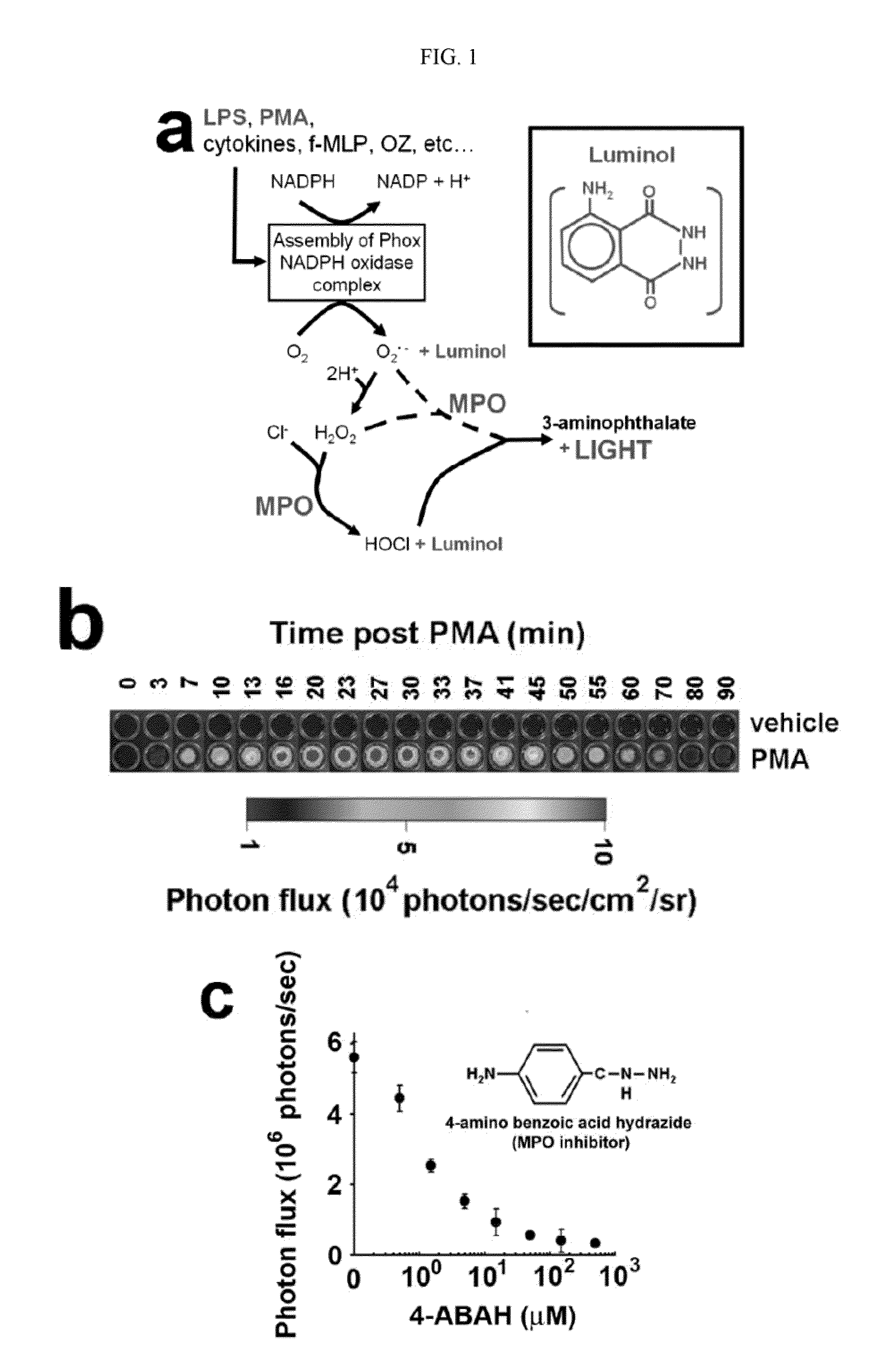
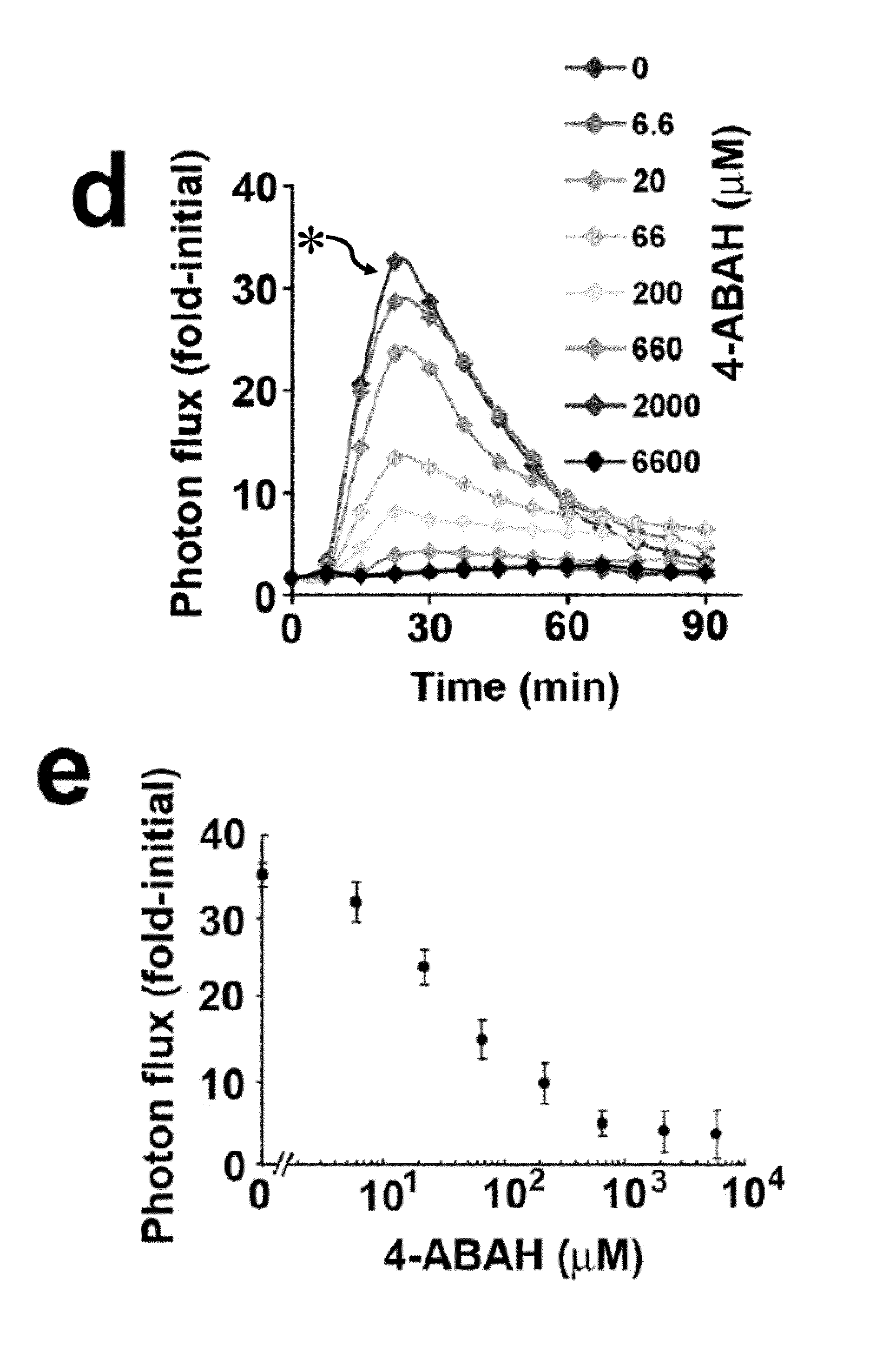
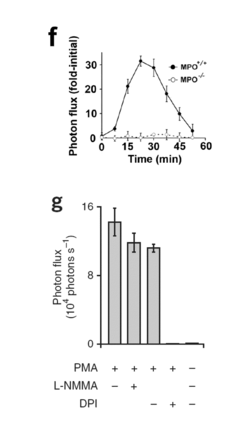
How Luminol Becomes Central to Research Innovation?
