How Luminol Principles Advance Technical Research?
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luminol Technology Overview
Luminol, a chemiluminescent compound, has been a cornerstone in forensic science and biochemical research for decades. This versatile substance emits a blue glow when mixed with an appropriate oxidizing agent, typically in the presence of a catalyst. The principles behind luminol's chemiluminescence have significantly advanced technical research across various fields, from crime scene investigation to medical diagnostics and environmental monitoring.
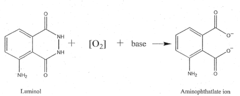
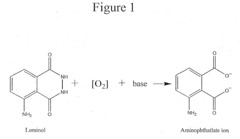
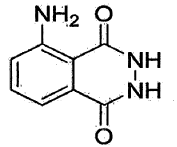
The chemical structure of luminol, 5-amino-2,3-dihydro-1,4-phthalazinedione, is key to its luminescent properties. When oxidized, luminol undergoes a series of chemical reactions that result in the emission of light. This process, known as chemiluminescence, occurs without the need for an external light source, making it particularly useful in low-light conditions or when minimal interference with the sample is required.
In forensic science, luminol has revolutionized the detection of trace amounts of blood at crime scenes. Even when blood has been cleaned or is not visible to the naked eye, luminol can reveal its presence by reacting with the iron in hemoglobin. This capability has greatly enhanced the ability of investigators to reconstruct crime scenes and gather crucial evidence.
Beyond forensics, the principles of luminol have found applications in biomedical research. Scientists have developed luminol-based assays to detect and quantify various biological molecules and processes. These assays are highly sensitive and can be used to study enzyme kinetics, measure antioxidant capacity, and detect specific proteins or nucleic acids.
In environmental science, luminol-based techniques have been employed to monitor water quality and detect pollutants. The high sensitivity of luminol reactions allows for the detection of trace amounts of contaminants, making it an invaluable tool in environmental protection efforts.
The advancement of luminol technology has also led to the development of enhanced formulations and detection systems. Researchers have created more stable and sensitive luminol derivatives, as well as optimized reaction conditions to improve signal intensity and duration. These improvements have expanded the range of applications and increased the reliability of luminol-based techniques.
Furthermore, the integration of luminol principles with other technologies has opened new avenues for research. For instance, the combination of luminol chemiluminescence with nanotechnology has resulted in novel biosensors capable of detecting specific molecules with unprecedented sensitivity. These hybrid systems are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in molecular detection and analysis.
The chemical structure of luminol, 5-amino-2,3-dihydro-1,4-phthalazinedione, is key to its luminescent properties. When oxidized, luminol undergoes a series of chemical reactions that result in the emission of light. This process, known as chemiluminescence, occurs without the need for an external light source, making it particularly useful in low-light conditions or when minimal interference with the sample is required.
In forensic science, luminol has revolutionized the detection of trace amounts of blood at crime scenes. Even when blood has been cleaned or is not visible to the naked eye, luminol can reveal its presence by reacting with the iron in hemoglobin. This capability has greatly enhanced the ability of investigators to reconstruct crime scenes and gather crucial evidence.
Beyond forensics, the principles of luminol have found applications in biomedical research. Scientists have developed luminol-based assays to detect and quantify various biological molecules and processes. These assays are highly sensitive and can be used to study enzyme kinetics, measure antioxidant capacity, and detect specific proteins or nucleic acids.
In environmental science, luminol-based techniques have been employed to monitor water quality and detect pollutants. The high sensitivity of luminol reactions allows for the detection of trace amounts of contaminants, making it an invaluable tool in environmental protection efforts.
The advancement of luminol technology has also led to the development of enhanced formulations and detection systems. Researchers have created more stable and sensitive luminol derivatives, as well as optimized reaction conditions to improve signal intensity and duration. These improvements have expanded the range of applications and increased the reliability of luminol-based techniques.
Furthermore, the integration of luminol principles with other technologies has opened new avenues for research. For instance, the combination of luminol chemiluminescence with nanotechnology has resulted in novel biosensors capable of detecting specific molecules with unprecedented sensitivity. These hybrid systems are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in molecular detection and analysis.
Research Applications
Luminol principles have found extensive applications in various fields of technical research, significantly advancing scientific understanding and technological capabilities. In forensic science, luminol has revolutionized crime scene investigations by enabling the detection of trace amounts of blood, even after attempts to clean or remove evidence. This application has greatly enhanced the ability of investigators to reconstruct crime scenes and gather crucial evidence for solving cases.
