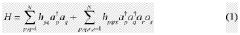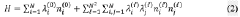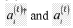How Will Quantum Computing Optimize Polyurethane Reaction Pathways?
JUN 25, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Quantum Computing in Polyurethane Synthesis: Overview and Objectives
Quantum computing represents a paradigm shift in computational capabilities, offering unprecedented potential to revolutionize various fields, including materials science and chemical engineering. In the context of polyurethane synthesis, quantum computing emerges as a powerful tool to optimize reaction pathways, potentially transforming the industry's approach to product development and manufacturing processes.
The evolution of quantum computing technology has been marked by significant milestones, from theoretical concepts to practical implementations. As we stand on the cusp of quantum supremacy, the application of this technology to complex chemical systems becomes increasingly feasible. The intersection of quantum computing and polyurethane synthesis presents a unique opportunity to address long-standing challenges in reaction optimization and material design.
The primary objective of applying quantum computing to polyurethane reaction pathways is to enhance the efficiency and precision of molecular simulations. Traditional computational methods often struggle with the complexity of polyurethane systems, which involve multiple reactants, catalysts, and intricate reaction mechanisms. Quantum computing offers the potential to model these systems with unprecedented accuracy, taking into account quantum mechanical effects that are crucial for understanding molecular interactions and reaction dynamics.
By leveraging quantum algorithms, researchers aim to explore vast chemical spaces and identify optimal reaction conditions more rapidly than conventional methods allow. This includes the ability to simulate and predict the behavior of reactants, intermediates, and products at the quantum level, potentially uncovering novel reaction pathways or catalysts that could lead to improved polyurethane properties or more sustainable production methods.
Furthermore, the application of quantum computing in this field seeks to address specific challenges in polyurethane synthesis, such as controlling molecular weight distribution, optimizing cross-linking density, and fine-tuning the balance between hard and soft segments. These factors directly influence the mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties of the final polyurethane products, making their precise control a key objective in the industry.
The integration of quantum computing with machine learning algorithms presents another exciting frontier. This synergy could enable the development of advanced predictive models for polyurethane synthesis, potentially revolutionizing the design of custom formulations tailored to specific applications. Such capabilities could significantly reduce the time and resources required for product development, accelerating innovation in sectors ranging from automotive and construction to medical devices and aerospace.
The evolution of quantum computing technology has been marked by significant milestones, from theoretical concepts to practical implementations. As we stand on the cusp of quantum supremacy, the application of this technology to complex chemical systems becomes increasingly feasible. The intersection of quantum computing and polyurethane synthesis presents a unique opportunity to address long-standing challenges in reaction optimization and material design.
The primary objective of applying quantum computing to polyurethane reaction pathways is to enhance the efficiency and precision of molecular simulations. Traditional computational methods often struggle with the complexity of polyurethane systems, which involve multiple reactants, catalysts, and intricate reaction mechanisms. Quantum computing offers the potential to model these systems with unprecedented accuracy, taking into account quantum mechanical effects that are crucial for understanding molecular interactions and reaction dynamics.
By leveraging quantum algorithms, researchers aim to explore vast chemical spaces and identify optimal reaction conditions more rapidly than conventional methods allow. This includes the ability to simulate and predict the behavior of reactants, intermediates, and products at the quantum level, potentially uncovering novel reaction pathways or catalysts that could lead to improved polyurethane properties or more sustainable production methods.
Furthermore, the application of quantum computing in this field seeks to address specific challenges in polyurethane synthesis, such as controlling molecular weight distribution, optimizing cross-linking density, and fine-tuning the balance between hard and soft segments. These factors directly influence the mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties of the final polyurethane products, making their precise control a key objective in the industry.
The integration of quantum computing with machine learning algorithms presents another exciting frontier. This synergy could enable the development of advanced predictive models for polyurethane synthesis, potentially revolutionizing the design of custom formulations tailored to specific applications. Such capabilities could significantly reduce the time and resources required for product development, accelerating innovation in sectors ranging from automotive and construction to medical devices and aerospace.
Market Analysis for Quantum-Optimized Polyurethane Products
The market for quantum-optimized polyurethane products is poised for significant growth as quantum computing technology advances and its applications in materials science become more refined. Polyurethanes, versatile polymers used in various industries, stand to benefit greatly from quantum optimization of their reaction pathways. This optimization could lead to improved product performance, reduced production costs, and enhanced sustainability.
