Luminol's Practicality in Research Application Trends
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luminol Research Background and Objectives
Luminol, a chemiluminescent compound, has been a subject of scientific interest for decades. Initially discovered in the early 20th century, this organic compound has gained significant attention in various research fields due to its unique light-emitting properties. The evolution of luminol's applications has been closely tied to advancements in analytical chemistry, forensic science, and biomedical research.
The primary objective of luminol research is to harness its chemiluminescent properties for practical applications. In forensic science, luminol has become an indispensable tool for detecting trace amounts of blood at crime scenes. Its ability to react with the iron in hemoglobin, producing a bright blue glow, has revolutionized crime scene investigation techniques. This application has driven much of the early research and development efforts surrounding luminol.
In the field of analytical chemistry, luminol has found applications in the detection and quantification of various substances. Researchers aim to develop more sensitive and specific luminol-based assays for environmental monitoring, food safety testing, and industrial quality control. The goal is to create robust, reliable, and cost-effective detection methods that can be widely adopted in laboratory and field settings.
Biomedical research represents another frontier for luminol applications. Scientists are exploring its potential in diagnostic imaging, drug discovery, and disease monitoring. The non-invasive nature of luminol-based imaging techniques makes it an attractive option for studying biological processes in living organisms. Researchers are working towards developing luminol derivatives with enhanced stability, sensitivity, and specificity for in vivo applications.
The current trend in luminol research is focused on expanding its practicality and versatility. This includes efforts to improve its chemical stability, enhance its light emission intensity, and broaden its reactivity with different analytes. Additionally, there is a growing interest in developing luminol-based nanomaterials and hybrid systems that combine the benefits of luminol with other advanced materials.
As research progresses, the objectives extend beyond traditional applications. Emerging areas of interest include using luminol in biosensors for rapid disease detection, incorporating it into smart materials for environmental monitoring, and exploring its potential in photodynamic therapy for cancer treatment. These diverse research directions reflect the multidisciplinary nature of luminol studies and its potential to address various technological and societal challenges.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of luminol research encompass a wide range of scientific disciplines and practical applications. From its origins in forensic science to its potential in cutting-edge biomedical technologies, luminol continues to captivate researchers with its unique properties and versatile applications. The ongoing research aims to unlock new possibilities and overcome existing limitations, driving innovation in multiple fields and potentially revolutionizing detection and imaging technologies.
The primary objective of luminol research is to harness its chemiluminescent properties for practical applications. In forensic science, luminol has become an indispensable tool for detecting trace amounts of blood at crime scenes. Its ability to react with the iron in hemoglobin, producing a bright blue glow, has revolutionized crime scene investigation techniques. This application has driven much of the early research and development efforts surrounding luminol.
In the field of analytical chemistry, luminol has found applications in the detection and quantification of various substances. Researchers aim to develop more sensitive and specific luminol-based assays for environmental monitoring, food safety testing, and industrial quality control. The goal is to create robust, reliable, and cost-effective detection methods that can be widely adopted in laboratory and field settings.
Biomedical research represents another frontier for luminol applications. Scientists are exploring its potential in diagnostic imaging, drug discovery, and disease monitoring. The non-invasive nature of luminol-based imaging techniques makes it an attractive option for studying biological processes in living organisms. Researchers are working towards developing luminol derivatives with enhanced stability, sensitivity, and specificity for in vivo applications.
The current trend in luminol research is focused on expanding its practicality and versatility. This includes efforts to improve its chemical stability, enhance its light emission intensity, and broaden its reactivity with different analytes. Additionally, there is a growing interest in developing luminol-based nanomaterials and hybrid systems that combine the benefits of luminol with other advanced materials.
As research progresses, the objectives extend beyond traditional applications. Emerging areas of interest include using luminol in biosensors for rapid disease detection, incorporating it into smart materials for environmental monitoring, and exploring its potential in photodynamic therapy for cancer treatment. These diverse research directions reflect the multidisciplinary nature of luminol studies and its potential to address various technological and societal challenges.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of luminol research encompass a wide range of scientific disciplines and practical applications. From its origins in forensic science to its potential in cutting-edge biomedical technologies, luminol continues to captivate researchers with its unique properties and versatile applications. The ongoing research aims to unlock new possibilities and overcome existing limitations, driving innovation in multiple fields and potentially revolutionizing detection and imaging technologies.
