How to Foster Growth in Emerging HEV Markets?
AUG 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HEV Market Evolution and Objectives
The evolution of the Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) market has been marked by significant technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences over the past two decades. Initially driven by environmental concerns and fuel efficiency, HEVs have transitioned from niche products to mainstream alternatives in many developed markets. This evolution has been characterized by improvements in battery technology, powertrain efficiency, and overall vehicle performance.
As emerging markets begin to embrace HEV technology, the objectives for fostering growth in these regions are multifaceted. Primarily, there is a need to adapt HEV technologies to suit local conditions, including climate, road infrastructure, and driving habits. This localization effort is crucial for ensuring the relevance and appeal of HEVs in diverse global markets.
Another key objective is to address the cost barriers that often hinder HEV adoption in price-sensitive emerging markets. This involves developing more affordable HEV models without compromising on quality or performance. Manufacturers are exploring strategies such as local production and sourcing to reduce costs and make HEVs more accessible to a broader consumer base.
Regulatory support plays a vital role in shaping the HEV market in emerging economies. Objectives in this area include working with governments to establish supportive policies, such as tax incentives, subsidies, and emissions regulations that favor HEV adoption. These measures can significantly accelerate market growth and technological innovation.
Education and awareness campaigns form another critical objective. Many consumers in emerging markets may be unfamiliar with HEV technology and its benefits. Therefore, initiatives aimed at informing potential buyers about the long-term cost savings, environmental impact, and performance advantages of HEVs are essential for market expansion.
Infrastructure development is also a key focus area. While HEVs do not require the extensive charging network needed for fully electric vehicles, the availability of maintenance facilities and trained technicians is crucial. Objectives in this realm include establishing service networks and training programs to support the growing HEV fleet.
Lastly, fostering local innovation and research capabilities is vital for long-term market growth. This involves collaborations between international automakers and local institutions to develop HEV technologies tailored to emerging market needs. Such partnerships can lead to breakthroughs in areas like heat-resistant battery technologies for tropical climates or ruggedized powertrains for challenging road conditions.
As emerging markets begin to embrace HEV technology, the objectives for fostering growth in these regions are multifaceted. Primarily, there is a need to adapt HEV technologies to suit local conditions, including climate, road infrastructure, and driving habits. This localization effort is crucial for ensuring the relevance and appeal of HEVs in diverse global markets.
Another key objective is to address the cost barriers that often hinder HEV adoption in price-sensitive emerging markets. This involves developing more affordable HEV models without compromising on quality or performance. Manufacturers are exploring strategies such as local production and sourcing to reduce costs and make HEVs more accessible to a broader consumer base.
Regulatory support plays a vital role in shaping the HEV market in emerging economies. Objectives in this area include working with governments to establish supportive policies, such as tax incentives, subsidies, and emissions regulations that favor HEV adoption. These measures can significantly accelerate market growth and technological innovation.
Education and awareness campaigns form another critical objective. Many consumers in emerging markets may be unfamiliar with HEV technology and its benefits. Therefore, initiatives aimed at informing potential buyers about the long-term cost savings, environmental impact, and performance advantages of HEVs are essential for market expansion.
Infrastructure development is also a key focus area. While HEVs do not require the extensive charging network needed for fully electric vehicles, the availability of maintenance facilities and trained technicians is crucial. Objectives in this realm include establishing service networks and training programs to support the growing HEV fleet.
Lastly, fostering local innovation and research capabilities is vital for long-term market growth. This involves collaborations between international automakers and local institutions to develop HEV technologies tailored to emerging market needs. Such partnerships can lead to breakthroughs in areas like heat-resistant battery technologies for tropical climates or ruggedized powertrains for challenging road conditions.
HEV Demand Analysis in Emerging Markets
The demand for Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) in emerging markets is experiencing a significant upward trend, driven by a combination of factors including increasing environmental awareness, government incentives, and rising fuel costs. These markets, primarily comprising countries in Asia, Latin America, and parts of Africa, are showing a growing appetite for more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly transportation options.
In China, the largest emerging market for HEVs, demand has been steadily increasing over the past few years. The government's push for new energy vehicles, including HEVs, through subsidies and tax incentives has been a major driver. The country's focus on reducing air pollution in urban areas has also contributed to the growing popularity of HEVs among consumers.
India, another key emerging market, is witnessing a surge in HEV demand. The government's FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles) scheme has been instrumental in promoting HEV adoption. Additionally, the rising middle class and increasing urbanization are fueling the demand for more efficient and cleaner vehicles.
In Southeast Asian countries like Thailand and Indonesia, HEV demand is also on the rise. These markets are particularly attractive due to their large populations and growing economies. Government initiatives to promote cleaner transportation and reduce dependence on fossil fuels are playing a crucial role in driving HEV adoption.
