How Luminol Spurs Creative Scientific Configurations?
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luminol Science Background
Luminol, a chemical compound with the formula C8H7N3O2, has been a subject of fascination in scientific research for decades. This organic compound, also known as 3-aminophthalhydrazide, exhibits remarkable chemiluminescent properties when oxidized. The discovery of luminol's light-emitting capabilities dates back to 1928 when German chemist H. O. Albrecht first synthesized and described its luminescent characteristics.
The science behind luminol's glow lies in its unique molecular structure and chemical reactivity. When exposed to an oxidizing agent in the presence of a catalyst, luminol undergoes a complex series of reactions that result in the emission of blue light. This process, known as chemiluminescence, occurs without the need for external energy input, making luminol an intriguing subject for various scientific applications.
The chemical reaction that produces luminol's signature blue glow involves several steps. Initially, luminol is oxidized to form an excited state intermediate. This unstable intermediate then rapidly decomposes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The wavelength of the emitted light is approximately 425 nanometers, corresponding to the blue region of the visible spectrum.
One of the most notable aspects of luminol's chemistry is its sensitivity to certain metal ions, particularly iron. This property has led to its widespread use in forensic science for detecting trace amounts of blood at crime scenes. When luminol comes into contact with the iron in hemoglobin, it produces a bright, long-lasting chemiluminescence that can be easily detected and photographed in dark environments.
Beyond forensics, luminol has found applications in various scientific fields. In biochemistry, it serves as a valuable tool for detecting and quantifying specific enzymes and metabolites. Environmental scientists utilize luminol-based assays to monitor water quality and detect pollutants. In medical research, luminol derivatives have been explored for their potential in imaging techniques and as diagnostic tools for certain diseases.
The versatility of luminol in scientific research stems from its unique chemical properties and the ability to fine-tune its reactivity. Researchers have developed numerous analogs and derivatives of luminol, each with specific characteristics tailored to different applications. These modifications have expanded the range of detectable substances and improved the sensitivity and specificity of luminol-based assays.
As scientific understanding of luminol's properties has grown, so too has the creativity in its applications. From enhancing the visualization of cellular processes to developing novel biosensors, luminol continues to inspire innovative scientific configurations across multiple disciplines. Its enduring relevance in research underscores the importance of fundamental chemical discoveries in driving scientific progress and technological advancements.
The science behind luminol's glow lies in its unique molecular structure and chemical reactivity. When exposed to an oxidizing agent in the presence of a catalyst, luminol undergoes a complex series of reactions that result in the emission of blue light. This process, known as chemiluminescence, occurs without the need for external energy input, making luminol an intriguing subject for various scientific applications.
The chemical reaction that produces luminol's signature blue glow involves several steps. Initially, luminol is oxidized to form an excited state intermediate. This unstable intermediate then rapidly decomposes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The wavelength of the emitted light is approximately 425 nanometers, corresponding to the blue region of the visible spectrum.
One of the most notable aspects of luminol's chemistry is its sensitivity to certain metal ions, particularly iron. This property has led to its widespread use in forensic science for detecting trace amounts of blood at crime scenes. When luminol comes into contact with the iron in hemoglobin, it produces a bright, long-lasting chemiluminescence that can be easily detected and photographed in dark environments.
Beyond forensics, luminol has found applications in various scientific fields. In biochemistry, it serves as a valuable tool for detecting and quantifying specific enzymes and metabolites. Environmental scientists utilize luminol-based assays to monitor water quality and detect pollutants. In medical research, luminol derivatives have been explored for their potential in imaging techniques and as diagnostic tools for certain diseases.
The versatility of luminol in scientific research stems from its unique chemical properties and the ability to fine-tune its reactivity. Researchers have developed numerous analogs and derivatives of luminol, each with specific characteristics tailored to different applications. These modifications have expanded the range of detectable substances and improved the sensitivity and specificity of luminol-based assays.
As scientific understanding of luminol's properties has grown, so too has the creativity in its applications. From enhancing the visualization of cellular processes to developing novel biosensors, luminol continues to inspire innovative scientific configurations across multiple disciplines. Its enduring relevance in research underscores the importance of fundamental chemical discoveries in driving scientific progress and technological advancements.