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luminol Research Background and Objectives
Luminol, a chemiluminescent compound, has emerged as a pivotal tool in scientific research and innovation. Its journey from a simple chemical curiosity to a central component in various fields of study spans over a century. The discovery of luminol's chemiluminescent properties in 1928 by German chemist H. O. Albrecht marked the beginning of its scientific exploration. Since then, luminol has undergone extensive research and development, leading to its widespread application in forensic science, biochemistry, and environmental studies.
The primary objective of luminol research is to harness and enhance its unique light-emitting properties for practical applications. Scientists aim to improve its sensitivity, specificity, and stability to expand its utility across diverse scientific disciplines. One key focus is optimizing luminol's role in forensic investigations, particularly in the detection of trace amounts of blood at crime scenes. Researchers strive to develop more efficient and reliable luminol-based techniques that can withstand various environmental conditions and provide accurate results.
In the field of biochemistry, luminol research targets the development of highly sensitive assays for detecting and quantifying specific biomolecules. The goal is to create luminol-based systems that can detect minute quantities of proteins, enzymes, or other biological compounds with high precision. This has significant implications for medical diagnostics, drug discovery, and understanding cellular processes at a molecular level.
Environmental scientists are exploring luminol's potential in monitoring water quality and detecting pollutants. The research aims to develop luminol-based sensors that can rapidly and accurately identify contaminants in water sources, contributing to more effective environmental protection strategies. Additionally, researchers are investigating luminol's applications in studying marine bioluminescence, which could provide insights into ocean ecosystems and climate change impacts.
The evolution of luminol research also encompasses the exploration of novel synthesis methods and chemical modifications. Scientists are working on creating luminol derivatives with enhanced properties, such as increased light output, longer emission duration, or specific reactivity to target molecules. These advancements could lead to the development of new analytical tools and expand luminol's applicability in various scientific and industrial sectors.
As luminol continues to play a central role in research innovation, the scientific community is focusing on interdisciplinary approaches. Collaborations between chemists, biologists, forensic experts, and environmental scientists are driving the development of cutting-edge luminol-based technologies. These collaborative efforts aim to push the boundaries of luminol's capabilities and uncover new applications that could revolutionize scientific research and practical problem-solving across multiple domains.
The primary objective of luminol research is to harness and enhance its unique light-emitting properties for practical applications. Scientists aim to improve its sensitivity, specificity, and stability to expand its utility across diverse scientific disciplines. One key focus is optimizing luminol's role in forensic investigations, particularly in the detection of trace amounts of blood at crime scenes. Researchers strive to develop more efficient and reliable luminol-based techniques that can withstand various environmental conditions and provide accurate results.
In the field of biochemistry, luminol research targets the development of highly sensitive assays for detecting and quantifying specific biomolecules. The goal is to create luminol-based systems that can detect minute quantities of proteins, enzymes, or other biological compounds with high precision. This has significant implications for medical diagnostics, drug discovery, and understanding cellular processes at a molecular level.
Environmental scientists are exploring luminol's potential in monitoring water quality and detecting pollutants. The research aims to develop luminol-based sensors that can rapidly and accurately identify contaminants in water sources, contributing to more effective environmental protection strategies. Additionally, researchers are investigating luminol's applications in studying marine bioluminescence, which could provide insights into ocean ecosystems and climate change impacts.
The evolution of luminol research also encompasses the exploration of novel synthesis methods and chemical modifications. Scientists are working on creating luminol derivatives with enhanced properties, such as increased light output, longer emission duration, or specific reactivity to target molecules. These advancements could lead to the development of new analytical tools and expand luminol's applicability in various scientific and industrial sectors.