Latin American countries, particularly Brazil and Mexico, are showing promising growth in HEV demand. The increasing awareness of environmental issues and the desire for fuel efficiency in these markets are key factors contributing to this trend. However, the lack of robust government incentives in some countries is slowing the pace of adoption compared to Asian markets.
The demand for HEVs in emerging markets is not without challenges. High initial costs compared to conventional vehicles remain a significant barrier to widespread adoption. Additionally, the lack of charging infrastructure in many emerging markets poses a challenge to the growth of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs).
Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for HEV demand in emerging markets remains positive. As battery technology improves and production costs decrease, HEVs are expected to become more affordable and attractive to a broader range of consumers in these markets. The growing emphasis on sustainable transportation and the gradual shift away from fossil fuels are likely to further boost HEV demand in the coming years.
In China, the largest emerging market for HEVs, demand has been steadily increasing over the past few years. The government's push for new energy vehicles, including HEVs, through subsidies and tax incentives has been a major driver. The country's focus on reducing air pollution in urban areas has also contributed to the growing popularity of HEVs among consumers.
India, another key emerging market, is witnessing a surge in HEV demand. The government's FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles) scheme has been instrumental in promoting HEV adoption. Additionally, the rising middle class and increasing urbanization are fueling the demand for more efficient and cleaner vehicles.
In Southeast Asian countries like Thailand and Indonesia, HEV demand is also on the rise. These markets are particularly attractive due to their large populations and growing economies. Government initiatives to promote cleaner transportation and reduce dependence on fossil fuels are playing a crucial role in driving HEV adoption.
Latin American countries, particularly Brazil and Mexico, are showing promising growth in HEV demand. The increasing awareness of environmental issues and the desire for fuel efficiency in these markets are key factors contributing to this trend. However, the lack of robust government incentives in some countries is slowing the pace of adoption compared to Asian markets.
The demand for HEVs in emerging markets is not without challenges. High initial costs compared to conventional vehicles remain a significant barrier to widespread adoption. Additionally, the lack of charging infrastructure in many emerging markets poses a challenge to the growth of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs).
Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for HEV demand in emerging markets remains positive. As battery technology improves and production costs decrease, HEVs are expected to become more affordable and attractive to a broader range of consumers in these markets. The growing emphasis on sustainable transportation and the gradual shift away from fossil fuels are likely to further boost HEV demand in the coming years.
HEV Technology Status and Barriers
The current status of Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) technology has made significant strides in recent years, yet several barriers still hinder its widespread adoption in emerging markets. HEVs have become increasingly sophisticated, with improvements in battery technology, power management systems, and overall vehicle efficiency. Many automakers now offer a range of HEV models, from compact cars to SUVs, demonstrating the versatility of this technology.
One of the primary technological advancements in HEVs is the development of more efficient and compact battery systems. Lithium-ion batteries have largely replaced older nickel-metal hydride batteries, offering higher energy density and longer lifespan. This has resulted in improved electric-only driving range and overall fuel economy. Additionally, regenerative braking systems have become more advanced, capturing and storing more energy that would otherwise be lost during deceleration.
However, despite these advancements, several barriers persist, particularly in emerging markets. The most significant challenge is the high initial cost of HEVs compared to conventional vehicles. The complex powertrain and advanced battery technology contribute to higher manufacturing costs, which are often passed on to consumers. This price premium can be a substantial deterrent in price-sensitive markets where affordability is a key consideration.
Another barrier is the lack of charging infrastructure in many emerging markets. While HEVs do not rely solely on electric charging, the availability of charging stations can enhance their appeal and functionality. The absence of a robust charging network may limit the perceived value of HEVs and hinder their adoption.
Technical complexity also poses a challenge, particularly in markets with limited experience in advanced automotive technologies. Maintenance and repair of HEVs require specialized knowledge and equipment, which may not be readily available in all regions. This can lead to higher maintenance costs and potential reliability concerns among consumers.
Furthermore, the performance of HEVs in extreme climatic conditions, common in many emerging markets, remains a concern. Battery efficiency and overall vehicle performance can be affected by very high or low temperatures, potentially impacting the perceived reliability and suitability of HEVs in these regions.
Regulatory frameworks in emerging markets often lag behind those in developed countries, creating uncertainty for manufacturers and consumers alike. The absence of clear policies regarding emissions standards, tax incentives, and other supportive measures can slow the adoption of HEV technology.
Lastly, there is a need for greater public awareness and education about HEV technology in emerging markets. Misconceptions about the technology's reliability, performance, and environmental benefits can create hesitation among potential buyers. Overcoming these information gaps is crucial for fostering growth in these markets.