Market Applications Analysis
Luminol, a chemiluminescent compound, has sparked numerous creative scientific configurations across various market applications. The healthcare sector has been a primary beneficiary of luminol-based technologies, particularly in forensic science and medical diagnostics. In forensic investigations, luminol's ability to detect trace amounts of blood has revolutionized crime scene analysis, leading to the development of advanced detection kits and imaging systems. This market segment has seen steady growth, driven by increasing demand for more sophisticated forensic tools in law enforcement agencies worldwide.
In the medical field, luminol-based assays have found applications in diagnostic testing, particularly for detecting specific proteins or enzymes associated with various diseases. The market for these diagnostic tools has expanded significantly, with luminol-based tests offering high sensitivity and rapid results. This has led to the development of point-of-care testing devices, which are increasingly in demand for their ability to provide quick and accurate diagnoses in resource-limited settings.
The environmental monitoring sector has also embraced luminol-based technologies. Water quality testing applications have emerged as a promising market, with luminol-based sensors capable of detecting trace contaminants in water supplies. This market segment is expected to grow as concerns about water pollution and the need for real-time monitoring systems increase globally.
In the industrial sector, luminol has found applications in leak detection systems for pipelines and storage tanks. The ability to quickly and accurately identify small leaks has made luminol-based systems valuable in preventing environmental damage and ensuring workplace safety. This market niche has seen steady growth, particularly in the oil and gas industry, where leak prevention is critical.
The research and development sector represents another significant market for luminol-based technologies. Academic and industrial laboratories utilize luminol in various experimental setups, from studying cellular processes to developing new analytical techniques. This market segment is characterized by continuous innovation and the creation of specialized luminol derivatives tailored for specific research applications.
Emerging applications in biosecurity and food safety testing are opening new market opportunities for luminol-based technologies. The development of rapid screening methods for detecting pathogens or contaminants in food products has gained traction, driven by increasing regulatory requirements and consumer demand for food safety assurance.
As luminol continues to inspire creative scientific configurations, its market applications are likely to expand further. The compound's versatility and the ongoing research into enhancing its properties suggest that new market niches will emerge, potentially in areas such as wearable biosensors, advanced imaging technologies, and novel drug delivery systems.
In the medical field, luminol-based assays have found applications in diagnostic testing, particularly for detecting specific proteins or enzymes associated with various diseases. The market for these diagnostic tools has expanded significantly, with luminol-based tests offering high sensitivity and rapid results. This has led to the development of point-of-care testing devices, which are increasingly in demand for their ability to provide quick and accurate diagnoses in resource-limited settings.
The environmental monitoring sector has also embraced luminol-based technologies. Water quality testing applications have emerged as a promising market, with luminol-based sensors capable of detecting trace contaminants in water supplies. This market segment is expected to grow as concerns about water pollution and the need for real-time monitoring systems increase globally.
In the industrial sector, luminol has found applications in leak detection systems for pipelines and storage tanks. The ability to quickly and accurately identify small leaks has made luminol-based systems valuable in preventing environmental damage and ensuring workplace safety. This market niche has seen steady growth, particularly in the oil and gas industry, where leak prevention is critical.
The research and development sector represents another significant market for luminol-based technologies. Academic and industrial laboratories utilize luminol in various experimental setups, from studying cellular processes to developing new analytical techniques. This market segment is characterized by continuous innovation and the creation of specialized luminol derivatives tailored for specific research applications.
Emerging applications in biosecurity and food safety testing are opening new market opportunities for luminol-based technologies. The development of rapid screening methods for detecting pathogens or contaminants in food products has gained traction, driven by increasing regulatory requirements and consumer demand for food safety assurance.
As luminol continues to inspire creative scientific configurations, its market applications are likely to expand further. The compound's versatility and the ongoing research into enhancing its properties suggest that new market niches will emerge, potentially in areas such as wearable biosensors, advanced imaging technologies, and novel drug delivery systems.
Current Challenges in Luminol Use
Despite its widespread use in forensic science and creative applications, luminol faces several significant challenges that limit its effectiveness and reliability. One of the primary issues is its lack of specificity. While luminol is highly sensitive to the presence of blood, it can also react with other substances such as certain metals, plant materials, and cleaning agents. This non-specificity can lead to false positives, potentially compromising the integrity of forensic investigations or scientific experiments.