As luminol continues to play a central role in research innovation, the scientific community is focusing on interdisciplinary approaches. Collaborations between chemists, biologists, forensic experts, and environmental scientists are driving the development of cutting-edge luminol-based technologies. These collaborative efforts aim to push the boundaries of luminol's capabilities and uncover new applications that could revolutionize scientific research and practical problem-solving across multiple domains.
Market Demand for Luminol Applications
The market demand for luminol applications has been steadily growing across various sectors, driven by its unique chemiluminescent properties and versatility in research and forensic applications. Luminol's ability to detect trace amounts of blood has made it an indispensable tool in crime scene investigations, leading to increased adoption by law enforcement agencies worldwide. This has resulted in a robust demand from forensic laboratories and police departments, contributing significantly to the market growth.
In the field of biomedical research, luminol has found extensive applications in studying cellular processes, particularly in the detection of reactive oxygen species and the analysis of enzyme activities. The pharmaceutical industry has shown increasing interest in luminol-based assays for drug discovery and development processes. These applications have expanded the market beyond traditional forensic uses, creating new opportunities for luminol manufacturers and suppliers.
The environmental monitoring sector has also emerged as a promising market for luminol applications. Its sensitivity in detecting metal ions and other pollutants in water and soil samples has led to its adoption in environmental testing laboratories and water treatment facilities. This trend is expected to continue as global concerns about environmental pollution and water quality grow.
The healthcare industry represents another significant market for luminol, particularly in diagnostic applications. Luminol-based chemiluminescence immunoassays are being increasingly used for the detection of various biomarkers, hormones, and pathogens. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the importance of rapid and sensitive diagnostic tools, potentially boosting the demand for luminol in clinical laboratories.
Academic and research institutions continue to be major consumers of luminol, driving demand through their ongoing studies in biochemistry, molecular biology, and materials science. The exploration of novel applications for luminol in fields such as nanotechnology and biosensors is opening up new market opportunities and fueling innovation in luminol-based technologies.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as the development of alternative technologies and regulatory constraints in certain applications may impact future growth. However, the continuous research into improving luminol's sensitivity, specificity, and ease of use is expected to maintain its relevance and expand its market potential in the coming years.
In the field of biomedical research, luminol has found extensive applications in studying cellular processes, particularly in the detection of reactive oxygen species and the analysis of enzyme activities. The pharmaceutical industry has shown increasing interest in luminol-based assays for drug discovery and development processes. These applications have expanded the market beyond traditional forensic uses, creating new opportunities for luminol manufacturers and suppliers.
The environmental monitoring sector has also emerged as a promising market for luminol applications. Its sensitivity in detecting metal ions and other pollutants in water and soil samples has led to its adoption in environmental testing laboratories and water treatment facilities. This trend is expected to continue as global concerns about environmental pollution and water quality grow.
The healthcare industry represents another significant market for luminol, particularly in diagnostic applications. Luminol-based chemiluminescence immunoassays are being increasingly used for the detection of various biomarkers, hormones, and pathogens. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the importance of rapid and sensitive diagnostic tools, potentially boosting the demand for luminol in clinical laboratories.
Academic and research institutions continue to be major consumers of luminol, driving demand through their ongoing studies in biochemistry, molecular biology, and materials science. The exploration of novel applications for luminol in fields such as nanotechnology and biosensors is opening up new market opportunities and fueling innovation in luminol-based technologies.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as the development of alternative technologies and regulatory constraints in certain applications may impact future growth. However, the continuous research into improving luminol's sensitivity, specificity, and ease of use is expected to maintain its relevance and expand its market potential in the coming years.
Current Luminol Technology Challenges
Luminol, a chemiluminescent compound, has been a cornerstone in forensic science and biomedical research for decades. However, as research demands evolve, several challenges have emerged in the current luminol technology, limiting its full potential in innovative applications.
One of the primary challenges is the sensitivity and specificity of luminol-based detection systems. While luminol is known for its ability to detect trace amounts of blood, false positives can occur due to its reactivity with other substances containing iron or copper. This lack of specificity can lead to misinterpretation of results, particularly in complex biological samples or crime scene investigations.
