How to Develop a Robust HEV Supply Chain Strategy?
AUG 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HEV Supply Chain Evolution and Objectives
The evolution of the Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) supply chain has been marked by significant technological advancements and shifting market dynamics. Initially, HEV supply chains were characterized by limited scale and high costs, primarily due to the nascent nature of the technology and low production volumes. As consumer demand for more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles grew, automakers began to invest heavily in HEV technology, leading to a rapid expansion of the supply chain.
The early stages of HEV supply chain development focused on battery technology, electric motors, and power control systems. These components were often sourced from a small number of specialized suppliers, creating potential bottlenecks and vulnerabilities in the supply chain. Over time, as HEV technology matured, the supply chain became more diverse and robust, with an increasing number of suppliers entering the market and offering more competitive pricing and innovative solutions.
A key objective in developing a robust HEV supply chain strategy is to ensure a stable and cost-effective supply of critical components. This includes securing long-term agreements with battery manufacturers, as battery technology remains a crucial factor in HEV performance and cost. Additionally, automakers aim to diversify their supplier base to mitigate risks associated with single-source dependencies and geopolitical uncertainties.
Another important objective is to improve the sustainability and environmental impact of the HEV supply chain. This involves sourcing materials responsibly, reducing the carbon footprint of manufacturing processes, and implementing circular economy principles to maximize resource efficiency and minimize waste. As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, HEV manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing supply chains that can meet these evolving standards.
Flexibility and scalability are also critical objectives in HEV supply chain strategy. The ability to rapidly adjust production volumes in response to market demand fluctuations is essential for maintaining competitiveness. This requires close collaboration with suppliers and the implementation of advanced manufacturing technologies and processes that can easily adapt to changing requirements.
Furthermore, the integration of digital technologies throughout the supply chain has become a key objective. This includes the use of artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and blockchain technology to enhance supply chain visibility, improve forecasting accuracy, and streamline logistics operations. These digital innovations are crucial for creating a more responsive and efficient HEV supply chain.
As the HEV market continues to evolve, supply chain strategies must also address the challenges of global expansion. This involves navigating complex international trade regulations, establishing regional production hubs, and developing localized supplier networks to meet specific market demands and reduce transportation costs.
The early stages of HEV supply chain development focused on battery technology, electric motors, and power control systems. These components were often sourced from a small number of specialized suppliers, creating potential bottlenecks and vulnerabilities in the supply chain. Over time, as HEV technology matured, the supply chain became more diverse and robust, with an increasing number of suppliers entering the market and offering more competitive pricing and innovative solutions.
A key objective in developing a robust HEV supply chain strategy is to ensure a stable and cost-effective supply of critical components. This includes securing long-term agreements with battery manufacturers, as battery technology remains a crucial factor in HEV performance and cost. Additionally, automakers aim to diversify their supplier base to mitigate risks associated with single-source dependencies and geopolitical uncertainties.
Another important objective is to improve the sustainability and environmental impact of the HEV supply chain. This involves sourcing materials responsibly, reducing the carbon footprint of manufacturing processes, and implementing circular economy principles to maximize resource efficiency and minimize waste. As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, HEV manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing supply chains that can meet these evolving standards.
Flexibility and scalability are also critical objectives in HEV supply chain strategy. The ability to rapidly adjust production volumes in response to market demand fluctuations is essential for maintaining competitiveness. This requires close collaboration with suppliers and the implementation of advanced manufacturing technologies and processes that can easily adapt to changing requirements.
Furthermore, the integration of digital technologies throughout the supply chain has become a key objective. This includes the use of artificial intelligence, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and blockchain technology to enhance supply chain visibility, improve forecasting accuracy, and streamline logistics operations. These digital innovations are crucial for creating a more responsive and efficient HEV supply chain.
As the HEV market continues to evolve, supply chain strategies must also address the challenges of global expansion. This involves navigating complex international trade regulations, establishing regional production hubs, and developing localized supplier networks to meet specific market demands and reduce transportation costs.