Market Demand Analysis for Luminol Applications
The market demand for luminol applications has been steadily growing across various sectors, driven by its unique chemiluminescent properties and versatility in research and forensic applications. In the forensic science field, luminol remains a crucial tool for crime scene investigations, particularly in detecting trace amounts of blood. The global forensic technology market, which includes luminol-based products, is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, fueled by increasing crime rates and advancements in forensic techniques.
Beyond forensics, luminol has found applications in biomedical research, environmental monitoring, and industrial quality control. In the biomedical sector, luminol-based assays are increasingly used for detecting and quantifying various biomolecules, offering high sensitivity and low background interference. This has led to a growing demand in pharmaceutical research and development, as well as in clinical diagnostics.
The environmental monitoring sector has also shown interest in luminol applications, particularly for detecting pollutants and assessing water quality. As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, the demand for sensitive and reliable detection methods, including those based on luminol, is expected to rise.
In the industrial sector, luminol-based systems are being developed for quality control processes, especially in the food and beverage industry. These applications leverage luminol's ability to detect minute quantities of contaminants or adulterants, ensuring product safety and quality.
The academic research market continues to be a significant driver of luminol demand, with ongoing studies exploring new applications and improving existing techniques. This sustained interest from the research community contributes to the overall market growth and innovation in luminol-based technologies.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for luminol applications, primarily due to their advanced forensic and research infrastructure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are showing rapid growth in adoption, driven by increasing investments in forensic capabilities and research facilities.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as the development of alternative technologies and the need for skilled personnel to interpret results may impact the growth rate. However, ongoing research into enhancing luminol's sensitivity and specificity, as well as efforts to simplify its application, are expected to address some of these challenges and further expand its market potential.
Beyond forensics, luminol has found applications in biomedical research, environmental monitoring, and industrial quality control. In the biomedical sector, luminol-based assays are increasingly used for detecting and quantifying various biomolecules, offering high sensitivity and low background interference. This has led to a growing demand in pharmaceutical research and development, as well as in clinical diagnostics.
The environmental monitoring sector has also shown interest in luminol applications, particularly for detecting pollutants and assessing water quality. As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, the demand for sensitive and reliable detection methods, including those based on luminol, is expected to rise.
In the industrial sector, luminol-based systems are being developed for quality control processes, especially in the food and beverage industry. These applications leverage luminol's ability to detect minute quantities of contaminants or adulterants, ensuring product safety and quality.
The academic research market continues to be a significant driver of luminol demand, with ongoing studies exploring new applications and improving existing techniques. This sustained interest from the research community contributes to the overall market growth and innovation in luminol-based technologies.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for luminol applications, primarily due to their advanced forensic and research infrastructure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are showing rapid growth in adoption, driven by increasing investments in forensic capabilities and research facilities.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as the development of alternative technologies and the need for skilled personnel to interpret results may impact the growth rate. However, ongoing research into enhancing luminol's sensitivity and specificity, as well as efforts to simplify its application, are expected to address some of these challenges and further expand its market potential.
Current Challenges in Luminol Research
Despite the widespread use of luminol in forensic science and biomedical research, several challenges persist in its application and development. One of the primary obstacles is the sensitivity and specificity of luminol-based detection methods. While luminol is known for its ability to detect trace amounts of blood, it can also produce false positives when reacting with other substances such as certain plant materials, cleaning agents, and metals. This lack of absolute specificity can lead to misinterpretation of results, particularly in forensic investigations where accuracy is paramount.
Another significant challenge lies in the optimization of luminol formulations for different applications. The luminol reaction is influenced by various factors, including pH, temperature, and the presence of catalysts or enhancers. Researchers continue to grapple with finding the ideal balance of these parameters to maximize sensitivity while maintaining reliability across diverse environmental conditions. This is particularly crucial in field applications where controlled laboratory conditions cannot be replicated.
The stability and longevity of luminol solutions also present ongoing challenges. Once prepared, luminol solutions can degrade over time, affecting their luminescence intensity and overall performance. This necessitates careful handling and storage procedures, as well as the development of more stable formulations that can withstand prolonged periods without significant loss of efficacy.
In the realm of quantitative analysis, researchers face difficulties in standardizing luminol-based measurements. The intensity and duration of the chemiluminescent reaction can vary based on numerous factors, making it challenging to establish consistent quantitative relationships between signal intensity and the amount of blood or other target substances present. This variability hampers efforts to use luminol for precise quantitative assessments in both forensic and biomedical applications.
