PMMA's Future in Customizable Building Components
AUG 7, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PMMA in Construction: Past and Future
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic or plexiglass, has a rich history in the construction industry dating back to the 1930s. Initially used as a lightweight, shatter-resistant alternative to glass, PMMA quickly gained popularity for its optical clarity and weather resistance. In the early stages, its applications were primarily limited to windows, skylights, and decorative elements.
As manufacturing techniques improved, PMMA's versatility in construction expanded. The 1960s and 1970s saw a surge in its use for signage, lighting fixtures, and architectural features. The material's ability to be molded into various shapes and its compatibility with different coloring techniques made it a favorite among designers and architects seeking to create bold, modern structures.
The late 20th century brought about significant advancements in PMMA technology. Improved formulations enhanced its durability, UV resistance, and fire retardancy, making it suitable for a wider range of building applications. This period also saw the development of cast and extruded PMMA sheets with varying properties, catering to specific construction needs.
In recent years, PMMA has found new life in sustainable building practices. Its recyclability and long lifespan align well with green building initiatives. Moreover, the material's excellent light transmission properties have made it a key component in energy-efficient designs, particularly in daylighting solutions.
Looking to the future, PMMA is poised to play a crucial role in customizable building components. The advent of 3D printing and advanced manufacturing techniques opens up possibilities for creating complex, bespoke PMMA elements. This shift towards customization allows architects and builders to design unique, site-specific components that can be easily modified or replaced.
Furthermore, ongoing research into PMMA composites and hybrid materials promises to expand its capabilities. These innovations aim to enhance the material's structural properties, thermal performance, and integration with smart building technologies. As the construction industry moves towards more adaptive and responsive buildings, PMMA's potential for incorporating sensors, lighting elements, and even energy-harvesting capabilities positions it as a material of choice for future-forward designs.
The evolution of PMMA in construction reflects a broader trend towards materials that offer both functionality and aesthetic flexibility. As we look ahead, the continued development of PMMA technologies is likely to yield building components that are not only customizable but also intelligent and interactive, contributing to the creation of more efficient, sustainable, and visually striking architectural solutions.
As manufacturing techniques improved, PMMA's versatility in construction expanded. The 1960s and 1970s saw a surge in its use for signage, lighting fixtures, and architectural features. The material's ability to be molded into various shapes and its compatibility with different coloring techniques made it a favorite among designers and architects seeking to create bold, modern structures.
The late 20th century brought about significant advancements in PMMA technology. Improved formulations enhanced its durability, UV resistance, and fire retardancy, making it suitable for a wider range of building applications. This period also saw the development of cast and extruded PMMA sheets with varying properties, catering to specific construction needs.
In recent years, PMMA has found new life in sustainable building practices. Its recyclability and long lifespan align well with green building initiatives. Moreover, the material's excellent light transmission properties have made it a key component in energy-efficient designs, particularly in daylighting solutions.
Looking to the future, PMMA is poised to play a crucial role in customizable building components. The advent of 3D printing and advanced manufacturing techniques opens up possibilities for creating complex, bespoke PMMA elements. This shift towards customization allows architects and builders to design unique, site-specific components that can be easily modified or replaced.
Furthermore, ongoing research into PMMA composites and hybrid materials promises to expand its capabilities. These innovations aim to enhance the material's structural properties, thermal performance, and integration with smart building technologies. As the construction industry moves towards more adaptive and responsive buildings, PMMA's potential for incorporating sensors, lighting elements, and even energy-harvesting capabilities positions it as a material of choice for future-forward designs.
The evolution of PMMA in construction reflects a broader trend towards materials that offer both functionality and aesthetic flexibility. As we look ahead, the continued development of PMMA technologies is likely to yield building components that are not only customizable but also intelligent and interactive, contributing to the creation of more efficient, sustainable, and visually striking architectural solutions.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for PMMA in customizable building components has been steadily increasing, driven by the growing trend towards personalized and sustainable architecture. As urbanization continues to accelerate globally, there is a rising need for innovative building materials that can offer both aesthetic appeal and functional versatility. PMMA, with its unique properties of transparency, durability, and moldability, is well-positioned to meet these evolving market requirements.