HEV Market Demand Analysis
The global market for Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns, stricter emissions regulations, and rising fuel costs. This trend is expected to continue, with the HEV market projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 8% from 2021 to 2026.
Consumer demand for HEVs is primarily fueled by the desire for improved fuel efficiency and reduced environmental impact. As awareness of climate change and air pollution grows, more consumers are seeking eco-friendly transportation options. HEVs offer a compelling compromise between traditional internal combustion engine vehicles and fully electric vehicles, providing improved fuel economy without the range anxiety associated with pure electric vehicles.
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in shaping HEV market demand. Many countries have implemented stringent emissions standards and offer tax breaks or subsidies for purchasing hybrid vehicles, further stimulating market growth. For instance, in the European Union, the implementation of CO2 emissions targets has led to increased adoption of HEVs by automakers to meet these standards.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and Japan, is expected to dominate the HEV market in terms of sales volume. This is due to a combination of factors, including government support, advanced manufacturing capabilities, and high consumer acceptance of hybrid technology. North America and Europe are also significant markets, with steady growth projected in the coming years.
In terms of vehicle segments, the passenger car segment currently holds the largest market share for HEVs. However, there is growing demand for hybrid technology in other vehicle categories, including SUVs, light commercial vehicles, and even heavy-duty trucks. This diversification of HEV applications is expected to create new opportunities for market expansion and supply chain development.
The increasing demand for HEVs has significant implications for the automotive supply chain. Key components such as electric motors, batteries, power electronics, and control systems are in high demand, creating both opportunities and challenges for suppliers. The need for specialized components and technologies is driving innovation and collaboration across the automotive industry, with many traditional suppliers adapting their product offerings to meet the needs of HEV manufacturers.
To develop a robust HEV supply chain strategy, companies must consider the evolving market dynamics and regional variations in demand. This includes understanding consumer preferences, regulatory landscapes, and technological advancements that may impact future HEV designs and component requirements. Additionally, supply chain strategies must account for potential disruptions, such as raw material shortages or geopolitical tensions, to ensure resilience and continuity of production.
Consumer demand for HEVs is primarily fueled by the desire for improved fuel efficiency and reduced environmental impact. As awareness of climate change and air pollution grows, more consumers are seeking eco-friendly transportation options. HEVs offer a compelling compromise between traditional internal combustion engine vehicles and fully electric vehicles, providing improved fuel economy without the range anxiety associated with pure electric vehicles.
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in shaping HEV market demand. Many countries have implemented stringent emissions standards and offer tax breaks or subsidies for purchasing hybrid vehicles, further stimulating market growth. For instance, in the European Union, the implementation of CO2 emissions targets has led to increased adoption of HEVs by automakers to meet these standards.
The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and Japan, is expected to dominate the HEV market in terms of sales volume. This is due to a combination of factors, including government support, advanced manufacturing capabilities, and high consumer acceptance of hybrid technology. North America and Europe are also significant markets, with steady growth projected in the coming years.
In terms of vehicle segments, the passenger car segment currently holds the largest market share for HEVs. However, there is growing demand for hybrid technology in other vehicle categories, including SUVs, light commercial vehicles, and even heavy-duty trucks. This diversification of HEV applications is expected to create new opportunities for market expansion and supply chain development.
The increasing demand for HEVs has significant implications for the automotive supply chain. Key components such as electric motors, batteries, power electronics, and control systems are in high demand, creating both opportunities and challenges for suppliers. The need for specialized components and technologies is driving innovation and collaboration across the automotive industry, with many traditional suppliers adapting their product offerings to meet the needs of HEV manufacturers.
To develop a robust HEV supply chain strategy, companies must consider the evolving market dynamics and regional variations in demand. This includes understanding consumer preferences, regulatory landscapes, and technological advancements that may impact future HEV designs and component requirements. Additionally, supply chain strategies must account for potential disruptions, such as raw material shortages or geopolitical tensions, to ensure resilience and continuity of production.
