How to Implement Comprehensive Hydrochloric Acid Training Programs?
JUL 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HCl Training Background and Objectives
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is a widely used chemical compound in various industries, including manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment. As its handling requires specific safety measures and technical knowledge, comprehensive training programs are essential for ensuring workplace safety and operational efficiency.
The evolution of HCl training has been closely tied to advancements in industrial safety standards and chemical handling practices. Initially, training focused primarily on basic safety precautions and emergency procedures. However, as industries became more complex and regulations more stringent, the scope of HCl training expanded to encompass a broader range of topics and skills.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on developing holistic training programs that address not only safety concerns but also environmental impact, quality control, and process optimization. This shift reflects the increasing recognition of the interconnected nature of chemical handling processes and their wider implications for organizational performance and sustainability.
The primary objective of implementing comprehensive HCl training programs is to create a workforce that is not only proficient in handling the acid safely but also understands its properties, applications, and potential risks in various industrial contexts. This includes developing a deep understanding of HCl's chemical behavior, its interactions with other substances, and the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) required for different handling scenarios.
Another key goal is to foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement within organizations that work with HCl. This involves regular updates to training materials, incorporation of lessons learned from incidents or near-misses, and adaptation to new technologies and best practices in the field. By doing so, companies can ensure that their workforce remains at the forefront of HCl handling expertise.
Furthermore, comprehensive training programs aim to address the diverse learning needs of different employee groups, from new hires to experienced technicians and supervisors. This may involve developing tiered training modules that cater to various skill levels and job responsibilities, ensuring that each employee receives targeted instruction relevant to their role in HCl-related processes.
Ultimately, the implementation of comprehensive HCl training programs is driven by the need to balance operational efficiency with stringent safety and environmental standards. By equipping employees with in-depth knowledge and practical skills, organizations can minimize the risks associated with HCl handling while maximizing its benefits in industrial applications.
The evolution of HCl training has been closely tied to advancements in industrial safety standards and chemical handling practices. Initially, training focused primarily on basic safety precautions and emergency procedures. However, as industries became more complex and regulations more stringent, the scope of HCl training expanded to encompass a broader range of topics and skills.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on developing holistic training programs that address not only safety concerns but also environmental impact, quality control, and process optimization. This shift reflects the increasing recognition of the interconnected nature of chemical handling processes and their wider implications for organizational performance and sustainability.
The primary objective of implementing comprehensive HCl training programs is to create a workforce that is not only proficient in handling the acid safely but also understands its properties, applications, and potential risks in various industrial contexts. This includes developing a deep understanding of HCl's chemical behavior, its interactions with other substances, and the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) required for different handling scenarios.
Another key goal is to foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement within organizations that work with HCl. This involves regular updates to training materials, incorporation of lessons learned from incidents or near-misses, and adaptation to new technologies and best practices in the field. By doing so, companies can ensure that their workforce remains at the forefront of HCl handling expertise.
Furthermore, comprehensive training programs aim to address the diverse learning needs of different employee groups, from new hires to experienced technicians and supervisors. This may involve developing tiered training modules that cater to various skill levels and job responsibilities, ensuring that each employee receives targeted instruction relevant to their role in HCl-related processes.
Ultimately, the implementation of comprehensive HCl training programs is driven by the need to balance operational efficiency with stringent safety and environmental standards. By equipping employees with in-depth knowledge and practical skills, organizations can minimize the risks associated with HCl handling while maximizing its benefits in industrial applications.
Industry Demand Analysis
The demand for comprehensive hydrochloric acid training programs has been steadily increasing across various industries. This surge is primarily driven by the widespread use of hydrochloric acid in manufacturing processes, chemical production, and industrial cleaning applications. As safety regulations become more stringent and companies focus on minimizing workplace hazards, the need for well-trained personnel in handling this corrosive substance has become paramount.
In the chemical manufacturing sector, the demand for skilled workers proficient in hydrochloric acid handling is particularly high. This industry relies heavily on hydrochloric acid for producing a wide range of products, including plastics, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment chemicals. The complexity of these processes and the potential risks associated with mishandling hydrochloric acid have led to a growing emphasis on comprehensive training programs.
