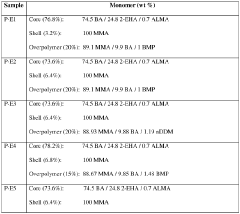
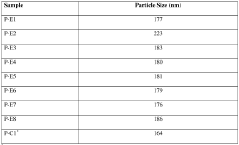
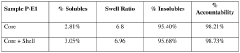
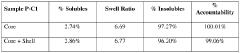
How to Boost PMMA's Structural Versatility?
AUG 7, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PMMA Evolution & Objectives
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic or plexiglass, has undergone significant evolution since its discovery in the 1930s. Initially valued for its optical clarity and weather resistance, PMMA has become a versatile material with applications spanning various industries. The journey of PMMA's development has been marked by continuous efforts to enhance its properties and expand its utility.
In the early stages, PMMA was primarily used as a lightweight, shatter-resistant alternative to glass. However, as manufacturing techniques improved, researchers began to explore ways to modify PMMA's structure to broaden its applications. The introduction of copolymerization techniques in the 1950s and 1960s allowed for the incorporation of other monomers, leading to improvements in impact resistance and thermal stability.
The 1970s and 1980s saw a focus on enhancing PMMA's mechanical properties through the development of impact-modified grades. This innovation expanded PMMA's use in automotive and construction industries. Concurrently, advancements in polymer processing technologies enabled the production of PMMA in various forms, including sheets, rods, and molded parts, further increasing its versatility.
In recent decades, the emphasis has shifted towards improving PMMA's environmental sustainability and functional properties. Research has been directed at developing bio-based PMMA alternatives and improving recycling processes. Additionally, efforts to enhance PMMA's scratch resistance, UV stability, and fire retardancy have opened up new application areas in electronics and aerospace industries.
The current objectives in PMMA research and development are multifaceted, aimed at addressing the material's limitations while expanding its capabilities. Key goals include improving PMMA's heat resistance to broaden its use in high-temperature applications, enhancing its impact strength without compromising optical clarity, and developing more efficient methods for recycling and reprocessing PMMA products.
Another significant objective is to increase PMMA's structural versatility through novel modification techniques. This includes exploring nanocomposite formulations to impart unique properties such as self-healing capabilities or enhanced electrical conductivity. Researchers are also investigating ways to improve PMMA's compatibility with other materials for advanced composite applications.
As we look to the future, the evolution of PMMA is likely to continue along paths that emphasize sustainability, multifunctionality, and adaptability to emerging technologies. The ultimate goal is to transform PMMA from a conventional plastic into an advanced, high-performance material capable of meeting the complex demands of modern industries while addressing environmental concerns.
In the early stages, PMMA was primarily used as a lightweight, shatter-resistant alternative to glass. However, as manufacturing techniques improved, researchers began to explore ways to modify PMMA's structure to broaden its applications. The introduction of copolymerization techniques in the 1950s and 1960s allowed for the incorporation of other monomers, leading to improvements in impact resistance and thermal stability.
The 1970s and 1980s saw a focus on enhancing PMMA's mechanical properties through the development of impact-modified grades. This innovation expanded PMMA's use in automotive and construction industries. Concurrently, advancements in polymer processing technologies enabled the production of PMMA in various forms, including sheets, rods, and molded parts, further increasing its versatility.
In recent decades, the emphasis has shifted towards improving PMMA's environmental sustainability and functional properties. Research has been directed at developing bio-based PMMA alternatives and improving recycling processes. Additionally, efforts to enhance PMMA's scratch resistance, UV stability, and fire retardancy have opened up new application areas in electronics and aerospace industries.
The current objectives in PMMA research and development are multifaceted, aimed at addressing the material's limitations while expanding its capabilities. Key goals include improving PMMA's heat resistance to broaden its use in high-temperature applications, enhancing its impact strength without compromising optical clarity, and developing more efficient methods for recycling and reprocessing PMMA products.
Another significant objective is to increase PMMA's structural versatility through novel modification techniques. This includes exploring nanocomposite formulations to impart unique properties such as self-healing capabilities or enhanced electrical conductivity. Researchers are also investigating ways to improve PMMA's compatibility with other materials for advanced composite applications.
