Innovations in Hydrochloric Acid Distribution Channels
JUL 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HCl Distribution Evolution
The distribution of hydrochloric acid (HCl) has undergone significant evolution over the past decades, driven by technological advancements, safety concerns, and environmental regulations. Initially, HCl was primarily transported in glass containers, which were fragile and posed significant safety risks. This method was gradually phased out in favor of more robust and secure options.
In the mid-20th century, the introduction of rubber-lined steel tanks marked a major milestone in HCl distribution. These tanks offered improved durability and chemical resistance, allowing for safer transportation of larger volumes. This innovation facilitated the growth of industrial applications for HCl, as it became more feasible to transport the acid over longer distances.
The 1970s and 1980s saw the emergence of specialized tanker trucks and rail cars designed specifically for HCl transport. These vehicles featured advanced corrosion-resistant materials and safety systems, further enhancing the efficiency and safety of distribution. Concurrently, the development of pipeline systems for HCl transport in industrial complexes revolutionized on-site distribution, enabling continuous supply for large-scale manufacturing processes.
The late 20th century brought about a shift towards more environmentally conscious distribution methods. The introduction of intermediate bulk containers (IBCs) provided a versatile and reusable option for HCl transport, reducing waste and improving handling efficiency. These containers, typically made of high-density polyethylene or other chemically resistant materials, offered a balance between capacity and maneuverability.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards smart distribution systems. The integration of IoT sensors and real-time monitoring technologies has enhanced the safety and efficiency of HCl transport. These systems provide continuous data on temperature, pressure, and container integrity, allowing for proactive maintenance and rapid response to potential issues.
The advent of digital supply chain management has further transformed HCl distribution. Advanced logistics platforms now optimize routing, track shipments in real-time, and manage inventory levels across the supply chain. This has led to more efficient resource allocation and reduced environmental impact through optimized transportation routes.
Looking ahead, the HCl distribution landscape is poised for further innovation. Emerging technologies such as autonomous vehicles and blockchain-based tracking systems hold the potential to revolutionize the industry once again. These advancements promise to enhance safety, increase efficiency, and provide unprecedented levels of transparency in the HCl supply chain.
In the mid-20th century, the introduction of rubber-lined steel tanks marked a major milestone in HCl distribution. These tanks offered improved durability and chemical resistance, allowing for safer transportation of larger volumes. This innovation facilitated the growth of industrial applications for HCl, as it became more feasible to transport the acid over longer distances.
The 1970s and 1980s saw the emergence of specialized tanker trucks and rail cars designed specifically for HCl transport. These vehicles featured advanced corrosion-resistant materials and safety systems, further enhancing the efficiency and safety of distribution. Concurrently, the development of pipeline systems for HCl transport in industrial complexes revolutionized on-site distribution, enabling continuous supply for large-scale manufacturing processes.
The late 20th century brought about a shift towards more environmentally conscious distribution methods. The introduction of intermediate bulk containers (IBCs) provided a versatile and reusable option for HCl transport, reducing waste and improving handling efficiency. These containers, typically made of high-density polyethylene or other chemically resistant materials, offered a balance between capacity and maneuverability.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards smart distribution systems. The integration of IoT sensors and real-time monitoring technologies has enhanced the safety and efficiency of HCl transport. These systems provide continuous data on temperature, pressure, and container integrity, allowing for proactive maintenance and rapid response to potential issues.
The advent of digital supply chain management has further transformed HCl distribution. Advanced logistics platforms now optimize routing, track shipments in real-time, and manage inventory levels across the supply chain. This has led to more efficient resource allocation and reduced environmental impact through optimized transportation routes.
Looking ahead, the HCl distribution landscape is poised for further innovation. Emerging technologies such as autonomous vehicles and blockchain-based tracking systems hold the potential to revolutionize the industry once again. These advancements promise to enhance safety, increase efficiency, and provide unprecedented levels of transparency in the HCl supply chain.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for innovations in hydrochloric acid distribution channels has been steadily growing, driven by the increasing use of hydrochloric acid across various industries. The global hydrochloric acid market is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate projected to be robust. This growth is primarily fueled by the rising demand from end-use industries such as steel pickling, oil well acidizing, ore processing, and chemical manufacturing.
In the steel industry, hydrochloric acid plays a crucial role in the pickling process, removing rust and scale from steel surfaces. As the global steel production continues to rise, particularly in emerging economies, the demand for efficient and cost-effective hydrochloric acid distribution channels is increasing. The oil and gas sector also presents a substantial market opportunity, with hydrochloric acid being extensively used in well acidizing operations to enhance oil recovery.