HEV Supply Chain Challenges
The development of a robust Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) supply chain strategy faces numerous challenges due to the complex nature of HEV production and the rapidly evolving automotive industry. One of the primary challenges is the sourcing and management of critical components, particularly batteries and electric powertrains. These components require specialized manufacturing processes and materials, often leading to supply constraints and potential bottlenecks in the production pipeline.
The global nature of the HEV supply chain adds another layer of complexity. Manufacturers must navigate diverse regulatory environments, trade policies, and geopolitical tensions that can disrupt the flow of components and raw materials. This challenge is particularly acute for rare earth elements and other critical minerals essential for HEV production, as their supply is often concentrated in specific regions, making the chain vulnerable to geopolitical risks.
Technological advancements and rapid innovation in the HEV sector pose significant challenges for supply chain management. As new technologies emerge and consumer preferences shift, manufacturers must maintain flexibility in their supply chains to adapt quickly. This requires a delicate balance between maintaining efficient, cost-effective production and being agile enough to incorporate new technologies or shift production focus as market demands change.
Quality control and consistency across the supply chain present another major challenge. With components sourced from multiple suppliers across different countries, ensuring uniform quality standards and compatibility can be difficult. This is particularly crucial for safety-critical components in HEVs, where any compromise in quality could have severe consequences.
The transition to HEV production also necessitates significant changes in workforce skills and manufacturing processes. Many traditional automotive suppliers may struggle to adapt to the new technologies required for HEV components, potentially creating gaps in the supply chain. This challenge extends to the need for specialized training and education to develop a workforce capable of supporting HEV production and maintenance.
Sustainability and environmental concerns add another dimension to HEV supply chain challenges. As HEVs are positioned as more environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional vehicles, there is increasing pressure to ensure that the entire supply chain adheres to strict environmental and ethical standards. This includes considerations for sustainable sourcing of raw materials, reducing carbon footprint in manufacturing and transportation, and implementing effective recycling and end-of-life strategies for HEV components, particularly batteries.
Lastly, the HEV supply chain must contend with intense competition and market pressures. As more automotive manufacturers enter the HEV market, competition for limited resources and suppliers intensifies. This can lead to supply shortages, price volatility, and potential compromises in quality or innovation as companies strive to secure their supply chains while maintaining cost competitiveness.
The global nature of the HEV supply chain adds another layer of complexity. Manufacturers must navigate diverse regulatory environments, trade policies, and geopolitical tensions that can disrupt the flow of components and raw materials. This challenge is particularly acute for rare earth elements and other critical minerals essential for HEV production, as their supply is often concentrated in specific regions, making the chain vulnerable to geopolitical risks.
Technological advancements and rapid innovation in the HEV sector pose significant challenges for supply chain management. As new technologies emerge and consumer preferences shift, manufacturers must maintain flexibility in their supply chains to adapt quickly. This requires a delicate balance between maintaining efficient, cost-effective production and being agile enough to incorporate new technologies or shift production focus as market demands change.
Quality control and consistency across the supply chain present another major challenge. With components sourced from multiple suppliers across different countries, ensuring uniform quality standards and compatibility can be difficult. This is particularly crucial for safety-critical components in HEVs, where any compromise in quality could have severe consequences.
The transition to HEV production also necessitates significant changes in workforce skills and manufacturing processes. Many traditional automotive suppliers may struggle to adapt to the new technologies required for HEV components, potentially creating gaps in the supply chain. This challenge extends to the need for specialized training and education to develop a workforce capable of supporting HEV production and maintenance.
Sustainability and environmental concerns add another dimension to HEV supply chain challenges. As HEVs are positioned as more environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional vehicles, there is increasing pressure to ensure that the entire supply chain adheres to strict environmental and ethical standards. This includes considerations for sustainable sourcing of raw materials, reducing carbon footprint in manufacturing and transportation, and implementing effective recycling and end-of-life strategies for HEV components, particularly batteries.