The global polyurethane market, valued at approximately $70 billion in 2020, is expected to grow steadily over the next decade. With quantum computing optimization, this growth could accelerate further. Industries such as automotive, construction, furniture, and electronics are likely to be early adopters of quantum-optimized polyurethanes, driven by the demand for higher-performance materials and more efficient production processes.
In the automotive sector, quantum-optimized polyurethanes could lead to lighter, stronger, and more durable components, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and vehicle safety. The construction industry may benefit from polyurethane products with enhanced insulation properties and longer lifespans, addressing energy efficiency concerns in buildings. The furniture market could see innovations in comfort and durability, while the electronics industry might leverage these advanced materials for better protection and thermal management of devices.
The market potential for quantum-optimized polyurethanes extends beyond traditional applications. Emerging fields such as 3D printing and biomedical engineering could see revolutionary advancements. For instance, precisely tailored polyurethane formulations could enable the creation of customized medical implants or tissue scaffolds with optimized biocompatibility and mechanical properties.
Environmental concerns and sustainability goals are driving market demand for more eco-friendly polyurethane products. Quantum computing optimization of reaction pathways could lead to reduced energy consumption in production, minimized waste, and the development of bio-based or recyclable polyurethanes. This aligns with global trends towards circular economy principles and could open new market segments for environmentally conscious consumers and industries.
As quantum computing becomes more accessible and its capabilities in simulating complex molecular interactions improve, we can expect a surge in research and development activities. This could lead to a new generation of polyurethane products with properties that were previously unattainable or economically unfeasible. Companies that invest early in this technology may gain a significant competitive advantage in the market.
However, the market for quantum-optimized polyurethanes is still in its infancy. The full realization of its potential depends on overcoming current limitations in quantum computing technology and developing practical, scalable applications for industrial use. As these challenges are addressed, we can anticipate a gradual but transformative impact on the polyurethane market, potentially reshaping industry standards and consumer expectations over the next decade.
The global polyurethane market, valued at approximately $70 billion in 2020, is expected to grow steadily over the next decade. With quantum computing optimization, this growth could accelerate further. Industries such as automotive, construction, furniture, and electronics are likely to be early adopters of quantum-optimized polyurethanes, driven by the demand for higher-performance materials and more efficient production processes.
In the automotive sector, quantum-optimized polyurethanes could lead to lighter, stronger, and more durable components, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and vehicle safety. The construction industry may benefit from polyurethane products with enhanced insulation properties and longer lifespans, addressing energy efficiency concerns in buildings. The furniture market could see innovations in comfort and durability, while the electronics industry might leverage these advanced materials for better protection and thermal management of devices.
The market potential for quantum-optimized polyurethanes extends beyond traditional applications. Emerging fields such as 3D printing and biomedical engineering could see revolutionary advancements. For instance, precisely tailored polyurethane formulations could enable the creation of customized medical implants or tissue scaffolds with optimized biocompatibility and mechanical properties.
Environmental concerns and sustainability goals are driving market demand for more eco-friendly polyurethane products. Quantum computing optimization of reaction pathways could lead to reduced energy consumption in production, minimized waste, and the development of bio-based or recyclable polyurethanes. This aligns with global trends towards circular economy principles and could open new market segments for environmentally conscious consumers and industries.
As quantum computing becomes more accessible and its capabilities in simulating complex molecular interactions improve, we can expect a surge in research and development activities. This could lead to a new generation of polyurethane products with properties that were previously unattainable or economically unfeasible. Companies that invest early in this technology may gain a significant competitive advantage in the market.
However, the market for quantum-optimized polyurethanes is still in its infancy. The full realization of its potential depends on overcoming current limitations in quantum computing technology and developing practical, scalable applications for industrial use. As these challenges are addressed, we can anticipate a gradual but transformative impact on the polyurethane market, potentially reshaping industry standards and consumer expectations over the next decade.
Current Challenges in Polyurethane Reaction Pathway Optimization
The optimization of polyurethane reaction pathways faces several significant challenges in the current landscape. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of the reaction mechanisms involved. Polyurethane synthesis involves multiple simultaneous reactions, including the formation of urethane linkages, urea bonds, and allophanate structures. This intricate network of reactions makes it difficult to predict and control the final product properties accurately.
Another major challenge is the vast parameter space that needs to be explored for optimization. Factors such as temperature, pressure, catalyst type and concentration, reactant ratios, and mixing conditions all play crucial roles in determining the reaction kinetics and final product characteristics. Traditional experimental approaches to optimize these parameters are time-consuming and resource-intensive, often relying on trial-and-error methods.