The chemical manufacturing industry, another major consumer of hydrochloric acid, is witnessing a surge in demand for the compound in the production of various chemicals and pharmaceuticals. This trend is further amplified by the growing emphasis on sustainable and environmentally friendly production processes, which often require specialized handling and distribution of hydrochloric acid.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific region leads the market demand for hydrochloric acid, followed by North America and Europe. The rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India are driving the demand for hydrochloric acid in various applications, consequently creating a need for innovative distribution channels to meet the growing market requirements.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards on-site generation of hydrochloric acid, particularly in water treatment applications. This trend is creating new opportunities for innovations in distribution channels, focusing on compact, efficient, and safe on-site generation systems.
Safety and environmental concerns associated with the transportation and handling of hydrochloric acid are pushing the industry towards developing more secure and eco-friendly distribution methods. This has led to an increased focus on developing corrosion-resistant materials for storage and transportation, as well as advanced monitoring and control systems for distribution networks.
The digital transformation of supply chains is also impacting the hydrochloric acid distribution landscape. There is a growing demand for smart distribution systems that can provide real-time tracking, predictive maintenance, and optimized routing to ensure timely and safe delivery of hydrochloric acid to end-users.
In conclusion, the market demand for innovations in hydrochloric acid distribution channels is robust and multifaceted, driven by industrial growth, safety requirements, and technological advancements. The industry is poised for significant developments in distribution technologies to meet the evolving needs of various sectors while addressing environmental and safety concerns.
In the steel industry, hydrochloric acid plays a crucial role in the pickling process, removing rust and scale from steel surfaces. As the global steel production continues to rise, particularly in emerging economies, the demand for efficient and cost-effective hydrochloric acid distribution channels is increasing. The oil and gas sector also presents a substantial market opportunity, with hydrochloric acid being extensively used in well acidizing operations to enhance oil recovery.
The chemical manufacturing industry, another major consumer of hydrochloric acid, is witnessing a surge in demand for the compound in the production of various chemicals and pharmaceuticals. This trend is further amplified by the growing emphasis on sustainable and environmentally friendly production processes, which often require specialized handling and distribution of hydrochloric acid.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific region leads the market demand for hydrochloric acid, followed by North America and Europe. The rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India are driving the demand for hydrochloric acid in various applications, consequently creating a need for innovative distribution channels to meet the growing market requirements.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards on-site generation of hydrochloric acid, particularly in water treatment applications. This trend is creating new opportunities for innovations in distribution channels, focusing on compact, efficient, and safe on-site generation systems.
Safety and environmental concerns associated with the transportation and handling of hydrochloric acid are pushing the industry towards developing more secure and eco-friendly distribution methods. This has led to an increased focus on developing corrosion-resistant materials for storage and transportation, as well as advanced monitoring and control systems for distribution networks.
The digital transformation of supply chains is also impacting the hydrochloric acid distribution landscape. There is a growing demand for smart distribution systems that can provide real-time tracking, predictive maintenance, and optimized routing to ensure timely and safe delivery of hydrochloric acid to end-users.
In conclusion, the market demand for innovations in hydrochloric acid distribution channels is robust and multifaceted, driven by industrial growth, safety requirements, and technological advancements. The industry is poised for significant developments in distribution technologies to meet the evolving needs of various sectors while addressing environmental and safety concerns.
Current Challenges
The distribution of hydrochloric acid faces several significant challenges in the current market landscape. One of the primary issues is the corrosive nature of the acid, which necessitates specialized handling and transportation equipment. This requirement increases the overall cost of distribution and limits the number of carriers capable of safely transporting the product.
Safety concerns also pose a major challenge in hydrochloric acid distribution. The potential for spills or leaks during transport can lead to environmental damage and pose serious health risks to workers and nearby communities. As a result, stringent regulations and safety protocols must be adhered to, further complicating the distribution process and increasing operational costs.
The volatility of hydrochloric acid prices presents another obstacle for distributors. Fluctuations in raw material costs, energy prices, and market demand can lead to unpredictable pricing, making it difficult for distributors to maintain stable profit margins and plan for long-term investments in infrastructure and equipment.