Lastly, the HEV supply chain must contend with intense competition and market pressures. As more automotive manufacturers enter the HEV market, competition for limited resources and suppliers intensifies. This can lead to supply shortages, price volatility, and potential compromises in quality or innovation as companies strive to secure their supply chains while maintaining cost competitiveness.
Current HEV Supply Chain Strategies
01 Supply chain management for HEV components
This point focuses on the management of supply chains specific to hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) components. It involves strategies for sourcing, procurement, and logistics of specialized parts such as batteries, electric motors, and power electronics. The approach aims to optimize the flow of materials and components from suppliers to manufacturers, ensuring efficient production of HEVs.- Supply chain management for HEV components: Efficient supply chain management is crucial for the production of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). This involves coordinating the sourcing, manufacturing, and distribution of various components specific to HEVs, such as batteries, electric motors, and power control units. Implementing advanced logistics systems and inventory management techniques can help optimize the supply chain, reduce costs, and ensure timely delivery of components to manufacturers.
- Battery technology and production for HEVs: The development and production of high-performance batteries are critical for the HEV supply chain. This includes research into new battery chemistries, improving energy density, and enhancing battery life cycles. Establishing efficient battery production facilities and securing a stable supply of raw materials for battery manufacturing are essential aspects of the HEV supply chain.
- Electric motor and power electronics supply: The supply chain for electric motors and power electronics is a crucial aspect of HEV production. This involves sourcing specialized materials, developing advanced manufacturing processes, and ensuring quality control for components such as electric motors, inverters, and power control units. Establishing partnerships with suppliers specializing in these technologies is essential for maintaining a robust HEV supply chain.
- Integration of sustainable practices in HEV supply chain: Incorporating sustainable practices throughout the HEV supply chain is becoming increasingly important. This includes implementing eco-friendly manufacturing processes, reducing carbon emissions in transportation and logistics, and ensuring responsible sourcing of raw materials. Developing circular economy initiatives, such as battery recycling programs, can also contribute to a more sustainable HEV supply chain.
- Supply chain risk management for HEV production: Managing risks in the HEV supply chain is crucial for ensuring uninterrupted production and meeting market demands. This involves identifying potential disruptions, such as geopolitical issues or natural disasters, and developing contingency plans. Implementing advanced forecasting techniques, diversifying supplier networks, and maintaining strategic inventory levels can help mitigate supply chain risks in the HEV industry.
02 HEV battery supply and recycling
This aspect covers the supply chain for HEV batteries, including their production, distribution, and end-of-life management. It encompasses strategies for securing raw materials, manufacturing processes, and establishing recycling networks to address environmental concerns and resource scarcity. The focus is on creating a sustainable circular economy for HEV batteries.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of advanced technologies in HEV supply chain
This point explores the incorporation of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and Internet of Things (IoT) into HEV supply chain management. These technologies enhance transparency, traceability, and efficiency throughout the supply network, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery and after-sales services.Expand Specific Solutions04 Collaborative HEV supply chain networks
This aspect focuses on establishing collaborative networks among various stakeholders in the HEV supply chain, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. It involves strategies for information sharing, joint planning, and risk management to create a more resilient and responsive supply chain ecosystem for HEVs.Expand Specific Solutions05 Localization and regionalization of HEV supply chains
This point addresses the trend towards localizing and regionalizing HEV supply chains to reduce dependence on global networks and mitigate risks associated with international trade disruptions. It involves strategies for developing local supplier networks, establishing regional manufacturing hubs, and adapting supply chain models to specific geographic contexts.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HEV Supply Chain
The development of a robust HEV supply chain strategy is currently in a mature growth phase, with the market size expanding rapidly due to increasing demand for eco-friendly vehicles. The technology has reached a high level of maturity, with major players like GM Global Technology Operations, Ford Global Technologies, and Hyundai Motor Co. leading innovation. Chinese manufacturers such as SAIC Motor, Great Wall Motor, and Chery Automobile are also making significant strides. The competitive landscape is intense, with established automotive giants competing alongside newer entrants and specialized suppliers like Allison Transmission and Visteon Global Technologies. Academic institutions, including Beijing Institute of Technology and Wuhan University of Technology, are contributing to technological advancements, further intensifying the competition in this sector.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM's robust HEV supply chain strategy focuses on vertical integration and strategic partnerships. They have invested in battery cell manufacturing through a joint venture with LG Energy Solution, aiming to produce Ultium battery cells[1]. This approach allows GM to control critical components of their HEV supply chain. Additionally, GM has implemented a modular design for their electric vehicle platforms, which enables flexibility in sourcing and manufacturing[2]. They have also established partnerships with key suppliers for other critical components, such as electric motors and power electronics[3]. GM's strategy includes diversifying their supplier base geographically to mitigate risks associated with regional disruptions[4].