Another challenge is the potential for luminol to interfere with subsequent DNA analysis. The chemical reaction that produces the characteristic blue glow can potentially degrade or alter DNA evidence, making it more difficult to obtain accurate genetic profiles from blood samples. This limitation is particularly problematic in criminal investigations where DNA evidence is crucial for identifying suspects or exonerating the innocent.
The luminol reaction's sensitivity to environmental factors poses additional challenges. Factors such as temperature, pH, and the presence of contaminants can significantly affect the intensity and duration of the chemiluminescent reaction. This variability can make it difficult to standardize results across different experimental conditions or crime scenes, potentially leading to inconsistencies in data interpretation.
Furthermore, the transient nature of the luminol reaction presents practical difficulties. The blue glow produced by the reaction is relatively short-lived, typically lasting only a few minutes. This brief window of visibility can make it challenging to document and analyze the results thoroughly, especially in complex or large-scale investigations.
Safety concerns also arise from the use of luminol. While generally considered non-toxic, prolonged exposure or ingestion can cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. This necessitates careful handling and appropriate safety measures, which can be challenging to maintain in diverse experimental or investigative settings.
Lastly, the preparation and application of luminol solutions require precise mixing and timing. The solution's effectiveness decreases rapidly after preparation, limiting its shelf life and necessitating on-site mixing. This requirement for fresh preparation can be logistically challenging, especially in field applications or resource-limited settings.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for expanding the creative and scientific applications of luminol. Innovations in formulation to increase specificity, methods to preserve DNA integrity, and techniques to prolong the luminescent reaction could significantly enhance luminol's utility across various fields, from forensic science to biomedical research and artistic expression.
Another challenge is the potential for luminol to interfere with subsequent DNA analysis. The chemical reaction that produces the characteristic blue glow can potentially degrade or alter DNA evidence, making it more difficult to obtain accurate genetic profiles from blood samples. This limitation is particularly problematic in criminal investigations where DNA evidence is crucial for identifying suspects or exonerating the innocent.
The luminol reaction's sensitivity to environmental factors poses additional challenges. Factors such as temperature, pH, and the presence of contaminants can significantly affect the intensity and duration of the chemiluminescent reaction. This variability can make it difficult to standardize results across different experimental conditions or crime scenes, potentially leading to inconsistencies in data interpretation.
Furthermore, the transient nature of the luminol reaction presents practical difficulties. The blue glow produced by the reaction is relatively short-lived, typically lasting only a few minutes. This brief window of visibility can make it challenging to document and analyze the results thoroughly, especially in complex or large-scale investigations.
Safety concerns also arise from the use of luminol. While generally considered non-toxic, prolonged exposure or ingestion can cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. This necessitates careful handling and appropriate safety measures, which can be challenging to maintain in diverse experimental or investigative settings.
Lastly, the preparation and application of luminol solutions require precise mixing and timing. The solution's effectiveness decreases rapidly after preparation, limiting its shelf life and necessitating on-site mixing. This requirement for fresh preparation can be logistically challenging, especially in field applications or resource-limited settings.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for expanding the creative and scientific applications of luminol. Innovations in formulation to increase specificity, methods to preserve DNA integrity, and techniques to prolong the luminescent reaction could significantly enhance luminol's utility across various fields, from forensic science to biomedical research and artistic expression.
Existing Luminol Configurations
01 Luminol-based detection systems
Luminol is used in creative scientific configurations for detection purposes. These systems utilize the chemiluminescent properties of luminol to detect various substances or conditions. The configurations may include specialized sensors, reagents, and detection mechanisms to enhance sensitivity and specificity.- Luminol-based detection systems: Luminol is used in creative scientific configurations for detection purposes. These systems utilize the chemiluminescent properties of luminol to detect various substances or conditions. The configurations may include specialized sensors, reagents, and detection methods to enhance sensitivity and specificity.
- Innovative imaging techniques using luminol: Advanced imaging techniques incorporate luminol for creative scientific applications. These may include novel camera systems, image processing algorithms, or visualization methods that leverage luminol's light-emitting properties. Such configurations can be used in forensic science, medical imaging, or environmental monitoring.