Geographic constraints also impact the efficiency of hydrochloric acid distribution. The acid is often produced in industrial clusters, but demand may be dispersed across various regions. This mismatch between production sites and end-users can result in longer transportation routes and increased logistics complexity.
The lack of standardization in packaging and handling procedures across different regions and industries creates additional challenges. Distributors must adapt to varying customer requirements and local regulations, which can lead to inefficiencies and increased operational costs.
Environmental regulations pose another significant hurdle for hydrochloric acid distributors. Stricter emissions controls and waste management requirements necessitate investments in cleaner technologies and more sustainable distribution practices, putting pressure on profit margins.
Lastly, the digital transformation of the chemical industry has highlighted the need for improved supply chain visibility and real-time tracking capabilities in hydrochloric acid distribution. Many distributors struggle to implement advanced technologies such as IoT sensors and blockchain-based tracking systems, hindering their ability to optimize routes, monitor product quality, and provide timely information to customers.
Safety concerns also pose a major challenge in hydrochloric acid distribution. The potential for spills or leaks during transport can lead to environmental damage and pose serious health risks to workers and nearby communities. As a result, stringent regulations and safety protocols must be adhered to, further complicating the distribution process and increasing operational costs.
The volatility of hydrochloric acid prices presents another obstacle for distributors. Fluctuations in raw material costs, energy prices, and market demand can lead to unpredictable pricing, making it difficult for distributors to maintain stable profit margins and plan for long-term investments in infrastructure and equipment.
Geographic constraints also impact the efficiency of hydrochloric acid distribution. The acid is often produced in industrial clusters, but demand may be dispersed across various regions. This mismatch between production sites and end-users can result in longer transportation routes and increased logistics complexity.
The lack of standardization in packaging and handling procedures across different regions and industries creates additional challenges. Distributors must adapt to varying customer requirements and local regulations, which can lead to inefficiencies and increased operational costs.
Environmental regulations pose another significant hurdle for hydrochloric acid distributors. Stricter emissions controls and waste management requirements necessitate investments in cleaner technologies and more sustainable distribution practices, putting pressure on profit margins.
Lastly, the digital transformation of the chemical industry has highlighted the need for improved supply chain visibility and real-time tracking capabilities in hydrochloric acid distribution. Many distributors struggle to implement advanced technologies such as IoT sensors and blockchain-based tracking systems, hindering their ability to optimize routes, monitor product quality, and provide timely information to customers.
Existing Distribution Methods
01 Transportation and storage systems
Specialized systems for transporting and storing hydrochloric acid, including tanks, containers, and pipelines designed to handle corrosive materials safely and efficiently. These systems often incorporate protective coatings, monitoring devices, and safety features to prevent leaks and ensure proper handling throughout the distribution process.- Transportation and storage systems: Specialized systems for transporting and storing hydrochloric acid, including tanks, containers, and pipelines designed to handle corrosive materials. These systems ensure safe and efficient distribution of hydrochloric acid from production facilities to end-users, while minimizing risks associated with handling hazardous chemicals.
- Industrial production and distribution: Methods and equipment for large-scale production and distribution of hydrochloric acid in industrial settings. This includes manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and distribution networks that cater to various industries requiring hydrochloric acid as a raw material or reagent.
- Safety and environmental considerations: Techniques and protocols for ensuring safe handling, transportation, and disposal of hydrochloric acid. This encompasses measures to prevent spills, leaks, and environmental contamination, as well as safety equipment and procedures for workers involved in the distribution process.
- Packaging and labeling: Specialized packaging solutions and labeling requirements for hydrochloric acid distribution. This includes corrosion-resistant containers, tamper-evident seals, and clear hazard communication through proper labeling and documentation to ensure safe handling throughout the supply chain.
- Market analysis and supply chain optimization: Strategies for analyzing market demand, optimizing supply chains, and improving distribution efficiency for hydrochloric acid. This involves forecasting techniques, inventory management, and logistics planning to ensure timely delivery and cost-effective distribution to various end-users across different industries.