Strengths: Vertical integration reduces dependency on external suppliers; modular design increases flexibility. Weaknesses: High initial investment costs; potential challenges in managing complex partnerships.
Zhejiang Geely Holding Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Geely's HEV supply chain strategy revolves around a combination of in-house development and strategic acquisitions. They have invested heavily in their own R&D capabilities, particularly in battery technology and powertrain systems[5]. Geely has also acquired stakes in key suppliers, such as their investment in LG Chem for battery production[6]. The company has established a global network of innovation centers to tap into diverse talent pools and technologies[7]. Geely's strategy includes the development of a modular architecture for hybrid vehicles, which allows for greater standardization and economies of scale across their brand portfolio[8]. They have also focused on localizing production in key markets to reduce supply chain risks and improve responsiveness to market demands[9].
Strengths: Strong in-house R&D capabilities; global innovation network. Weaknesses: Potential over-reliance on specific suppliers; challenges in managing a diverse brand portfolio.
Critical Technologies in HEV Supply Chain
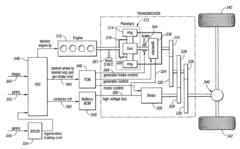
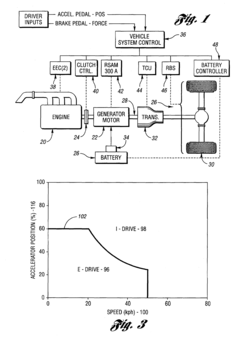
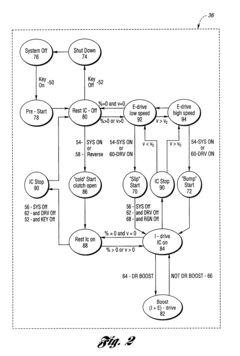
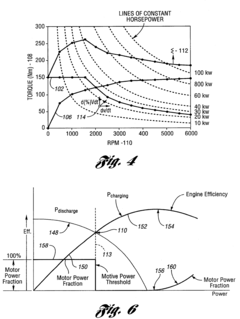
Control system for a hybrid electric vehicle to anticipate the need for a mode change
PatentInactiveUS7753150B2
Innovation
- A control strategy that monitors vehicle speed and driver demand, along with their rates of change, to anticipate and seamlessly transition between driving modes, preventing unwanted engine starts and ensuring timely engine activation, using a mathematical function of system variables like master cylinder brake pressure, throttle position, vehicle speed, and road grade.
Hybrid electric vehicle with electric motor providing strategic power assist to load balance internal combustion engine
PatentPendingIN202441000035A
Innovation
- A Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) system with an electric motor providing strategic power assist to the internal combustion engine, optimizing power distribution and energy management through advanced control algorithms.
Sustainability in HEV Supply Chain
Sustainability in the HEV (Hybrid Electric Vehicle) supply chain is a critical aspect of developing a robust strategy for the industry. As environmental concerns continue to grow, automotive manufacturers and suppliers are increasingly focusing on sustainable practices throughout the supply chain.
