How to Master Regulatory Approvals for Hydrochloric Acid Utilities?
JUL 2, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Regulatory Landscape for HCl Utilities
The regulatory landscape for hydrochloric acid (HCl) utilities is complex and multifaceted, encompassing various national and international regulations, standards, and guidelines. At the federal level in the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating HCl under the Clean Air Act and the Toxic Substances Control Act. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) also sets standards for workplace safety related to HCl handling and exposure.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use and import of HCl. The Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) regulation further ensures proper hazard communication. These regulations aim to protect human health and the environment while promoting innovation and competitiveness in the chemical industry.
On a global scale, the United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to chemical hazard classification and communication. Many countries have adopted or are in the process of implementing GHS, which facilitates international trade and enhances safety across borders.
Industry-specific regulations also apply to HCl utilities. For instance, in the semiconductor industry, ultra-high purity HCl must meet stringent quality standards set by organizations like SEMI. The pharmaceutical industry follows Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines, which include specific requirements for HCl used in drug production.
Environmental regulations are particularly stringent for HCl utilities due to the potential for air and water pollution. Emission limits, monitoring requirements, and best available techniques (BAT) are often mandated to minimize environmental impact. The Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) in the EU and the National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) in the US are examples of such regulatory frameworks.
Transportation of HCl is subject to dangerous goods regulations, such as the US Department of Transportation's Hazardous Materials Regulations and the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code. These regulations dictate packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements for the safe transport of HCl.
Compliance with these diverse regulations requires a comprehensive approach, including robust quality management systems, regular audits, and continuous monitoring. Companies must stay informed about regulatory changes and emerging trends, such as the increasing focus on sustainability and circular economy principles in chemical regulation.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use and import of HCl. The Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) regulation further ensures proper hazard communication. These regulations aim to protect human health and the environment while promoting innovation and competitiveness in the chemical industry.
On a global scale, the United Nations' Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS) provides a standardized approach to chemical hazard classification and communication. Many countries have adopted or are in the process of implementing GHS, which facilitates international trade and enhances safety across borders.
Industry-specific regulations also apply to HCl utilities. For instance, in the semiconductor industry, ultra-high purity HCl must meet stringent quality standards set by organizations like SEMI. The pharmaceutical industry follows Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines, which include specific requirements for HCl used in drug production.
Environmental regulations are particularly stringent for HCl utilities due to the potential for air and water pollution. Emission limits, monitoring requirements, and best available techniques (BAT) are often mandated to minimize environmental impact. The Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) in the EU and the National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) in the US are examples of such regulatory frameworks.
Transportation of HCl is subject to dangerous goods regulations, such as the US Department of Transportation's Hazardous Materials Regulations and the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code. These regulations dictate packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements for the safe transport of HCl.
Compliance with these diverse regulations requires a comprehensive approach, including robust quality management systems, regular audits, and continuous monitoring. Companies must stay informed about regulatory changes and emerging trends, such as the increasing focus on sustainability and circular economy principles in chemical regulation.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for hydrochloric acid utilities has shown steady growth in recent years, driven by its widespread applications across various industries. The global hydrochloric acid market size was valued at approximately $7.8 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $9.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 3.2% during the forecast period.
The primary sectors contributing to this demand include chemical manufacturing, steel pickling, oil well acidizing, and water treatment. In the chemical industry, hydrochloric acid is a crucial raw material for producing various chemicals, including vinyl chloride, chlorides, and other organic compounds. The steel industry utilizes hydrochloric acid for pickling and descaling processes, which are essential for surface treatment and corrosion prevention.
The oil and gas sector represents another significant market for hydrochloric acid, where it is used in well acidizing to enhance oil recovery and stimulate production. As global energy demand continues to rise, this application is expected to drive further growth in the hydrochloric acid market.
Water treatment applications, including pH adjustment and chlorine production, also contribute substantially to the market demand. With increasing concerns about water quality and stringent environmental regulations, the use of hydrochloric acid in water treatment facilities is anticipated to grow.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the hydrochloric acid market, accounting for over 40% of the global demand. This is primarily due to the rapid industrialization and infrastructure development in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow, with significant consumption in their chemical and manufacturing sectors.
The market demand analysis reveals a growing trend towards higher purity grades of hydrochloric acid, particularly in electronics and semiconductor industries. This shift is driven by the need for ultra-pure chemicals in advanced manufacturing processes.