02 Purification and concentration methods
Techniques for purifying and concentrating hydrochloric acid before distribution, including distillation, membrane separation, and absorption processes. These methods aim to improve the quality and consistency of the acid, making it suitable for various industrial applications and meeting specific customer requirements.Expand Specific Solutions03 Recycling and waste management
Processes for recycling and managing hydrochloric acid waste, including recovery systems and neutralization techniques. These methods help minimize environmental impact and improve the overall efficiency of hydrochloric acid distribution by reducing waste and promoting circular economy principles.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety and handling protocols
Comprehensive safety measures and handling protocols for the distribution of hydrochloric acid, including personal protective equipment, emergency response procedures, and training programs. These protocols ensure the safe transportation, storage, and use of the acid while minimizing risks to workers and the environment.Expand Specific Solutions05 Market analysis and supply chain optimization
Strategies for analyzing market trends, optimizing supply chains, and improving distribution efficiency for hydrochloric acid. This includes demand forecasting, inventory management, and logistics optimization to ensure timely delivery and cost-effective distribution across various industries and geographical regions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for innovations in hydrochloric acid distribution channels is in a growth phase, driven by increasing industrial applications and demand for efficient chemical handling. The global market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years, with key players like Schlumberger, Bayer AG, and Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. leading the way. These companies are investing in advanced technologies to improve safety, efficiency, and environmental sustainability in acid distribution. The technology is maturing rapidly, with companies like Aquaox, Inc. and WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB focusing on specialized solutions for water treatment and purification. As the industry evolves, we can expect to see more collaborative efforts and strategic partnerships to address the complex challenges in hydrochloric acid distribution and management.
WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB
Technical Solution: WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB has developed an innovative approach to hydrochloric acid distribution through their advanced water treatment systems. Their technology focuses on the in-situ generation of hydrochloric acid using electrolysis of salt water, which eliminates the need for traditional transportation and storage of concentrated acid[1]. This method allows for on-demand production of hydrochloric acid at the point of use, significantly reducing distribution costs and safety risks associated with acid transport[2]. The company's system integrates seamlessly with existing water treatment infrastructure, providing a more sustainable and efficient solution for industries requiring hydrochloric acid in their processes[3].
Strengths: On-demand production reduces transportation costs and risks; environmentally friendly approach; integrates with existing infrastructure. Weaknesses: May require initial investment in electrolysis equipment; dependent on salt water availability; potential limitations in acid concentration levels.
Covestro Intellectual Property GmbH & Co. KG
Technical Solution: Covestro has pioneered a novel distribution channel for hydrochloric acid by developing a closed-loop recycling system within their production processes. This innovative approach focuses on capturing and purifying hydrochloric acid byproducts from various chemical reactions, particularly in the production of polyurethanes and polycarbonates[1]. The purified acid is then redistributed internally or to nearby industrial partners, creating a localized, circular economy for hydrochloric acid[2]. Covestro's system utilizes advanced membrane separation technologies and distillation techniques to ensure high-purity acid recovery, reducing the need for external acid procurement by up to 80% in some facilities[3]. This closed-loop distribution model not only minimizes environmental impact but also significantly reduces transportation and storage costs associated with traditional hydrochloric acid supply chains[4].
Strengths: Reduces reliance on external acid sources; minimizes environmental impact; cost-effective for large-scale operations. Weaknesses: Limited to areas with high concentration of chemical industries; requires significant initial investment in purification technologies; may not be suitable for small-scale operations.
Innovative HCl Handling Tech
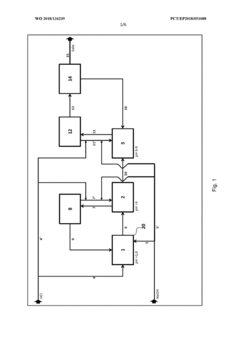
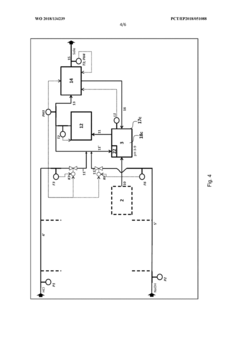
Method for flexibly controlling the use of hydrochloric acid from chemical production
PatentWO2018134239A1
Innovation
- A flexible control process for hydrochloric acid management involves neutralizing hydrochloric acid with concentrated alkali, specifically sodium hydroxide, in a multi-stage continuous process that adjusts pH values and compensates for flow and concentration variations, allowing for efficient handling and recycling of hydrochloric acid even when traditional acceptance points are unavailable.