The stability of luminol solutions presents another significant hurdle. The compound's tendency to degrade over time, especially when exposed to light or heat, affects the reliability and reproducibility of experiments. This instability necessitates frequent preparation of fresh solutions, which can be time-consuming and may introduce variability in results across different batches.
The duration of the luminol reaction poses a challenge in certain applications. The light emission from the luminol reaction, while intense, is relatively short-lived. This brief duration can make it difficult to capture and analyze the signal in some experimental setups, particularly those requiring extended observation periods or real-time monitoring.
Another limitation lies in the pH dependency of the luminol reaction. The optimal pH range for the luminol chemiluminescence is relatively narrow, typically between 10 and 11. This restriction can be problematic when working with biological samples or in environments where maintaining a consistent alkaline pH is challenging.
The potential interference from environmental factors also presents a significant challenge. Ambient light, temperature fluctuations, and the presence of other chemicals can all affect the luminol reaction, potentially leading to inconsistent or unreliable results. This sensitivity to external conditions can complicate field applications and limit the use of luminol in certain research environments.
Furthermore, the quantification of luminol signals remains a challenge in many applications. While the intensity of light emission can be correlated with the concentration of the target substance, achieving accurate and reproducible quantitative measurements across different experimental setups and conditions is often difficult.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for expanding the utility of luminol in research innovation. Overcoming these limitations could open up new avenues for luminol applications in fields ranging from advanced biosensing to environmental monitoring, potentially revolutionizing detection methodologies across multiple scientific disciplines.
One of the primary challenges is the sensitivity and specificity of luminol-based detection systems. While luminol is known for its ability to detect trace amounts of blood, false positives can occur due to its reactivity with other substances containing iron or copper. This lack of specificity can lead to misinterpretation of results, particularly in complex biological samples or crime scene investigations.
The stability of luminol solutions presents another significant hurdle. The compound's tendency to degrade over time, especially when exposed to light or heat, affects the reliability and reproducibility of experiments. This instability necessitates frequent preparation of fresh solutions, which can be time-consuming and may introduce variability in results across different batches.
The duration of the luminol reaction poses a challenge in certain applications. The light emission from the luminol reaction, while intense, is relatively short-lived. This brief duration can make it difficult to capture and analyze the signal in some experimental setups, particularly those requiring extended observation periods or real-time monitoring.
Another limitation lies in the pH dependency of the luminol reaction. The optimal pH range for the luminol chemiluminescence is relatively narrow, typically between 10 and 11. This restriction can be problematic when working with biological samples or in environments where maintaining a consistent alkaline pH is challenging.
The potential interference from environmental factors also presents a significant challenge. Ambient light, temperature fluctuations, and the presence of other chemicals can all affect the luminol reaction, potentially leading to inconsistent or unreliable results. This sensitivity to external conditions can complicate field applications and limit the use of luminol in certain research environments.
Furthermore, the quantification of luminol signals remains a challenge in many applications. While the intensity of light emission can be correlated with the concentration of the target substance, achieving accurate and reproducible quantitative measurements across different experimental setups and conditions is often difficult.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for expanding the utility of luminol in research innovation. Overcoming these limitations could open up new avenues for luminol applications in fields ranging from advanced biosensing to environmental monitoring, potentially revolutionizing detection methodologies across multiple scientific disciplines.
Current Luminol-based Solutions
01 Luminol in forensic applications
Luminol is widely used in forensic science for detecting trace amounts of blood at crime scenes. When mixed with an oxidizing agent, it produces a blue chemiluminescence in the presence of iron in hemoglobin. This reaction is highly sensitive and can detect blood even after cleaning attempts.- Luminol in chemiluminescence detection: Luminol is widely used in chemiluminescence detection methods for various applications. It produces a bright blue light when oxidized, making it useful for detecting blood traces in forensic investigations, measuring oxidative stress in biological systems, and developing sensitive analytical techniques.
