How to Simplify PMMA Processes for Efficient Manufacturing?
AUG 7, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PMMA Manufacturing Evolution and Objectives
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic or plexiglass, has been a cornerstone material in various industries since its development in the 1930s. The evolution of PMMA manufacturing processes has been driven by the need for more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly production methods. Initially, PMMA was primarily produced through bulk polymerization, which, while effective, was time-consuming and energy-intensive.
As demand grew, the industry saw a shift towards continuous processes, such as emulsion polymerization and suspension polymerization. These methods allowed for better control over molecular weight distribution and improved product consistency. However, they also introduced new challenges, including the need for complex equipment and the use of potentially harmful solvents.
The current objectives in PMMA manufacturing focus on simplifying these processes while maintaining or improving product quality. Key goals include reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste generation, and shortening production cycles. There is also a growing emphasis on developing more sustainable manufacturing methods that align with circular economy principles.
One significant area of development is the exploration of alternative initiators and catalysts that can accelerate polymerization reactions at lower temperatures. This approach not only reduces energy requirements but also allows for better control over the final product's properties. Additionally, researchers are investigating novel reactor designs that enhance heat transfer and mixing efficiency, potentially leading to more compact and less energy-intensive production lines.
Another important objective is the integration of in-line monitoring and control systems. Advanced sensors and real-time data analysis can help optimize process parameters on the fly, reducing variability and improving overall yield. This move towards smart manufacturing aligns with Industry 4.0 principles and promises to revolutionize PMMA production.
The simplification of post-processing steps is also a critical focus. Traditional methods often require extensive purification and drying stages, which add time and cost to the manufacturing process. Developing techniques that produce PMMA with fewer impurities or that allow for easier separation of the polymer from reaction media could significantly streamline production.
Lastly, there is a growing interest in exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived monomers. While still in early stages, this research aims to create more sustainable PMMA products that maintain the material's desirable properties while reducing its environmental footprint. The ultimate goal is to establish a manufacturing process that is not only efficient and cost-effective but also environmentally responsible and adaptable to future sustainability requirements.
As demand grew, the industry saw a shift towards continuous processes, such as emulsion polymerization and suspension polymerization. These methods allowed for better control over molecular weight distribution and improved product consistency. However, they also introduced new challenges, including the need for complex equipment and the use of potentially harmful solvents.
The current objectives in PMMA manufacturing focus on simplifying these processes while maintaining or improving product quality. Key goals include reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste generation, and shortening production cycles. There is also a growing emphasis on developing more sustainable manufacturing methods that align with circular economy principles.
One significant area of development is the exploration of alternative initiators and catalysts that can accelerate polymerization reactions at lower temperatures. This approach not only reduces energy requirements but also allows for better control over the final product's properties. Additionally, researchers are investigating novel reactor designs that enhance heat transfer and mixing efficiency, potentially leading to more compact and less energy-intensive production lines.
Another important objective is the integration of in-line monitoring and control systems. Advanced sensors and real-time data analysis can help optimize process parameters on the fly, reducing variability and improving overall yield. This move towards smart manufacturing aligns with Industry 4.0 principles and promises to revolutionize PMMA production.
The simplification of post-processing steps is also a critical focus. Traditional methods often require extensive purification and drying stages, which add time and cost to the manufacturing process. Developing techniques that produce PMMA with fewer impurities or that allow for easier separation of the polymer from reaction media could significantly streamline production.
Lastly, there is a growing interest in exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived monomers. While still in early stages, this research aims to create more sustainable PMMA products that maintain the material's desirable properties while reducing its environmental footprint. The ultimate goal is to establish a manufacturing process that is not only efficient and cost-effective but also environmentally responsible and adaptable to future sustainability requirements.
Market Demand for Streamlined PMMA Production
The market demand for streamlined PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate) production has been steadily increasing due to the material's versatile applications across various industries. PMMA, also known as acrylic, is widely used in automotive, construction, electronics, and medical sectors, driving the need for more efficient manufacturing processes.
In the automotive industry, PMMA is increasingly utilized for lightweight components, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. The growing trend towards electric vehicles has further boosted the demand for PMMA in battery casings and transparent components. This shift has created a significant market opportunity for manufacturers who can offer streamlined PMMA production methods.