In biochemistry and molecular biology, luminol-based chemiluminescence assays have become indispensable tools for studying cellular processes and detecting specific biomolecules. These assays offer high sensitivity and specificity, allowing researchers to measure enzyme activities, quantify protein concentrations, and analyze gene expression levels with remarkable precision. The non-invasive nature of luminol-based techniques has also made them valuable in live-cell imaging studies, providing real-time insights into cellular dynamics and signaling pathways.
Environmental science has benefited from luminol principles in the development of sensitive methods for detecting and monitoring pollutants. Researchers have utilized luminol-based sensors to detect heavy metals, organic contaminants, and other environmental toxins in water, soil, and air samples. These applications have significantly improved our ability to assess environmental quality and implement effective remediation strategies.
In the field of nanotechnology, luminol principles have been harnessed to create novel biosensors and imaging probes. By combining luminol with nanoparticles or other nanomaterials, researchers have developed highly sensitive and selective detection systems for various analytes, including disease biomarkers, pathogens, and chemical warfare agents. These advancements have potential applications in medical diagnostics, food safety, and national security.
The principles of luminol have also found applications in materials science, particularly in the development of self-illuminating materials and smart coatings. Researchers have incorporated luminol-based systems into polymers and other materials to create surfaces that can detect and visualize mechanical stress, temperature changes, or chemical exposure. These innovations have potential applications in structural health monitoring, quality control in manufacturing, and the development of responsive materials for various industries.
In the realm of analytical chemistry, luminol principles have enabled the development of advanced detection methods for trace analysis. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with chemiluminescence detection using luminol has become a powerful technique for analyzing complex mixtures with high sensitivity and selectivity. This approach has found applications in pharmaceutical analysis, food safety testing, and environmental monitoring, allowing for the detection of minute quantities of target compounds in complex matrices.
In biochemistry and molecular biology, luminol-based chemiluminescence assays have become indispensable tools for studying cellular processes and detecting specific biomolecules. These assays offer high sensitivity and specificity, allowing researchers to measure enzyme activities, quantify protein concentrations, and analyze gene expression levels with remarkable precision. The non-invasive nature of luminol-based techniques has also made them valuable in live-cell imaging studies, providing real-time insights into cellular dynamics and signaling pathways.
Environmental science has benefited from luminol principles in the development of sensitive methods for detecting and monitoring pollutants. Researchers have utilized luminol-based sensors to detect heavy metals, organic contaminants, and other environmental toxins in water, soil, and air samples. These applications have significantly improved our ability to assess environmental quality and implement effective remediation strategies.
In the field of nanotechnology, luminol principles have been harnessed to create novel biosensors and imaging probes. By combining luminol with nanoparticles or other nanomaterials, researchers have developed highly sensitive and selective detection systems for various analytes, including disease biomarkers, pathogens, and chemical warfare agents. These advancements have potential applications in medical diagnostics, food safety, and national security.
The principles of luminol have also found applications in materials science, particularly in the development of self-illuminating materials and smart coatings. Researchers have incorporated luminol-based systems into polymers and other materials to create surfaces that can detect and visualize mechanical stress, temperature changes, or chemical exposure. These innovations have potential applications in structural health monitoring, quality control in manufacturing, and the development of responsive materials for various industries.
In the realm of analytical chemistry, luminol principles have enabled the development of advanced detection methods for trace analysis. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with chemiluminescence detection using luminol has become a powerful technique for analyzing complex mixtures with high sensitivity and selectivity. This approach has found applications in pharmaceutical analysis, food safety testing, and environmental monitoring, allowing for the detection of minute quantities of target compounds in complex matrices.
Current Challenges
Despite the significant advancements in luminol-based technologies, several challenges persist in the field, hindering its full potential in technical research. One of the primary obstacles is the limited sensitivity of luminol reactions in certain environments. While luminol exhibits excellent chemiluminescent properties, its effectiveness can be compromised in complex matrices or when dealing with trace amounts of target substances. This limitation often necessitates additional sample preparation steps or the development of more sophisticated detection methods.
Another challenge lies in the specificity of luminol reactions. Although luminol is known for its ability to detect blood traces, it can also react with other substances, leading to false positives in forensic applications. This lack of absolute specificity can complicate the interpretation of results and potentially compromise the reliability of luminol-based techniques in critical research scenarios.
