How to Address Challenges in Carbon Tetrachloride Utilization?
CCl4 Utilization Background and Objectives
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) utilization has been a subject of significant interest and concern in the chemical industry for decades. Initially widely used as a solvent, refrigerant, and fire extinguishing agent, CCl4 has since been recognized as a potent ozone-depleting substance and greenhouse gas. This realization led to its phase-out under the Montreal Protocol, drastically reducing its production and use globally.
Despite these restrictions, CCl4 remains an important intermediate in various industrial processes, particularly in the production of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and their alternatives. The challenge now lies in finding ways to utilize existing CCl4 stocks and unavoidable by-products in a manner that is both economically viable and environmentally responsible.
The primary objective in addressing CCl4 utilization challenges is to develop innovative technologies and processes that can transform this problematic compound into valuable products or safely dispose of it without environmental harm. This goal aligns with broader sustainability initiatives and circular economy principles, aiming to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency.
Key areas of focus include the development of catalytic processes for CCl4 conversion, exploration of its potential as a feedstock for other chemicals, and investigation of novel destruction technologies. Researchers are also examining ways to capture and recycle CCl4 emissions from existing industrial processes, thereby reducing its release into the atmosphere.
The evolution of CCl4 utilization strategies reflects a broader trend in the chemical industry towards green chemistry and sustainable practices. As regulatory pressures increase and environmental concerns grow, there is a pressing need for solutions that can address the dual challenges of economic viability and environmental stewardship.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of CCl4 utilization research is likely to intersect with emerging fields such as nanotechnology, advanced materials science, and artificial intelligence-driven process optimization. These intersections may yield breakthrough technologies that could revolutionize how we approach not just CCl4, but other challenging chemical compounds as well.
In summary, the background and objectives of CCl4 utilization research encompass a complex interplay of historical usage, environmental impacts, regulatory frameworks, and technological innovation. The ultimate aim is to transform a once-problematic substance into a valuable resource, while simultaneously mitigating its environmental footprint and contributing to the broader goals of sustainable industrial practices.
Market Analysis for CCl4 Applications
The market for carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) applications has undergone significant changes in recent years due to environmental regulations and shifting industrial demands. Historically, CCl4 was widely used as a solvent, cleaning agent, and feedstock in various industries. However, its ozone-depleting properties led to restrictions under the Montreal Protocol, drastically reducing its production and consumption.
Despite these limitations, CCl4 still maintains a presence in certain niche markets. The pharmaceutical industry continues to utilize CCl4 as a reagent in the synthesis of specific drugs and intermediates. Its unique properties make it valuable in certain chemical processes where alternatives are less effective or more costly.
In the agrochemical sector, CCl4 finds application in the production of some pesticides and herbicides. While efforts are being made to phase out its use, certain formulations still rely on CCl4 as a key ingredient or processing aid. This creates a small but persistent demand in the agricultural market.
The electronics industry represents another area where CCl4 maintains a foothold. It is used in the manufacture of semiconductors and in some cleaning processes for electronic components. Although alternatives are being developed, CCl4 remains preferred in some specialized applications due to its effectiveness and established protocols.
Market analysis indicates a gradual decline in overall CCl4 consumption, with global production volumes decreasing year-over-year. However, this decline is not uniform across all sectors. While traditional large-scale applications have largely been phased out, specialized uses in high-value industries continue to support a reduced but stable market.
Geographically, the market for CCl4 applications shows regional variations. Developed countries have implemented stricter regulations, leading to faster phase-out rates. In contrast, some developing nations still permit limited use in certain industries, creating pockets of demand. This geographical disparity presents both challenges and opportunities for companies operating in the CCl4 market.
Looking ahead, the market for CCl4 applications is expected to further contract as environmental concerns intensify and alternative technologies mature. However, the rate of decline is likely to slow as the remaining applications become increasingly specialized and difficult to replace. Innovation in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing processes will play a crucial role in shaping the future landscape of CCl4 utilization.
Current Challenges in CCl4 Usage
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) utilization faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread application and sustainable use. One of the primary concerns is its high toxicity and potential environmental impact. CCl4 is known to be a potent ozone-depleting substance, contributing to the depletion of the Earth's protective ozone layer. This has led to strict regulations and limitations on its production and use in many countries, making it difficult for industries to incorporate CCl4 in their processes.
Another major challenge is the health risks associated with CCl4 exposure. Inhalation or skin contact with CCl4 can cause severe damage to the liver, kidneys, and central nervous system. This necessitates stringent safety measures and protective equipment in industrial settings, increasing operational costs and complexity. The potential for accidental releases and occupational exposure remains a significant concern for workers and surrounding communities.
The chemical stability of CCl4 presents both advantages and challenges. While its stability makes it useful in certain applications, it also means that CCl4 persists in the environment for extended periods. This persistence leads to long-term environmental contamination and potential bioaccumulation in ecosystems, further complicating its use and disposal.
Waste management and disposal of CCl4 and CCl4-containing products pose additional challenges. Due to its hazardous nature, special handling and treatment processes are required, which can be costly and technologically demanding. Improper disposal can lead to soil and groundwater contamination, creating long-lasting environmental issues.