The non-linear nature of polyurethane reactions further complicates optimization efforts. Small changes in reaction conditions can lead to significant variations in product properties, making it challenging to establish reliable structure-property relationships. This non-linearity also hinders the development of accurate predictive models using conventional computational methods.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures pose additional challenges to polyurethane reaction pathway optimization. There is a growing need to develop more sustainable and eco-friendly processes, which often requires the exploration of alternative raw materials and reaction routes. However, these new pathways may introduce unfamiliar reaction dynamics and require extensive re-optimization of existing processes.
The lack of real-time monitoring and control techniques for polyurethane reactions is another significant hurdle. Current methods often rely on offline analysis, which limits the ability to make rapid adjustments during the reaction process. This gap in process analytical technology hampers efforts to implement advanced control strategies for optimizing reaction pathways.
Scalability of optimized reaction pathways from laboratory to industrial scale presents yet another challenge. Reactions that are well-controlled and optimized at small scales may behave differently when scaled up, due to factors such as heat transfer limitations and mixing inefficiencies. This scale-up problem often necessitates additional optimization steps and can lead to unexpected product variations.
Another major challenge is the vast parameter space that needs to be explored for optimization. Factors such as temperature, pressure, catalyst type and concentration, reactant ratios, and mixing conditions all play crucial roles in determining the reaction kinetics and final product characteristics. Traditional experimental approaches to optimize these parameters are time-consuming and resource-intensive, often relying on trial-and-error methods.
The non-linear nature of polyurethane reactions further complicates optimization efforts. Small changes in reaction conditions can lead to significant variations in product properties, making it challenging to establish reliable structure-property relationships. This non-linearity also hinders the development of accurate predictive models using conventional computational methods.
Environmental concerns and regulatory pressures pose additional challenges to polyurethane reaction pathway optimization. There is a growing need to develop more sustainable and eco-friendly processes, which often requires the exploration of alternative raw materials and reaction routes. However, these new pathways may introduce unfamiliar reaction dynamics and require extensive re-optimization of existing processes.
The lack of real-time monitoring and control techniques for polyurethane reactions is another significant hurdle. Current methods often rely on offline analysis, which limits the ability to make rapid adjustments during the reaction process. This gap in process analytical technology hampers efforts to implement advanced control strategies for optimizing reaction pathways.
Scalability of optimized reaction pathways from laboratory to industrial scale presents yet another challenge. Reactions that are well-controlled and optimized at small scales may behave differently when scaled up, due to factors such as heat transfer limitations and mixing inefficiencies. This scale-up problem often necessitates additional optimization steps and can lead to unexpected product variations.
Existing Quantum Algorithms for Chemical Reaction Optimization
01 Quantum algorithms for simulating chemical reactions
Quantum computing techniques are applied to simulate and analyze chemical reaction pathways. These algorithms leverage quantum mechanics principles to model complex molecular interactions and predict reaction outcomes with higher accuracy than classical methods. This approach enables researchers to explore reaction mechanisms, transition states, and energy landscapes more efficiently.- Quantum algorithms for simulating chemical reactions: Quantum computing techniques are applied to simulate and analyze chemical reaction pathways. These algorithms leverage quantum mechanics principles to model complex molecular interactions and predict reaction outcomes more accurately than classical methods. This approach can significantly accelerate drug discovery and materials design processes.
- Optimization of reaction pathways using quantum annealing: Quantum annealing techniques are utilized to optimize reaction pathways in chemical processes. This method helps identify the most efficient routes for chemical reactions, potentially reducing energy consumption and improving yield in industrial applications. The approach is particularly useful for complex reaction networks with multiple intermediates.
- Quantum-classical hybrid methods for reaction prediction: Hybrid approaches combining quantum and classical computing techniques are developed to predict and analyze reaction pathways. These methods leverage the strengths of both quantum and classical systems to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of reaction simulations, particularly for large molecular systems.
- Quantum machine learning for reaction mechanism discovery: Quantum machine learning algorithms are applied to discover and elucidate reaction mechanisms. These techniques can identify patterns and relationships in chemical data that are difficult to detect using classical methods, leading to new insights into reaction pathways and potentially uncovering novel reaction mechanisms.