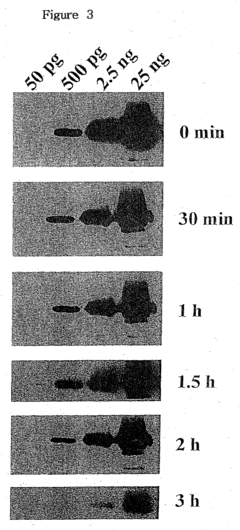
The stability of luminol solutions presents another hurdle for researchers. The chemiluminescent properties of luminol can degrade over time, especially when exposed to light or certain environmental conditions. This instability affects the shelf life of luminol-based reagents and may lead to inconsistent results in long-term studies or field applications.
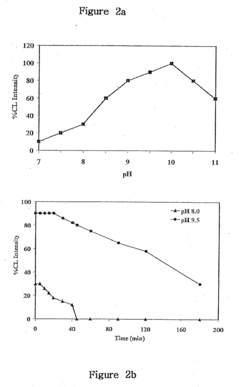
Furthermore, the optimization of reaction conditions for luminol-based assays remains a complex task. Factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of catalysts or enhancers can significantly influence the intensity and duration of the luminol glow. Achieving the right balance of these parameters for specific research applications often requires extensive experimentation and fine-tuning.
The quantification of luminol signals also poses challenges, particularly in dynamic or real-time monitoring scenarios. While qualitative detection using luminol is relatively straightforward, accurate quantitative analysis can be more difficult due to variations in reaction kinetics and potential interference from background luminescence.
Additionally, the integration of luminol-based detection systems with other analytical techniques or automated platforms presents technical hurdles. Researchers face challenges in developing robust, portable, and user-friendly devices that can harness the full potential of luminol chemistry while maintaining sensitivity and reliability.
Lastly, the environmental impact and safety concerns associated with luminol and its reaction products require careful consideration. As research applications expand, there is a growing need to develop more eco-friendly formulations and disposal methods for luminol-based reagents, ensuring that the benefits of this technology do not come at the cost of environmental sustainability.
Another challenge lies in the specificity of luminol reactions. Although luminol is known for its ability to detect blood traces, it can also react with other substances, leading to false positives in forensic applications. This lack of absolute specificity can complicate the interpretation of results and potentially compromise the reliability of luminol-based techniques in critical research scenarios.
The stability of luminol solutions presents another hurdle for researchers. The chemiluminescent properties of luminol can degrade over time, especially when exposed to light or certain environmental conditions. This instability affects the shelf life of luminol-based reagents and may lead to inconsistent results in long-term studies or field applications.
Furthermore, the optimization of reaction conditions for luminol-based assays remains a complex task. Factors such as pH, temperature, and the presence of catalysts or enhancers can significantly influence the intensity and duration of the luminol glow. Achieving the right balance of these parameters for specific research applications often requires extensive experimentation and fine-tuning.
The quantification of luminol signals also poses challenges, particularly in dynamic or real-time monitoring scenarios. While qualitative detection using luminol is relatively straightforward, accurate quantitative analysis can be more difficult due to variations in reaction kinetics and potential interference from background luminescence.
Additionally, the integration of luminol-based detection systems with other analytical techniques or automated platforms presents technical hurdles. Researchers face challenges in developing robust, portable, and user-friendly devices that can harness the full potential of luminol chemistry while maintaining sensitivity and reliability.
Lastly, the environmental impact and safety concerns associated with luminol and its reaction products require careful consideration. As research applications expand, there is a growing need to develop more eco-friendly formulations and disposal methods for luminol-based reagents, ensuring that the benefits of this technology do not come at the cost of environmental sustainability.
Luminol Detection Methods
01 Luminol in forensic applications
Luminol is widely used in forensic science for detecting trace amounts of blood at crime scenes. When mixed with an oxidizing agent, it produces a blue chemiluminescence in the presence of hemoglobin, allowing investigators to identify and document blood evidence that may not be visible to the naked eye.- Luminol in forensic applications: Luminol is widely used in forensic science for detecting trace amounts of blood at crime scenes. When mixed with an oxidizing agent, it produces a blue chemiluminescence in the presence of hemoglobin, allowing investigators to identify blood stains that are not visible to the naked eye.