One of the primary technological advancements in HEVs is the development of more efficient and compact battery systems. Lithium-ion batteries have largely replaced older nickel-metal hydride batteries, offering higher energy density and longer lifespan. This has resulted in improved electric-only driving range and overall fuel economy. Additionally, regenerative braking systems have become more advanced, capturing and storing more energy that would otherwise be lost during deceleration.
However, despite these advancements, several barriers persist, particularly in emerging markets. The most significant challenge is the high initial cost of HEVs compared to conventional vehicles. The complex powertrain and advanced battery technology contribute to higher manufacturing costs, which are often passed on to consumers. This price premium can be a substantial deterrent in price-sensitive markets where affordability is a key consideration.
Another barrier is the lack of charging infrastructure in many emerging markets. While HEVs do not rely solely on electric charging, the availability of charging stations can enhance their appeal and functionality. The absence of a robust charging network may limit the perceived value of HEVs and hinder their adoption.
Technical complexity also poses a challenge, particularly in markets with limited experience in advanced automotive technologies. Maintenance and repair of HEVs require specialized knowledge and equipment, which may not be readily available in all regions. This can lead to higher maintenance costs and potential reliability concerns among consumers.
Furthermore, the performance of HEVs in extreme climatic conditions, common in many emerging markets, remains a concern. Battery efficiency and overall vehicle performance can be affected by very high or low temperatures, potentially impacting the perceived reliability and suitability of HEVs in these regions.
Regulatory frameworks in emerging markets often lag behind those in developed countries, creating uncertainty for manufacturers and consumers alike. The absence of clear policies regarding emissions standards, tax incentives, and other supportive measures can slow the adoption of HEV technology.
Lastly, there is a need for greater public awareness and education about HEV technology in emerging markets. Misconceptions about the technology's reliability, performance, and environmental benefits can create hesitation among potential buyers. Overcoming these information gaps is crucial for fostering growth in these markets.
Current HEV Market Strategies
01 Battery thermal management systems
Advanced thermal management systems are crucial for HEV growth, ensuring optimal battery performance and longevity. These systems regulate battery temperature, preventing overheating and maintaining efficiency across various operating conditions. Innovations in this area include improved cooling circuits, heat exchangers, and intelligent temperature control algorithms.- Battery thermal management systems: Advanced thermal management systems are crucial for HEV growth, ensuring optimal battery performance and longevity. These systems regulate battery temperature, preventing overheating and maintaining efficiency across various operating conditions. Innovations in this area include liquid cooling systems, phase change materials, and intelligent thermal control algorithms.
- Powertrain optimization: Improving powertrain efficiency is key to HEV growth. This involves optimizing the integration of electric motors with internal combustion engines, enhancing power distribution, and developing sophisticated control strategies. Advanced powertrain designs focus on reducing energy losses, improving fuel economy, and maximizing overall vehicle performance.
- Charging infrastructure development: The growth of HEVs is closely tied to the expansion of charging infrastructure. This includes the development of fast-charging technologies, wireless charging systems, and the integration of charging stations into existing urban environments. Innovations in this area aim to reduce charging times, increase convenience, and address range anxiety concerns.
- Lightweight materials and design: Advancements in lightweight materials and vehicle design contribute significantly to HEV growth. The use of high-strength, low-weight materials such as advanced composites and alloys helps improve fuel efficiency and extend electric range. Innovative design approaches focus on aerodynamics and weight distribution to enhance overall vehicle performance.
- Energy recovery and regenerative braking: Enhancing energy recovery systems, particularly regenerative braking, is crucial for improving HEV efficiency. Advanced regenerative braking technologies capture and convert kinetic energy into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. Innovations in this area focus on maximizing energy recovery, improving system responsiveness, and integrating with other vehicle systems for optimal performance.
02 Powertrain integration and control
Efficient integration and control of hybrid powertrains are key to HEV growth. This involves optimizing the interaction between electric motors, internal combustion engines, and transmission systems. Advanced control strategies and power management algorithms enhance fuel efficiency, performance, and overall vehicle dynamics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Charging infrastructure and systems
The development of charging infrastructure is essential for HEV market expansion. This includes innovations in charging stations, fast-charging technologies, and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems. Improved charging solutions contribute to increased adoption by addressing range anxiety and enhancing user convenience.Expand Specific Solutions04 Lightweight materials and design
Advancements in lightweight materials and vehicle design contribute significantly to HEV growth. The use of high-strength, low-weight materials in body structures and components improves energy efficiency and overall performance. Innovative design approaches also focus on aerodynamics and space optimization for battery placement.Expand Specific Solutions05 Energy recovery and regenerative braking
Enhanced energy recovery systems, particularly regenerative braking, play a crucial role in HEV efficiency. These systems capture and store kinetic energy during deceleration, converting it into electrical energy for battery recharging. Improvements in this area contribute to extended electric driving range and overall energy efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key HEV Industry Players
The emerging HEV market is in a growth phase, with increasing global demand driven by environmental concerns and government incentives. Market size is expanding rapidly, expected to reach significant volumes in the coming years. Technologically, HEVs are maturing, with established players like Toyota, Honda, and Ford leading innovation. However, newer entrants such as Chery Automobile and Great Wall Motor are gaining ground, particularly in developing markets. Chinese companies and universities, including Jilin University and Chongqing University, are contributing to technological advancements. The competitive landscape is evolving, with traditional automakers facing challenges from tech-focused companies and startups, especially in areas like battery technology and power electronics.