- Luminol-based biosensors and immunoassays: Luminol is incorporated into biosensors and immunoassays to enhance sensitivity and detection limits. These systems utilize the chemiluminescent properties of luminol to detect and quantify specific biomolecules, pathogens, or environmental contaminants with high accuracy and low background noise.
- Luminol in environmental monitoring: Luminol-based systems are employed in environmental monitoring applications, such as detecting pollutants in water, air, and soil. The chemiluminescent reaction of luminol with specific contaminants allows for rapid and sensitive detection of environmental hazards and helps in assessing water quality and pollution levels.
- Luminol in medical diagnostics: Luminol finds applications in medical diagnostics, particularly in detecting and measuring various biomarkers associated with diseases. It is used in assays for detecting oxidative stress, inflammation, and certain types of cancer, providing valuable information for early diagnosis and treatment monitoring.
- Luminol in imaging and visualization techniques: Luminol is utilized in imaging and visualization techniques, particularly in biological and medical research. It enables the visualization of cellular processes, enzyme activities, and molecular interactions through chemiluminescent imaging, providing valuable insights into biological mechanisms and disease progression.
02 Luminol-based detection systems
Various detection systems incorporate luminol for its chemiluminescent properties. These systems are used in environmental monitoring, food safety testing, and medical diagnostics. The high sensitivity of luminol allows for the detection of minute quantities of target substances.Expand Specific Solutions03 Luminol in analytical chemistry
Luminol is employed in analytical chemistry for quantitative and qualitative analysis. It is used in flow injection analysis, high-performance liquid chromatography, and other analytical techniques. The chemiluminescent reaction of luminol enables the detection and measurement of various analytes with high sensitivity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Luminol derivatives and modifications
Research focuses on developing luminol derivatives and modifications to enhance its properties. These modifications aim to improve sensitivity, selectivity, and stability of the luminol reaction. Some derivatives are designed for specific applications or to overcome limitations of the original compound.Expand Specific Solutions05 Luminol in biosensors and imaging
Luminol is incorporated into biosensors and imaging techniques for various biological and medical applications. These include the detection of specific biomolecules, cellular imaging, and monitoring of biological processes. The chemiluminescent properties of luminol allow for sensitive and non-invasive detection methods.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Luminol Research
The luminol research landscape is evolving rapidly, with the market showing significant growth potential as the technology matures. Currently, the industry is in a transitional phase, moving from early-stage research to more applied innovations. The global market size for luminol-based applications is expanding, driven by increasing demand in forensics, biomedical research, and environmental monitoring. Technologically, luminol research is advancing, with key players like Washington University in St. Louis, Fudan University, and FUJIFILM Corp. leading innovation. These institutions are developing novel applications and improving luminol's sensitivity and specificity, pushing the boundaries of its use in various fields.
Washington University in St. Louis
Technical Solution: Washington University in St. Louis has made significant strides in luminol-based research innovation. Their team has developed a novel luminol-based chemiluminescent probe for detecting hydrogen peroxide in living cells with high specificity and sensitivity[4]. This advancement allows for real-time monitoring of cellular oxidative stress. Additionally, they have explored the use of luminol derivatives in creating "light-stick" technology for portable, electricity-free light sources in resource-limited settings[5]. The university has also pioneered the application of luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence for studying neutrophil function in immunological research, providing insights into inflammatory processes and immune responses[6].
Strengths: Cutting-edge applications in cellular biology and immunology, potential for point-of-care diagnostics. Weaknesses: Some techniques may require specialized training and equipment, limiting widespread adoption.
FUJIFILM Corp.
Technical Solution: FUJIFILM has leveraged luminol technology in developing advanced imaging solutions. Their luminol-based chemiluminescence systems have been integrated into high-sensitivity medical imaging devices, particularly for in vivo molecular imaging[7]. FUJIFILM has also applied luminol chemistry to enhance their photographic film technology, creating ultra-sensitive films for scientific and industrial applications[8]. In the field of diagnostics, the company has developed luminol-enhanced immunoassay platforms that offer rapid and highly sensitive detection of various biomarkers, potentially revolutionizing point-of-care testing[9].