Furthermore, the potential interference of luminol with subsequent DNA analysis remains a concern in forensic science. While luminol is generally considered non-destructive to DNA, there is ongoing debate and research regarding its impact on DNA recovery and analysis, particularly in cases where multiple forensic tests need to be performed on the same sample.
Lastly, the development of more environmentally friendly and safer luminol formulations presents an ongoing challenge. Traditional luminol solutions often contain potentially harmful chemicals, raising concerns about user safety and environmental impact. Researchers are actively seeking alternative formulations that maintain or improve upon the performance of conventional luminol while reducing potential risks associated with its use and disposal.
Another significant challenge lies in the optimization of luminol formulations for different applications. The luminol reaction is influenced by various factors, including pH, temperature, and the presence of catalysts or enhancers. Researchers continue to grapple with finding the ideal balance of these parameters to maximize sensitivity while maintaining reliability across diverse environmental conditions. This is particularly crucial in field applications where controlled laboratory conditions cannot be replicated.
The stability and longevity of luminol solutions also present ongoing challenges. Once prepared, luminol solutions can degrade over time, affecting their luminescence intensity and overall performance. This necessitates careful handling and storage procedures, as well as the development of more stable formulations that can withstand prolonged periods without significant loss of efficacy.
In the realm of quantitative analysis, researchers face difficulties in standardizing luminol-based measurements. The intensity and duration of the chemiluminescent reaction can vary based on numerous factors, making it challenging to establish consistent quantitative relationships between signal intensity and the amount of blood or other target substances present. This variability hampers efforts to use luminol for precise quantitative assessments in both forensic and biomedical applications.
Furthermore, the potential interference of luminol with subsequent DNA analysis remains a concern in forensic science. While luminol is generally considered non-destructive to DNA, there is ongoing debate and research regarding its impact on DNA recovery and analysis, particularly in cases where multiple forensic tests need to be performed on the same sample.
Lastly, the development of more environmentally friendly and safer luminol formulations presents an ongoing challenge. Traditional luminol solutions often contain potentially harmful chemicals, raising concerns about user safety and environmental impact. Researchers are actively seeking alternative formulations that maintain or improve upon the performance of conventional luminol while reducing potential risks associated with its use and disposal.
Current Luminol Application Methodologies
01 Luminol-based detection systems
Luminol is widely used in detection systems for various applications. These systems utilize luminol's chemiluminescent properties to detect and analyze specific substances or conditions. The technology has been applied in forensic science, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnostics, offering high sensitivity and rapid results.- Luminol-based detection systems: Luminol is widely used in detection systems for various applications, including forensic science, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnostics. These systems utilize luminol's chemiluminescent properties to detect trace amounts of substances, such as blood or specific chemicals, by producing a visible blue light when oxidized.
- Enhanced luminol formulations: Researchers have developed improved luminol formulations to increase sensitivity and stability. These enhancements may include the addition of catalysts, stabilizers, or other reagents to optimize the chemiluminescent reaction, resulting in more reliable and efficient detection methods for various applications.
- Luminol in portable detection devices: Luminol-based detection systems have been miniaturized and integrated into portable devices for on-site analysis. These handheld or compact instruments allow for rapid and convenient detection of target substances in field conditions, making them valuable tools for law enforcement, environmental monitoring, and point-of-care diagnostics.
- Luminol applications in environmental monitoring: Luminol-based techniques have been adapted for environmental monitoring purposes, such as detecting pollutants in water or air. These methods offer high sensitivity and rapid results, enabling real-time monitoring of environmental contaminants and facilitating timely responses to potential hazards.
- Luminol in medical diagnostics: The chemiluminescent properties of luminol have been harnessed for various medical diagnostic applications. These include detecting specific biomarkers, analyzing blood samples, and imaging techniques. Luminol-based diagnostic methods offer high sensitivity and rapid results, potentially improving disease detection and monitoring.