Ford Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Ford's approach to fostering growth in emerging HEV markets involves a multi-faceted strategy. They are focusing on developing affordable hybrid powertrains tailored for emerging markets, with an emphasis on fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. Ford is investing in localized production facilities to reduce costs and adapt to local preferences. They are also implementing innovative financing options and leasing programs to make HEVs more accessible to a broader range of consumers[1]. Additionally, Ford is collaborating with local governments and energy providers to develop charging infrastructure and promote supportive policies for HEV adoption[2]. The company is leveraging its global expertise while customizing its offerings to meet specific market needs, such as developing hybrid versions of popular local models[3].
Strengths: Global brand recognition, extensive R&D capabilities, and experience in diverse markets. Weaknesses: Potential higher initial costs compared to local manufacturers, and the need to adapt to varying regulatory environments in emerging markets.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM's strategy for emerging HEV markets focuses on a combination of technology innovation and market-specific approaches. They are developing a flexible global electric vehicle platform that can be easily adapted to different market requirements[4]. GM is investing in battery technology to improve range and reduce costs, making HEVs more attractive in price-sensitive markets. The company is also forming strategic partnerships with local manufacturers and suppliers to gain market insights and optimize their supply chain[5]. GM is implementing a phased approach, introducing plug-in hybrids as a transitional technology before full electrification in many emerging markets. They are also emphasizing the development of compact HEVs suited for urban environments, which are common in many emerging economies[6].
Strengths: Strong technological capabilities, extensive global presence, and experience in diverse market conditions. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in competing with established local brands and adapting to rapidly changing market preferences in emerging economies.
HEV Innovation Breakthroughs
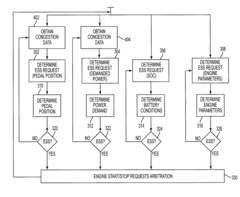
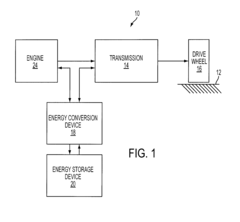
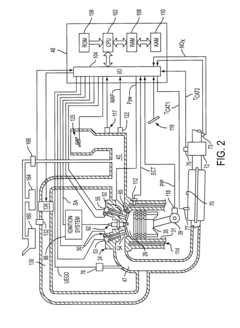
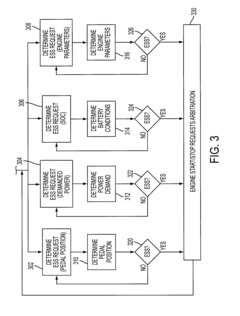
Congestion-based control of vehicle hybrid propulsion system
PatentInactiveUS7806210B2
Innovation
- A method for controlling a hybrid propulsion system that detects congestion using external data and adjusts transitions between propulsion modes to minimize the costs associated with mode changes, such as disabling or modifying engine start/stop requests based on congestion levels.