The construction sector has also witnessed a surge in PMMA demand, particularly for energy-efficient windows, skylights, and architectural elements. As sustainable building practices gain traction globally, the market for PMMA products in construction is expected to expand further. Manufacturers capable of simplifying PMMA processes can capitalize on this growing market segment.
In the electronics industry, PMMA is crucial for producing display screens, light guides, and optical components. With the rapid advancement of consumer electronics and the increasing adoption of smart devices, the demand for high-quality PMMA products has skyrocketed. This trend underscores the need for more efficient manufacturing techniques to meet the escalating market requirements.
The medical sector represents another significant driver for streamlined PMMA production. PMMA is extensively used in medical devices, implants, and diagnostic equipment. The aging population and advancements in healthcare technologies have led to a sustained increase in demand for PMMA-based medical products. Manufacturers who can offer simplified PMMA processes are well-positioned to serve this critical market segment.
Market analysis indicates that the global PMMA market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5% in the coming years. This growth is primarily attributed to the expanding applications of PMMA in emerging technologies and the increasing demand for sustainable materials. The Asia-Pacific region, in particular, is expected to witness the highest growth rate due to rapid industrialization and urbanization.
The demand for streamlined PMMA production is further intensified by the industry's focus on cost reduction and sustainability. Manufacturers are under pressure to develop more efficient processes that minimize waste, reduce energy consumption, and lower production costs. This market trend aligns perfectly with the goal of simplifying PMMA processes for efficient manufacturing.
In the automotive industry, PMMA is increasingly utilized for lightweight components, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. The growing trend towards electric vehicles has further boosted the demand for PMMA in battery casings and transparent components. This shift has created a significant market opportunity for manufacturers who can offer streamlined PMMA production methods.
The construction sector has also witnessed a surge in PMMA demand, particularly for energy-efficient windows, skylights, and architectural elements. As sustainable building practices gain traction globally, the market for PMMA products in construction is expected to expand further. Manufacturers capable of simplifying PMMA processes can capitalize on this growing market segment.
In the electronics industry, PMMA is crucial for producing display screens, light guides, and optical components. With the rapid advancement of consumer electronics and the increasing adoption of smart devices, the demand for high-quality PMMA products has skyrocketed. This trend underscores the need for more efficient manufacturing techniques to meet the escalating market requirements.
The medical sector represents another significant driver for streamlined PMMA production. PMMA is extensively used in medical devices, implants, and diagnostic equipment. The aging population and advancements in healthcare technologies have led to a sustained increase in demand for PMMA-based medical products. Manufacturers who can offer simplified PMMA processes are well-positioned to serve this critical market segment.
Market analysis indicates that the global PMMA market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 5% in the coming years. This growth is primarily attributed to the expanding applications of PMMA in emerging technologies and the increasing demand for sustainable materials. The Asia-Pacific region, in particular, is expected to witness the highest growth rate due to rapid industrialization and urbanization.
The demand for streamlined PMMA production is further intensified by the industry's focus on cost reduction and sustainability. Manufacturers are under pressure to develop more efficient processes that minimize waste, reduce energy consumption, and lower production costs. This market trend aligns perfectly with the goal of simplifying PMMA processes for efficient manufacturing.
Current PMMA Process Challenges
The current PMMA manufacturing process faces several significant challenges that hinder efficient production and limit its widespread adoption in various industries. One of the primary issues is the complexity of the polymerization process, which requires precise control of temperature, pressure, and reaction time. This complexity often leads to inconsistencies in product quality and increases the likelihood of batch-to-batch variations.
Another major challenge is the high energy consumption associated with PMMA production. The process typically involves heating monomers to high temperatures, which not only increases production costs but also raises environmental concerns due to the associated carbon footprint. This energy-intensive nature of PMMA manufacturing makes it less attractive in an era of increasing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency.
The use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the production process poses both environmental and health risks. These compounds contribute to air pollution and can be hazardous to workers' health, necessitating stringent safety measures and environmental controls. This adds to the overall complexity and cost of PMMA manufacturing.
Material waste is another significant challenge in current PMMA processes. The polymerization reaction often results in the formation of oligomers and other by-products, which need to be separated and disposed of properly. This not only reduces the overall yield of the process but also creates additional waste management issues.