02 Enhanced luminol formulations
Researchers have developed improved luminol formulations to enhance its practicality. These advancements include increasing luminescence intensity, prolonging the duration of light emission, and improving stability. Enhanced formulations may incorporate additional reagents or catalysts to optimize the chemiluminescent reaction for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Luminol in portable devices
The integration of luminol-based detection into portable devices has expanded its practical applications. These devices allow for on-site analysis in various fields, including crime scene investigation, water quality testing, and point-of-care diagnostics. Miniaturization and automation of luminol-based systems have improved their usability and accessibility.Expand Specific Solutions04 Luminol in environmental monitoring
Luminol has found practical applications in environmental monitoring, particularly for detecting pollutants and assessing water quality. Its high sensitivity allows for the detection of trace amounts of contaminants, making it valuable for monitoring industrial effluents, natural water bodies, and wastewater treatment processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Luminol in biomedical applications
The practicality of luminol extends to biomedical applications, including disease diagnosis and research. It has been used to detect specific biomolecules, study cellular processes, and develop novel imaging techniques. The non-invasive nature of luminol-based detection makes it particularly useful in medical diagnostics and biological research.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Luminol Research and Development
The competitive landscape for Luminol's research application trends is evolving rapidly, reflecting the technology's growing importance in various scientific fields. The market is in a growth phase, with increasing adoption across forensic science, biochemistry, and medical diagnostics sectors. The global market size for chemiluminescence-based technologies, including Luminol applications, is expanding, driven by advancements in sensitivity and specificity. Companies like MetrioPharm AG, Alverix, Inc., and Galderma Research & Development SNC are at the forefront, leveraging Luminol's properties for innovative diagnostic and research tools. Academic institutions such as Washington University in St. Louis and the National University of Singapore are contributing significantly to the technology's development, pushing the boundaries of its applications in biomedical research and forensic analysis.
FUJIFILM Corp.
Technical Solution: FUJIFILM Corp. has leveraged its expertise in imaging technologies to develop advanced luminol-based detection systems for medical diagnostics and life science research. Their LAS-4000 and LAS-X Series of imaging systems incorporate highly sensitive CCD cameras and optimized luminol chemiluminescence substrates for quantitative Western blot analysis and other protein detection applications [9]. FUJIFILM has also developed proprietary luminol-based reagents designed for maximum sensitivity and extended signal duration. Recent research has focused on creating multiplex chemiluminescence systems that allow simultaneous detection of multiple targets using spectrally distinct luminol derivatives. The company is also exploring the integration of AI-based image analysis tools to enhance data interpretation and automate quantification in luminol-based assays [10].
Strengths: High-performance imaging systems, integrated hardware/reagent solutions. Weaknesses: High cost of specialized equipment, may require technical expertise to operate.
Cyanagen Srl
Technical Solution: Cyanagen Srl has developed proprietary luminol derivatives and formulations optimized for specific research and diagnostic applications. Their LUMIGEN ECL Plus reagents utilize acridinium ester-labeled luminol analogs to achieve femtomolar detection limits in immunoassays and blotting techniques [2]. The company has also created stabilized luminol solutions with extended shelf-life and consistent performance across a wide pH range. Cyanagen's luminol-based substrates are designed for compatibility with a variety of enzymes like horseradish peroxidase and alkaline phosphatase, allowing flexible assay design. Recent research has focused on developing water-soluble luminol derivatives to improve reagent stability and reduce background signal in aqueous systems [4].
Strengths: High sensitivity, extended shelf-life, enzyme compatibility. Weaknesses: May require specialized detection equipment, potential for matrix effects in complex samples.
Innovative Luminol Research Breakthroughs
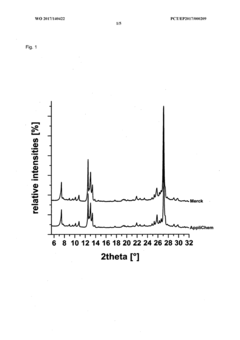
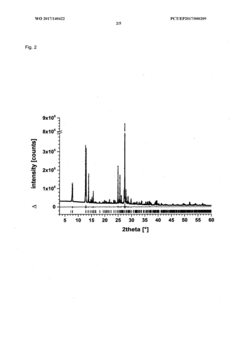
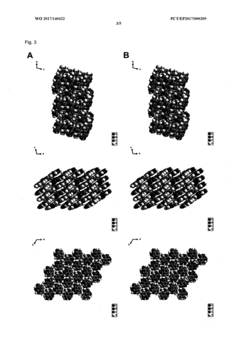
Method for producing a crystalline form of 5-amino-2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione
PatentWO2017140422A1
Innovation
- A method involving dissolving 5-amino-2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione in a refluxing ethanol-water solution, cooling, separating the precipitated crystals, and drying to produce a phase-pure crystalline form of luminol, which can be resuspended and washed for enhanced purity.