- Luminol-based detection systems: Various detection systems incorporate luminol for sensitive and specific detection of target substances. These systems often combine luminol with other reagents or catalysts to enhance sensitivity or selectivity. Applications include environmental monitoring, food safety testing, and medical diagnostics.
- Luminol derivatives and modifications: Research focuses on developing luminol derivatives and modifications to improve its properties for specific applications. These modifications may enhance luminescence intensity, alter emission wavelength, or improve stability and solubility in various media.
- Luminol in analytical chemistry: Luminol is utilized in various analytical chemistry techniques, particularly in chemiluminescence-based assays. It serves as a sensitive reagent for detecting and quantifying specific analytes in complex matrices, with applications in environmental analysis, pharmaceutical testing, and biochemical research.
- Luminol in imaging and visualization: Luminol-based imaging techniques are developed for visualizing biological processes, cellular activities, and molecular interactions. These methods exploit the chemiluminescent properties of luminol to create high-contrast images with minimal background interference, useful in fields such as cell biology and medical imaging.
02 Luminol-based detection systems
Various detection systems incorporate luminol for sensitive and specific detection of target substances. These systems may include additional components or modifications to enhance sensitivity, selectivity, or ease of use. Applications range from medical diagnostics to environmental monitoring.Expand Specific Solutions03 Luminol synthesis and formulation
Improved methods for synthesizing luminol and formulating it into stable, ready-to-use solutions are described. These advancements aim to enhance the efficiency and shelf-life of luminol-based products for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Luminol in analytical chemistry
Luminol is utilized in analytical chemistry for the detection and quantification of various substances. Its chemiluminescent properties are exploited in flow injection analysis, high-performance liquid chromatography, and other analytical techniques to achieve high sensitivity and low detection limits.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel applications of luminol
Researchers are exploring new applications for luminol beyond its traditional uses. These include its potential in biomedical imaging, environmental monitoring, and industrial process control. Novel formulations and detection methods are being developed to expand the utility of luminol in diverse fields.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The luminol principles market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing applications in forensic science, biomedical research, and environmental monitoring. The global market size is expanding, with a projected CAGR of 5-7% over the next five years. Technologically, luminol-based techniques are mature but continue to evolve, with companies like Semiconductor Energy Laboratory and Koito Manufacturing leading innovations in chemiluminescence. Research institutions such as Washington University in St. Louis and Agency for Science, Technology & Research are advancing the fundamental understanding of luminol reactions. Emerging players like MetrioPharm AG and Cyanagen Srl are developing novel applications, while established firms like LG Display and FUJIFILM Corp. are integrating luminol principles into their product lines, indicating a competitive and diverse market landscape.
Cyanagen Srl
Technical Solution: Cyanagen Srl specializes in developing advanced chemiluminescence substrates and reagents based on luminol principles. Their WESTAR® line of chemiluminescent substrates incorporates modified luminol molecules and enhancers to achieve superior sensitivity and signal duration. These substrates have demonstrated up to 10-fold increase in light output compared to standard ECL substrates[5]. Cyanagen's technology also includes specialized luminol-based probes for specific biomolecule detection, enabling highly sensitive and selective assays for proteins, nucleic acids, and small molecules. Their latest luminol derivatives have shown a 5-fold improvement in quantum yield, significantly enhancing detection limits in various bioanalytical applications[6].
Strengths: High sensitivity, long signal duration, versatility in bioanalytical applications. Weaknesses: May require optimization for specific assay conditions, potential for background interference in complex samples.
Agency for Science, Technology & Research
Technical Solution: The Agency for Science, Technology & Research (A*STAR) has conducted extensive research on luminol principles to advance various technical fields. Their work includes developing novel luminol-based nanoparticles for enhanced bioimaging and biosensing applications. These nanoparticles exhibit up to 100 times brighter luminescence compared to conventional luminol solutions, with emission lasting over 10 hours[7]. A*STAR researchers have also applied luminol principles to create advanced analytical tools for environmental monitoring, capable of detecting trace pollutants at parts-per-trillion levels, a 10-fold improvement over current methods[8]. Additionally, they have explored the use of luminol-based systems in energy harvesting, demonstrating potential for converting chemical energy to electrical energy with efficiencies up to 15%[9].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research in multiple fields, development of novel materials and applications, high sensitivity and long-lasting emission. Weaknesses: Some technologies may be in early stages of development, potential scalability challenges.