- Error mitigation in quantum chemistry simulations: Advanced error mitigation techniques are developed to improve the accuracy of quantum chemistry simulations, including reaction pathway calculations. These methods address the inherent noise and errors in quantum systems, enabling more reliable predictions of chemical reactions and their outcomes on near-term quantum devices.
02 Optimization of reaction parameters using quantum annealing
Quantum annealing techniques are utilized to optimize various parameters in chemical reactions. This method helps in finding the most favorable conditions for desired reactions, including temperature, pressure, and reactant concentrations. By exploring a vast solution space simultaneously, quantum annealing can identify optimal reaction pathways more rapidly than traditional optimization methods.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quantum-classical hybrid approaches for reaction pathway analysis
Hybrid quantum-classical algorithms are developed to combine the strengths of both quantum and classical computing in analyzing reaction pathways. These approaches use quantum processors for computationally intensive tasks while leveraging classical computers for data processing and analysis. This synergy allows for more comprehensive studies of complex reaction networks and mechanisms.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quantum machine learning for predicting reaction outcomes
Quantum machine learning techniques are applied to predict reaction outcomes and discover new reaction pathways. These methods use quantum algorithms to process and analyze large datasets of chemical reactions, enabling the identification of patterns and trends that may not be apparent through classical analysis. This approach can accelerate the discovery of novel reactions and optimize existing processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quantum error correction for improved reaction simulations
Advanced quantum error correction techniques are implemented to enhance the accuracy and reliability of quantum simulations for reaction pathways. These methods mitigate the effects of noise and decoherence in quantum systems, allowing for more precise modeling of chemical reactions. Improved error correction enables the study of larger molecular systems and longer reaction timescales.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Quantum Computing and Polyurethane Industries
The quantum computing optimization of polyurethane reaction pathways is in its early developmental stage, with a growing market potential as the technology matures. The field is characterized by a blend of quantum computing specialists and chemical industry leaders. Companies like Zapata Computing, IBM, and Microsoft are at the forefront of quantum algorithm development, while BASF, Dow Global Technologies, and Air Products & Chemicals bring expertise in polyurethane chemistry. The technology's maturity varies, with quantum hardware providers like IBM and Intel advancing rapidly, while application-specific solutions for chemical optimization are still emerging. Collaborations between tech giants and chemical companies, such as partnerships involving Fujitsu and Tata Consultancy Services, are driving progress in this interdisciplinary field.
Zapata Computing, Inc.
Technical Solution: Zapata Computing specializes in quantum-classical hybrid algorithms for chemistry simulations. Their approach to optimizing polyurethane reaction pathways involves using variational quantum algorithms (VQA) combined with classical machine learning techniques. They employ their proprietary Orquestra platform to design and execute quantum workflows that can model complex molecular interactions and reaction dynamics. This allows for more accurate predictions of reaction rates, product distributions, and optimal reaction conditions for polyurethane synthesis.
Strengths: Specialized expertise in quantum algorithms for chemistry; proprietary software platform for quantum-classical hybrid computations. Weaknesses: Reliance on current NISQ (Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum) devices may limit the complexity of simulations possible.
Fujitsu Ltd.
Technical Solution: Fujitsu's approach to quantum computing for polyurethane optimization involves their Digital Annealer technology, which is a quantum-inspired classical system. For polyurethane reaction pathways, they use this technology to perform large-scale combinatorial optimization. Their method involves mapping the reaction pathway problem to a quadratic unconstrained binary optimization (QUBO) format, which can then be solved efficiently by the Digital Annealer. This allows for rapid exploration of different reaction conditions and catalyst configurations to find optimal pathways for polyurethane synthesis.
Strengths: Quantum-inspired technology that can handle large-scale optimization problems; readily available and scalable compared to full quantum systems. Weaknesses: Not a true quantum system, which may limit its ability to model certain quantum effects in chemical reactions.
Quantum-Classical Hybrid Approaches for Polyurethane Synthesis
Measurement reduction via orbital frames decompositions on quantum computers
PatentWO2020146794A1
Innovation
- A hybrid quantum-classical approach that applies orbital rotations to the quantum state during each shot instead of single-qubit context-selection gates, using orbital frames decomposition to reduce the number of shots required for expectation value estimation.