The regulatory landscape surrounding CCl4 usage is complex and often restrictive. Many countries have implemented phase-out programs or strict controls on CCl4 production and use, in line with international agreements such as the Montreal Protocol. This regulatory environment creates challenges for industries that have historically relied on CCl4, forcing them to seek alternatives or develop new processes.
From a technical perspective, finding suitable replacements for CCl4 in various applications has proven challenging. CCl4's unique properties, such as its non-flammability and excellent solvency, make it difficult to find direct substitutes that offer the same performance without the associated risks. This has slowed down the transition away from CCl4 in certain specialized applications.
Lastly, the economic implications of CCl4 utilization present a significant challenge. The costs associated with safety measures, environmental protection, and regulatory compliance can make CCl4-based processes economically unviable. Industries must weigh the benefits of CCl4 use against these increased operational and compliance costs, often leading to difficult decisions regarding process changes or product reformulations.
Existing CCl4 Utilization Methods
01 Production and purification of carbon tetrachloride
Various methods for producing and purifying carbon tetrachloride are described. These include chemical synthesis processes, distillation techniques, and purification methods to obtain high-quality carbon tetrachloride for industrial and laboratory use.- Production and purification of carbon tetrachloride: Various methods for producing and purifying carbon tetrachloride are described. These include chemical synthesis processes, distillation techniques, and purification methods to obtain high-quality carbon tetrachloride for industrial and laboratory use.
- Applications of carbon tetrachloride in chemical processes: Carbon tetrachloride is utilized in various chemical processes, including as a solvent, reagent, or intermediate in the production of other chemicals. Its applications span across different industries, such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Due to its environmental impact and health hazards, research focuses on developing alternatives to carbon tetrachloride and methods for its safe handling, storage, and disposal. This includes techniques for detecting and monitoring carbon tetrachloride in various environments.
- Carbon tetrachloride in analytical chemistry: Carbon tetrachloride plays a role in analytical chemistry, particularly in spectroscopic and chromatographic techniques. It is used as a solvent or reference material in various analytical methods for identifying and quantifying chemical compounds.
- Historical uses and patents related to carbon tetrachloride: Early patents and historical documents reveal the evolution of carbon tetrachloride's applications, including its use in fire extinguishers, dry cleaning, and as a refrigerant. These sources provide insight into the compound's discovery, initial industrial uses, and subsequent regulations.
02 Applications of carbon tetrachloride in chemical processes
Carbon tetrachloride is utilized in various chemical processes, including as a solvent, reagent, or intermediate in the production of other chemicals. Its applications span across different industries, such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental and safety considerations
Due to its environmental impact and health hazards, research focuses on developing alternatives to carbon tetrachloride and methods for its safe handling, storage, and disposal. This includes studies on its effects on the ozone layer and strategies for reducing its use in industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Detection and analysis methods
Various analytical techniques and methods have been developed for detecting and quantifying carbon tetrachloride in different matrices. These include spectroscopic methods, chromatography, and sensor-based approaches for environmental monitoring and quality control purposes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Historical uses and patents
Early patents and historical documents reveal the diverse applications of carbon tetrachloride in the past, including its use as a cleaning agent, fire extinguishing medium, and in various industrial processes. Many of these applications have since been phased out due to safety and environmental concerns.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in CCl4 Sector
The carbon tetrachloride utilization market is in a transitional phase, moving from limited applications to exploring new sustainable uses. The global market size is relatively small but growing, driven by increasing environmental regulations and industrial demand. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like DuPont, Bayer, and BASF leading research into safer handling methods and novel applications. Wacker Chemie and Dow Global Technologies are also making strides in developing more efficient utilization processes. While challenges remain, particularly in toxicity management, collaborative efforts between industry leaders and academic institutions like Central South University and Guizhou University are accelerating progress towards more sustainable carbon tetrachloride utilization solutions.
Wacker Chemie AG
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Innovative CCl4 Processing Techniques
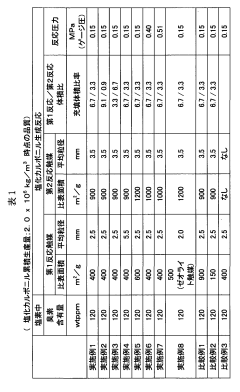
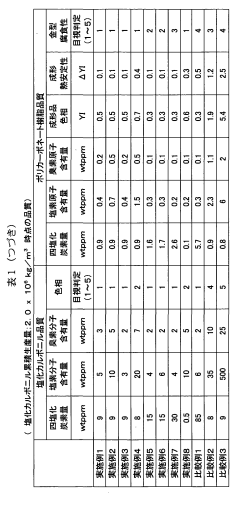
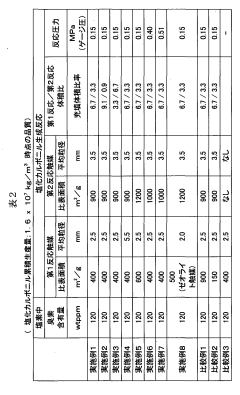
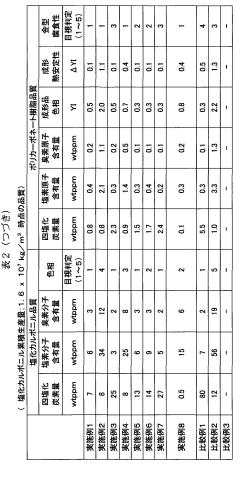
- A method involving the use of two types of water with different surface areas to optimize the distribution of carbon tetrachloride and chlorine, combined with specific catalyst conditions and reaction parameters, such as contact surfaces and pressures, to minimize impurities and enhance the quality and longevity of polycarbonate production.