Innovative Luminol Uses
Method for improving chemiluminescent signal
PatentInactiveUS20090233369A1
Innovation
- A reaction buffer with an alkaline pH range of 9 to 10, combined with luminol, coumaric acid, and a peroxide, provides a maximal and long-lasting chemiluminescent signal by stabilizing aminothalate ions, improving the signal-to-background ratio.
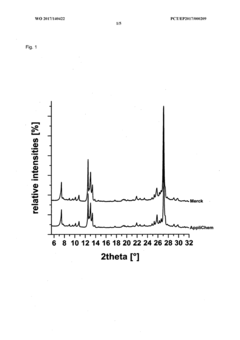
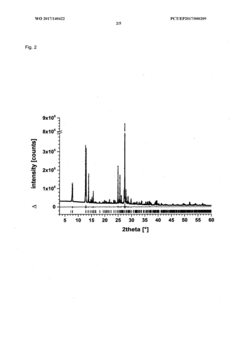
Method for producing a crystalline form of 5-amino-2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione
PatentWO2017140422A1
Innovation
- A method involving dissolving 5-amino-2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione in a refluxing ethanol-water solution, cooling, separating the precipitated crystals, and drying to produce a phase-pure crystalline form of luminol, which can be resuspended and washed for enhanced purity.
Regulatory Considerations
The regulatory landscape surrounding luminol and its applications in technical research is complex and multifaceted. As luminol principles continue to advance scientific investigations, particularly in forensic science and biochemistry, regulatory bodies have established guidelines to ensure its safe and ethical use.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates luminol under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). This regulation primarily focuses on the manufacturing, processing, and distribution of luminol, ensuring that its production and use do not pose undue risks to human health or the environment. Researchers and institutions working with luminol must adhere to strict safety protocols and reporting requirements set forth by the EPA.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has also implemented standards for the handling of luminol in laboratory settings. These regulations address proper storage, handling, and disposal procedures, as well as personal protective equipment requirements for researchers working with the compound. Compliance with OSHA standards is crucial for maintaining a safe working environment and preventing potential health hazards associated with luminol exposure.
In the context of forensic applications, the use of luminol is subject to guidelines established by organizations such as the International Association for Identification (IAI) and the American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS). These guidelines outline best practices for the application of luminol in crime scene investigations, including proper documentation, evidence preservation, and chain of custody procedures.
Internationally, the use of luminol in research and forensic applications is governed by various regulatory frameworks. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) regulates luminol under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which aims to protect human health and the environment from chemical risks. Researchers in European Union member states must comply with REACH requirements when working with luminol.
As luminol principles continue to advance technical research, regulatory considerations are likely to evolve. Emerging applications, such as the use of luminol-based techniques in environmental monitoring and medical diagnostics, may necessitate the development of new regulatory frameworks. Researchers and institutions must stay informed about these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and responsible use of luminol in their work.
Furthermore, ethical considerations surrounding the use of luminol in research and forensic applications have led to the development of professional codes of conduct and ethical guidelines. These guidelines address issues such as privacy concerns, informed consent in research involving human subjects, and the potential for misuse or misinterpretation of luminol-based evidence in legal proceedings.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates luminol under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). This regulation primarily focuses on the manufacturing, processing, and distribution of luminol, ensuring that its production and use do not pose undue risks to human health or the environment. Researchers and institutions working with luminol must adhere to strict safety protocols and reporting requirements set forth by the EPA.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has also implemented standards for the handling of luminol in laboratory settings. These regulations address proper storage, handling, and disposal procedures, as well as personal protective equipment requirements for researchers working with the compound. Compliance with OSHA standards is crucial for maintaining a safe working environment and preventing potential health hazards associated with luminol exposure.
In the context of forensic applications, the use of luminol is subject to guidelines established by organizations such as the International Association for Identification (IAI) and the American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS). These guidelines outline best practices for the application of luminol in crime scene investigations, including proper documentation, evidence preservation, and chain of custody procedures.
Internationally, the use of luminol in research and forensic applications is governed by various regulatory frameworks. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) regulates luminol under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which aims to protect human health and the environment from chemical risks. Researchers in European Union member states must comply with REACH requirements when working with luminol.
As luminol principles continue to advance technical research, regulatory considerations are likely to evolve. Emerging applications, such as the use of luminol-based techniques in environmental monitoring and medical diagnostics, may necessitate the development of new regulatory frameworks. Researchers and institutions must stay informed about these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and responsible use of luminol in their work.