In the residential sector, homeowners are increasingly seeking customizable solutions that allow them to express their individual style while maintaining energy efficiency. PMMA's ability to be molded into various shapes and colors makes it an attractive option for custom window designs, decorative panels, and light-diffusing elements. The material's excellent light transmission properties also contribute to its popularity in creating energy-efficient building envelopes.
The commercial construction industry has shown significant interest in PMMA-based customizable components, particularly for office buildings, retail spaces, and hospitality venues. Architects and designers are leveraging PMMA's versatility to create unique facades, interior partitions, and lighting fixtures that can be tailored to specific brand identities or design concepts. The material's resistance to weathering and UV radiation makes it suitable for both interior and exterior applications, expanding its market potential.
The healthcare sector represents another growing market for PMMA customizable components. Hospitals and medical facilities are increasingly adopting modular design approaches, where PMMA can be used to create hygienic, easy-to-clean surfaces and partitions. The material's compatibility with various sanitization methods makes it particularly valuable in environments where cleanliness is paramount.
Sustainability concerns are also driving demand for PMMA in the building industry. As more developers and property owners seek LEED certification or other green building standards, PMMA's recyclability and potential for incorporating recycled content make it an attractive option. Additionally, its light weight compared to traditional building materials can contribute to reduced transportation costs and carbon footprint.
The education sector is emerging as a promising market for PMMA customizable components. Schools and universities are modernizing their facilities with flexible, adaptable spaces that can be reconfigured to suit different learning environments. PMMA's durability and ease of maintenance make it well-suited for high-traffic areas in educational institutions.
As smart building technologies continue to advance, there is growing interest in integrating PMMA with electronic components to create interactive surfaces and displays. This trend is opening up new market opportunities in both residential and commercial sectors, where customizable PMMA components can serve as platforms for embedded sensors, lighting systems, and information displays.
In the residential sector, homeowners are increasingly seeking customizable solutions that allow them to express their individual style while maintaining energy efficiency. PMMA's ability to be molded into various shapes and colors makes it an attractive option for custom window designs, decorative panels, and light-diffusing elements. The material's excellent light transmission properties also contribute to its popularity in creating energy-efficient building envelopes.
The commercial construction industry has shown significant interest in PMMA-based customizable components, particularly for office buildings, retail spaces, and hospitality venues. Architects and designers are leveraging PMMA's versatility to create unique facades, interior partitions, and lighting fixtures that can be tailored to specific brand identities or design concepts. The material's resistance to weathering and UV radiation makes it suitable for both interior and exterior applications, expanding its market potential.
The healthcare sector represents another growing market for PMMA customizable components. Hospitals and medical facilities are increasingly adopting modular design approaches, where PMMA can be used to create hygienic, easy-to-clean surfaces and partitions. The material's compatibility with various sanitization methods makes it particularly valuable in environments where cleanliness is paramount.
Sustainability concerns are also driving demand for PMMA in the building industry. As more developers and property owners seek LEED certification or other green building standards, PMMA's recyclability and potential for incorporating recycled content make it an attractive option. Additionally, its light weight compared to traditional building materials can contribute to reduced transportation costs and carbon footprint.
The education sector is emerging as a promising market for PMMA customizable components. Schools and universities are modernizing their facilities with flexible, adaptable spaces that can be reconfigured to suit different learning environments. PMMA's durability and ease of maintenance make it well-suited for high-traffic areas in educational institutions.
As smart building technologies continue to advance, there is growing interest in integrating PMMA with electronic components to create interactive surfaces and displays. This trend is opening up new market opportunities in both residential and commercial sectors, where customizable PMMA components can serve as platforms for embedded sensors, lighting systems, and information displays.
Technical Challenges
PMMA, or polymethyl methacrylate, faces several technical challenges in its application as a customizable building component. One of the primary obstacles is its limited thermal performance. While PMMA offers excellent optical clarity and weather resistance, its thermal insulation properties are inferior to many traditional building materials. This limitation restricts its use in energy-efficient building designs, particularly in regions with extreme climates.