As we look to the future, the evolution of PMMA is likely to continue along paths that emphasize sustainability, multifunctionality, and adaptability to emerging technologies. The ultimate goal is to transform PMMA from a conventional plastic into an advanced, high-performance material capable of meeting the complex demands of modern industries while addressing environmental concerns.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for enhancing PMMA's structural versatility has been steadily growing across various industries. PMMA, or polymethyl methacrylate, is widely used in applications ranging from automotive and aerospace to construction and medical devices. However, its inherent limitations in terms of mechanical properties and thermal stability have created a significant market gap for improved versions of this versatile polymer.
In the automotive sector, there is a strong demand for lightweight materials that can replace traditional glass and metal components. PMMA with enhanced structural properties could potentially meet this need, offering improved impact resistance and durability while maintaining its optical clarity. This would enable manufacturers to create more fuel-efficient vehicles without compromising on safety or aesthetics.
The construction industry has also shown increasing interest in structurally enhanced PMMA. The material's transparency and weather resistance make it an attractive option for architectural applications, but concerns about its strength and fire resistance have limited its widespread adoption. A more structurally versatile PMMA could open up new possibilities in building design, particularly for facades, skylights, and interior partitions.
In the medical field, there is a growing demand for biocompatible materials with improved mechanical properties. PMMA is already used in various medical applications, including bone cements and intraocular lenses. However, enhancing its structural versatility could lead to the development of more durable and long-lasting implants, reducing the need for revision surgeries and improving patient outcomes.
The electronics industry has also expressed interest in PMMA with enhanced structural properties. As consumer electronics become increasingly compact and multifunctional, there is a need for materials that can provide both optical clarity and mechanical strength. Structurally versatile PMMA could be used in display screens, touchpads, and other components that require both transparency and durability.
Market analysts predict that the global demand for high-performance PMMA will continue to grow in the coming years. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of lightweight materials in various industries and the ongoing trend towards sustainable and recyclable plastics. The ability to enhance PMMA's structural versatility without compromising its other desirable properties could potentially unlock new market opportunities and drive innovation across multiple sectors.
However, it is important to note that any improvements in PMMA's structural versatility must be balanced against cost considerations. While there is a clear market demand for enhanced properties, the commercial viability of new PMMA formulations will depend on their ability to deliver improved performance at a competitive price point. This balance between performance and cost will be crucial in determining the market success of structurally enhanced PMMA products.
In the automotive sector, there is a strong demand for lightweight materials that can replace traditional glass and metal components. PMMA with enhanced structural properties could potentially meet this need, offering improved impact resistance and durability while maintaining its optical clarity. This would enable manufacturers to create more fuel-efficient vehicles without compromising on safety or aesthetics.
The construction industry has also shown increasing interest in structurally enhanced PMMA. The material's transparency and weather resistance make it an attractive option for architectural applications, but concerns about its strength and fire resistance have limited its widespread adoption. A more structurally versatile PMMA could open up new possibilities in building design, particularly for facades, skylights, and interior partitions.
In the medical field, there is a growing demand for biocompatible materials with improved mechanical properties. PMMA is already used in various medical applications, including bone cements and intraocular lenses. However, enhancing its structural versatility could lead to the development of more durable and long-lasting implants, reducing the need for revision surgeries and improving patient outcomes.
The electronics industry has also expressed interest in PMMA with enhanced structural properties. As consumer electronics become increasingly compact and multifunctional, there is a need for materials that can provide both optical clarity and mechanical strength. Structurally versatile PMMA could be used in display screens, touchpads, and other components that require both transparency and durability.
Market analysts predict that the global demand for high-performance PMMA will continue to grow in the coming years. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of lightweight materials in various industries and the ongoing trend towards sustainable and recyclable plastics. The ability to enhance PMMA's structural versatility without compromising its other desirable properties could potentially unlock new market opportunities and drive innovation across multiple sectors.
However, it is important to note that any improvements in PMMA's structural versatility must be balanced against cost considerations. While there is a clear market demand for enhanced properties, the commercial viability of new PMMA formulations will depend on their ability to deliver improved performance at a competitive price point. This balance between performance and cost will be crucial in determining the market success of structurally enhanced PMMA products.