Photodynamic therapy using chemiluminescence and a ligand-photosensitiser conjugate
PatentInactiveUS20100297762A1
Innovation
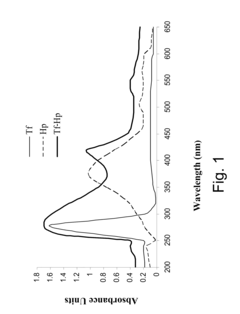
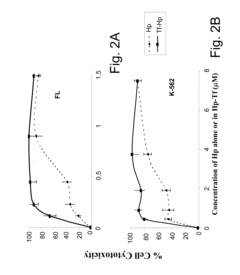
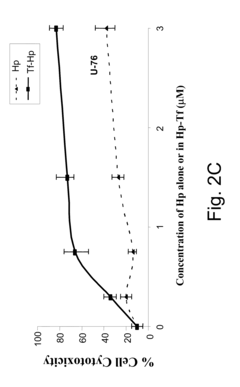
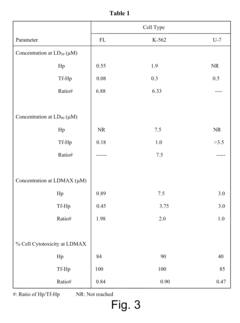
- A method involving a ligand-toxin conjugate (LTC) comprising a photosensitizer like hematoporphyrin conjugated with transferrin, combined with a chemiluminescent agent such as luminol, which activates the photosensitizer intracellularly to produce reactive oxygen species, thereby enhancing target cell destruction without requiring external light.
Regulatory Framework for Luminol Usage
The regulatory framework for luminol usage is a critical aspect of its application in forensic science and research. Various governmental bodies and professional organizations have established guidelines and protocols to ensure the safe and effective use of luminol in crime scene investigations and laboratory settings.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set forth specific regulations regarding the handling and storage of luminol. These guidelines mandate proper personal protective equipment (PPE) for individuals working with the chemical, including gloves, protective eyewear, and appropriate respiratory protection when necessary. Additionally, OSHA requires proper labeling and storage of luminol in accordance with hazardous material regulations.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a role in regulating luminol usage, particularly concerning its disposal. As luminol can potentially impact aquatic ecosystems, strict protocols are in place for its proper disposal to minimize environmental contamination. Research institutions and forensic laboratories must adhere to these guidelines to maintain compliance with environmental regulations.
Internationally, the use of luminol is subject to varying degrees of regulation. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has classified luminol under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which governs the production and use of chemical substances in the European Union. This classification imposes specific requirements on manufacturers, importers, and users of luminol within the EU.
Professional organizations such as the International Association for Identification (IAI) and the American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS) have developed best practice guidelines for the use of luminol in forensic investigations. These guidelines cover aspects such as proper application techniques, documentation procedures, and quality control measures to ensure the reliability and admissibility of evidence obtained through luminol testing.
In the realm of research applications, institutional review boards (IRBs) often play a crucial role in overseeing the use of luminol in scientific studies. IRBs are responsible for ensuring that research protocols involving luminol adhere to ethical standards and safety regulations, particularly when human subjects or sensitive biological materials are involved.
The regulatory landscape for luminol usage continues to evolve as new research emerges regarding its potential health and environmental impacts. Ongoing studies are examining the long-term effects of luminol exposure on forensic professionals and the potential for false positives in certain testing scenarios. These findings may lead to further refinements in regulatory frameworks and best practices for luminol application in both forensic and research settings.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set forth specific regulations regarding the handling and storage of luminol. These guidelines mandate proper personal protective equipment (PPE) for individuals working with the chemical, including gloves, protective eyewear, and appropriate respiratory protection when necessary. Additionally, OSHA requires proper labeling and storage of luminol in accordance with hazardous material regulations.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a role in regulating luminol usage, particularly concerning its disposal. As luminol can potentially impact aquatic ecosystems, strict protocols are in place for its proper disposal to minimize environmental contamination. Research institutions and forensic laboratories must adhere to these guidelines to maintain compliance with environmental regulations.
Internationally, the use of luminol is subject to varying degrees of regulation. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has classified luminol under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which governs the production and use of chemical substances in the European Union. This classification imposes specific requirements on manufacturers, importers, and users of luminol within the EU.
Professional organizations such as the International Association for Identification (IAI) and the American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS) have developed best practice guidelines for the use of luminol in forensic investigations. These guidelines cover aspects such as proper application techniques, documentation procedures, and quality control measures to ensure the reliability and admissibility of evidence obtained through luminol testing.
In the realm of research applications, institutional review boards (IRBs) often play a crucial role in overseeing the use of luminol in scientific studies. IRBs are responsible for ensuring that research protocols involving luminol adhere to ethical standards and safety regulations, particularly when human subjects or sensitive biological materials are involved.