Another significant challenge lies in PMMA's mechanical properties. Although it possesses high tensile strength and impact resistance compared to glass, it is still vulnerable to scratching and can be brittle under certain conditions. This susceptibility to surface damage can affect the long-term aesthetics and structural integrity of building components, potentially leading to increased maintenance costs and reduced lifespan.
The customization of PMMA for building applications also presents technical hurdles. While the material can be easily molded and shaped, achieving complex geometries or integrating additional functionalities such as embedded sensors or smart technologies remains challenging. The development of advanced manufacturing techniques that can seamlessly incorporate these features without compromising the material's inherent properties is an ongoing area of research.
Fire safety is another critical concern for PMMA in building applications. The material is combustible and can contribute to the spread of fire if not properly treated or engineered. Developing effective fire-retardant additives or coatings that do not significantly alter PMMA's desirable properties, such as transparency and weatherability, is a key technical challenge that researchers and manufacturers are actively addressing.
Environmental sustainability and recyclability pose additional challenges for PMMA in the construction industry. While the material is theoretically recyclable, the process is often not economically viable on a large scale. Developing more efficient recycling methods and exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived PMMA are crucial areas of focus to improve the material's environmental footprint and align with increasingly stringent sustainability regulations in the construction sector.
Lastly, the integration of PMMA with other building materials and systems presents technical difficulties. Ensuring compatible thermal expansion rates, developing effective joining and sealing methods, and maintaining long-term structural integrity in composite applications are all areas that require ongoing research and innovation. Overcoming these challenges is essential for expanding PMMA's role in modern, high-performance building envelopes and architectural designs.
Another significant challenge lies in PMMA's mechanical properties. Although it possesses high tensile strength and impact resistance compared to glass, it is still vulnerable to scratching and can be brittle under certain conditions. This susceptibility to surface damage can affect the long-term aesthetics and structural integrity of building components, potentially leading to increased maintenance costs and reduced lifespan.
The customization of PMMA for building applications also presents technical hurdles. While the material can be easily molded and shaped, achieving complex geometries or integrating additional functionalities such as embedded sensors or smart technologies remains challenging. The development of advanced manufacturing techniques that can seamlessly incorporate these features without compromising the material's inherent properties is an ongoing area of research.
Fire safety is another critical concern for PMMA in building applications. The material is combustible and can contribute to the spread of fire if not properly treated or engineered. Developing effective fire-retardant additives or coatings that do not significantly alter PMMA's desirable properties, such as transparency and weatherability, is a key technical challenge that researchers and manufacturers are actively addressing.
Environmental sustainability and recyclability pose additional challenges for PMMA in the construction industry. While the material is theoretically recyclable, the process is often not economically viable on a large scale. Developing more efficient recycling methods and exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived PMMA are crucial areas of focus to improve the material's environmental footprint and align with increasingly stringent sustainability regulations in the construction sector.
Lastly, the integration of PMMA with other building materials and systems presents technical difficulties. Ensuring compatible thermal expansion rates, developing effective joining and sealing methods, and maintaining long-term structural integrity in composite applications are all areas that require ongoing research and innovation. Overcoming these challenges is essential for expanding PMMA's role in modern, high-performance building envelopes and architectural designs.
Current PMMA Solutions
01 Modification of PMMA properties
PMMA can be customized by modifying its properties through various methods such as blending with other polymers, adding fillers, or adjusting the polymerization process. These modifications can enhance characteristics like impact resistance, thermal stability, or optical properties, making PMMA suitable for diverse applications.- Modification of PMMA properties: PMMA can be customized by modifying its properties through various methods such as blending with other polymers, adding fillers, or adjusting the polymerization process. These modifications can enhance specific characteristics like impact resistance, thermal stability, or optical properties to suit different applications.
- Surface treatment and coating techniques: Customization of PMMA can be achieved through surface treatments and coating techniques. These methods can alter the surface properties of PMMA, improving its adhesion, wear resistance, or hydrophobicity. Various coating materials and processes can be applied to tailor PMMA for specific uses.
- Nanocomposite formulations: PMMA can be customized by incorporating nanoparticles or nanostructures to create nanocomposites. These formulations can significantly enhance the mechanical, thermal, and optical properties of PMMA, allowing for tailored performance in advanced applications such as optoelectronics or biomedical devices.