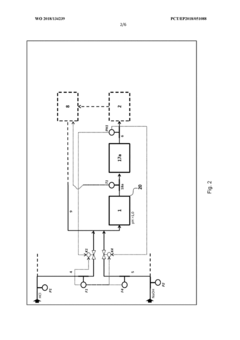
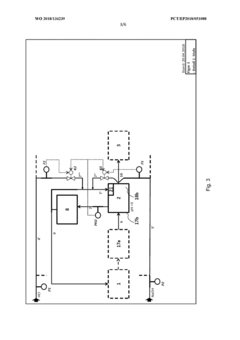
Treatment systems and methods using encapsulated corrosive fluids
PatentInactiveUS20210148212A1
Innovation
- Particle-encapsulated fluids are created using high-speed blending processes, where corrosive fluids are encapsulated in nanoparticles or silica particles, forming a dry or powdered form that can be safely handled and transported, with controlled release mechanisms for timed delivery.
Safety Regulations
Safety regulations play a crucial role in the distribution of hydrochloric acid, a highly corrosive and potentially dangerous substance. These regulations are designed to protect workers, the public, and the environment from the risks associated with handling and transporting this chemical.
In recent years, there have been significant innovations in safety protocols and equipment for hydrochloric acid distribution. One major development is the implementation of advanced leak detection systems in storage tanks and transport vehicles. These systems utilize sophisticated sensors and real-time monitoring to quickly identify and alert operators to any potential leaks or spills, allowing for rapid response and containment.
Another important innovation is the use of improved personal protective equipment (PPE) for workers handling hydrochloric acid. New materials and designs have enhanced the effectiveness of protective suits, gloves, and respiratory equipment, providing better resistance to acid exposure and improving overall worker safety.
Transportation safety has also seen advancements, with the introduction of smart tracking systems for vehicles carrying hydrochloric acid. These systems provide real-time location data, route optimization, and emergency response coordination, ensuring that shipments can be monitored and managed more effectively throughout the distribution process.
Regulatory bodies have responded to these technological advancements by updating safety standards and guidelines. For instance, many countries now require the use of double-walled tanks and pipelines for hydrochloric acid storage and transport, significantly reducing the risk of leaks and environmental contamination.
Training and certification programs for personnel involved in hydrochloric acid distribution have also evolved. Virtual reality and augmented reality technologies are now being used to provide more immersive and effective safety training, allowing workers to practice emergency procedures in simulated environments without exposure to actual hazards.
Environmental protection measures have been strengthened as well. New regulations mandate the use of advanced filtration and neutralization systems at distribution facilities to prevent the release of acid vapors and ensure proper treatment of any waste or runoff.
As the industry continues to innovate, regulatory frameworks are adapting to keep pace. There is an increasing focus on harmonizing international safety standards for hydrochloric acid distribution, facilitating safer and more efficient global trade while maintaining stringent safety protocols across different regions.
These ongoing developments in safety regulations and technologies are not only improving the safety record of hydrochloric acid distribution but also driving innovation in the broader chemical industry. As companies invest in research and development to meet and exceed regulatory requirements, new solutions emerge that have the potential to revolutionize safety practices across various hazardous material sectors.
In recent years, there have been significant innovations in safety protocols and equipment for hydrochloric acid distribution. One major development is the implementation of advanced leak detection systems in storage tanks and transport vehicles. These systems utilize sophisticated sensors and real-time monitoring to quickly identify and alert operators to any potential leaks or spills, allowing for rapid response and containment.
Another important innovation is the use of improved personal protective equipment (PPE) for workers handling hydrochloric acid. New materials and designs have enhanced the effectiveness of protective suits, gloves, and respiratory equipment, providing better resistance to acid exposure and improving overall worker safety.
Transportation safety has also seen advancements, with the introduction of smart tracking systems for vehicles carrying hydrochloric acid. These systems provide real-time location data, route optimization, and emergency response coordination, ensuring that shipments can be monitored and managed more effectively throughout the distribution process.
Regulatory bodies have responded to these technological advancements by updating safety standards and guidelines. For instance, many countries now require the use of double-walled tanks and pipelines for hydrochloric acid storage and transport, significantly reducing the risk of leaks and environmental contamination.
Training and certification programs for personnel involved in hydrochloric acid distribution have also evolved. Virtual reality and augmented reality technologies are now being used to provide more immersive and effective safety training, allowing workers to practice emergency procedures in simulated environments without exposure to actual hazards.
Environmental protection measures have been strengthened as well. New regulations mandate the use of advanced filtration and neutralization systems at distribution facilities to prevent the release of acid vapors and ensure proper treatment of any waste or runoff.
As the industry continues to innovate, regulatory frameworks are adapting to keep pace. There is an increasing focus on harmonizing international safety standards for hydrochloric acid distribution, facilitating safer and more efficient global trade while maintaining stringent safety protocols across different regions.