The regulatory landscape for luminol usage continues to evolve as new research emerges regarding its potential health and environmental impacts. Ongoing studies are examining the long-term effects of luminol exposure on forensic professionals and the potential for false positives in certain testing scenarios. These findings may lead to further refinements in regulatory frameworks and best practices for luminol application in both forensic and research settings.
Environmental Impact of Luminol Applications
The environmental impact of luminol applications is a critical consideration in the expanding use of this chemiluminescent compound. Luminol's primary application in forensic science for blood detection has relatively minimal environmental consequences due to its controlled and limited use. However, as research trends indicate a growing interest in broader applications, the potential environmental effects warrant closer examination.
In aquatic environments, luminol's impact is generally low due to its rapid degradation in water. Studies have shown that luminol and its byproducts break down quickly, with minimal persistence in natural water bodies. This characteristic reduces the risk of long-term aquatic ecosystem disruption. Nevertheless, increased use in large-scale applications could potentially lead to localized, short-term effects on aquatic organisms, particularly in sensitive habitats.
Soil interactions with luminol are more complex. While luminol itself has limited soil mobility, its reaction products may have varying degrees of soil retention and transport. Research suggests that these compounds generally have low toxicity to soil microorganisms and plants. However, repeated or high-volume applications in specific areas could potentially alter soil chemistry and microbial communities, necessitating further investigation into long-term effects on soil ecosystems.
Air quality impacts from luminol use are typically negligible due to its non-volatile nature and the controlled conditions of its application. However, the production and disposal of luminol and associated chemicals may contribute to industrial emissions and waste streams, albeit on a relatively small scale compared to other industrial processes.
The expanding use of luminol in biosensors and medical diagnostics presents new environmental considerations. While these applications often involve minute quantities, the potential for increased production and disposal of luminol-based materials raises questions about lifecycle environmental impacts, including resource extraction, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life management.
As luminol finds new applications in environmental monitoring, such as detecting pollutants in water or soil, it paradoxically becomes both a tool for environmental protection and a potential contaminant itself. This dual role underscores the importance of developing sustainable practices for its use and disposal, particularly as its applications expand beyond traditional forensic contexts.
In conclusion, while current evidence suggests that luminol's environmental impact is generally low, the trend towards broader and more diverse applications necessitates ongoing research and vigilance. Future studies should focus on long-term ecological effects, potential bioaccumulation in food chains, and the development of eco-friendly alternatives or improved formulations to mitigate any adverse environmental impacts as luminol's use continues to grow across various fields.
In aquatic environments, luminol's impact is generally low due to its rapid degradation in water. Studies have shown that luminol and its byproducts break down quickly, with minimal persistence in natural water bodies. This characteristic reduces the risk of long-term aquatic ecosystem disruption. Nevertheless, increased use in large-scale applications could potentially lead to localized, short-term effects on aquatic organisms, particularly in sensitive habitats.
Soil interactions with luminol are more complex. While luminol itself has limited soil mobility, its reaction products may have varying degrees of soil retention and transport. Research suggests that these compounds generally have low toxicity to soil microorganisms and plants. However, repeated or high-volume applications in specific areas could potentially alter soil chemistry and microbial communities, necessitating further investigation into long-term effects on soil ecosystems.
Air quality impacts from luminol use are typically negligible due to its non-volatile nature and the controlled conditions of its application. However, the production and disposal of luminol and associated chemicals may contribute to industrial emissions and waste streams, albeit on a relatively small scale compared to other industrial processes.
The expanding use of luminol in biosensors and medical diagnostics presents new environmental considerations. While these applications often involve minute quantities, the potential for increased production and disposal of luminol-based materials raises questions about lifecycle environmental impacts, including resource extraction, manufacturing processes, and end-of-life management.
As luminol finds new applications in environmental monitoring, such as detecting pollutants in water or soil, it paradoxically becomes both a tool for environmental protection and a potential contaminant itself. This dual role underscores the importance of developing sustainable practices for its use and disposal, particularly as its applications expand beyond traditional forensic contexts.
In conclusion, while current evidence suggests that luminol's environmental impact is generally low, the trend towards broader and more diverse applications necessitates ongoing research and vigilance. Future studies should focus on long-term ecological effects, potential bioaccumulation in food chains, and the development of eco-friendly alternatives or improved formulations to mitigate any adverse environmental impacts as luminol's use continues to grow across various fields.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!