Method for internally generating electric energy in electric vehicles
PatentInactiveUS20130154363A1
Innovation
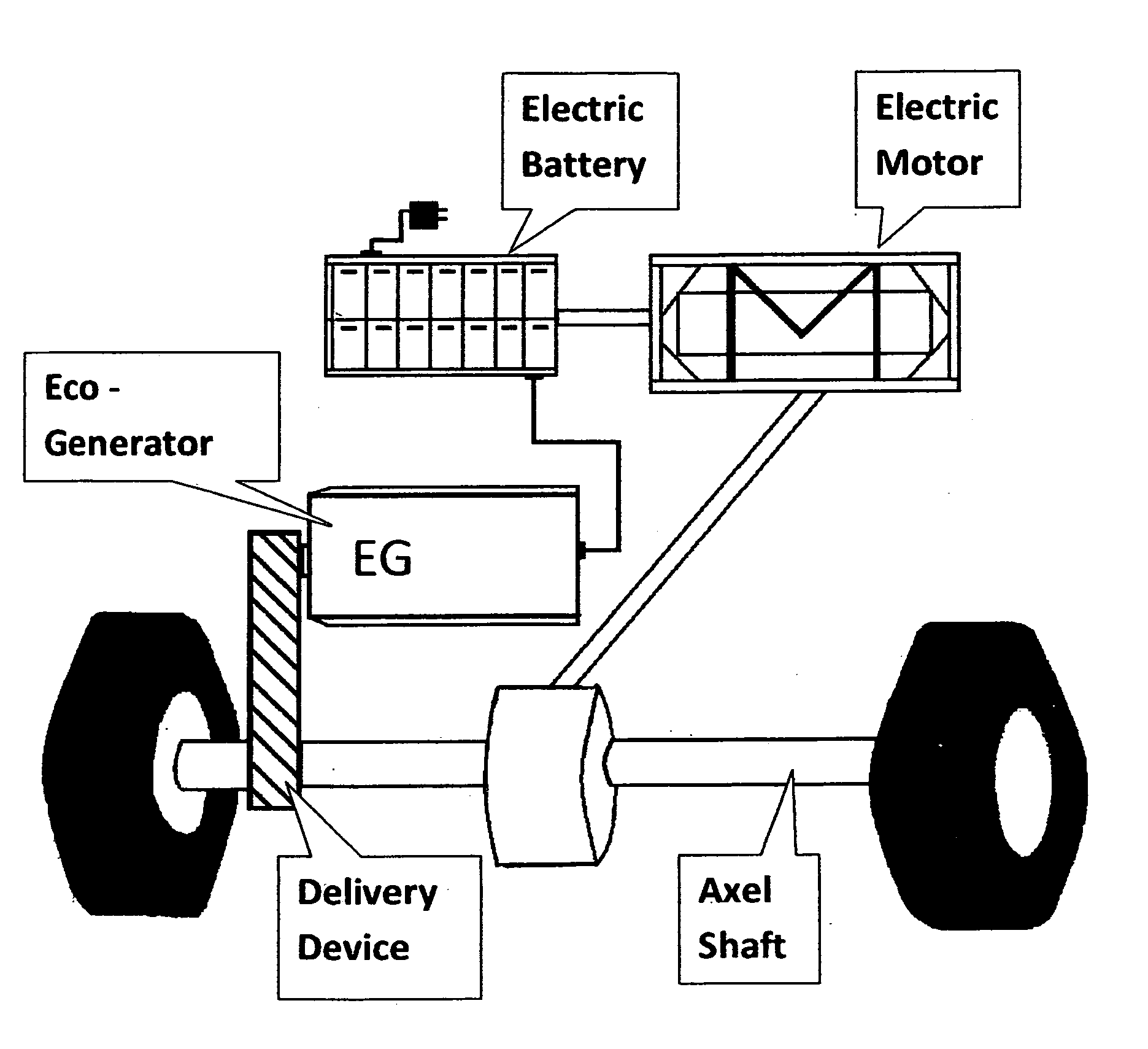
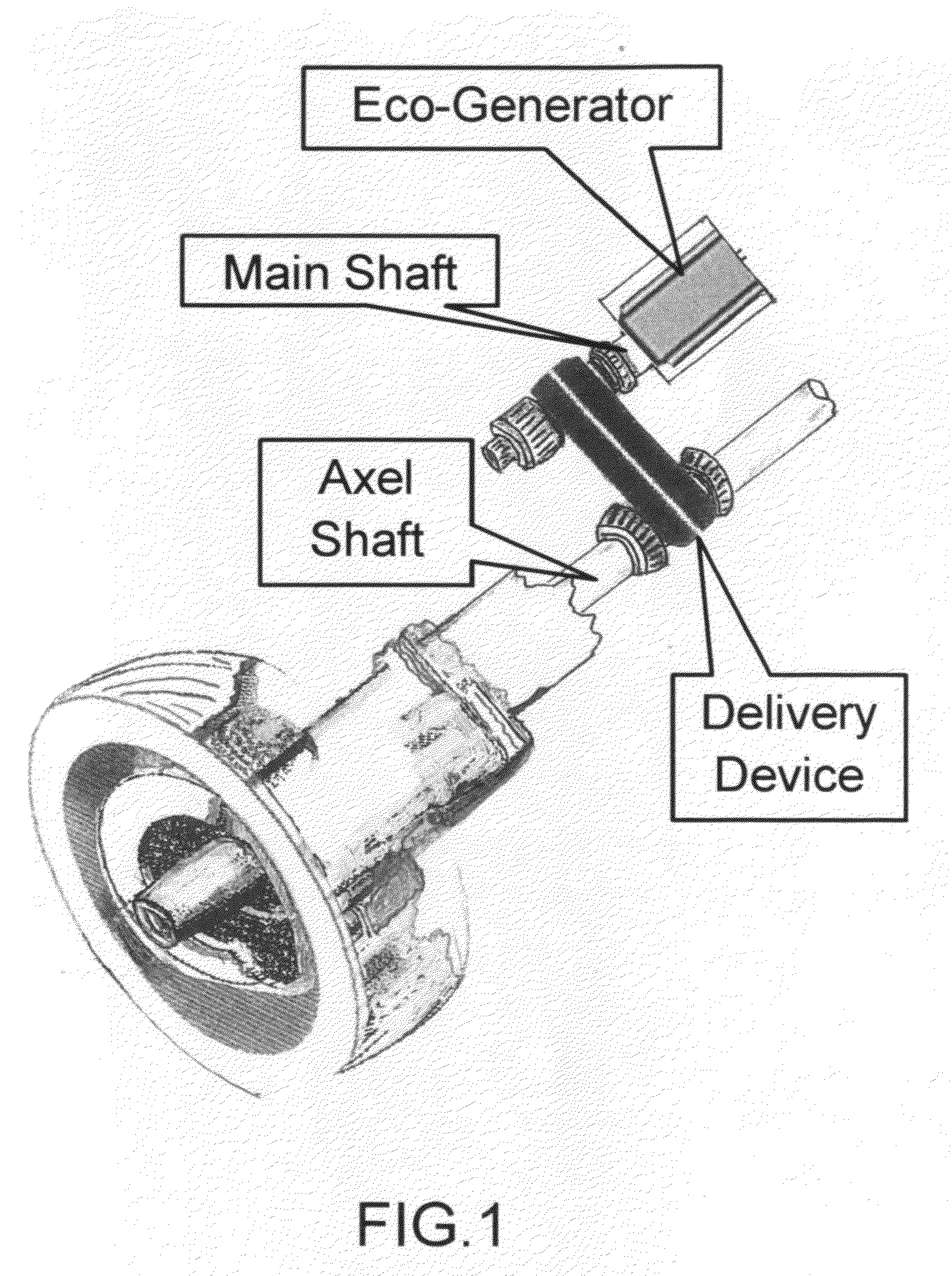
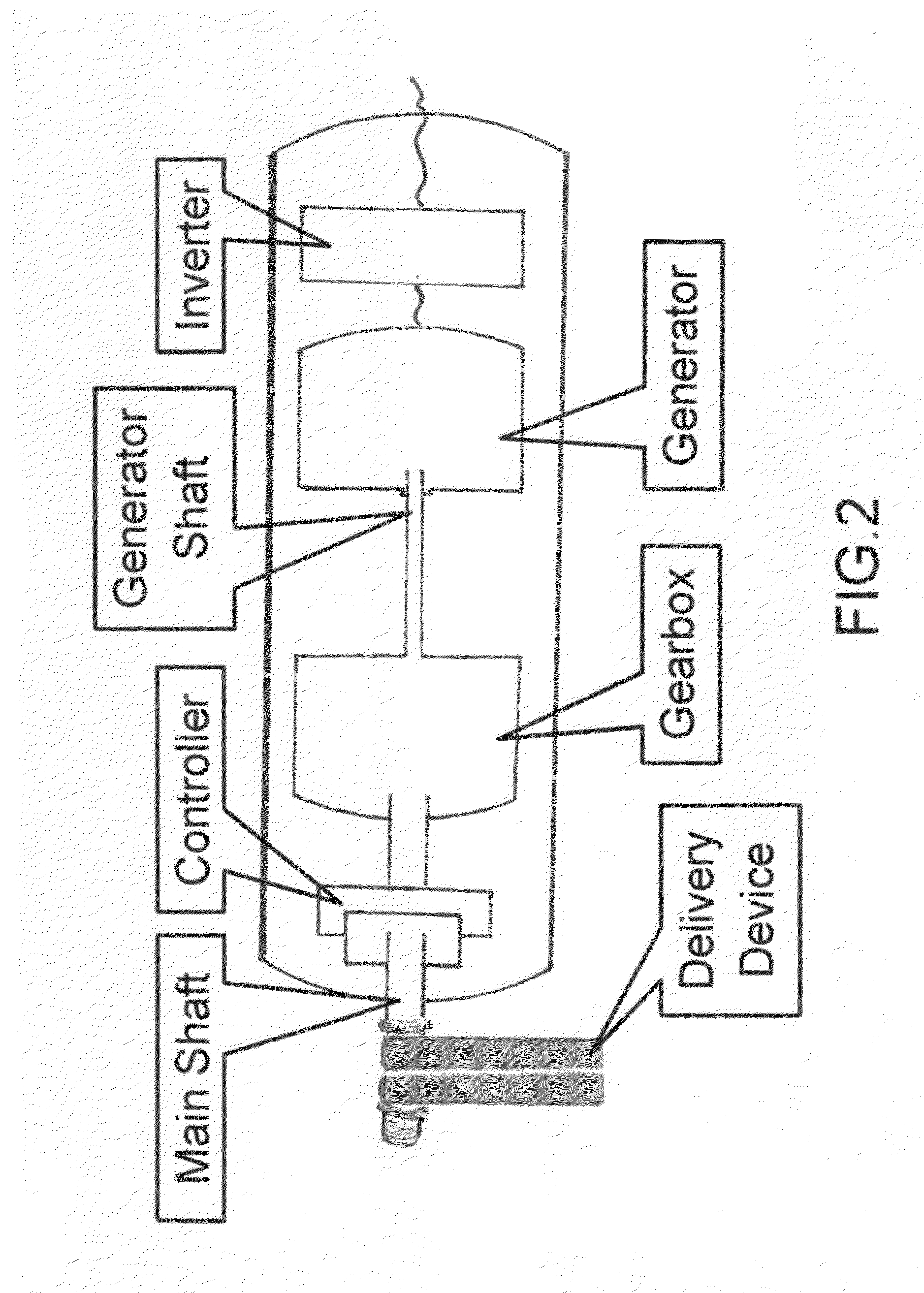
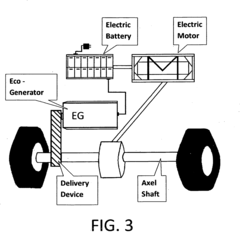
- A system that harnesses mechanical rotational energy from the axel shaft to generate electric energy through a specially designed Eco-Generator, converting kinetic energy into a rechargeable power source while the vehicle is in motion, using a delivery device like a belt or chain to transfer energy to the Eco-Generator, comprising a controller, gearbox, generator, and inverter to manage and convert energy for battery recharging.
HEV Policy and Incentives
Fostering growth in emerging HEV markets requires a comprehensive approach to policy and incentives. Governments play a crucial role in shaping the adoption of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) through targeted measures that address both supply and demand-side factors.
Financial incentives are often at the forefront of HEV promotion strategies. These may include purchase subsidies, tax credits, or rebates for consumers who choose to buy HEVs. Such incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost of these vehicles, making them more competitive with conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Additionally, governments may offer reduced registration fees, lower annual road taxes, or exemptions from congestion charges to further incentivize HEV ownership.