PMMA Challenges & Limitations
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), widely known as acrylic or plexiglass, has been a staple in various industries due to its optical clarity, weather resistance, and ease of processing. However, its structural versatility faces several challenges and limitations that hinder its broader application in high-performance sectors.
One of the primary challenges of PMMA is its inherent brittleness. While it exhibits high tensile strength and excellent optical properties, its low impact resistance and poor fracture toughness limit its use in applications requiring high mechanical durability. This brittleness makes PMMA susceptible to cracking and shattering under sudden impacts or stress, restricting its use in safety-critical components or high-stress environments.
Another significant limitation is PMMA's relatively low heat resistance. With a glass transition temperature (Tg) of around 105°C, PMMA softens and deforms at elevated temperatures, limiting its application in high-temperature environments or in products that may be exposed to heat during use or processing. This thermal sensitivity also affects its dimensional stability, potentially causing warping or distortion in precision applications.
PMMA's poor chemical resistance presents another challenge. While it exhibits good resistance to many common chemicals, it is vulnerable to attack by organic solvents, acids, and alkaline solutions. This susceptibility to chemical degradation limits its use in certain industrial or laboratory settings where exposure to harsh chemicals is common.
The material's low scratch resistance is an additional drawback. Despite its excellent optical clarity, PMMA surfaces are prone to scratching and abrasion, which can compromise both aesthetics and functionality over time. This limitation is particularly problematic in applications where surface quality is critical, such as in optical components or high-end consumer products.
PMMA also faces challenges in terms of its environmental impact and recyclability. While it is theoretically recyclable, the process is often not economically viable, and the material's durability means it persists in the environment for extended periods if not properly disposed of. This aspect raises concerns about its long-term sustainability in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Lastly, PMMA's limited functionalization options restrict its adaptability to diverse applications. Unlike some other polymers, PMMA's chemical structure offers fewer opportunities for easy modification or functionalization, making it challenging to tailor its properties for specific high-performance applications without significant alterations to its core structure.
Addressing these challenges and limitations is crucial for expanding PMMA's structural versatility and broadening its application scope in advanced materials and high-performance products.
One of the primary challenges of PMMA is its inherent brittleness. While it exhibits high tensile strength and excellent optical properties, its low impact resistance and poor fracture toughness limit its use in applications requiring high mechanical durability. This brittleness makes PMMA susceptible to cracking and shattering under sudden impacts or stress, restricting its use in safety-critical components or high-stress environments.
Another significant limitation is PMMA's relatively low heat resistance. With a glass transition temperature (Tg) of around 105°C, PMMA softens and deforms at elevated temperatures, limiting its application in high-temperature environments or in products that may be exposed to heat during use or processing. This thermal sensitivity also affects its dimensional stability, potentially causing warping or distortion in precision applications.
PMMA's poor chemical resistance presents another challenge. While it exhibits good resistance to many common chemicals, it is vulnerable to attack by organic solvents, acids, and alkaline solutions. This susceptibility to chemical degradation limits its use in certain industrial or laboratory settings where exposure to harsh chemicals is common.
The material's low scratch resistance is an additional drawback. Despite its excellent optical clarity, PMMA surfaces are prone to scratching and abrasion, which can compromise both aesthetics and functionality over time. This limitation is particularly problematic in applications where surface quality is critical, such as in optical components or high-end consumer products.
PMMA also faces challenges in terms of its environmental impact and recyclability. While it is theoretically recyclable, the process is often not economically viable, and the material's durability means it persists in the environment for extended periods if not properly disposed of. This aspect raises concerns about its long-term sustainability in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Lastly, PMMA's limited functionalization options restrict its adaptability to diverse applications. Unlike some other polymers, PMMA's chemical structure offers fewer opportunities for easy modification or functionalization, making it challenging to tailor its properties for specific high-performance applications without significant alterations to its core structure.
Addressing these challenges and limitations is crucial for expanding PMMA's structural versatility and broadening its application scope in advanced materials and high-performance products.
Current PMMA Enhancement Methods
01 Optical applications of PMMA
PMMA's high transparency and light transmission properties make it suitable for various optical applications. It can be used in lenses, optical fibers, and light guides. The material's ability to be molded into different shapes allows for the creation of complex optical components.- Optical applications of PMMA: PMMA's high transparency and light transmission properties make it suitable for various optical applications. It can be used in lenses, optical fibers, and light guides. The material's ability to be molded into different shapes allows for the creation of complex optical components.