However, the market faces challenges related to environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. Stringent regulations on the production, transportation, and use of hydrochloric acid are influencing market dynamics. This has led to increased focus on developing safer handling methods and more environmentally friendly alternatives.
In conclusion, the market demand for hydrochloric acid utilities remains robust, with steady growth projected across various industries. The key to mastering regulatory approvals in this sector lies in understanding these market trends, addressing environmental concerns, and adapting to evolving industry standards and requirements.
The primary sectors contributing to this demand include chemical manufacturing, steel pickling, oil well acidizing, and water treatment. In the chemical industry, hydrochloric acid is a crucial raw material for producing various chemicals, including vinyl chloride, chlorides, and other organic compounds. The steel industry utilizes hydrochloric acid for pickling and descaling processes, which are essential for surface treatment and corrosion prevention.
The oil and gas sector represents another significant market for hydrochloric acid, where it is used in well acidizing to enhance oil recovery and stimulate production. As global energy demand continues to rise, this application is expected to drive further growth in the hydrochloric acid market.
Water treatment applications, including pH adjustment and chlorine production, also contribute substantially to the market demand. With increasing concerns about water quality and stringent environmental regulations, the use of hydrochloric acid in water treatment facilities is anticipated to grow.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the hydrochloric acid market, accounting for over 40% of the global demand. This is primarily due to the rapid industrialization and infrastructure development in countries like China and India. North America and Europe follow, with significant consumption in their chemical and manufacturing sectors.
The market demand analysis reveals a growing trend towards higher purity grades of hydrochloric acid, particularly in electronics and semiconductor industries. This shift is driven by the need for ultra-pure chemicals in advanced manufacturing processes.
However, the market faces challenges related to environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. Stringent regulations on the production, transportation, and use of hydrochloric acid are influencing market dynamics. This has led to increased focus on developing safer handling methods and more environmentally friendly alternatives.
In conclusion, the market demand for hydrochloric acid utilities remains robust, with steady growth projected across various industries. The key to mastering regulatory approvals in this sector lies in understanding these market trends, addressing environmental concerns, and adapting to evolving industry standards and requirements.
Current Challenges in HCl Utility Approvals
The regulatory landscape for hydrochloric acid (HCl) utilities presents a complex array of challenges for manufacturers and operators. One of the primary hurdles is the stringent safety requirements imposed by regulatory bodies due to the corrosive and hazardous nature of HCl. These regulations often demand extensive documentation, rigorous safety protocols, and frequent inspections, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive for companies.
Environmental concerns pose another significant challenge in the approval process. Regulatory agencies require comprehensive environmental impact assessments, focusing on potential air and water pollution risks associated with HCl production and use. Companies must demonstrate robust containment measures, emission control systems, and waste management protocols to meet increasingly strict environmental standards.
The variability in regulatory frameworks across different regions and countries further complicates the approval process. Companies operating in multiple jurisdictions face the daunting task of navigating diverse and sometimes conflicting regulations, necessitating a nuanced approach to compliance strategies and often requiring separate approval processes for each location.
Technological advancements in HCl production and handling methods also present challenges in the regulatory landscape. As new technologies emerge, regulatory bodies must adapt their approval processes to assess novel safety features and potential risks accurately. This can lead to delays in approvals as regulators work to understand and evaluate these innovations.
The transportation of HCl presents its own set of regulatory hurdles. Strict guidelines govern the movement of hazardous materials, requiring specialized containers, specific routing plans, and detailed emergency response procedures. Obtaining approvals for transportation can be a complex process, involving multiple agencies and extensive documentation.
Worker safety is another critical area of focus in HCl utility approvals. Regulatory bodies demand comprehensive training programs, personal protective equipment protocols, and emergency response plans. Companies must demonstrate their ability to protect workers from potential exposure and handle incidents effectively, which often requires significant investment in safety infrastructure and training.
The evolving nature of regulations poses an ongoing challenge for HCl utility operators. As scientific understanding of environmental and health impacts advances, regulatory requirements are subject to frequent updates. This necessitates a proactive approach to compliance, with companies needing to anticipate and prepare for potential regulatory changes to maintain their approvals.