The construction industry has also seen an uptick in demand for hydrochloric acid training. With the increasing use of acid etching techniques in concrete preparation and surface treatment, workers need to be well-versed in the safe handling and application of hydrochloric acid. This trend is expected to continue as sustainable building practices gain traction, requiring more specialized surface preparation methods.
Environmental services and waste management companies are another significant driver of demand for hydrochloric acid training. These organizations frequently deal with acid neutralization and disposal, necessitating a workforce that is knowledgeable about the properties and safe handling procedures of hydrochloric acid. The growing focus on environmental protection and proper hazardous waste management has further amplified this need.
The healthcare sector, particularly in laboratory settings, has also contributed to the increased demand for hydrochloric acid training. Medical and research laboratories routinely use hydrochloric acid in various analytical procedures and experiments. Ensuring that laboratory personnel are adequately trained in handling this substance is crucial for maintaining safety standards and the integrity of research outcomes.
Market analysis indicates that small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are increasingly recognizing the importance of comprehensive hydrochloric acid training. These businesses, which may not have had formal training programs in the past, are now seeking to implement structured training to comply with regulations and improve workplace safety. This trend represents a significant growth opportunity for training providers specializing in hazardous material handling.
The global nature of supply chains and the internationalization of safety standards have further fueled the demand for standardized hydrochloric acid training programs. Multinational corporations are looking for consistent training solutions that can be implemented across their global operations, ensuring a uniform level of competence and safety practices among their workforce.
In the chemical manufacturing sector, the demand for skilled workers proficient in hydrochloric acid handling is particularly high. This industry relies heavily on hydrochloric acid for producing a wide range of products, including plastics, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment chemicals. The complexity of these processes and the potential risks associated with mishandling hydrochloric acid have led to a growing emphasis on comprehensive training programs.
The construction industry has also seen an uptick in demand for hydrochloric acid training. With the increasing use of acid etching techniques in concrete preparation and surface treatment, workers need to be well-versed in the safe handling and application of hydrochloric acid. This trend is expected to continue as sustainable building practices gain traction, requiring more specialized surface preparation methods.
Environmental services and waste management companies are another significant driver of demand for hydrochloric acid training. These organizations frequently deal with acid neutralization and disposal, necessitating a workforce that is knowledgeable about the properties and safe handling procedures of hydrochloric acid. The growing focus on environmental protection and proper hazardous waste management has further amplified this need.
The healthcare sector, particularly in laboratory settings, has also contributed to the increased demand for hydrochloric acid training. Medical and research laboratories routinely use hydrochloric acid in various analytical procedures and experiments. Ensuring that laboratory personnel are adequately trained in handling this substance is crucial for maintaining safety standards and the integrity of research outcomes.
Market analysis indicates that small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are increasingly recognizing the importance of comprehensive hydrochloric acid training. These businesses, which may not have had formal training programs in the past, are now seeking to implement structured training to comply with regulations and improve workplace safety. This trend represents a significant growth opportunity for training providers specializing in hazardous material handling.
The global nature of supply chains and the internationalization of safety standards have further fueled the demand for standardized hydrochloric acid training programs. Multinational corporations are looking for consistent training solutions that can be implemented across their global operations, ensuring a uniform level of competence and safety practices among their workforce.
Current Training Challenges
The implementation of comprehensive hydrochloric acid training programs faces several significant challenges in the current industrial landscape. One of the primary obstacles is the diverse nature of workforce backgrounds and experience levels. Employees in chemical industries often come from varied educational and professional backgrounds, making it difficult to design a one-size-fits-all training program that effectively addresses the needs of all participants.
Safety concerns pose another critical challenge in hydrochloric acid training. The corrosive and hazardous nature of the substance requires stringent safety protocols, which must be thoroughly ingrained in all trainees. However, ensuring consistent adherence to these protocols across different operational contexts and maintaining a high level of safety awareness over time can be challenging.