The long production cycle time is a further impediment to efficient PMMA manufacturing. The polymerization reaction, followed by cooling and post-processing steps, can take several hours to complete, limiting production capacity and flexibility in meeting market demands.
Additionally, the current PMMA processes often struggle with achieving consistent optical properties across different batches. This is particularly crucial for applications in the optics and display industries, where even minor variations in transparency or refractive index can significantly impact product performance.
Scalability remains a challenge for many PMMA manufacturers. As demand for PMMA products grows, scaling up production while maintaining product quality and process efficiency becomes increasingly difficult. This is partly due to the sensitive nature of the polymerization reaction and the need for precise control over a larger volume of material.
Lastly, the limited recyclability of PMMA products poses a challenge in terms of sustainability and circular economy principles. While PMMA can be recycled, the process is often energy-intensive and can result in a degradation of material properties, making it less attractive for manufacturers and consumers alike.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for simplifying PMMA processes and achieving more efficient manufacturing. Innovations in reaction chemistry, process control, and equipment design are needed to overcome these hurdles and unlock the full potential of PMMA as a versatile and sustainable material.
Another major challenge is the high energy consumption associated with PMMA production. The process typically involves heating monomers to high temperatures, which not only increases production costs but also raises environmental concerns due to the associated carbon footprint. This energy-intensive nature of PMMA manufacturing makes it less attractive in an era of increasing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency.
The use of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the production process poses both environmental and health risks. These compounds contribute to air pollution and can be hazardous to workers' health, necessitating stringent safety measures and environmental controls. This adds to the overall complexity and cost of PMMA manufacturing.
Material waste is another significant challenge in current PMMA processes. The polymerization reaction often results in the formation of oligomers and other by-products, which need to be separated and disposed of properly. This not only reduces the overall yield of the process but also creates additional waste management issues.
The long production cycle time is a further impediment to efficient PMMA manufacturing. The polymerization reaction, followed by cooling and post-processing steps, can take several hours to complete, limiting production capacity and flexibility in meeting market demands.
Additionally, the current PMMA processes often struggle with achieving consistent optical properties across different batches. This is particularly crucial for applications in the optics and display industries, where even minor variations in transparency or refractive index can significantly impact product performance.
Scalability remains a challenge for many PMMA manufacturers. As demand for PMMA products grows, scaling up production while maintaining product quality and process efficiency becomes increasingly difficult. This is partly due to the sensitive nature of the polymerization reaction and the need for precise control over a larger volume of material.
Lastly, the limited recyclability of PMMA products poses a challenge in terms of sustainability and circular economy principles. While PMMA can be recycled, the process is often energy-intensive and can result in a degradation of material properties, making it less attractive for manufacturers and consumers alike.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for simplifying PMMA processes and achieving more efficient manufacturing. Innovations in reaction chemistry, process control, and equipment design are needed to overcome these hurdles and unlock the full potential of PMMA as a versatile and sustainable material.
Existing PMMA Process Optimization Solutions
01 Improved polymerization processes
Various methods to enhance the polymerization process of PMMA are proposed, including optimized reaction conditions, novel catalysts, and innovative reactor designs. These improvements aim to increase conversion rates, reduce reaction times, and enhance overall production efficiency.- Improved polymerization process: Enhancing the polymerization process of PMMA can significantly improve manufacturing efficiency. This includes optimizing reaction conditions, using advanced catalysts, and implementing continuous flow reactors. These improvements can lead to faster reaction times, higher yields, and better control over the molecular weight distribution of the polymer.
- Advanced purification techniques: Implementing advanced purification techniques can increase the quality and efficiency of PMMA production. This may involve using novel separation methods, improved distillation processes, or membrane technologies to remove impurities and unreacted monomers more effectively. These techniques can result in higher-grade PMMA and reduced processing time.
- Process automation and control: Integrating advanced automation and control systems in PMMA manufacturing can lead to improved efficiency. This includes implementing real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and adaptive process control. Such systems can optimize production parameters, reduce downtime, and ensure consistent product quality.
- Recycling and waste reduction: Developing efficient recycling processes and waste reduction strategies can improve overall manufacturing efficiency. This may involve techniques for recovering and reprocessing PMMA waste, as well as implementing closed-loop systems to minimize material loss. These approaches can lead to reduced raw material costs and improved sustainability.