Infrastructure development is another key area where policy can drive HEV adoption. Governments can invest in or provide incentives for the installation of charging stations, both in public spaces and private residences. This addresses the "range anxiety" concern that potential buyers may have, even though HEVs are less dependent on charging infrastructure compared to full electric vehicles.
Regulatory measures also play a significant role in promoting HEVs. Implementing stricter emissions standards and fuel economy regulations can indirectly benefit HEVs by making them more attractive compared to traditional ICE vehicles. Some countries have introduced low-emission zones in urban areas, where HEVs may enjoy preferential access or exemptions from restrictions placed on conventional vehicles.
Public procurement policies can serve as a powerful tool to boost HEV adoption. Governments can lead by example by mandating a certain percentage of HEVs in public fleets, including government vehicles, public transportation, and taxi services. This not only increases HEV visibility but also helps to develop the market and infrastructure.
Education and awareness campaigns are essential components of a comprehensive HEV policy. Governments can fund initiatives to inform the public about the benefits of HEVs, including lower operating costs, reduced environmental impact, and improved energy security. These campaigns can help overcome misconceptions and build consumer confidence in HEV technology.
Collaboration with industry stakeholders is crucial for effective policy implementation. Governments should work closely with automakers, energy providers, and other relevant industries to align policies with technological advancements and market realities. This can include supporting research and development efforts, providing incentives for local HEV manufacturing, and fostering innovation in battery technology and vehicle design.
Financial incentives are often at the forefront of HEV promotion strategies. These may include purchase subsidies, tax credits, or rebates for consumers who choose to buy HEVs. Such incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost of these vehicles, making them more competitive with conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Additionally, governments may offer reduced registration fees, lower annual road taxes, or exemptions from congestion charges to further incentivize HEV ownership.
Infrastructure development is another key area where policy can drive HEV adoption. Governments can invest in or provide incentives for the installation of charging stations, both in public spaces and private residences. This addresses the "range anxiety" concern that potential buyers may have, even though HEVs are less dependent on charging infrastructure compared to full electric vehicles.
Regulatory measures also play a significant role in promoting HEVs. Implementing stricter emissions standards and fuel economy regulations can indirectly benefit HEVs by making them more attractive compared to traditional ICE vehicles. Some countries have introduced low-emission zones in urban areas, where HEVs may enjoy preferential access or exemptions from restrictions placed on conventional vehicles.