- PMMA in biomedical applications: The biocompatibility and moldability of PMMA make it valuable in biomedical applications. It is used in dental implants, bone cements, and artificial corneas. PMMA can be modified to enhance its properties for specific medical uses, such as improved wear resistance or drug delivery capabilities.
- PMMA composites and blends: PMMA can be combined with other materials to create composites and blends with enhanced properties. These combinations can improve mechanical strength, thermal stability, or introduce new functionalities. Examples include PMMA-carbon nanotube composites for improved conductivity or PMMA-silica blends for increased hardness.
- Surface modification of PMMA: The surface of PMMA can be modified to alter its properties or introduce new functionalities. Techniques such as plasma treatment, chemical etching, or grafting can be used to change surface energy, improve adhesion, or add specific chemical groups. This versatility allows PMMA to be adapted for various applications.
- PMMA in additive manufacturing: PMMA's ability to be processed into various forms makes it suitable for additive manufacturing techniques. It can be used in 3D printing processes, allowing for the creation of complex structures and customized parts. This versatility enables rapid prototyping and production of specialized components in fields such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
02 PMMA in biomedical applications
The biocompatibility and moldability of PMMA make it valuable in biomedical applications. It is used in dental prosthetics, bone cements, and intraocular lenses. PMMA can be modified to enhance its properties for specific medical uses, such as improved wear resistance or drug delivery capabilities.Expand Specific Solutions03 PMMA-based composites and blends
PMMA can be combined with other materials to create composites and blends with enhanced properties. These combinations can improve mechanical strength, thermal stability, or introduce new functionalities. Examples include PMMA-based nanocomposites and polymer blends for specific industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Surface modification of PMMA
The surface of PMMA can be modified to alter its properties or introduce new functionalities. Techniques such as plasma treatment, chemical grafting, or coating can be used to improve adhesion, hydrophobicity, or introduce specific chemical groups. This versatility allows PMMA to be adapted for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 PMMA in additive manufacturing
PMMA's thermoplastic nature and ease of processing make it suitable for additive manufacturing techniques. It can be used in 3D printing processes to create complex structures and customized parts. The material's properties allow for the production of both functional prototypes and end-use products in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The competition landscape for boosting PMMA's structural versatility is characterized by a mature market with significant growth potential. The industry is in a phase of innovation and expansion, driven by increasing demand for high-performance materials across various sectors. Major players like Wanhua Chemical Group, China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., and Kingfa Sci. & Tech. Co., Ltd. are investing heavily in research and development to enhance PMMA's properties. The market size is substantial, with a global reach and diverse applications in automotive, construction, and electronics industries. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Shanghai KUMHO-SUNNY Plastics and Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd. developing novel formulations and manufacturing processes to improve PMMA's versatility. Academic institutions such as Fudan University and the Chinese Academy of Science Institute of Chemistry are also contributing significantly to the technological advancements in this area.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical has developed a novel PMMA modification technique using reactive extrusion with specially designed multifunctional monomers. This process enhances PMMA's impact resistance and heat deflection temperature while maintaining its optical clarity. The company has also introduced nano-reinforced PMMA composites, incorporating silica nanoparticles to improve scratch resistance and durability[1][3]. Their latest innovation involves the development of bio-based PMMA using renewable resources, which addresses sustainability concerns while maintaining the polymer's structural versatility[5].
Strengths: Advanced modification techniques, improved mechanical properties, and eco-friendly solutions. Weaknesses: Potential increase in production costs and complexity in manufacturing processes.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has focused on enhancing PMMA's structural versatility through copolymerization with other monomers. They have developed a series of MMA-based copolymers with improved heat resistance and impact strength. Their proprietary process involves the use of controlled radical polymerization techniques to create well-defined copolymer structures[2]. Additionally, Sinopec has invested in the development of PMMA blends with other polymers, such as ABS and PC, to create materials with synergistic properties suitable for a wide range of applications[4].
Strengths: Diverse product portfolio, ability to tailor properties through copolymerization. Weaknesses: Potential loss of some characteristic PMMA properties in copolymers and blends.