- Novel reactor designs: Implementing innovative reactor designs can significantly enhance PMMA manufacturing efficiency. This may include using microreactors, oscillatory flow reactors, or other novel configurations that improve heat and mass transfer. These designs can lead to better control over reaction conditions, reduced processing times, and improved product consistency.
02 Advanced purification techniques
Novel purification methods are developed to improve the quality and purity of PMMA products. These techniques include enhanced filtration systems, advanced distillation processes, and innovative separation methods, resulting in higher-grade PMMA and reduced waste.Expand Specific Solutions03 Continuous flow manufacturing
Continuous flow manufacturing processes are implemented to increase PMMA production efficiency. These systems allow for better control of reaction parameters, improved heat transfer, and reduced downtime, leading to higher throughput and consistent product quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recycling and waste reduction
Innovative recycling methods and waste reduction strategies are developed to improve the overall efficiency of PMMA manufacturing. These approaches include the reuse of monomers, recovery of solvents, and utilization of by-products, resulting in reduced raw material costs and environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions05 Process monitoring and control
Advanced process monitoring and control systems are implemented to optimize PMMA manufacturing. These technologies include real-time sensors, machine learning algorithms, and automated control systems, enabling precise adjustment of process parameters and rapid response to deviations, ultimately improving production efficiency and product quality.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PMMA Industry Players
The competitive landscape for simplifying PMMA processes for efficient manufacturing is characterized by a mature industry in a growth phase. The global PMMA market size is projected to reach $5.5 billion by 2025, driven by demand in automotive, electronics, and construction sectors. Technologically, the field is advancing with companies like Röhm GmbH, Mitsubishi Rayon, and Evonik leading innovation. Research institutions such as Fudan University and Harbin Institute of Technology are contributing to process improvements. Emerging players like Jiangsu Huasheng and Huahe New Material are also entering the market, intensifying competition and driving further advancements in PMMA manufacturing efficiency.
Röhm GmbH
Technical Solution: Röhm GmbH has developed an innovative PMMA production process called AVENEER®. This method significantly simplifies PMMA manufacturing by reducing the number of process steps and eliminating the need for intermediate products. The AVENEER® process directly converts methyl methacrylate (MMA) to PMMA in a single step, using a proprietary catalyst system. This approach results in a 20% reduction in energy consumption and a 40% decrease in investment costs compared to conventional methods[1][2]. Additionally, the process achieves a near 100% yield, minimizing waste and improving overall efficiency[3].
Strengths: Significantly reduced energy consumption and investment costs, higher yield, and simplified process. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment and expertise to implement, potentially limiting adoption by smaller manufacturers.
Trinseo Europe GmbH
Technical Solution: Trinseo has developed a continuous mass polymerization process for PMMA production, which offers several advantages over traditional suspension or emulsion polymerization methods. This process involves the continuous feeding of raw materials into a series of reactors, where polymerization occurs under carefully controlled conditions. The resulting PMMA is then continuously extruded and pelletized. This method allows for better control of molecular weight distribution and reduces the need for post-processing steps[4]. Trinseo's process also incorporates advanced heat management techniques, resulting in a 15% reduction in energy consumption compared to batch processes[5].
Strengths: Improved product consistency, reduced energy consumption, and continuous production capability. Weaknesses: May require significant initial investment to transition from batch to continuous processing.
Innovative PMMA Manufacturing Techniques
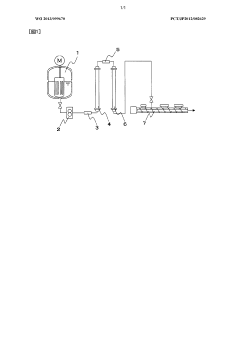
Method for manufacturing methacrylic polymer
PatentWO2013099670A1
Innovation
- A method involving continuous bulk polymerization using a complete mixing reactor and plug flow reactor, with specific conditions for adding radical polymerization initiators and controlling temperatures and half-lives to stabilize the polymerization process, ensuring high productivity and thermal decomposition resistance.