The rapidly evolving regulatory environment adds another layer of complexity to training programs. Keeping up with changing safety standards, environmental regulations, and industry best practices requires constant updates to training materials and methodologies. This necessitates a flexible and adaptable training framework that can quickly incorporate new information and requirements.
Technical complexity is a significant hurdle in comprehensive hydrochloric acid training. The chemical properties, handling procedures, and potential reactions of hydrochloric acid in various industrial processes can be intricate and nuanced. Conveying this technical information in a manner that is both accurate and accessible to trainees with different levels of scientific background is a considerable challenge.
Resource constraints, both in terms of time and budget, often limit the scope and effectiveness of training programs. Balancing the need for thorough, hands-on training with the operational demands of maintaining productivity can be difficult for many organizations. This challenge is particularly acute in smaller companies or those with limited dedicated training resources.
The retention and practical application of training content present ongoing challenges. Ensuring that employees not only understand but can effectively apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios is crucial. This requires innovative training methods that go beyond traditional classroom-style learning to include practical, scenario-based exercises and ongoing reinforcement strategies.
Lastly, the global nature of many chemical industries introduces challenges related to language barriers and cultural differences. Developing training programs that are effective across diverse cultural contexts and can be accurately translated into multiple languages without losing critical safety and technical information is a complex undertaking.
Safety concerns pose another critical challenge in hydrochloric acid training. The corrosive and hazardous nature of the substance requires stringent safety protocols, which must be thoroughly ingrained in all trainees. However, ensuring consistent adherence to these protocols across different operational contexts and maintaining a high level of safety awareness over time can be challenging.
The rapidly evolving regulatory environment adds another layer of complexity to training programs. Keeping up with changing safety standards, environmental regulations, and industry best practices requires constant updates to training materials and methodologies. This necessitates a flexible and adaptable training framework that can quickly incorporate new information and requirements.
Technical complexity is a significant hurdle in comprehensive hydrochloric acid training. The chemical properties, handling procedures, and potential reactions of hydrochloric acid in various industrial processes can be intricate and nuanced. Conveying this technical information in a manner that is both accurate and accessible to trainees with different levels of scientific background is a considerable challenge.
Resource constraints, both in terms of time and budget, often limit the scope and effectiveness of training programs. Balancing the need for thorough, hands-on training with the operational demands of maintaining productivity can be difficult for many organizations. This challenge is particularly acute in smaller companies or those with limited dedicated training resources.
The retention and practical application of training content present ongoing challenges. Ensuring that employees not only understand but can effectively apply their knowledge in real-world scenarios is crucial. This requires innovative training methods that go beyond traditional classroom-style learning to include practical, scenario-based exercises and ongoing reinforcement strategies.
Lastly, the global nature of many chemical industries introduces challenges related to language barriers and cultural differences. Developing training programs that are effective across diverse cultural contexts and can be accurately translated into multiple languages without losing critical safety and technical information is a complex undertaking.
Existing Training Methodologies
01 Safety training programs for handling hydrochloric acid
Comprehensive safety training programs are essential for personnel working with hydrochloric acid. These programs cover proper handling techniques, personal protective equipment usage, emergency response procedures, and risk assessment. They aim to minimize accidents and ensure worker safety in environments where hydrochloric acid is present.- Safety training programs for handling hydrochloric acid: Comprehensive safety training programs are essential for personnel working with hydrochloric acid. These programs cover proper handling techniques, personal protective equipment usage, emergency procedures, and risk assessment. They aim to minimize accidents and ensure compliance with safety regulations in industrial and laboratory settings.
- Equipment and facilities for hydrochloric acid training: Specialized equipment and facilities are designed for conducting hydrochloric acid training programs. These may include simulation units, containment systems, and dedicated training areas that allow for hands-on experience in a controlled environment. Such facilities enable trainees to practice safe handling and emergency response procedures without exposure to actual hazards.
- Virtual reality and computer-based training for hydrochloric acid handling: Advanced training methods utilizing virtual reality and computer-based simulations are developed for hydrochloric acid handling. These technologies provide immersive and interactive learning experiences, allowing trainees to practice scenarios and procedures in a safe, virtual environment before working with the actual chemical.
