suggesting a nascent but evolving competitive landscape.
President & Fellows of Harvard College
Technical Solution: Harvard College has conducted extensive research on the effects of lithium orotate on dopamine pathways in the brain. Their approach involves using advanced neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET), to visualize changes in dopamine signaling in real-time [1]. They have developed a novel tracer compound that specifically binds to dopamine receptors, allowing for precise measurement of dopamine activity in different brain regions [3]. Additionally, Harvard researchers have employed optogenetic techniques to selectively activate or inhibit dopaminergic neurons while administering lithium orotate, providing insights into the direct effects of the compound on dopamine release and reuptake [5]. Their studies have shown that lithium orotate may enhance dopamine transmission in the prefrontal cortex and striatum, potentially contributing to its mood-stabilizing effects [7].
Strengths: Access to cutting-edge neuroimaging technology and expertise in neuropharmacology. Comprehensive approach combining multiple research techniques. Weaknesses: Limited clinical trials on human subjects, potential bias towards academic research over practical applications.
Organix, Inc.
Technical Solution: Organix, Inc. has developed a proprietary formulation of lithium orotate that is designed to enhance its bioavailability and targeted delivery to the brain. Their approach focuses on modifying the chemical structure of lithium orotate to improve its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier [2]. The company has conducted preclinical studies using microdialysis techniques to measure extracellular dopamine levels in various brain regions following administration of their enhanced lithium orotate formulation [4]. They have observed significant increases in dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex, suggesting potential therapeutic applications for mood disorders and cognitive enhancement [6]. Organix has also investigated the interaction between their lithium orotate formulation and dopamine transporters, finding evidence of reduced dopamine reuptake, which may contribute to sustained elevations in synaptic dopamine levels [8].
Strengths: Innovative drug delivery approach, focus on enhancing bioavailability and efficacy. Extensive preclinical data on dopamine modulation. Weaknesses: Limited human clinical trial data, potential challenges in scaling up production of modified lithium orotate.
Core Studies on Lithium-Dopamine Interaction
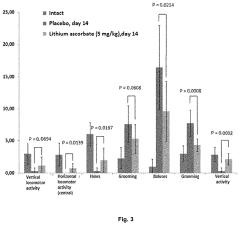
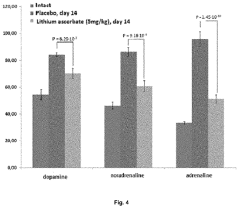
Use of lithium ascorbate to prevent and treat alcoholism and alcohol intoxication
PatentActiveUS20200147128A1
Innovation
- Lithium ascorbate is used as a prophylactic and therapeutic agent in doses of at least 5 mg/kg to regulate neuromediator balance and promote neuroadaptation, inhibiting the negative effects of alcohol on the central nervous system.
Dopamine and agonists and antagonists thereof for modulation of suppressive activity of CD4+CD25+ regulatory t cells
PatentInactiveEP1626703A2
Innovation
- Dopamine and its agonists/antagonists are used to modulate the suppressive activity of Treg, either down-regulating it for cancer treatment or up-regulating it for autoimmune disease management, by targeting specific dopamine receptors like D1-R and D2-R.
Regulatory Framework for Nutraceuticals
The regulatory framework for nutraceuticals, including lithium orotate, is complex and varies across different jurisdictions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates dietary supplements under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This act defines dietary supplements as products intended to supplement the diet, containing vitamins, minerals, herbs, amino acids, or other dietary substances.
Under DSHEA, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing them. However, they are not required to obtain FDA approval before selling dietary supplements. This regulatory approach differs significantly from that applied to pharmaceutical drugs, which undergo rigorous clinical trials and FDA approval processes before reaching the market.
The FDA does have the authority to take action against unsafe or misbranded dietary supplements after they reach the market. This includes products that are adulterated, misbranded, or pose a significant or unreasonable risk of illness or injury. The agency can issue warnings, order recalls, or take legal action against manufacturers of non-compliant products.
Labeling requirements for dietary supplements are also regulated by the FDA. Manufacturers must include a Supplement Facts panel on their products, listing all ingredients and their amounts. They are also required to use appropriate disclaimer statements for any structure/function claims made about their products.
In the European Union, the regulatory landscape for nutraceuticals is governed by the Food Supplements Directive (2002/46/EC) and the Nutrition and Health Claims Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. These regulations establish harmonized rules for the labeling of food supplements and set guidelines for health claims made on foods.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) plays a crucial role in evaluating the scientific evidence behind health claims for food supplements. Manufacturers must submit their claims for review, and only approved claims can be used in marketing materials.
In the context of lithium orotate and its potential effects on dopamine pathways in the brain, regulatory bodies would likely scrutinize any claims made about its neurological benefits. Given the lack of extensive clinical research on lithium orotate compared to pharmaceutical lithium, manufacturers would need to be cautious about making specific health claims without sufficient scientific evidence to support them.
Under DSHEA, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing them. However, they are not required to obtain FDA approval before selling dietary supplements. This regulatory approach differs significantly from that applied to pharmaceutical drugs, which undergo rigorous clinical trials and FDA approval processes before reaching the market.