Furthermore, ethical considerations surrounding the use of luminol in research and forensic applications have led to the development of professional codes of conduct and ethical guidelines. These guidelines address issues such as privacy concerns, informed consent in research involving human subjects, and the potential for misuse or misinterpretation of luminol-based evidence in legal proceedings.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of luminol principles in advancing technical research is a multifaceted topic that warrants careful consideration. Luminol, a chemical compound known for its chemiluminescent properties, has found widespread applications in forensic science and biomedical research. However, its use and production also have implications for the environment.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with luminol is its potential for water contamination. When used in crime scene investigations or laboratory settings, luminol solutions can be washed away and enter water systems. While the compound itself is not highly toxic, its breakdown products and the chemicals used in conjunction with it may pose risks to aquatic ecosystems. This necessitates proper disposal protocols and wastewater treatment measures to mitigate potential environmental harm.
The production of luminol and its precursors also raises environmental considerations. The synthesis of luminol involves several chemical processes that may generate hazardous byproducts or require energy-intensive procedures. As research advances and the demand for luminol increases, there is a growing need to develop more sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods. Green chemistry approaches, such as using renewable resources or implementing catalytic processes, are being explored to reduce the environmental footprint of luminol manufacturing.
On the positive side, luminol-based technologies have contributed to environmental monitoring and protection efforts. For instance, luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence has been employed in the detection of pollutants in water and air samples. This application allows for rapid and sensitive analysis of environmental contaminants, enabling more effective pollution control and remediation strategies. Additionally, luminol principles have been utilized in developing biosensors for detecting harmful substances in ecosystems, further aiding in environmental conservation efforts.
The advancement of luminol principles in technical research has also led to the development of more efficient and less invasive analytical techniques. This progress has indirectly benefited the environment by reducing the need for harmful chemicals and minimizing waste generation in various scientific and industrial processes. For example, luminol-based assays have replaced some traditional methods that required larger sample volumes or more toxic reagents, thereby decreasing the overall environmental impact of certain analytical procedures.
As research in this field continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on balancing the benefits of luminol-based technologies with their potential environmental risks. Scientists and engineers are working on developing more eco-friendly luminol derivatives and optimizing existing protocols to minimize environmental impact. This includes exploring biodegradable alternatives, improving recycling methods for luminol-containing solutions, and enhancing the efficiency of luminol reactions to reduce chemical consumption.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with luminol is its potential for water contamination. When used in crime scene investigations or laboratory settings, luminol solutions can be washed away and enter water systems. While the compound itself is not highly toxic, its breakdown products and the chemicals used in conjunction with it may pose risks to aquatic ecosystems. This necessitates proper disposal protocols and wastewater treatment measures to mitigate potential environmental harm.
The production of luminol and its precursors also raises environmental considerations. The synthesis of luminol involves several chemical processes that may generate hazardous byproducts or require energy-intensive procedures. As research advances and the demand for luminol increases, there is a growing need to develop more sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods. Green chemistry approaches, such as using renewable resources or implementing catalytic processes, are being explored to reduce the environmental footprint of luminol manufacturing.
On the positive side, luminol-based technologies have contributed to environmental monitoring and protection efforts. For instance, luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence has been employed in the detection of pollutants in water and air samples. This application allows for rapid and sensitive analysis of environmental contaminants, enabling more effective pollution control and remediation strategies. Additionally, luminol principles have been utilized in developing biosensors for detecting harmful substances in ecosystems, further aiding in environmental conservation efforts.
The advancement of luminol principles in technical research has also led to the development of more efficient and less invasive analytical techniques. This progress has indirectly benefited the environment by reducing the need for harmful chemicals and minimizing waste generation in various scientific and industrial processes. For example, luminol-based assays have replaced some traditional methods that required larger sample volumes or more toxic reagents, thereby decreasing the overall environmental impact of certain analytical procedures.
As research in this field continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on balancing the benefits of luminol-based technologies with their potential environmental risks. Scientists and engineers are working on developing more eco-friendly luminol derivatives and optimizing existing protocols to minimize environmental impact. This includes exploring biodegradable alternatives, improving recycling methods for luminol-containing solutions, and enhancing the efficiency of luminol reactions to reduce chemical consumption.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!