These ongoing developments in safety regulations and technologies are not only improving the safety record of hydrochloric acid distribution but also driving innovation in the broader chemical industry. As companies invest in research and development to meet and exceed regulatory requirements, new solutions emerge that have the potential to revolutionize safety practices across various hazardous material sectors.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of innovations in hydrochloric acid distribution channels is a critical aspect that requires thorough examination. Traditional methods of hydrochloric acid distribution have been associated with significant environmental risks, including soil and water contamination, air pollution, and potential harm to ecosystems. However, recent innovations in distribution channels are aimed at mitigating these adverse effects while improving efficiency and safety.
One of the primary environmental concerns in hydrochloric acid distribution is the risk of spills and leaks during transportation and storage. Innovative containment systems and advanced monitoring technologies have been developed to address this issue. These systems utilize state-of-the-art materials and sensors to detect and prevent leaks, significantly reducing the likelihood of environmental contamination. Additionally, the implementation of smart logistics and route optimization algorithms has led to more efficient transportation, resulting in reduced fuel consumption and lower carbon emissions.
The development of closed-loop distribution systems represents another significant innovation in minimizing environmental impact. These systems aim to recycle and reuse hydrochloric acid, reducing the need for new production and minimizing waste. By implementing advanced purification and regeneration techniques, companies can significantly decrease the volume of acid that needs to be disposed of, thereby lessening the burden on waste treatment facilities and reducing the potential for environmental contamination.
Innovations in packaging and container design have also contributed to improved environmental performance. New materials and designs that are more resistant to corrosion and degradation have extended the lifespan of storage containers, reducing the frequency of replacement and associated waste. Furthermore, the introduction of reusable and recyclable packaging solutions has helped to minimize the environmental footprint of hydrochloric acid distribution.
The adoption of digital technologies in distribution channels has led to more precise inventory management and demand forecasting. This enhanced accuracy helps to prevent overproduction and reduces the likelihood of expired product disposal, which can have severe environmental consequences. Real-time monitoring and data analytics enable distributors to optimize their operations, leading to reduced energy consumption and more efficient use of resources throughout the supply chain.
Lastly, innovations in neutralization and treatment technologies have improved the handling of hydrochloric acid waste. Advanced chemical processes and biological treatment methods have been developed to neutralize acid residues more effectively, ensuring that any discharged materials meet or exceed environmental standards. These technologies not only protect ecosystems but also enable the recovery of valuable byproducts, further promoting resource efficiency and circular economy principles in the hydrochloric acid industry.
One of the primary environmental concerns in hydrochloric acid distribution is the risk of spills and leaks during transportation and storage. Innovative containment systems and advanced monitoring technologies have been developed to address this issue. These systems utilize state-of-the-art materials and sensors to detect and prevent leaks, significantly reducing the likelihood of environmental contamination. Additionally, the implementation of smart logistics and route optimization algorithms has led to more efficient transportation, resulting in reduced fuel consumption and lower carbon emissions.
The development of closed-loop distribution systems represents another significant innovation in minimizing environmental impact. These systems aim to recycle and reuse hydrochloric acid, reducing the need for new production and minimizing waste. By implementing advanced purification and regeneration techniques, companies can significantly decrease the volume of acid that needs to be disposed of, thereby lessening the burden on waste treatment facilities and reducing the potential for environmental contamination.
Innovations in packaging and container design have also contributed to improved environmental performance. New materials and designs that are more resistant to corrosion and degradation have extended the lifespan of storage containers, reducing the frequency of replacement and associated waste. Furthermore, the introduction of reusable and recyclable packaging solutions has helped to minimize the environmental footprint of hydrochloric acid distribution.
The adoption of digital technologies in distribution channels has led to more precise inventory management and demand forecasting. This enhanced accuracy helps to prevent overproduction and reduces the likelihood of expired product disposal, which can have severe environmental consequences. Real-time monitoring and data analytics enable distributors to optimize their operations, leading to reduced energy consumption and more efficient use of resources throughout the supply chain.
Lastly, innovations in neutralization and treatment technologies have improved the handling of hydrochloric acid waste. Advanced chemical processes and biological treatment methods have been developed to neutralize acid residues more effectively, ensuring that any discharged materials meet or exceed environmental standards. These technologies not only protect ecosystems but also enable the recovery of valuable byproducts, further promoting resource efficiency and circular economy principles in the hydrochloric acid industry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!