- Copolymerization and grafting: Customizability of PMMA can be achieved through copolymerization with other monomers or grafting of functional groups. This approach allows for the fine-tuning of properties such as glass transition temperature, solubility, or reactivity, enabling the creation of PMMA variants with specific characteristics for diverse applications.
- Processing and fabrication techniques: PMMA can be customized through various processing and fabrication techniques such as injection molding, extrusion, or 3D printing. These methods allow for the creation of complex shapes, controlled porosity, or specific surface textures, enabling the customization of PMMA for particular end-use requirements.
02 Surface treatment and coating techniques
The customizability of PMMA can be improved through surface treatments and coating techniques. These methods allow for the alteration of surface properties, such as hydrophobicity, scratch resistance, or anti-reflective characteristics, without significantly changing the bulk properties of the material.Expand Specific Solutions03 Incorporation of functional additives
PMMA can be customized by incorporating various functional additives during the manufacturing process. These additives can impart specific properties like UV resistance, flame retardancy, or antimicrobial activity, expanding the range of potential applications for PMMA-based products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Nanocomposite formulations
The development of PMMA nanocomposites offers enhanced customizability. By incorporating nanoparticles or nanostructures into the PMMA matrix, it is possible to achieve unique combinations of properties, such as improved mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, or electrical properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Processing and fabrication techniques
Advanced processing and fabrication techniques contribute to the customizability of PMMA. Methods such as 3D printing, injection molding, or extrusion can be optimized to create complex shapes, fine structures, or gradient properties, allowing for tailored PMMA products to meet specific requirements in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The PMMA customizable building components market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for sustainable and versatile construction materials. The market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth potential in the coming years. Technologically, PMMA applications in building components are advancing, with companies like Covestro Deutschland AG, Wanhua Chemical Group, and Toray Industries leading innovation. These firms are developing enhanced PMMA formulations for improved durability, energy efficiency, and customization options. However, the technology is not yet fully mature, as research institutions like Vanderbilt University and Fudan University continue to explore new PMMA applications and properties for construction use.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Technical Solution: Covestro has developed a novel PMMA-based technology for customizable building components. Their approach involves incorporating advanced additives and modifiers into PMMA to enhance its properties for specific architectural applications. The company has created a range of PMMA formulations with improved impact resistance, weatherability, and fire retardancy[1]. These formulations can be tailored to meet various building codes and performance requirements. Covestro's PMMA solutions also feature color stability and high light transmission, making them ideal for facades, skylights, and decorative elements[2]. The company has implemented a modular production process that allows for rapid customization of PMMA components, enabling architects and builders to create unique designs with shorter lead times[3].
Strengths: Highly customizable formulations, improved material properties, and modular production process. Weaknesses: Potentially higher costs compared to traditional materials and limited track record in large-scale building applications.
Kingfa Sci. & Tech. Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Kingfa has developed a proprietary PMMA composite technology for customizable building components. Their approach combines PMMA with other polymers and reinforcing agents to create high-performance materials suitable for various architectural applications. The company's PMMA composites offer enhanced mechanical strength, thermal insulation, and acoustic properties[4]. Kingfa has also developed a unique surface treatment technology that allows for the creation of textured and patterned PMMA components, providing architects with greater design flexibility[5]. Their manufacturing process utilizes advanced extrusion and molding techniques, enabling the production of complex shapes and large-scale components with consistent quality[6].
Strengths: Enhanced material properties, unique surface treatments, and capability to produce complex shapes. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in transparency compared to pure PMMA and higher production costs.
Innovative PMMA Patents
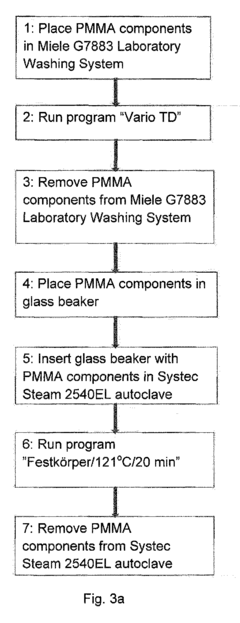
Sterilisation method of dental components comprising polymethyl methacrylate
PatentInactiveEP2698171A1
Innovation
- Steam sterilization of thermoset PMMA dental components at temperatures between 121°C and 134°C for up to 30 minutes, which surprisingly does not degrade the material and maintains its mechanical and biocompatibility properties.