- Certification and assessment programs for hydrochloric acid handlers: Structured certification and assessment programs are implemented to evaluate and validate the competency of individuals handling hydrochloric acid. These programs include theoretical examinations and practical assessments to ensure that personnel possess the necessary knowledge and skills for safe chemical handling.
- Specialized training for hydrochloric acid production and processing: Tailored training programs are developed for personnel involved in the production and processing of hydrochloric acid. These programs focus on specific industrial processes, quality control measures, and advanced handling techniques relevant to large-scale manufacturing and chemical processing operations.
02 Equipment and facilities for hydrochloric acid training
Specialized equipment and facilities are designed for conducting hydrochloric acid training programs. These may include simulation units, safety showers, eye wash stations, and ventilation systems. Such facilities provide a controlled environment for hands-on training and practical demonstrations of acid handling procedures.Expand Specific Solutions03 Virtual reality and simulation-based training for hydrochloric acid handling
Advanced training methods utilizing virtual reality and simulation technologies are employed to create realistic scenarios for hydrochloric acid handling. These immersive training experiences allow trainees to practice emergency responses and handling procedures in a safe, controlled virtual environment before working with actual acid.Expand Specific Solutions04 Waste management and environmental safety training for hydrochloric acid
Training programs focusing on proper disposal and environmental safety aspects of hydrochloric acid use. These programs cover topics such as neutralization techniques, spill containment, and compliance with environmental regulations to minimize ecological impact and ensure responsible acid management.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial process-specific hydrochloric acid training
Tailored training programs designed for specific industrial processes involving hydrochloric acid. These programs address the unique challenges and safety considerations in various applications such as metal treatment, chemical manufacturing, and water treatment. They focus on process optimization, quality control, and industry-specific safety protocols.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Training Providers
The implementation of comprehensive hydrochloric acid training programs is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market demand driven by safety regulations and industry standards. The global market for such training is expanding, particularly in chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and industrial sectors. Technological advancements in training methodologies, including virtual reality simulations and interactive e-learning platforms, are enhancing program effectiveness. Companies like Covestro Deutschland AG, Arkema France SA, and Schlumberger Canada Ltd. are at the forefront of developing and implementing these training programs, leveraging their industry expertise and global presence. The technology's maturity is moderate, with ongoing innovations in delivery methods and content customization to meet specific industry needs.
Saudi Arabian Oil Co.
Technical Solution: Saudi Arabian Oil Co. (Saudi Aramco) has implemented a comprehensive hydrochloric acid training program that focuses on safety, handling, and application in oil and gas operations. The program includes theoretical and practical modules, covering topics such as acid properties, personal protective equipment (PPE), emergency response, and proper disposal techniques. Saudi Aramco utilizes advanced simulation technology to create realistic scenarios for trainees, allowing them to practice handling acid-related emergencies in a controlled environment[1]. The company also incorporates virtual reality (VR) training modules to enhance learning experiences and improve retention of critical safety procedures[2].
Strengths: Extensive resources for training, cutting-edge simulation technology, and global industry expertise. Weaknesses: Potential over-reliance on technology-based training, which may not fully replicate real-world scenarios.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed a multi-tiered hydrochloric acid training program that addresses various aspects of acid handling and application in petrochemical processes. The program includes online learning modules, on-site practical training, and regular safety drills. Sinopec's approach emphasizes the importance of understanding the chemical properties of hydrochloric acid and its reactions with different materials commonly found in industrial settings. The company has also implemented a mentorship system where experienced personnel guide new employees through real-world applications of acid handling procedures[3]. Sinopec's training program incorporates case studies from past incidents to highlight the importance of proper acid management and to prevent future accidents[4].
Strengths: Comprehensive approach combining theory and practice, strong emphasis on safety, and utilization of real-world case studies. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in standardizing training across diverse operational sites and language barriers in international operations.