- Luminol-enhanced analytical methods: Creative scientific configurations involving luminol are developed for analytical purposes. These may include new spectroscopic techniques, chromatography methods, or microfluidic devices that utilize luminol's chemical properties for improved analysis and quantification of various substances.
- Luminol applications in data analysis and visualization: Luminol-inspired configurations are used in data analysis and visualization techniques. These may involve software algorithms, data processing methods, or visual representation tools that draw inspiration from luminol's characteristics to enhance data interpretation and presentation in scientific research.
- Luminol-based biosensors and diagnostic tools: Creative scientific configurations incorporate luminol in the development of biosensors and diagnostic tools. These may include novel sensor designs, biomarker detection methods, or point-of-care devices that utilize luminol's properties for rapid and sensitive detection of biological molecules or disease markers.
02 Innovative imaging techniques using luminol
Advanced imaging techniques incorporate luminol for creative scientific applications. These may include specialized cameras, image processing algorithms, and visualization methods to capture and analyze luminol-based reactions. Such configurations can be used in forensic science, medical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring.Expand Specific Solutions03 Luminol-enhanced analytical methods
Creative scientific configurations utilize luminol to enhance analytical methods. These may involve combining luminol with other chemicals or techniques to improve detection limits, increase specificity, or enable multiplexed analysis. Such configurations can be applied in fields like biochemistry, environmental science, and materials analysis.Expand Specific Solutions04 Automated luminol-based systems
Automated systems incorporating luminol for scientific applications are developed. These configurations may include robotics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning algorithms to optimize luminol-based detection and analysis processes. Such systems can enhance efficiency and accuracy in various scientific fields.Expand Specific Solutions05 Luminol applications in data analysis and visualization
Creative scientific configurations integrate luminol-based data into advanced analysis and visualization tools. These may include specialized software, data processing algorithms, and interactive interfaces to interpret and present results from luminol-based experiments or detection systems. Such configurations can enhance data interpretation and decision-making in scientific research.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Luminol Research
The luminol technology landscape is characterized by a diverse and competitive market in its early growth stage. While the market size remains relatively modest, it shows promising potential for expansion across various applications. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with key players like Seoul Semiconductor, Beijing Yuji Science & Technology, and Washington University in St. Louis driving innovation. These companies are at different stages of development, from established semiconductor manufacturers to emerging research institutions, indicating a dynamic ecosystem. The field is seeing creative scientific configurations, with academic institutions like CSIC and Federal University of Rio de Janeiro contributing to fundamental research, while companies like LI-COR and Diasorin Italia focus on practical applications in biotechnology and diagnostics.
Seoul Semiconductor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Seoul Semiconductor has developed innovative luminol-based technologies for advanced lighting solutions. Their approach involves incorporating luminol into LED designs to create hybrid luminescent-electronic devices. This configuration enhances light output and efficiency by combining chemiluminescence with electroluminescence. The company has patented methods for stabilizing luminol compounds within solid-state lighting structures, allowing for prolonged luminescence without degradation[1]. Their research has also explored using luminol derivatives with tailored emission spectra to produce tunable white light sources with high color rendering indices[2].
Strengths: Innovative integration of chemical and electronic light sources, potential for highly efficient and tunable lighting. Weaknesses: Complexity of manufacturing hybrid devices, potential issues with long-term stability of luminol compounds in solid-state configurations.
Washington University in St. Louis
Technical Solution: Washington University in St. Louis has pioneered the use of luminol in biomedical imaging and diagnostics. Their research team has developed a novel luminol-based probe for detecting myeloperoxidase activity in vivo, which is crucial for studying inflammatory processes[3]. This configuration utilizes luminol's chemiluminescent properties to visualize neutrophil activity in real-time, providing a non-invasive method for monitoring inflammation in various diseases. The university has also explored the use of luminol derivatives with enhanced tissue penetration capabilities, allowing for deeper imaging in biological samples[4]. Additionally, they have investigated the combination of luminol with nanoparticles to create targeted imaging agents for specific cellular processes[5].