Environmental concerns pose another significant challenge in the approval process. Regulatory agencies require comprehensive environmental impact assessments, focusing on potential air and water pollution risks associated with HCl production and use. Companies must demonstrate robust containment measures, emission control systems, and waste management protocols to meet increasingly strict environmental standards.
The variability in regulatory frameworks across different regions and countries further complicates the approval process. Companies operating in multiple jurisdictions face the daunting task of navigating diverse and sometimes conflicting regulations, necessitating a nuanced approach to compliance strategies and often requiring separate approval processes for each location.
Technological advancements in HCl production and handling methods also present challenges in the regulatory landscape. As new technologies emerge, regulatory bodies must adapt their approval processes to assess novel safety features and potential risks accurately. This can lead to delays in approvals as regulators work to understand and evaluate these innovations.
The transportation of HCl presents its own set of regulatory hurdles. Strict guidelines govern the movement of hazardous materials, requiring specialized containers, specific routing plans, and detailed emergency response procedures. Obtaining approvals for transportation can be a complex process, involving multiple agencies and extensive documentation.
Worker safety is another critical area of focus in HCl utility approvals. Regulatory bodies demand comprehensive training programs, personal protective equipment protocols, and emergency response plans. Companies must demonstrate their ability to protect workers from potential exposure and handle incidents effectively, which often requires significant investment in safety infrastructure and training.
The evolving nature of regulations poses an ongoing challenge for HCl utility operators. As scientific understanding of environmental and health impacts advances, regulatory requirements are subject to frequent updates. This necessitates a proactive approach to compliance, with companies needing to anticipate and prepare for potential regulatory changes to maintain their approvals.
Existing Approval Strategies
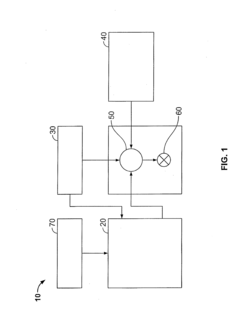
01 Production and purification of hydrochloric acid
Various methods and systems for producing and purifying hydrochloric acid are described. These include processes for manufacturing high-purity hydrochloric acid, as well as techniques for removing impurities and contaminants from the acid. The methods aim to improve the quality and efficiency of hydrochloric acid production for industrial applications.- Production and purification of hydrochloric acid: Various methods and systems for producing and purifying hydrochloric acid are described. These include processes for manufacturing high-purity hydrochloric acid, as well as techniques for removing impurities and contaminants from the acid. The methods aim to improve the efficiency and quality of hydrochloric acid production for industrial applications.
- Applications of hydrochloric acid in chemical processes: Hydrochloric acid is widely used in various chemical processes and industrial applications. It serves as a key reagent in the production of other chemicals, metal treatment, and as a catalyst in organic synthesis reactions. The acid's versatility makes it an essential component in many manufacturing processes across different industries.
- Handling and storage of hydrochloric acid: Specialized equipment and methods for handling and storing hydrochloric acid are crucial due to its corrosive nature. This includes the design of storage tanks, transportation containers, and safety systems to prevent leaks and protect workers. Proper handling procedures and protective measures are essential to ensure safe use of the acid in industrial settings.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Environmental and safety aspects of hydrochloric acid use are important considerations. This includes methods for neutralizing and disposing of the acid, controlling emissions, and implementing safety protocols to protect workers and the environment. Techniques for reducing the environmental impact of hydrochloric acid production and use are also addressed.
- Recovery and recycling of hydrochloric acid: Processes for recovering and recycling hydrochloric acid from industrial waste streams are described. These methods aim to reduce waste and improve resource efficiency by reclaiming the acid for reuse in various applications. The recovery techniques include separation processes, purification methods, and systems for reintegrating the recovered acid into production cycles.