Innovative Training Techniques
Using Synthetic Acid Compositions as Alternatives to Conventional Acids in The Oil And Gas Industry
PatentActiveUS20230086463A1
Innovation
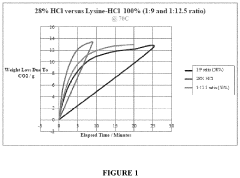
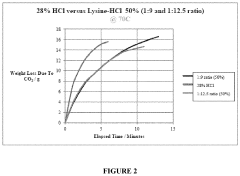
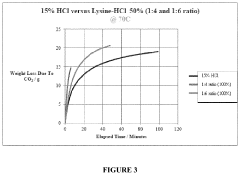
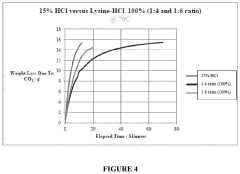
- An aqueous synthetic acid composition comprising lysine and hydrogen chloride in specific molar ratios, which provides low corrosion rates, biodegradability, controlled reaction rates, and thermal stability up to 220°C, reducing toxicity and environmental impact while maintaining the effectiveness of hydrochloric acid.
Methods for treating subterranean formations
PatentWO2016018615A1
Innovation
- The use of treatment fluids comprising multivalent-cation reacting polymers, fatty acids with ethanolamine, insoluble calcium salts, urea derivatives, and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) to form protective films on carbonate surfaces, allowing controlled acid penetration and reaction, thereby optimizing acid distribution and reducing corrosion.
Regulatory Compliance
Implementing comprehensive hydrochloric acid training programs requires strict adherence to regulatory compliance standards. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States mandates specific guidelines for handling hazardous chemicals, including hydrochloric acid. These regulations are outlined in the OSHA Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200) and the Laboratory Standard (29 CFR 1910.1450).
Training programs must cover the requirements set forth by these standards, including proper labeling, safety data sheets (SDS), and employee training on hazard identification and protective measures. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also regulates the storage, handling, and disposal of hydrochloric acid under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA).
Compliance with international standards is crucial for global operations. The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to chemical hazard communication worldwide. Training programs should incorporate GHS principles to ensure consistency in hazard classification and labeling across different countries.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use of chemicals, including hydrochloric acid. Training programs for EU-based operations must address REACH requirements, such as registration of substances and communication of safety information throughout the supply chain.
To ensure regulatory compliance, training programs should include regular updates on changing regulations and industry best practices. This may involve establishing a system for monitoring regulatory changes and incorporating them into training materials promptly. Periodic audits of training programs can help identify gaps in compliance and areas for improvement.
Documentation plays a critical role in demonstrating regulatory compliance. Training programs should include robust record-keeping systems to track employee participation, comprehension assessments, and refresher training schedules. These records may be subject to inspection by regulatory agencies and should be maintained in accordance with applicable retention requirements.
Collaboration with legal and regulatory affairs departments is essential to ensure that training programs accurately reflect current compliance obligations. This interdepartmental approach can help identify potential regulatory risks and develop strategies to mitigate them through comprehensive training initiatives.
Training programs must cover the requirements set forth by these standards, including proper labeling, safety data sheets (SDS), and employee training on hazard identification and protective measures. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also regulates the storage, handling, and disposal of hydrochloric acid under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA).
Compliance with international standards is crucial for global operations. The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to chemical hazard communication worldwide. Training programs should incorporate GHS principles to ensure consistency in hazard classification and labeling across different countries.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use of chemicals, including hydrochloric acid. Training programs for EU-based operations must address REACH requirements, such as registration of substances and communication of safety information throughout the supply chain.
To ensure regulatory compliance, training programs should include regular updates on changing regulations and industry best practices. This may involve establishing a system for monitoring regulatory changes and incorporating them into training materials promptly. Periodic audits of training programs can help identify gaps in compliance and areas for improvement.
Documentation plays a critical role in demonstrating regulatory compliance. Training programs should include robust record-keeping systems to track employee participation, comprehension assessments, and refresher training schedules. These records may be subject to inspection by regulatory agencies and should be maintained in accordance with applicable retention requirements.