Strengths: Non-invasive imaging techniques, high sensitivity for detecting inflammatory processes, potential for early disease diagnosis. Weaknesses: Limited to specific biological processes, potential for background interference in complex biological environments.
Innovative Luminol Applications
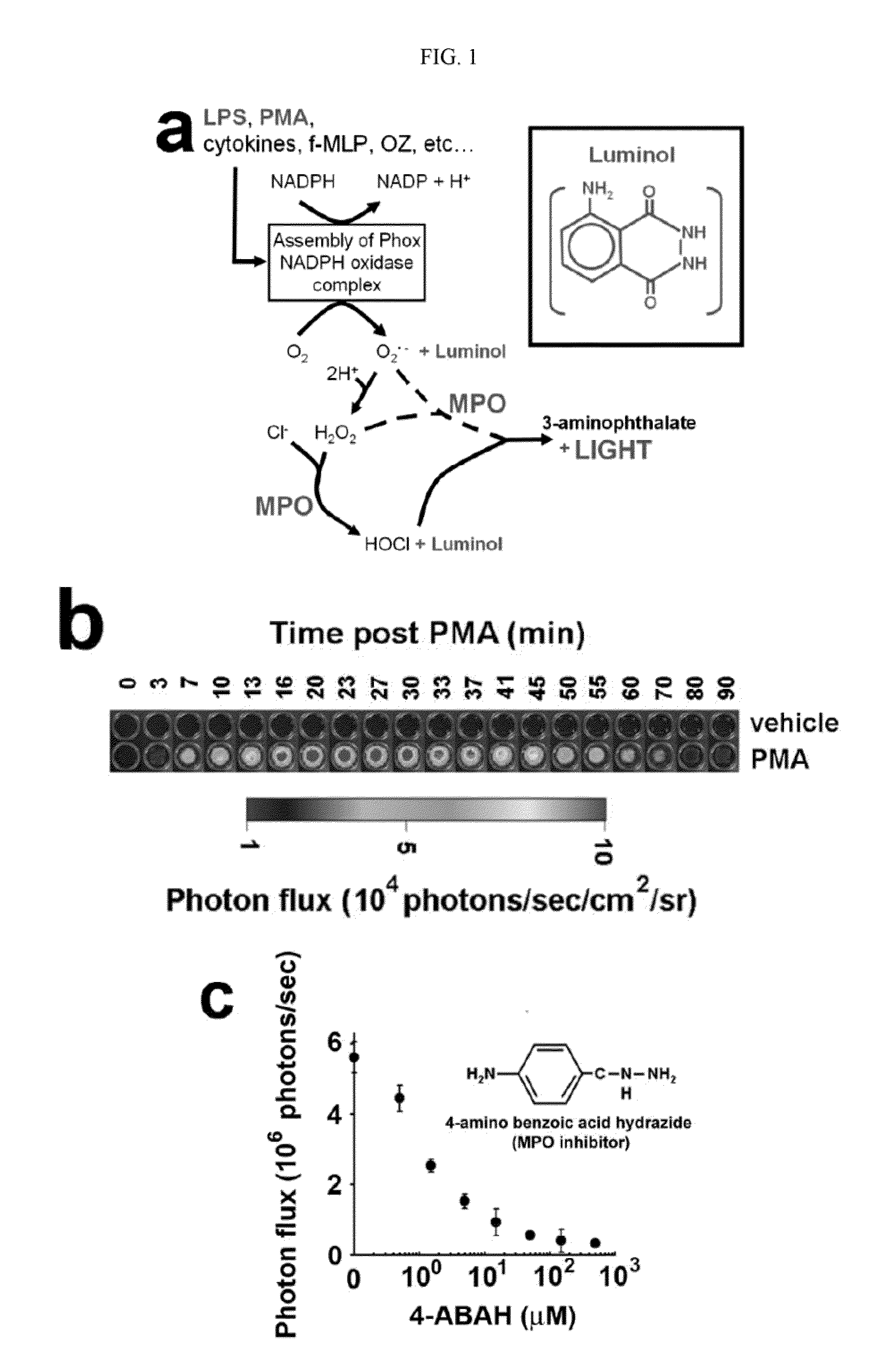
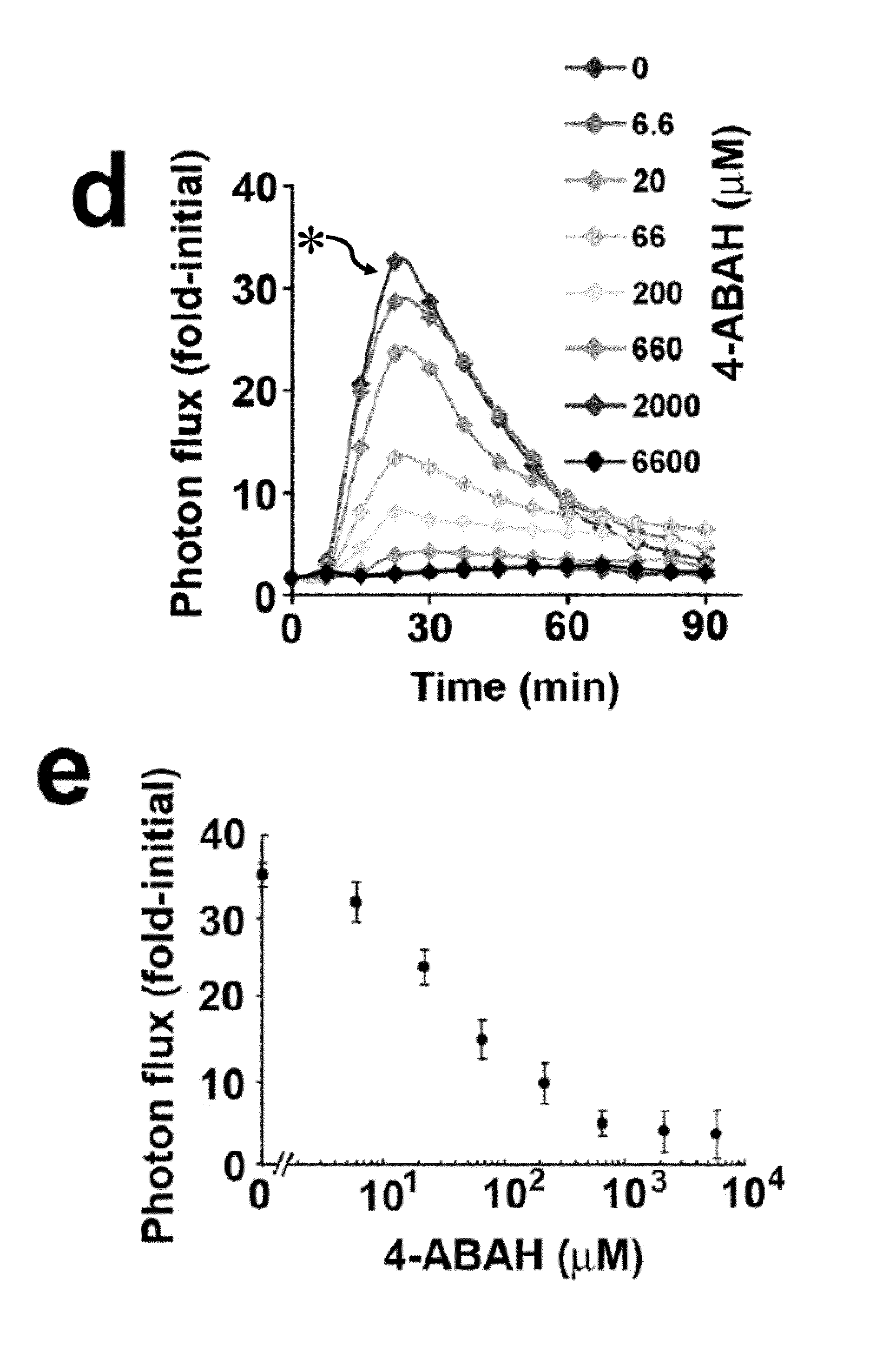
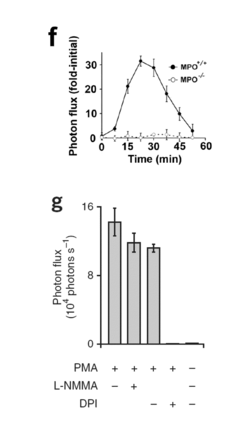
Bioluminescence imaging of myeloperoxidase activity in vivo, methods, compositions and apparatuses therefor
PatentInactiveUS20110250145A1
Innovation
- The development of methods for non-invasive imaging of MPO activity using luminogenic-optical probes that emit light upon contact with oxidizing agents, allowing for the visualization of MPO activity in vivo, particularly through bioluminescence imaging (BLI) techniques.