02 Applications of hydrochloric acid in chemical processes
Hydrochloric acid is widely used in various chemical processes and industrial applications. These include its use as a catalyst, reagent, or processing aid in the production of other chemicals, materials, and pharmaceuticals. The acid's properties make it valuable in diverse fields such as metallurgy, water treatment, and food processing.Expand Specific Solutions03 Handling and storage of hydrochloric acid
Specialized equipment and methods for handling, storing, and transporting hydrochloric acid are described. These include corrosion-resistant containers, safety systems, and dispensing mechanisms designed to manage the acid's corrosive nature and potential hazards. The focus is on ensuring safe and efficient handling of hydrochloric acid in industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recycling and recovery of hydrochloric acid
Processes and systems for recycling and recovering hydrochloric acid from industrial waste streams or byproducts are presented. These methods aim to reduce waste, improve resource efficiency, and minimize environmental impact by reusing or repurposing the acid in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations for hydrochloric acid
Technologies and methods addressing environmental and safety concerns related to hydrochloric acid use are described. These include emission control systems, neutralization techniques, and protective measures to mitigate the acid's potential negative impacts on the environment and human health. The focus is on ensuring responsible and sustainable use of hydrochloric acid in industrial processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Regulatory Bodies and Stakeholders
The regulatory approval landscape for hydrochloric acid utilities is characterized by a mature market with established players and stringent safety protocols. The industry is in a stable growth phase, with a global market size expected to reach $1.5 billion by 2025. Technological maturity is high, with companies like Halliburton Energy Services, Schlumberger Technologies, and Akzo Nobel Chemicals International leading innovation in safety and efficiency. These firms, along with others such as Dorf Ketal Chemicals and Covestro Deutschland, are investing in advanced containment systems and process optimization to meet evolving regulatory standards. The competitive environment is intense, driving continuous improvements in compliance strategies and environmental performance.
Dorf Ketal Chemicals FZE
Technical Solution: Dorf Ketal Chemicals FZE has developed a comprehensive approach to mastering regulatory approvals for hydrochloric acid utilities. Their strategy involves a multi-step process that includes thorough documentation, rigorous testing, and proactive engagement with regulatory bodies. The company utilizes advanced chemical analysis techniques to ensure product purity and consistency, which is crucial for regulatory compliance. They have implemented a state-of-the-art quality management system that tracks every batch of hydrochloric acid from production to distribution, allowing for complete traceability[1]. Additionally, Dorf Ketal has invested in specialized training programs for their staff to stay updated on the latest regulatory requirements and best practices in handling hydrochloric acid[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive quality management system, specialized staff training, and proactive regulatory engagement. Weaknesses: Potentially higher costs associated with rigorous compliance measures, which may impact pricing competitiveness.
Halliburton Energy Services, Inc.
Technical Solution: Halliburton Energy Services, Inc. has developed a sophisticated approach to regulatory approvals for hydrochloric acid utilities, particularly in the context of oilfield services. Their strategy focuses on developing environmentally friendly formulations of hydrochloric acid that meet or exceed regulatory standards. The company has invested in research to create acid systems that are less corrosive and more biodegradable, while maintaining effectiveness in well stimulation and other applications[2]. Halliburton's approach also includes advanced monitoring and control systems for acid handling and storage, which help ensure compliance with safety regulations. They have implemented a global regulatory compliance program that tracks and adapts to changing regulations across different jurisdictions[4].
Strengths: Innovative acid formulations, advanced monitoring systems, and global regulatory compliance program. Weaknesses: Higher research and development costs, potential limitations in certain applications due to modified acid formulations.
Innovative Compliance Approaches
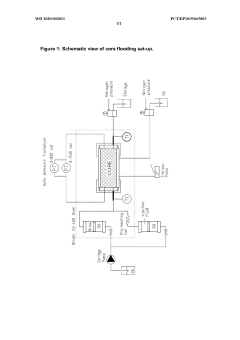
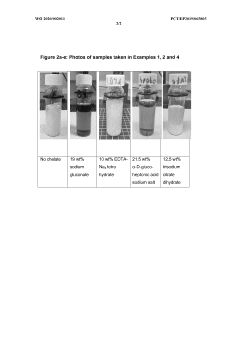
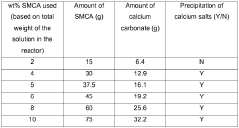
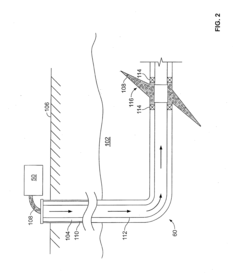
Salt of monochloroacetic acid with chelating agent for delayed acidification in the oil field industry
PatentWO2020002011A1
Innovation
- A process using a monovalent salt of monochloroacetic acid in combination with a chelating agent having a monovalent counterion and a carbon chain with at least five hydroxyl groups, such as sodium gluconate, to inhibit calcium glycolate formation and control acidification, forming stable wormholes without scaling.