Collaboration with legal and regulatory affairs departments is essential to ensure that training programs accurately reflect current compliance obligations. This interdepartmental approach can help identify potential regulatory risks and develop strategies to mitigate them through comprehensive training initiatives.
Risk Assessment Strategies
Implementing comprehensive hydrochloric acid training programs requires a robust risk assessment strategy to ensure the safety of personnel and the environment. A thorough risk assessment begins with identifying potential hazards associated with hydrochloric acid handling, storage, and use. These hazards include chemical burns, respiratory irritation, and equipment corrosion. The assessment should consider various scenarios, such as spills, leaks, and accidental exposure during routine operations and maintenance activities.
Once hazards are identified, the next step is to evaluate the likelihood and severity of potential incidents. This evaluation involves analyzing historical data, industry standards, and expert opinions to determine the probability of occurrence and the potential consequences of each hazard. Risk matrices can be utilized to visualize and prioritize risks based on their likelihood and impact.
A critical component of the risk assessment strategy is the identification of existing control measures and their effectiveness. This includes evaluating personal protective equipment (PPE), engineering controls such as ventilation systems, and administrative controls like standard operating procedures and emergency response plans. Any gaps in the current control measures should be noted and addressed in the training program.
The risk assessment should also consider the specific work environment and processes where hydrochloric acid is used. This may involve conducting on-site inspections, reviewing process flow diagrams, and consulting with operators and supervisors to gain a comprehensive understanding of potential exposure points and unique risks associated with the facility's operations.
Another crucial aspect of the risk assessment strategy is the evaluation of emergency preparedness. This includes assessing the adequacy of emergency response equipment, such as eyewash stations and safety showers, as well as the effectiveness of evacuation procedures and communication systems. The assessment should also consider the readiness of personnel to respond to acid-related emergencies and identify any gaps in their knowledge or skills.
The risk assessment strategy should incorporate a review of regulatory requirements and industry best practices related to hydrochloric acid handling and training. This ensures that the training program not only addresses site-specific risks but also complies with relevant standards and regulations.
Finally, the risk assessment strategy should include a mechanism for continuous improvement. This involves regularly reviewing and updating the risk assessment based on new information, changes in processes or equipment, and lessons learned from incidents or near-misses. By implementing a dynamic risk assessment process, organizations can ensure that their hydrochloric acid training programs remain comprehensive and effective in mitigating risks over time.
Once hazards are identified, the next step is to evaluate the likelihood and severity of potential incidents. This evaluation involves analyzing historical data, industry standards, and expert opinions to determine the probability of occurrence and the potential consequences of each hazard. Risk matrices can be utilized to visualize and prioritize risks based on their likelihood and impact.
A critical component of the risk assessment strategy is the identification of existing control measures and their effectiveness. This includes evaluating personal protective equipment (PPE), engineering controls such as ventilation systems, and administrative controls like standard operating procedures and emergency response plans. Any gaps in the current control measures should be noted and addressed in the training program.
The risk assessment should also consider the specific work environment and processes where hydrochloric acid is used. This may involve conducting on-site inspections, reviewing process flow diagrams, and consulting with operators and supervisors to gain a comprehensive understanding of potential exposure points and unique risks associated with the facility's operations.
Another crucial aspect of the risk assessment strategy is the evaluation of emergency preparedness. This includes assessing the adequacy of emergency response equipment, such as eyewash stations and safety showers, as well as the effectiveness of evacuation procedures and communication systems. The assessment should also consider the readiness of personnel to respond to acid-related emergencies and identify any gaps in their knowledge or skills.
The risk assessment strategy should incorporate a review of regulatory requirements and industry best practices related to hydrochloric acid handling and training. This ensures that the training program not only addresses site-specific risks but also complies with relevant standards and regulations.
Finally, the risk assessment strategy should include a mechanism for continuous improvement. This involves regularly reviewing and updating the risk assessment based on new information, changes in processes or equipment, and lessons learned from incidents or near-misses. By implementing a dynamic risk assessment process, organizations can ensure that their hydrochloric acid training programs remain comprehensive and effective in mitigating risks over time.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!