Strengths: Integration of luminol technology across multiple product lines, from medical imaging to diagnostic tools. Weaknesses: High development costs and potential regulatory hurdles for medical applications.
Breakthrough Luminol Studies
Bioluminescence imaging of myeloperoxidase activity in vivo, methods, compositions and apparatuses therefor
PatentInactiveUS20110250145A1
Innovation
- The development of methods for non-invasive imaging of MPO activity using luminogenic-optical probes that emit light upon contact with oxidizing agents, allowing for the visualization of MPO activity in vivo, particularly through bioluminescence imaging (BLI) techniques.
Luminol Safety and Regulations
As luminol continues to play a pivotal role in research innovation, ensuring its safe handling and compliance with regulations becomes increasingly important. The use of luminol in various scientific and forensic applications necessitates a comprehensive understanding of its safety profile and the regulatory framework governing its use.
Luminol is generally considered a low-toxicity compound, but it still requires proper handling and safety precautions. When working with luminol, researchers should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, lab coats, and safety goggles. Adequate ventilation is essential to minimize inhalation risks, particularly when luminol is in powder form or when preparing solutions.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established guidelines for the safe handling of chemicals in laboratory settings, which apply to luminol usage. These guidelines include proper labeling, storage, and disposal procedures. Luminol should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and incompatible materials.
Regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) have classified luminol under their respective chemical inventories. In the United States, luminol is listed in the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) inventory, while in Europe, it is registered under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation.
Research institutions and forensic laboratories must adhere to specific protocols when using luminol. These protocols often include detailed standard operating procedures (SOPs) for luminol preparation, application, and disposal. Proper documentation and record-keeping are crucial for maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements and ensuring the reproducibility of research results.
Environmental considerations are also important when using luminol. While the compound itself is not considered highly toxic to aquatic life, the disposal of luminol solutions and contaminated materials should follow local environmental regulations. Many institutions have implemented waste management programs to ensure proper handling and disposal of chemical waste, including luminol-containing solutions.
As research applications for luminol continue to expand, ongoing safety assessments and regulatory updates are necessary. Researchers and institutions must stay informed about any changes in safety guidelines or regulatory requirements related to luminol use. This proactive approach helps maintain a safe working environment and ensures compliance with evolving standards in scientific research and forensic applications.
Luminol is generally considered a low-toxicity compound, but it still requires proper handling and safety precautions. When working with luminol, researchers should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, lab coats, and safety goggles. Adequate ventilation is essential to minimize inhalation risks, particularly when luminol is in powder form or when preparing solutions.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established guidelines for the safe handling of chemicals in laboratory settings, which apply to luminol usage. These guidelines include proper labeling, storage, and disposal procedures. Luminol should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and incompatible materials.
Regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) have classified luminol under their respective chemical inventories. In the United States, luminol is listed in the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) inventory, while in Europe, it is registered under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation.
Research institutions and forensic laboratories must adhere to specific protocols when using luminol. These protocols often include detailed standard operating procedures (SOPs) for luminol preparation, application, and disposal. Proper documentation and record-keeping are crucial for maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements and ensuring the reproducibility of research results.
Environmental considerations are also important when using luminol. While the compound itself is not considered highly toxic to aquatic life, the disposal of luminol solutions and contaminated materials should follow local environmental regulations. Many institutions have implemented waste management programs to ensure proper handling and disposal of chemical waste, including luminol-containing solutions.
As research applications for luminol continue to expand, ongoing safety assessments and regulatory updates are necessary. Researchers and institutions must stay informed about any changes in safety guidelines or regulatory requirements related to luminol use. This proactive approach helps maintain a safe working environment and ensures compliance with evolving standards in scientific research and forensic applications.