Innovative PMMA Modifications
Poly(methyl methacrylate) resin composition
PatentWO2019018219A1
Innovation
- A PMMA resin composition incorporating a methyl methacrylate polymer and a multistage acrylic impact modifier, comprising a core-shell polymer and an overpolymer, which improves impact strength while preserving gloss and melt flow.
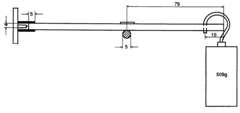
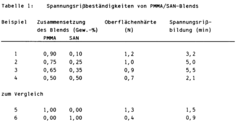
Thermoplastic, transparent moulding masses based on PMMA having increased stress-cracking resistance
PatentInactiveEP0508173A1
Innovation
- Blends of PMMA with styrene-acrylonitrile copolymers (SAN) are developed, with a high PMMA content and a specific range of SAN, along with a polymeric processing aid, to enhance stress crack resistance while maintaining surface hardness and flowability.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of boosting PMMA's structural versatility is a critical consideration in the development and application of this versatile polymer. PMMA, or polymethyl methacrylate, is widely used in various industries due to its optical clarity, weather resistance, and durability. However, enhancing its structural versatility may have both positive and negative environmental implications.
One of the primary environmental benefits of improving PMMA's structural versatility is the potential for increased material efficiency. By enhancing the polymer's mechanical properties, manufacturers can potentially use less material to achieve the same or better performance. This reduction in material usage can lead to decreased energy consumption during production and transportation, ultimately lowering the carbon footprint associated with PMMA-based products.
Furthermore, improved structural versatility may extend the lifespan of PMMA products, reducing the frequency of replacement and disposal. This longevity can contribute to a reduction in waste generation and the overall environmental impact of PMMA throughout its lifecycle. Additionally, enhanced structural properties may enable PMMA to replace less environmentally friendly materials in certain applications, further contributing to sustainability efforts.
However, the environmental impact assessment must also consider potential drawbacks. The processes and additives used to boost PMMA's structural versatility may introduce new environmental concerns. For instance, the use of certain chemical modifiers or reinforcing agents could potentially increase the toxicity of the material or make it more challenging to recycle at the end of its life cycle.
The recyclability of enhanced PMMA is a crucial factor in its environmental impact. While traditional PMMA is generally recyclable, modifications to improve its structural properties may affect its ability to be reprocessed or reused. It is essential to evaluate whether the enhanced PMMA can be effectively recycled without significant loss of properties or the need for energy-intensive processes.
Energy consumption during the production of structurally enhanced PMMA is another important consideration. If the processes required to boost its versatility are significantly more energy-intensive than traditional PMMA production, it could offset some of the environmental benefits gained from improved material efficiency and longevity.
Lastly, the environmental impact assessment should consider the end-of-life scenarios for enhanced PMMA products. This includes evaluating the biodegradability of the material, its potential to release harmful substances into the environment if improperly disposed of, and the feasibility of implementing effective recycling or disposal methods on a large scale.
One of the primary environmental benefits of improving PMMA's structural versatility is the potential for increased material efficiency. By enhancing the polymer's mechanical properties, manufacturers can potentially use less material to achieve the same or better performance. This reduction in material usage can lead to decreased energy consumption during production and transportation, ultimately lowering the carbon footprint associated with PMMA-based products.
Furthermore, improved structural versatility may extend the lifespan of PMMA products, reducing the frequency of replacement and disposal. This longevity can contribute to a reduction in waste generation and the overall environmental impact of PMMA throughout its lifecycle. Additionally, enhanced structural properties may enable PMMA to replace less environmentally friendly materials in certain applications, further contributing to sustainability efforts.
However, the environmental impact assessment must also consider potential drawbacks. The processes and additives used to boost PMMA's structural versatility may introduce new environmental concerns. For instance, the use of certain chemical modifiers or reinforcing agents could potentially increase the toxicity of the material or make it more challenging to recycle at the end of its life cycle.
The recyclability of enhanced PMMA is a crucial factor in its environmental impact. While traditional PMMA is generally recyclable, modifications to improve its structural properties may affect its ability to be reprocessed or reused. It is essential to evaluate whether the enhanced PMMA can be effectively recycled without significant loss of properties or the need for energy-intensive processes.