Luminol Safety Regulations
Luminol safety regulations are crucial for ensuring the proper handling and use of this chemiluminescent compound in scientific and forensic applications. The primary concern when working with luminol is its potential health hazards, particularly its irritant properties and possible carcinogenic effects. To mitigate these risks, strict safety protocols must be followed in laboratory settings.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential when handling luminol. This includes wearing appropriate gloves, safety goggles, and lab coats to prevent skin contact and eye exposure. Respiratory protection may also be necessary when working with luminol in powder form or in poorly ventilated areas. Proper training on the correct use of PPE and handling procedures is mandatory for all personnel working with luminol.
Storage and disposal of luminol require specific precautions. The compound should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Containers must be tightly sealed to prevent contamination and degradation. When disposing of luminol or its solutions, it is important to follow local environmental regulations and avoid releasing it into water systems or soil.
Workplace safety measures for luminol use include the provision of adequate ventilation systems in laboratories. Fume hoods should be used when preparing luminol solutions or conducting experiments that may generate vapors. Emergency eyewash stations and safety showers must be readily accessible in areas where luminol is handled.
Risk assessment and management protocols are essential components of luminol safety regulations. Regular safety audits should be conducted to ensure compliance with established guidelines. This includes maintaining up-to-date safety data sheets (SDS) for luminol and associated chemicals, as well as implementing proper labeling and signage in storage and work areas.
In the event of accidental exposure or spills, clear emergency procedures must be in place. This includes immediate decontamination steps, such as flushing affected areas with water, and seeking medical attention if necessary. Spill cleanup kits specifically designed for chemical accidents should be available, and personnel must be trained in their use.
Luminol safety regulations also extend to the transportation of the compound. When shipping luminol, it must be properly packaged and labeled according to international transportation safety standards. This includes using appropriate containment materials and providing necessary documentation detailing the nature of the substance and associated hazards.
By adhering to these comprehensive safety regulations, researchers and forensic professionals can harness the creative scientific configurations of luminol while minimizing potential risks to human health and the environment. Regular updates to these protocols, based on the latest scientific findings and regulatory requirements, ensure that luminol continues to be a valuable tool in various scientific disciplines.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential when handling luminol. This includes wearing appropriate gloves, safety goggles, and lab coats to prevent skin contact and eye exposure. Respiratory protection may also be necessary when working with luminol in powder form or in poorly ventilated areas. Proper training on the correct use of PPE and handling procedures is mandatory for all personnel working with luminol.
Storage and disposal of luminol require specific precautions. The compound should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Containers must be tightly sealed to prevent contamination and degradation. When disposing of luminol or its solutions, it is important to follow local environmental regulations and avoid releasing it into water systems or soil.
Workplace safety measures for luminol use include the provision of adequate ventilation systems in laboratories. Fume hoods should be used when preparing luminol solutions or conducting experiments that may generate vapors. Emergency eyewash stations and safety showers must be readily accessible in areas where luminol is handled.
Risk assessment and management protocols are essential components of luminol safety regulations. Regular safety audits should be conducted to ensure compliance with established guidelines. This includes maintaining up-to-date safety data sheets (SDS) for luminol and associated chemicals, as well as implementing proper labeling and signage in storage and work areas.
In the event of accidental exposure or spills, clear emergency procedures must be in place. This includes immediate decontamination steps, such as flushing affected areas with water, and seeking medical attention if necessary. Spill cleanup kits specifically designed for chemical accidents should be available, and personnel must be trained in their use.
Luminol safety regulations also extend to the transportation of the compound. When shipping luminol, it must be properly packaged and labeled according to international transportation safety standards. This includes using appropriate containment materials and providing necessary documentation detailing the nature of the substance and associated hazards.