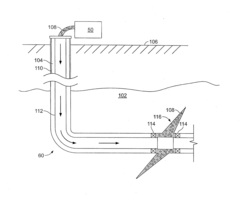
Hydrofluoric Based Invert Emulsions for Shale Stimulation
PatentInactiveUS20160264849A1
Innovation
- The use of hydrofluoric acid (HF) based invert emulsions, combined with hydrochloric acid (HCl) or organic acids, which are emulsified to create a retarded acid system that deeply penetrates the formation, reduces water content, and enhances proppant transport properties, minimizing residue and corrosion while maintaining formation permeability.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental Impact Assessment is a critical component in the regulatory approval process for hydrochloric acid utilities. This assessment evaluates the potential effects of hydrochloric acid production, storage, and use on the surrounding environment, including air, water, soil, and ecosystems.
The primary environmental concerns associated with hydrochloric acid utilities include air pollution, water contamination, and soil acidification. Emissions of hydrogen chloride gas can contribute to acid rain formation and pose respiratory risks to nearby populations. Accidental releases or improper disposal of hydrochloric acid can lead to severe water pollution, affecting aquatic life and drinking water sources.
To address these concerns, a comprehensive Environmental Impact Assessment typically includes air quality modeling, water quality analysis, and soil contamination studies. Advanced monitoring systems and dispersion models are employed to predict the potential spread of emissions and assess their impact on local air quality. Groundwater and surface water assessments evaluate the risk of contamination and potential effects on aquatic ecosystems.
Mitigation strategies play a crucial role in obtaining regulatory approvals. These may include implementing state-of-the-art emission control technologies, such as scrubbers and absorption systems, to minimize air pollution. Robust containment measures and spill prevention protocols are essential to protect soil and water resources. Additionally, the assessment often includes plans for emergency response and remediation in case of accidental releases.
The Environmental Impact Assessment also considers the cumulative effects of hydrochloric acid utilities in conjunction with other industrial activities in the area. This holistic approach helps regulatory bodies understand the overall environmental burden and make informed decisions regarding permit approvals.
Stakeholder engagement is an integral part of the assessment process. Public consultations and transparent communication of potential environmental impacts and mitigation measures help address community concerns and build trust. This engagement can significantly influence the regulatory approval process and the social license to operate.
To master regulatory approvals, it is crucial to demonstrate a commitment to continuous environmental monitoring and improvement. This may involve proposing advanced monitoring systems, regular environmental audits, and a plan for ongoing assessment of environmental performance. Such proactive measures can enhance the credibility of the project and facilitate smoother regulatory approvals.
The primary environmental concerns associated with hydrochloric acid utilities include air pollution, water contamination, and soil acidification. Emissions of hydrogen chloride gas can contribute to acid rain formation and pose respiratory risks to nearby populations. Accidental releases or improper disposal of hydrochloric acid can lead to severe water pollution, affecting aquatic life and drinking water sources.
To address these concerns, a comprehensive Environmental Impact Assessment typically includes air quality modeling, water quality analysis, and soil contamination studies. Advanced monitoring systems and dispersion models are employed to predict the potential spread of emissions and assess their impact on local air quality. Groundwater and surface water assessments evaluate the risk of contamination and potential effects on aquatic ecosystems.
Mitigation strategies play a crucial role in obtaining regulatory approvals. These may include implementing state-of-the-art emission control technologies, such as scrubbers and absorption systems, to minimize air pollution. Robust containment measures and spill prevention protocols are essential to protect soil and water resources. Additionally, the assessment often includes plans for emergency response and remediation in case of accidental releases.
The Environmental Impact Assessment also considers the cumulative effects of hydrochloric acid utilities in conjunction with other industrial activities in the area. This holistic approach helps regulatory bodies understand the overall environmental burden and make informed decisions regarding permit approvals.
Stakeholder engagement is an integral part of the assessment process. Public consultations and transparent communication of potential environmental impacts and mitigation measures help address community concerns and build trust. This engagement can significantly influence the regulatory approval process and the social license to operate.
To master regulatory approvals, it is crucial to demonstrate a commitment to continuous environmental monitoring and improvement. This may involve proposing advanced monitoring systems, regular environmental audits, and a plan for ongoing assessment of environmental performance. Such proactive measures can enhance the credibility of the project and facilitate smoother regulatory approvals.