One of the primary considerations in HEV supply chain sustainability is the sourcing of raw materials. Battery production, a key component of HEVs, relies heavily on rare earth elements and other minerals. Ensuring these materials are sourced responsibly and ethically is crucial. Companies are investing in traceability technologies, such as blockchain, to monitor the origin and journey of these materials through the supply chain.
Energy efficiency in manufacturing processes is another vital element of sustainability. HEV manufacturers are adopting lean manufacturing principles and investing in renewable energy sources to power their production facilities. This not only reduces the carbon footprint of the manufacturing process but also helps to offset the environmental impact of vehicle production.
Waste reduction and circular economy principles are being integrated into HEV supply chains. Manufacturers are designing components with recyclability in mind, implementing take-back programs for end-of-life vehicles, and exploring ways to repurpose used EV batteries for energy storage applications. These initiatives help to minimize waste and extend the lifecycle of valuable resources.
Logistics optimization plays a significant role in reducing the environmental impact of the HEV supply chain. Companies are adopting advanced route planning software, utilizing alternative fuels for transportation, and exploring multimodal shipping options to decrease emissions associated with the movement of components and finished vehicles.
Supplier engagement and collaboration are essential for achieving sustainability goals. HEV manufacturers are working closely with their suppliers to set sustainability targets, share best practices, and develop innovative solutions for reducing environmental impact. This collaborative approach helps to ensure that sustainability is prioritized throughout the entire supply chain.
As regulations around environmental protection and carbon emissions become more stringent, HEV supply chains must adapt to remain compliant. This includes implementing robust monitoring and reporting systems to track sustainability metrics and demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements.
Investing in research and development for more sustainable materials and processes is a key strategy for long-term sustainability in the HEV supply chain. This includes exploring alternatives to rare earth elements, developing more efficient battery technologies, and innovating in lightweight materials to improve vehicle efficiency.
One of the primary considerations in HEV supply chain sustainability is the sourcing of raw materials. Battery production, a key component of HEVs, relies heavily on rare earth elements and other minerals. Ensuring these materials are sourced responsibly and ethically is crucial. Companies are investing in traceability technologies, such as blockchain, to monitor the origin and journey of these materials through the supply chain.
Energy efficiency in manufacturing processes is another vital element of sustainability. HEV manufacturers are adopting lean manufacturing principles and investing in renewable energy sources to power their production facilities. This not only reduces the carbon footprint of the manufacturing process but also helps to offset the environmental impact of vehicle production.
Waste reduction and circular economy principles are being integrated into HEV supply chains. Manufacturers are designing components with recyclability in mind, implementing take-back programs for end-of-life vehicles, and exploring ways to repurpose used EV batteries for energy storage applications. These initiatives help to minimize waste and extend the lifecycle of valuable resources.
Logistics optimization plays a significant role in reducing the environmental impact of the HEV supply chain. Companies are adopting advanced route planning software, utilizing alternative fuels for transportation, and exploring multimodal shipping options to decrease emissions associated with the movement of components and finished vehicles.
Supplier engagement and collaboration are essential for achieving sustainability goals. HEV manufacturers are working closely with their suppliers to set sustainability targets, share best practices, and develop innovative solutions for reducing environmental impact. This collaborative approach helps to ensure that sustainability is prioritized throughout the entire supply chain.
As regulations around environmental protection and carbon emissions become more stringent, HEV supply chains must adapt to remain compliant. This includes implementing robust monitoring and reporting systems to track sustainability metrics and demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements.
Investing in research and development for more sustainable materials and processes is a key strategy for long-term sustainability in the HEV supply chain. This includes exploring alternatives to rare earth elements, developing more efficient battery technologies, and innovating in lightweight materials to improve vehicle efficiency.