Method for producing an impact-resistant polymethylmethacrylate, and corresponding polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA)
PatentInactiveEP1470169A1
Innovation
- A process involving dissolving impact modifiers in methyl methacrylate (MMA) or polymerized MMA, followed by polymerization in a chamber, using a formulation with stabilizers and additives, to produce a cast plastic molding with enhanced impact strength without interpenetrating networks or complicated isolation steps.
Environmental Impact of PMMA Manufacturing
The environmental impact of PMMA manufacturing is a critical consideration in the quest to simplify and enhance the efficiency of production processes. PMMA, or polymethyl methacrylate, is a widely used synthetic polymer with applications ranging from automotive parts to medical devices. However, its production can have significant environmental implications that need to be addressed.
One of the primary environmental concerns in PMMA manufacturing is the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These emissions occur during various stages of production, including polymerization and processing. VOCs contribute to air pollution and can have adverse effects on human health and the environment. Implementing advanced emission control technologies and optimizing production processes can help mitigate these impacts.
Energy consumption is another major environmental factor in PMMA production. The manufacturing process requires substantial energy inputs, particularly during polymerization and extrusion stages. This high energy demand often translates to increased greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change. Improving energy efficiency through process optimization and the adoption of renewable energy sources can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of PMMA manufacturing.
Water usage and wastewater generation are also important environmental considerations. PMMA production involves water-intensive processes, and the resulting wastewater may contain pollutants that require treatment before discharge. Implementing water recycling systems and more efficient cleaning processes can help reduce water consumption and minimize wastewater generation.
The use of raw materials in PMMA manufacturing also has environmental implications. The production of methyl methacrylate monomer, the primary raw material for PMMA, involves petrochemical processes that can have their own environmental impacts. Exploring alternative, bio-based raw materials or improving the efficiency of monomer production can help reduce the overall environmental footprint of PMMA.
Waste generation is another significant environmental aspect of PMMA manufacturing. Off-spec products, process scraps, and end-of-life PMMA products contribute to plastic waste. Implementing effective recycling programs and exploring closed-loop manufacturing systems can help minimize waste and promote a more circular economy for PMMA.
As the industry seeks to simplify PMMA processes for efficient manufacturing, it is crucial to integrate environmental considerations into process improvements. This may involve adopting cleaner production technologies, implementing life cycle assessments, and exploring innovative approaches to reduce environmental impacts across the entire PMMA value chain. By addressing these environmental challenges, the PMMA industry can work towards more sustainable and efficient manufacturing practices.
One of the primary environmental concerns in PMMA manufacturing is the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These emissions occur during various stages of production, including polymerization and processing. VOCs contribute to air pollution and can have adverse effects on human health and the environment. Implementing advanced emission control technologies and optimizing production processes can help mitigate these impacts.
Energy consumption is another major environmental factor in PMMA production. The manufacturing process requires substantial energy inputs, particularly during polymerization and extrusion stages. This high energy demand often translates to increased greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change. Improving energy efficiency through process optimization and the adoption of renewable energy sources can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of PMMA manufacturing.
Water usage and wastewater generation are also important environmental considerations. PMMA production involves water-intensive processes, and the resulting wastewater may contain pollutants that require treatment before discharge. Implementing water recycling systems and more efficient cleaning processes can help reduce water consumption and minimize wastewater generation.
The use of raw materials in PMMA manufacturing also has environmental implications. The production of methyl methacrylate monomer, the primary raw material for PMMA, involves petrochemical processes that can have their own environmental impacts. Exploring alternative, bio-based raw materials or improving the efficiency of monomer production can help reduce the overall environmental footprint of PMMA.
Waste generation is another significant environmental aspect of PMMA manufacturing. Off-spec products, process scraps, and end-of-life PMMA products contribute to plastic waste. Implementing effective recycling programs and exploring closed-loop manufacturing systems can help minimize waste and promote a more circular economy for PMMA.
As the industry seeks to simplify PMMA processes for efficient manufacturing, it is crucial to integrate environmental considerations into process improvements. This may involve adopting cleaner production technologies, implementing life cycle assessments, and exploring innovative approaches to reduce environmental impacts across the entire PMMA value chain. By addressing these environmental challenges, the PMMA industry can work towards more sustainable and efficient manufacturing practices.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of PMMA Process Improvements
The cost-benefit analysis of PMMA process improvements is crucial for evaluating the potential impact of simplifying manufacturing techniques. This analysis considers both the financial and operational aspects of implementing new processes, weighing the initial investment against long-term gains in efficiency and productivity.