- A process using thionyl chloride (SOCl2) or sulphuryl chloride (SO2Cl2) as catalysts in a gas-phase reaction between methane and phosphorus trichloride, avoiding carbon tetrachloride and other hazardous substances, with optimized reaction conditions for temperature, pressure, and residence time.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) utilization poses significant environmental challenges that require careful assessment and mitigation strategies. The production, use, and disposal of CCl4 can have far-reaching impacts on ecosystems, human health, and climate change. One of the primary concerns is its ozone-depleting potential, as CCl4 is known to contribute to the depletion of the stratospheric ozone layer. This can lead to increased ultraviolet radiation reaching the Earth's surface, potentially harming plant and animal life and increasing the risk of skin cancer in humans.
Furthermore, CCl4 is a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential significantly higher than carbon dioxide. Its release into the atmosphere contributes to climate change, exacerbating issues such as rising temperatures, sea-level rise, and extreme weather events. The persistence of CCl4 in the environment is another critical factor, as it can remain in the atmosphere for decades, prolonging its negative effects.
In aquatic environments, CCl4 contamination can have severe consequences for marine and freshwater ecosystems. It can accumulate in sediments and bioaccumulate in aquatic organisms, potentially disrupting food chains and biodiversity. Soil contamination is also a concern, as CCl4 can leach into groundwater, affecting both terrestrial ecosystems and human water supplies.
The toxicity of CCl4 to humans and wildlife is well-documented. Exposure can occur through inhalation, ingestion, or dermal contact, leading to various health issues, including liver and kidney damage, central nervous system depression, and potential carcinogenic effects. Occupational exposure in industries using CCl4 is a particular concern, necessitating strict safety protocols and protective measures.
To address these environmental challenges, a comprehensive approach is required. This includes developing alternative substances or processes to replace CCl4 in industrial applications, implementing stringent emission control technologies, and improving waste management practices to prevent environmental release. Enhanced monitoring and detection systems are crucial for identifying and addressing CCl4 contamination in various environmental media.
Regulatory frameworks play a vital role in mitigating the environmental impact of CCl4. International agreements such as the Montreal Protocol have been instrumental in phasing out the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances, including CCl4. However, continued efforts are needed to address legacy issues and prevent illegal production and trade.
Research into remediation technologies for CCl4-contaminated sites is ongoing, with promising developments in bioremediation and chemical treatment methods. These efforts aim to restore affected ecosystems and protect human health in areas with historical CCl4 contamination. Additionally, life cycle assessments of CCl4 and its alternatives are essential to ensure that proposed solutions do not create new environmental problems while solving existing ones.
Regulatory Framework for CCl4 Use
The regulatory framework for carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) utilization is complex and multifaceted, reflecting the compound's potential environmental and health hazards. At the international level, the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer plays a crucial role in regulating CCl4 production and consumption. This treaty, which came into force in 1989, has been instrumental in phasing out ozone-depleting substances, including CCl4.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees CCl4 regulation under various statutes. The Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) provides the EPA with authority to require reporting, record-keeping, and testing of chemical substances that may pose environmental or health risks. The Clean Air Act also addresses CCl4 emissions, classifying it as a hazardous air pollutant.
The European Union has implemented stringent regulations on CCl4 through the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation. This comprehensive framework aims to improve the protection of human health and the environment from risks posed by chemicals. Under REACH, companies must register their use of CCl4 and demonstrate safe handling practices.
Many countries have adopted similar regulatory approaches, often aligning with international standards. For instance, China has implemented regulations to control CCl4 production and use, in line with its commitments under the Montreal Protocol. Japan has also established strict controls on CCl4 under its Chemical Substances Control Law.
Despite these regulations, challenges remain in addressing CCl4 utilization. One significant issue is the continued use of CCl4 as a feedstock in chemical manufacturing processes. While such use is often exempted from phase-out schedules, it still contributes to emissions and potential environmental harm. Regulators are grappling with how to balance industrial needs with environmental protection goals.
Another challenge lies in monitoring and enforcing compliance with CCl4 regulations, particularly in developing countries where resources may be limited. Illegal trade and unreported production of CCl4 continue to pose threats to ozone layer recovery efforts.
To address these challenges, regulatory bodies are exploring innovative approaches. These include incentivizing the development of alternative substances and technologies, enhancing international cooperation for monitoring and enforcement, and implementing more stringent reporting requirements for CCl4 use in exempt applications.