By adhering to these comprehensive safety regulations, researchers and forensic professionals can harness the creative scientific configurations of luminol while minimizing potential risks to human health and the environment. Regular updates to these protocols, based on the latest scientific findings and regulatory requirements, ensure that luminol continues to be a valuable tool in various scientific disciplines.
Interdisciplinary Luminol Uses
Luminol, a versatile chemical compound, has found applications across various scientific disciplines, showcasing its potential for creative and innovative uses beyond its traditional role in forensic science. This interdisciplinary approach has led to the development of novel techniques and methodologies in fields such as biology, chemistry, and environmental science.
In biology, luminol has been employed as a powerful tool for visualizing cellular processes. Researchers have utilized its chemiluminescent properties to study enzyme activity, detect specific biomolecules, and track cellular signaling pathways. This has provided valuable insights into complex biological systems and has contributed to advancements in areas such as cancer research and drug discovery.
The chemistry field has also benefited from luminol's unique properties. Scientists have developed new analytical techniques based on luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence for the detection and quantification of various chemical species. These methods have proven particularly useful in environmental monitoring, allowing for the sensitive detection of pollutants and contaminants in water and soil samples.
In environmental science, luminol has been adapted for use in ecological studies. Researchers have employed luminol-based techniques to investigate microbial activity in soil and aquatic ecosystems, providing valuable information on nutrient cycling and ecosystem health. Additionally, luminol has been used to detect and monitor harmful algal blooms in marine environments, contributing to our understanding of these complex ecological phenomena.
The medical field has also embraced luminol's potential, with applications ranging from diagnostic tools to therapeutic approaches. Luminol-based imaging techniques have been developed for the visualization of inflammation and oxidative stress in living tissues, offering new possibilities for early disease detection and monitoring treatment efficacy.
Forensic science continues to benefit from innovative applications of luminol. Advanced formulations and detection methods have improved the sensitivity and specificity of blood detection at crime scenes. Furthermore, researchers have explored the use of luminol in conjunction with other technologies, such as hyperspectral imaging, to enhance the capabilities of forensic investigations.
The interdisciplinary nature of luminol research has fostered collaborations between scientists from diverse backgrounds, leading to the cross-pollination of ideas and the development of novel approaches. This collaborative environment has not only expanded the applications of luminol but has also inspired new research directions and technological innovations across multiple scientific domains.
In biology, luminol has been employed as a powerful tool for visualizing cellular processes. Researchers have utilized its chemiluminescent properties to study enzyme activity, detect specific biomolecules, and track cellular signaling pathways. This has provided valuable insights into complex biological systems and has contributed to advancements in areas such as cancer research and drug discovery.
The chemistry field has also benefited from luminol's unique properties. Scientists have developed new analytical techniques based on luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence for the detection and quantification of various chemical species. These methods have proven particularly useful in environmental monitoring, allowing for the sensitive detection of pollutants and contaminants in water and soil samples.
In environmental science, luminol has been adapted for use in ecological studies. Researchers have employed luminol-based techniques to investigate microbial activity in soil and aquatic ecosystems, providing valuable information on nutrient cycling and ecosystem health. Additionally, luminol has been used to detect and monitor harmful algal blooms in marine environments, contributing to our understanding of these complex ecological phenomena.
The medical field has also embraced luminol's potential, with applications ranging from diagnostic tools to therapeutic approaches. Luminol-based imaging techniques have been developed for the visualization of inflammation and oxidative stress in living tissues, offering new possibilities for early disease detection and monitoring treatment efficacy.
Forensic science continues to benefit from innovative applications of luminol. Advanced formulations and detection methods have improved the sensitivity and specificity of blood detection at crime scenes. Furthermore, researchers have explored the use of luminol in conjunction with other technologies, such as hyperspectral imaging, to enhance the capabilities of forensic investigations.
The interdisciplinary nature of luminol research has fostered collaborations between scientists from diverse backgrounds, leading to the cross-pollination of ideas and the development of novel approaches. This collaborative environment has not only expanded the applications of luminol but has also inspired new research directions and technological innovations across multiple scientific domains.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!