One of the primary benefits of simplifying PMMA processes is the reduction in production time. By streamlining manufacturing steps, companies can significantly decrease the overall cycle time, leading to increased output and improved capacity utilization. This time savings translates directly into cost savings, as labor hours per unit produced are reduced, and equipment utilization is optimized.
Material waste reduction is another significant advantage of simplified PMMA processes. Improved manufacturing techniques often result in fewer defects and less scrap material, which not only reduces raw material costs but also minimizes disposal expenses. This efficiency gain contributes to both cost savings and environmental sustainability, an increasingly important factor in modern manufacturing.
Energy consumption is a considerable cost factor in PMMA production. Simplified processes typically require less energy input, resulting in lower utility costs and reduced carbon footprint. This benefit aligns with global efforts to increase energy efficiency in industrial processes and can lead to potential cost savings through reduced energy bills and compliance with environmental regulations.
Initial investment costs for process improvements can be substantial, including expenses for new equipment, staff training, and potential production downtime during implementation. However, these upfront costs should be evaluated against the long-term savings and increased competitiveness they can bring. A thorough ROI analysis is essential to determine the payback period and overall financial viability of the improvements.
Quality improvements are an often-overlooked benefit of simplified PMMA processes. Enhanced manufacturing techniques can lead to more consistent product quality, reducing the need for extensive quality control measures and minimizing the risk of product recalls or customer returns. This improvement in quality can strengthen brand reputation and potentially lead to increased market share and customer loyalty.
Operational flexibility is another advantage of streamlined processes. Simplified manufacturing techniques often allow for quicker changeovers between different product types or sizes, enabling manufacturers to respond more rapidly to market demands and customer needs. This agility can provide a competitive edge in fast-paced markets and contribute to improved customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, while the initial costs of implementing simplified PMMA processes can be significant, the potential long-term benefits in terms of reduced production time, material waste, energy consumption, and improved quality and flexibility often outweigh these investments. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis should consider both immediate financial impacts and long-term strategic advantages to make informed decisions about process improvements in PMMA manufacturing.
One of the primary benefits of simplifying PMMA processes is the reduction in production time. By streamlining manufacturing steps, companies can significantly decrease the overall cycle time, leading to increased output and improved capacity utilization. This time savings translates directly into cost savings, as labor hours per unit produced are reduced, and equipment utilization is optimized.
Material waste reduction is another significant advantage of simplified PMMA processes. Improved manufacturing techniques often result in fewer defects and less scrap material, which not only reduces raw material costs but also minimizes disposal expenses. This efficiency gain contributes to both cost savings and environmental sustainability, an increasingly important factor in modern manufacturing.
Energy consumption is a considerable cost factor in PMMA production. Simplified processes typically require less energy input, resulting in lower utility costs and reduced carbon footprint. This benefit aligns with global efforts to increase energy efficiency in industrial processes and can lead to potential cost savings through reduced energy bills and compliance with environmental regulations.
Initial investment costs for process improvements can be substantial, including expenses for new equipment, staff training, and potential production downtime during implementation. However, these upfront costs should be evaluated against the long-term savings and increased competitiveness they can bring. A thorough ROI analysis is essential to determine the payback period and overall financial viability of the improvements.
Quality improvements are an often-overlooked benefit of simplified PMMA processes. Enhanced manufacturing techniques can lead to more consistent product quality, reducing the need for extensive quality control measures and minimizing the risk of product recalls or customer returns. This improvement in quality can strengthen brand reputation and potentially lead to increased market share and customer loyalty.
Operational flexibility is another advantage of streamlined processes. Simplified manufacturing techniques often allow for quicker changeovers between different product types or sizes, enabling manufacturers to respond more rapidly to market demands and customer needs. This agility can provide a competitive edge in fast-paced markets and contribute to improved customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, while the initial costs of implementing simplified PMMA processes can be significant, the potential long-term benefits in terms of reduced production time, material waste, energy consumption, and improved quality and flexibility often outweigh these investments. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis should consider both immediate financial impacts and long-term strategic advantages to make informed decisions about process improvements in PMMA manufacturing.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!