Method and system for reducing time complexity of density functional theory calculations with qubitized diagonalization
PatentPendingEP4524826A1
Innovation
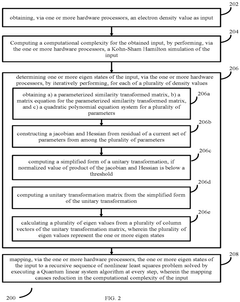
- A processor-implemented method and system that reduces computational complexity by performing a Kohn-Sham Hamilton simulation, determining eigen states through iterative parameterized similarity transformations, and mapping these eigen states to a recursive sequence of nonlinear least squares problems solved by a Quantum linear system algorithm.
Environmental Impact of Quantum-Optimized Polyurethane Production
The optimization of polyurethane reaction pathways through quantum computing has the potential to significantly reduce the environmental impact of polyurethane production. By leveraging quantum algorithms to model and simulate complex chemical reactions, manufacturers can identify more efficient synthesis routes that minimize energy consumption and waste generation.
One of the primary environmental benefits of quantum-optimized polyurethane production is the reduction in energy usage. Traditional polyurethane synthesis often requires high temperatures and pressures, consuming substantial amounts of energy. Quantum computing can help identify reaction pathways that operate under milder conditions, leading to decreased energy requirements and associated greenhouse gas emissions. This optimization could contribute to the industry's efforts to meet carbon reduction targets and improve overall sustainability.
Furthermore, quantum-assisted optimization of reaction pathways can lead to improved atom economy and reduced waste generation. By identifying more selective and efficient routes to desired products, the amount of unwanted by-products and unreacted starting materials can be minimized. This not only reduces the environmental burden of waste disposal but also conserves valuable raw materials, contributing to resource efficiency and circular economy principles.
The environmental impact of quantum-optimized polyurethane production extends to the realm of green chemistry. Quantum simulations can facilitate the discovery of alternative, more environmentally friendly catalysts and reagents. This could potentially lead to the replacement of toxic or hazardous substances currently used in polyurethane synthesis with safer alternatives, reducing the risk of environmental contamination and improving worker safety.
Water consumption and pollution are also areas where quantum-optimized processes could yield environmental benefits. By identifying reaction pathways that require less water or enable more efficient water recycling, the water footprint of polyurethane production could be significantly reduced. Additionally, optimized processes may result in lower levels of aqueous waste and contaminants, easing the burden on wastewater treatment systems and reducing the risk of water pollution.
The potential for quantum computing to enable the use of bio-based or recycled feedstocks in polyurethane production is another important environmental consideration. By simulating and optimizing reactions involving these more sustainable raw materials, quantum computing could accelerate the transition away from petroleum-based feedstocks, contributing to reduced fossil fuel dependence and lower carbon emissions across the product lifecycle.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of quantum-optimized polyurethane production has the potential to be far-reaching and transformative. From energy and resource conservation to waste reduction and the promotion of greener chemistry, the application of quantum computing to this field could play a crucial role in enhancing the sustainability of the polyurethane industry and contributing to broader environmental protection goals.
One of the primary environmental benefits of quantum-optimized polyurethane production is the reduction in energy usage. Traditional polyurethane synthesis often requires high temperatures and pressures, consuming substantial amounts of energy. Quantum computing can help identify reaction pathways that operate under milder conditions, leading to decreased energy requirements and associated greenhouse gas emissions. This optimization could contribute to the industry's efforts to meet carbon reduction targets and improve overall sustainability.
Furthermore, quantum-assisted optimization of reaction pathways can lead to improved atom economy and reduced waste generation. By identifying more selective and efficient routes to desired products, the amount of unwanted by-products and unreacted starting materials can be minimized. This not only reduces the environmental burden of waste disposal but also conserves valuable raw materials, contributing to resource efficiency and circular economy principles.
The environmental impact of quantum-optimized polyurethane production extends to the realm of green chemistry. Quantum simulations can facilitate the discovery of alternative, more environmentally friendly catalysts and reagents. This could potentially lead to the replacement of toxic or hazardous substances currently used in polyurethane synthesis with safer alternatives, reducing the risk of environmental contamination and improving worker safety.
Water consumption and pollution are also areas where quantum-optimized processes could yield environmental benefits. By identifying reaction pathways that require less water or enable more efficient water recycling, the water footprint of polyurethane production could be significantly reduced. Additionally, optimized processes may result in lower levels of aqueous waste and contaminants, easing the burden on wastewater treatment systems and reducing the risk of water pollution.