Risk Management in HEV Supply Chain
Risk management is a critical component of developing a robust HEV supply chain strategy. The hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) industry faces unique challenges due to its complex supply chain and reliance on advanced technologies. To mitigate risks effectively, companies must implement comprehensive risk assessment and management processes.
One of the primary risks in the HEV supply chain is the volatility of raw material prices, particularly for critical components such as batteries and rare earth elements. Fluctuations in these prices can significantly impact production costs and profit margins. To address this, companies should diversify their supplier base and establish long-term contracts with key suppliers to ensure price stability and consistent supply.
Another significant risk is the potential for supply chain disruptions due to natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, or other unforeseen events. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of building resilience into supply chains. HEV manufacturers should develop contingency plans, including alternative sourcing strategies and buffer inventory management, to minimize the impact of such disruptions.
Technological obsolescence is a constant threat in the rapidly evolving HEV industry. Companies must stay ahead of technological advancements and be prepared to adapt their supply chains accordingly. This involves maintaining close relationships with suppliers and investing in research and development to anticipate and respond to emerging technologies.
Quality control is paramount in the HEV supply chain, as defective components can lead to costly recalls and damage brand reputation. Implementing rigorous quality assurance processes throughout the supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final assembly, is essential. This may include regular supplier audits, in-process inspections, and advanced testing procedures.
Regulatory compliance presents another significant risk, as environmental and safety regulations for HEVs are becoming increasingly stringent. Companies must ensure that their supply chains adhere to all relevant regulations across different markets. This requires ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes and proactive adaptation of supply chain processes to maintain compliance.
Cybersecurity risks are growing concerns in the HEV supply chain, particularly as vehicles become more connected and reliant on software. Protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access to vehicle systems is crucial. Companies should implement robust cybersecurity measures throughout the supply chain and work closely with suppliers to ensure the integrity of all components and systems.
To effectively manage these risks, HEV manufacturers should establish a dedicated risk management team responsible for identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to the supply chain. This team should develop and maintain a comprehensive risk register, regularly review and update risk mitigation strategies, and conduct scenario planning exercises to prepare for various contingencies.
One of the primary risks in the HEV supply chain is the volatility of raw material prices, particularly for critical components such as batteries and rare earth elements. Fluctuations in these prices can significantly impact production costs and profit margins. To address this, companies should diversify their supplier base and establish long-term contracts with key suppliers to ensure price stability and consistent supply.
Another significant risk is the potential for supply chain disruptions due to natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, or other unforeseen events. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of building resilience into supply chains. HEV manufacturers should develop contingency plans, including alternative sourcing strategies and buffer inventory management, to minimize the impact of such disruptions.
Technological obsolescence is a constant threat in the rapidly evolving HEV industry. Companies must stay ahead of technological advancements and be prepared to adapt their supply chains accordingly. This involves maintaining close relationships with suppliers and investing in research and development to anticipate and respond to emerging technologies.
Quality control is paramount in the HEV supply chain, as defective components can lead to costly recalls and damage brand reputation. Implementing rigorous quality assurance processes throughout the supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final assembly, is essential. This may include regular supplier audits, in-process inspections, and advanced testing procedures.
Regulatory compliance presents another significant risk, as environmental and safety regulations for HEVs are becoming increasingly stringent. Companies must ensure that their supply chains adhere to all relevant regulations across different markets. This requires ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes and proactive adaptation of supply chain processes to maintain compliance.
Cybersecurity risks are growing concerns in the HEV supply chain, particularly as vehicles become more connected and reliant on software. Protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access to vehicle systems is crucial. Companies should implement robust cybersecurity measures throughout the supply chain and work closely with suppliers to ensure the integrity of all components and systems.
To effectively manage these risks, HEV manufacturers should establish a dedicated risk management team responsible for identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to the supply chain. This team should develop and maintain a comprehensive risk register, regularly review and update risk mitigation strategies, and conduct scenario planning exercises to prepare for various contingencies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!