Public procurement policies can serve as a powerful tool to boost HEV adoption. Governments can lead by example by mandating a certain percentage of HEVs in public fleets, including government vehicles, public transportation, and taxi services. This not only increases HEV visibility but also helps to develop the market and infrastructure.
Education and awareness campaigns are essential components of a comprehensive HEV policy. Governments can fund initiatives to inform the public about the benefits of HEVs, including lower operating costs, reduced environmental impact, and improved energy security. These campaigns can help overcome misconceptions and build consumer confidence in HEV technology.
Collaboration with industry stakeholders is crucial for effective policy implementation. Governments should work closely with automakers, energy providers, and other relevant industries to align policies with technological advancements and market realities. This can include supporting research and development efforts, providing incentives for local HEV manufacturing, and fostering innovation in battery technology and vehicle design.
HEV Infrastructure Development
The development of robust infrastructure is crucial for fostering growth in emerging Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) markets. A comprehensive approach to HEV infrastructure development encompasses charging stations, maintenance facilities, and supportive policies.
Charging infrastructure forms the backbone of HEV adoption. Strategic placement of charging stations in urban areas, along highways, and at popular destinations is essential. Fast-charging technologies should be prioritized to reduce charging times and enhance user convenience. Implementing smart grid systems can optimize power distribution and manage peak loads effectively.
Maintenance facilities specialized in HEV servicing are vital for long-term market growth. These facilities require trained technicians proficient in both conventional and electric powertrain systems. Establishing partnerships between automakers and local service centers can accelerate the development of such facilities and ensure proper maintenance of HEVs.
Supportive policies play a significant role in infrastructure development. Governments can incentivize private sector investment in charging infrastructure through tax breaks, subsidies, or public-private partnerships. Streamlining permitting processes for charging station installations can expedite infrastructure expansion. Additionally, standardization of charging protocols and payment systems across regions can enhance interoperability and user experience.
Education and awareness programs are essential components of infrastructure development. These initiatives should target potential HEV buyers, highlighting the benefits of hybrid technology and the availability of charging infrastructure. Collaborations with local utilities can help integrate HEVs into existing power grids more efficiently and promote off-peak charging habits.
Research and development efforts should focus on improving charging technologies, battery performance, and grid integration. Innovations in wireless charging and battery swapping systems could revolutionize HEV infrastructure. Exploring vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies can transform HEVs into mobile energy storage units, contributing to grid stability and potentially offering additional value to HEV owners.
Lastly, urban planning and building codes should be updated to accommodate HEV infrastructure. New construction projects should include provisions for charging stations, and existing buildings should be retrofitted where feasible. Creating dedicated HEV parking spaces with charging capabilities in public areas can further encourage adoption.
By addressing these key aspects of infrastructure development, emerging HEV markets can create a supportive ecosystem that fosters growth, increases consumer confidence, and accelerates the transition towards more sustainable transportation solutions.
Charging infrastructure forms the backbone of HEV adoption. Strategic placement of charging stations in urban areas, along highways, and at popular destinations is essential. Fast-charging technologies should be prioritized to reduce charging times and enhance user convenience. Implementing smart grid systems can optimize power distribution and manage peak loads effectively.
Maintenance facilities specialized in HEV servicing are vital for long-term market growth. These facilities require trained technicians proficient in both conventional and electric powertrain systems. Establishing partnerships between automakers and local service centers can accelerate the development of such facilities and ensure proper maintenance of HEVs.
Supportive policies play a significant role in infrastructure development. Governments can incentivize private sector investment in charging infrastructure through tax breaks, subsidies, or public-private partnerships. Streamlining permitting processes for charging station installations can expedite infrastructure expansion. Additionally, standardization of charging protocols and payment systems across regions can enhance interoperability and user experience.
Education and awareness programs are essential components of infrastructure development. These initiatives should target potential HEV buyers, highlighting the benefits of hybrid technology and the availability of charging infrastructure. Collaborations with local utilities can help integrate HEVs into existing power grids more efficiently and promote off-peak charging habits.
Research and development efforts should focus on improving charging technologies, battery performance, and grid integration. Innovations in wireless charging and battery swapping systems could revolutionize HEV infrastructure. Exploring vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies can transform HEVs into mobile energy storage units, contributing to grid stability and potentially offering additional value to HEV owners.
Lastly, urban planning and building codes should be updated to accommodate HEV infrastructure. New construction projects should include provisions for charging stations, and existing buildings should be retrofitted where feasible. Creating dedicated HEV parking spaces with charging capabilities in public areas can further encourage adoption.
By addressing these key aspects of infrastructure development, emerging HEV markets can create a supportive ecosystem that fosters growth, increases consumer confidence, and accelerates the transition towards more sustainable transportation solutions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!