Composition with increased stress cracking resistance
PatentInactiveEP2150582A1
Innovation
- A composition comprising 50.0% to 99.5% by weight of at least one (meth)acrylate copolymer and 0.5% to 50.0% by weight of a copolymer obtained from polymerizing a monomer mixture of 70% to 92% vinyl aromatic monomers and 8% to 30% acrylonitrile, with specific properties such as high tensile modulus, Vicat softening point, and impact strength, ensuring excellent thermal stability and optical constancy.
Sustainability Aspects
PMMA, or polymethyl methacrylate, has gained significant attention in the construction industry for its potential to enhance sustainability in customizable building components. As environmental concerns continue to shape the future of architecture and construction, PMMA offers several advantages that align with sustainable building practices.
One of the key sustainability aspects of PMMA is its recyclability. Unlike many traditional building materials, PMMA can be recycled multiple times without significant loss of quality. This characteristic contributes to a circular economy model, reducing waste and conserving resources. The recycling process for PMMA is relatively straightforward, involving mechanical grinding and reprocessing, which requires less energy compared to the production of virgin material.
PMMA's durability and longevity also play a crucial role in its sustainability profile. When used in building components, PMMA exhibits excellent resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and chemical exposure. This durability translates to extended product lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing the environmental impact associated with manufacturing and disposal of short-lived materials.
Energy efficiency is another area where PMMA contributes to sustainable building practices. The material's high light transmission properties make it an excellent choice for daylighting applications, potentially reducing the need for artificial lighting and lowering energy consumption. Additionally, PMMA can be engineered to have specific thermal insulation properties, contributing to better building envelope performance and reduced heating and cooling loads.
The customizability of PMMA allows for optimized material use in building components. Through advanced manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing and CNC machining, PMMA can be shaped and formed with minimal waste, adhering to the principles of material efficiency. This precision in manufacturing also enables the creation of lightweight structures, potentially reducing the overall material requirements and associated environmental impacts of construction projects.
PMMA's potential for integration with other sustainable technologies is noteworthy. For instance, it can be combined with photovoltaic cells to create transparent solar panels, merging energy generation with building aesthetics. Furthermore, PMMA's compatibility with various additives and coatings opens up possibilities for enhancing its performance in areas such as self-cleaning, air purification, and thermal regulation, contributing to overall building sustainability.
As the construction industry moves towards more sustainable practices, the life cycle assessment (LCA) of materials becomes increasingly important. Initial studies suggest that PMMA, when considering its entire life cycle from production to end-of-life, can offer environmental benefits compared to some traditional materials, particularly when its long lifespan and recyclability are factored in. However, ongoing research is needed to fully quantify its environmental impact across different applications and scenarios.
One of the key sustainability aspects of PMMA is its recyclability. Unlike many traditional building materials, PMMA can be recycled multiple times without significant loss of quality. This characteristic contributes to a circular economy model, reducing waste and conserving resources. The recycling process for PMMA is relatively straightforward, involving mechanical grinding and reprocessing, which requires less energy compared to the production of virgin material.
PMMA's durability and longevity also play a crucial role in its sustainability profile. When used in building components, PMMA exhibits excellent resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and chemical exposure. This durability translates to extended product lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing the environmental impact associated with manufacturing and disposal of short-lived materials.
Energy efficiency is another area where PMMA contributes to sustainable building practices. The material's high light transmission properties make it an excellent choice for daylighting applications, potentially reducing the need for artificial lighting and lowering energy consumption. Additionally, PMMA can be engineered to have specific thermal insulation properties, contributing to better building envelope performance and reduced heating and cooling loads.
The customizability of PMMA allows for optimized material use in building components. Through advanced manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing and CNC machining, PMMA can be shaped and formed with minimal waste, adhering to the principles of material efficiency. This precision in manufacturing also enables the creation of lightweight structures, potentially reducing the overall material requirements and associated environmental impacts of construction projects.