Luminol's Impact on Forensic Science
Luminol has revolutionized forensic science, becoming an indispensable tool in crime scene investigations and laboratory analyses. This chemiluminescent compound's ability to detect trace amounts of blood has significantly enhanced the capabilities of forensic teams worldwide.
The impact of luminol on forensic science is multifaceted. Primarily, it has dramatically improved the detection and visualization of blood evidence at crime scenes. Even in cases where attempts have been made to clean or conceal blood traces, luminol can reveal previously invisible stains, providing crucial leads for investigators. This capability has proven particularly valuable in cold cases, where traditional methods may have failed to uncover critical evidence.
In laboratory settings, luminol has enabled more precise and sensitive blood analysis. Its high reactivity with hemoglobin allows for the detection of blood diluted up to 1:1,000,000, far surpassing the sensitivity of previous methods. This enhanced sensitivity has not only improved the accuracy of forensic examinations but has also expanded the range of evidence that can be effectively analyzed.
The non-destructive nature of luminol testing has further cemented its importance in forensic science. Unlike some other blood detection methods, luminol does not interfere with subsequent DNA analysis, allowing for the preservation of genetic evidence. This characteristic has proven invaluable in cases where both the presence of blood and the identity of its source are crucial to the investigation.
Luminol's impact extends beyond its direct application in blood detection. It has spurred the development of new forensic techniques and technologies. For instance, researchers have explored modifications to the luminol formula to enhance its specificity and reduce false positives, leading to more reliable forensic results. Additionally, the principles behind luminol's chemiluminescence have inspired the creation of other luminescent compounds for various forensic applications.
The widespread adoption of luminol in forensic science has also influenced legal proceedings. The ability to present compelling visual evidence of blood presence, even in cases where it was not initially apparent, has strengthened prosecutions and, in some instances, led to the exoneration of wrongly accused individuals. This has underscored the importance of advanced forensic techniques in ensuring justice.
Moreover, luminol has played a significant role in forensic education and training. Its dramatic visual effect when reacting with blood has made it an effective teaching tool, helping to train new generations of forensic scientists and crime scene investigators. This educational aspect has contributed to the overall advancement of forensic science practices and standards.
The impact of luminol on forensic science is multifaceted. Primarily, it has dramatically improved the detection and visualization of blood evidence at crime scenes. Even in cases where attempts have been made to clean or conceal blood traces, luminol can reveal previously invisible stains, providing crucial leads for investigators. This capability has proven particularly valuable in cold cases, where traditional methods may have failed to uncover critical evidence.
In laboratory settings, luminol has enabled more precise and sensitive blood analysis. Its high reactivity with hemoglobin allows for the detection of blood diluted up to 1:1,000,000, far surpassing the sensitivity of previous methods. This enhanced sensitivity has not only improved the accuracy of forensic examinations but has also expanded the range of evidence that can be effectively analyzed.
The non-destructive nature of luminol testing has further cemented its importance in forensic science. Unlike some other blood detection methods, luminol does not interfere with subsequent DNA analysis, allowing for the preservation of genetic evidence. This characteristic has proven invaluable in cases where both the presence of blood and the identity of its source are crucial to the investigation.
Luminol's impact extends beyond its direct application in blood detection. It has spurred the development of new forensic techniques and technologies. For instance, researchers have explored modifications to the luminol formula to enhance its specificity and reduce false positives, leading to more reliable forensic results. Additionally, the principles behind luminol's chemiluminescence have inspired the creation of other luminescent compounds for various forensic applications.
The widespread adoption of luminol in forensic science has also influenced legal proceedings. The ability to present compelling visual evidence of blood presence, even in cases where it was not initially apparent, has strengthened prosecutions and, in some instances, led to the exoneration of wrongly accused individuals. This has underscored the importance of advanced forensic techniques in ensuring justice.
Moreover, luminol has played a significant role in forensic education and training. Its dramatic visual effect when reacting with blood has made it an effective teaching tool, helping to train new generations of forensic scientists and crime scene investigators. This educational aspect has contributed to the overall advancement of forensic science practices and standards.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!