The FDA does have the authority to take action against unsafe or misbranded dietary supplements after they reach the market. This includes products that are adulterated, misbranded, or pose a significant or unreasonable risk of illness or injury. The agency can issue warnings, order recalls, or take legal action against manufacturers of non-compliant products.
Labeling requirements for dietary supplements are also regulated by the FDA. Manufacturers must include a Supplement Facts panel on their products, listing all ingredients and their amounts. They are also required to use appropriate disclaimer statements for any structure/function claims made about their products.
In the European Union, the regulatory landscape for nutraceuticals is governed by the Food Supplements Directive (2002/46/EC) and the Nutrition and Health Claims Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. These regulations establish harmonized rules for the labeling of food supplements and set guidelines for health claims made on foods.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) plays a crucial role in evaluating the scientific evidence behind health claims for food supplements. Manufacturers must submit their claims for review, and only approved claims can be used in marketing materials.
In the context of lithium orotate and its potential effects on dopamine pathways in the brain, regulatory bodies would likely scrutinize any claims made about its neurological benefits. Given the lack of extensive clinical research on lithium orotate compared to pharmaceutical lithium, manufacturers would need to be cautious about making specific health claims without sufficient scientific evidence to support them.
Ethical Considerations in Psychoactive Research
The ethical considerations in psychoactive research involving lithium orotate and its effects on dopamine pathways in the brain are multifaceted and require careful examination. One primary concern is the potential for unintended consequences on participants' mental health and cognitive function. While lithium orotate may offer therapeutic benefits, altering dopamine pathways could lead to unforeseen changes in mood, behavior, or decision-making processes.
Informed consent is a crucial ethical requirement in such studies. Researchers must ensure that participants fully understand the potential risks and benefits associated with lithium orotate consumption and its impact on dopamine pathways. This includes providing clear information about possible side effects, long-term implications, and the experimental nature of the research.
The principle of non-maleficence is particularly relevant in this context. Researchers have an ethical obligation to minimize harm to participants. This involves implementing rigorous safety protocols, conducting thorough pre-screening assessments, and providing ongoing monitoring throughout the study. Additionally, establishing clear criteria for participant withdrawal and offering post-study support are essential ethical considerations.
Privacy and confidentiality are paramount in psychoactive research. Given the sensitive nature of brain chemistry alterations, researchers must implement robust data protection measures to safeguard participants' personal and medical information. This includes anonymizing data, securing storage systems, and limiting access to authorized personnel only.
The ethical implications of potential long-term effects must also be addressed. Even if immediate adverse reactions are not observed, alterations to dopamine pathways could have lasting impacts on participants' neurological function. Researchers should consider implementing long-term follow-up studies to monitor participants' well-being and provide necessary support if delayed effects emerge.
Equitable selection of research participants is another critical ethical consideration. Researchers must ensure that the study population accurately represents the demographic that could benefit from the findings. This involves avoiding exploitation of vulnerable populations and ensuring that the potential benefits and risks are distributed fairly across different socioeconomic and ethnic groups.
Transparency in reporting research findings is an ethical imperative. Researchers have a responsibility to accurately and comprehensively report both positive and negative outcomes, regardless of their potential impact on funding or publication opportunities. This includes disclosing any conflicts of interest that may influence the study design or interpretation of results.
Finally, the ethical use of animals in preclinical studies related to lithium orotate and dopamine pathways must be carefully considered. Researchers should adhere to the principles of the 3Rs (Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement) to minimize animal suffering and maximize the scientific value of the research.
Informed consent is a crucial ethical requirement in such studies. Researchers must ensure that participants fully understand the potential risks and benefits associated with lithium orotate consumption and its impact on dopamine pathways. This includes providing clear information about possible side effects, long-term implications, and the experimental nature of the research.
The principle of non-maleficence is particularly relevant in this context. Researchers have an ethical obligation to minimize harm to participants. This involves implementing rigorous safety protocols, conducting thorough pre-screening assessments, and providing ongoing monitoring throughout the study. Additionally, establishing clear criteria for participant withdrawal and offering post-study support are essential ethical considerations.
Privacy and confidentiality are paramount in psychoactive research. Given the sensitive nature of brain chemistry alterations, researchers must implement robust data protection measures to safeguard participants' personal and medical information. This includes anonymizing data, securing storage systems, and limiting access to authorized personnel only.
The ethical implications of potential long-term effects must also be addressed. Even if immediate adverse reactions are not observed, alterations to dopamine pathways could have lasting impacts on participants' neurological function. Researchers should consider implementing long-term follow-up studies to monitor participants' well-being and provide necessary support if delayed effects emerge.
Equitable selection of research participants is another critical ethical consideration. Researchers must ensure that the study population accurately represents the demographic that could benefit from the findings. This involves avoiding exploitation of vulnerable populations and ensuring that the potential benefits and risks are distributed fairly across different socioeconomic and ethnic groups.
Transparency in reporting research findings is an ethical imperative. Researchers have a responsibility to accurately and comprehensively report both positive and negative outcomes, regardless of their potential impact on funding or publication opportunities. This includes disclosing any conflicts of interest that may influence the study design or interpretation of results.
Finally, the ethical use of animals in preclinical studies related to lithium orotate and dopamine pathways must be carefully considered. Researchers should adhere to the principles of the 3Rs (Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement) to minimize animal suffering and maximize the scientific value of the research.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!