Energy consumption during the production of structurally enhanced PMMA is another important consideration. If the processes required to boost its versatility are significantly more energy-intensive than traditional PMMA production, it could offset some of the environmental benefits gained from improved material efficiency and longevity.
Lastly, the environmental impact assessment should consider the end-of-life scenarios for enhanced PMMA products. This includes evaluating the biodegradability of the material, its potential to release harmful substances into the environment if improperly disposed of, and the feasibility of implementing effective recycling or disposal methods on a large scale.
PMMA Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) plays a crucial role in shaping its structural versatility and applications across various industries. Understanding these regulations is essential for manufacturers, researchers, and end-users seeking to enhance PMMA's capabilities while ensuring compliance with safety and environmental standards.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates PMMA use in food contact materials, medical devices, and pharmaceutical packaging. The FDA's guidelines outline specific requirements for PMMA composition, manufacturing processes, and permissible additives. These regulations ensure that PMMA products maintain their structural integrity and safety when in contact with food or used in medical applications.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation governs the use of PMMA and its additives. REACH mandates thorough safety assessments and registration of chemical substances, including those used in PMMA production. This regulatory framework encourages the development of safer alternatives and promotes innovation in PMMA formulations that enhance its structural properties while minimizing environmental impact.
In the construction sector, building codes and standards significantly influence PMMA's use as a structural material. Organizations such as the International Code Council (ICC) and the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provide guidelines for PMMA's mechanical properties, fire resistance, and weatherability. Compliance with these standards is crucial for expanding PMMA's applications in architectural glazing, skylights, and other structural elements.
Environmental regulations also shape PMMA's development and use. Many countries have implemented policies to promote the recycling and sustainable disposal of PMMA products. These regulations incentivize research into improving PMMA's recyclability and the development of bio-based alternatives, potentially leading to new structural formulations with enhanced environmental profiles.
The automotive industry faces stringent safety and emissions regulations that impact PMMA use in vehicle components. Regulatory bodies like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the US and the European New Car Assessment Programme (Euro NCAP) set standards for materials used in automotive applications. These regulations drive innovation in PMMA formulations to meet requirements for impact resistance, light transmission, and weight reduction.
As nanotechnology advances, regulatory frameworks are evolving to address the potential risks and benefits of nanocomposite PMMA materials. Agencies such as the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) are developing guidelines for the safe development and use of nanomaterials in polymers, including PMMA. These emerging regulations will shape future research directions in enhancing PMMA's structural versatility through nanotechnology.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates PMMA use in food contact materials, medical devices, and pharmaceutical packaging. The FDA's guidelines outline specific requirements for PMMA composition, manufacturing processes, and permissible additives. These regulations ensure that PMMA products maintain their structural integrity and safety when in contact with food or used in medical applications.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation governs the use of PMMA and its additives. REACH mandates thorough safety assessments and registration of chemical substances, including those used in PMMA production. This regulatory framework encourages the development of safer alternatives and promotes innovation in PMMA formulations that enhance its structural properties while minimizing environmental impact.
In the construction sector, building codes and standards significantly influence PMMA's use as a structural material. Organizations such as the International Code Council (ICC) and the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provide guidelines for PMMA's mechanical properties, fire resistance, and weatherability. Compliance with these standards is crucial for expanding PMMA's applications in architectural glazing, skylights, and other structural elements.
Environmental regulations also shape PMMA's development and use. Many countries have implemented policies to promote the recycling and sustainable disposal of PMMA products. These regulations incentivize research into improving PMMA's recyclability and the development of bio-based alternatives, potentially leading to new structural formulations with enhanced environmental profiles.
The automotive industry faces stringent safety and emissions regulations that impact PMMA use in vehicle components. Regulatory bodies like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the US and the European New Car Assessment Programme (Euro NCAP) set standards for materials used in automotive applications. These regulations drive innovation in PMMA formulations to meet requirements for impact resistance, light transmission, and weight reduction.
As nanotechnology advances, regulatory frameworks are evolving to address the potential risks and benefits of nanocomposite PMMA materials. Agencies such as the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) are developing guidelines for the safe development and use of nanomaterials in polymers, including PMMA. These emerging regulations will shape future research directions in enhancing PMMA's structural versatility through nanotechnology.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!