PMMA's potential for integration with other sustainable technologies is noteworthy. For instance, it can be combined with photovoltaic cells to create transparent solar panels, merging energy generation with building aesthetics. Furthermore, PMMA's compatibility with various additives and coatings opens up possibilities for enhancing its performance in areas such as self-cleaning, air purification, and thermal regulation, contributing to overall building sustainability.
As the construction industry moves towards more sustainable practices, the life cycle assessment (LCA) of materials becomes increasingly important. Initial studies suggest that PMMA, when considering its entire life cycle from production to end-of-life, can offer environmental benefits compared to some traditional materials, particularly when its long lifespan and recyclability are factored in. However, ongoing research is needed to fully quantify its environmental impact across different applications and scenarios.
Regulatory Considerations
The regulatory landscape for PMMA in customizable building components is complex and evolving, with various standards and guidelines influencing its adoption and implementation. Building codes and safety regulations play a crucial role in determining the acceptable use of PMMA in construction. Many jurisdictions require compliance with fire safety standards, such as ASTM E84 for surface burning characteristics and NFPA 285 for exterior wall assemblies. These regulations often dictate the maximum allowable area and thickness of PMMA panels in building facades.
Environmental regulations also impact the use of PMMA in construction. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, regulations may require manufacturers to consider the entire lifecycle of PMMA products, including production, installation, and end-of-life disposal or recycling. Some regions have implemented strict guidelines on volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, which may affect the formulation and application of PMMA-based materials.
Energy efficiency standards are another regulatory consideration for PMMA in building components. As governments worldwide push for more energy-efficient buildings, regulations may specify minimum thermal performance requirements for building envelopes. PMMA manufacturers must ensure their products meet or exceed these standards to remain competitive in the market.
Accessibility regulations, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in the United States, may also influence the design and implementation of PMMA components in buildings. These regulations often specify requirements for slip resistance, glare reduction, and other factors that could affect the use of PMMA in flooring, signage, and other applications.
Product certification and labeling requirements vary by region and application. In the European Union, for example, the Construction Products Regulation (CPR) mandates CE marking for certain building materials, including those containing PMMA. This requires manufacturers to demonstrate compliance with harmonized technical specifications and provide a declaration of performance.
As the use of PMMA in customizable building components continues to grow, regulatory bodies may develop new standards specifically addressing its unique properties and applications. Industry stakeholders should actively engage with regulatory agencies to ensure that future regulations balance safety concerns with the innovative potential of PMMA-based solutions.
Compliance with these diverse regulatory requirements presents both challenges and opportunities for PMMA manufacturers and builders. While meeting stringent standards may increase production costs, it also drives innovation and can lead to the development of higher-quality, more versatile PMMA products for the construction industry.
Environmental regulations also impact the use of PMMA in construction. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, regulations may require manufacturers to consider the entire lifecycle of PMMA products, including production, installation, and end-of-life disposal or recycling. Some regions have implemented strict guidelines on volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, which may affect the formulation and application of PMMA-based materials.
Energy efficiency standards are another regulatory consideration for PMMA in building components. As governments worldwide push for more energy-efficient buildings, regulations may specify minimum thermal performance requirements for building envelopes. PMMA manufacturers must ensure their products meet or exceed these standards to remain competitive in the market.
Accessibility regulations, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in the United States, may also influence the design and implementation of PMMA components in buildings. These regulations often specify requirements for slip resistance, glare reduction, and other factors that could affect the use of PMMA in flooring, signage, and other applications.
Product certification and labeling requirements vary by region and application. In the European Union, for example, the Construction Products Regulation (CPR) mandates CE marking for certain building materials, including those containing PMMA. This requires manufacturers to demonstrate compliance with harmonized technical specifications and provide a declaration of performance.
As the use of PMMA in customizable building components continues to grow, regulatory bodies may develop new standards specifically addressing its unique properties and applications. Industry stakeholders should actively engage with regulatory agencies to ensure that future regulations balance safety concerns with the innovative potential of PMMA-based solutions.
Compliance with these diverse regulatory requirements presents both challenges and opportunities for PMMA manufacturers and builders. While meeting stringent standards may increase production costs, it also drives innovation and can lead to the development of higher-quality, more versatile PMMA products for the construction industry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!