Safety and Risk Management Protocols
Safety and risk management protocols are paramount when dealing with hydrochloric acid utilities, especially in the context of regulatory approvals. These protocols encompass a comprehensive set of guidelines and procedures designed to mitigate potential hazards and ensure compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
At the core of these protocols is the implementation of robust hazard identification and risk assessment processes. This involves systematic evaluation of all potential risks associated with the storage, handling, and use of hydrochloric acid. Factors such as chemical reactivity, corrosiveness, and potential for release are thoroughly analyzed to develop appropriate control measures.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements form a critical component of safety protocols. Workers must be equipped with appropriate acid-resistant clothing, gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection. Regular training on proper PPE use and maintenance is essential to ensure its effectiveness in preventing exposure incidents.
Containment and spill response procedures are meticulously designed to address potential leaks or accidental releases. This includes the installation of secondary containment systems, such as dikes or berms, around storage tanks and process areas. Emergency response plans detail specific actions to be taken in the event of a spill, including evacuation procedures, neutralization techniques, and proper disposal methods.
Ventilation systems play a crucial role in managing hydrochloric acid vapors. Adequate local exhaust ventilation must be installed in areas where acid is handled or stored to prevent the accumulation of harmful fumes. Regular monitoring of air quality and ventilation system performance is necessary to maintain a safe working environment.
Process safety management (PSM) principles are integrated into the overall safety strategy. This involves conducting process hazard analyses, developing and implementing standard operating procedures, and establishing a system for managing change. Regular audits and inspections are conducted to ensure ongoing compliance with safety protocols and identify areas for improvement.
Emergency preparedness is a key aspect of risk management. This includes the development of detailed emergency response plans, regular drills and simulations, and coordination with local emergency services. Employees must be trained in emergency procedures and have access to necessary equipment and resources for rapid response.
Documentation and record-keeping are essential components of safety and risk management protocols. Detailed logs of safety inspections, incident reports, training records, and maintenance activities must be maintained to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and facilitate continuous improvement of safety measures.
By implementing these comprehensive safety and risk management protocols, organizations can significantly enhance their ability to secure regulatory approvals for hydrochloric acid utilities. These measures not only ensure compliance with regulatory standards but also demonstrate a commitment to worker safety and environmental protection, which are critical factors in the approval process.
At the core of these protocols is the implementation of robust hazard identification and risk assessment processes. This involves systematic evaluation of all potential risks associated with the storage, handling, and use of hydrochloric acid. Factors such as chemical reactivity, corrosiveness, and potential for release are thoroughly analyzed to develop appropriate control measures.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements form a critical component of safety protocols. Workers must be equipped with appropriate acid-resistant clothing, gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection. Regular training on proper PPE use and maintenance is essential to ensure its effectiveness in preventing exposure incidents.
Containment and spill response procedures are meticulously designed to address potential leaks or accidental releases. This includes the installation of secondary containment systems, such as dikes or berms, around storage tanks and process areas. Emergency response plans detail specific actions to be taken in the event of a spill, including evacuation procedures, neutralization techniques, and proper disposal methods.
Ventilation systems play a crucial role in managing hydrochloric acid vapors. Adequate local exhaust ventilation must be installed in areas where acid is handled or stored to prevent the accumulation of harmful fumes. Regular monitoring of air quality and ventilation system performance is necessary to maintain a safe working environment.
Process safety management (PSM) principles are integrated into the overall safety strategy. This involves conducting process hazard analyses, developing and implementing standard operating procedures, and establishing a system for managing change. Regular audits and inspections are conducted to ensure ongoing compliance with safety protocols and identify areas for improvement.
Emergency preparedness is a key aspect of risk management. This includes the development of detailed emergency response plans, regular drills and simulations, and coordination with local emergency services. Employees must be trained in emergency procedures and have access to necessary equipment and resources for rapid response.
Documentation and record-keeping are essential components of safety and risk management protocols. Detailed logs of safety inspections, incident reports, training records, and maintenance activities must be maintained to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and facilitate continuous improvement of safety measures.
By implementing these comprehensive safety and risk management protocols, organizations can significantly enhance their ability to secure regulatory approvals for hydrochloric acid utilities. These measures not only ensure compliance with regulatory standards but also demonstrate a commitment to worker safety and environmental protection, which are critical factors in the approval process.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!