The potential for quantum computing to enable the use of bio-based or recycled feedstocks in polyurethane production is another important environmental consideration. By simulating and optimizing reactions involving these more sustainable raw materials, quantum computing could accelerate the transition away from petroleum-based feedstocks, contributing to reduced fossil fuel dependence and lower carbon emissions across the product lifecycle.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of quantum-optimized polyurethane production has the potential to be far-reaching and transformative. From energy and resource conservation to waste reduction and the promotion of greener chemistry, the application of quantum computing to this field could play a crucial role in enhancing the sustainability of the polyurethane industry and contributing to broader environmental protection goals.
Intellectual Property Landscape in Quantum Chemistry Applications
The intellectual property landscape in quantum chemistry applications for polyurethane reaction pathway optimization is rapidly evolving. As quantum computing technologies advance, there has been a surge in patent filings related to quantum algorithms and methods for simulating chemical reactions. Major technology companies and research institutions are leading the charge in securing intellectual property rights in this domain.
Several key patents have emerged focusing on quantum algorithms specifically designed for molecular simulations and reaction pathway analysis. These patents often cover novel approaches to representing molecular structures in quantum circuits, as well as methods for efficiently calculating electronic properties and transition states. Some notable patents include those addressing the challenge of mapping complex molecular systems onto quantum hardware with limited qubit connectivity.
In the realm of polyurethane chemistry, patents have been filed for quantum algorithms tailored to model the reaction kinetics and thermodynamics of isocyanate-polyol systems. These innovations aim to provide more accurate predictions of reaction rates, product distributions, and material properties compared to classical computational methods. Intellectual property in this area also extends to hybrid quantum-classical approaches, which leverage the strengths of both quantum and conventional computing resources.
Another significant trend in the patent landscape is the development of error mitigation techniques specific to quantum chemistry simulations. As current quantum hardware is prone to noise and decoherence, these patents address methods for improving the reliability and accuracy of quantum computations for molecular systems. This includes novel error correction schemes and algorithms designed to be resilient to hardware imperfections.
Software companies specializing in quantum chemistry applications have also been active in patenting user interfaces and workflow management systems. These patents often cover the integration of quantum algorithms with existing computational chemistry software, making quantum simulations more accessible to researchers in the polyurethane industry.
It's worth noting that many patents in this field are still in the early stages, with some being speculative in nature. As quantum hardware continues to improve, it is expected that more concrete and implementable patents will emerge, particularly those demonstrating practical advantages in polyurethane reaction optimization.
The global distribution of quantum chemistry patents shows a concentration in countries with advanced quantum computing research programs. The United States, China, and several European countries are at the forefront of patent filings in this domain. Collaborations between academic institutions and industry partners have also resulted in joint patent applications, highlighting the interdisciplinary nature of quantum chemistry research.
Several key patents have emerged focusing on quantum algorithms specifically designed for molecular simulations and reaction pathway analysis. These patents often cover novel approaches to representing molecular structures in quantum circuits, as well as methods for efficiently calculating electronic properties and transition states. Some notable patents include those addressing the challenge of mapping complex molecular systems onto quantum hardware with limited qubit connectivity.
In the realm of polyurethane chemistry, patents have been filed for quantum algorithms tailored to model the reaction kinetics and thermodynamics of isocyanate-polyol systems. These innovations aim to provide more accurate predictions of reaction rates, product distributions, and material properties compared to classical computational methods. Intellectual property in this area also extends to hybrid quantum-classical approaches, which leverage the strengths of both quantum and conventional computing resources.
Another significant trend in the patent landscape is the development of error mitigation techniques specific to quantum chemistry simulations. As current quantum hardware is prone to noise and decoherence, these patents address methods for improving the reliability and accuracy of quantum computations for molecular systems. This includes novel error correction schemes and algorithms designed to be resilient to hardware imperfections.
Software companies specializing in quantum chemistry applications have also been active in patenting user interfaces and workflow management systems. These patents often cover the integration of quantum algorithms with existing computational chemistry software, making quantum simulations more accessible to researchers in the polyurethane industry.
It's worth noting that many patents in this field are still in the early stages, with some being speculative in nature. As quantum hardware continues to improve, it is expected that more concrete and implementable patents will emerge, particularly those demonstrating practical advantages in polyurethane reaction optimization.
The global distribution of quantum chemistry patents shows a concentration in countries with advanced quantum computing research programs. The United States, China, and several European countries are at the forefront of patent filings in this domain. Collaborations between academic institutions and industry partners have also resulted in joint patent applications, highlighting the interdisciplinary nature of quantum chemistry research.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!