Optimizing Arrhenius Acid Concentrations for Reaction Efficiency
SEP 16, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Arrhenius Acid Reaction Optimization Background and Objectives
The Arrhenius acid theory, proposed by Swedish chemist Svante Arrhenius in 1884, has been a cornerstone of chemical reaction understanding for over a century. This theory defines acids as substances that dissociate in aqueous solutions to produce hydrogen ions (H+), with the concentration of these ions directly influencing reaction rates and efficiencies. The evolution of this concept has progressed through multiple refinements, including Brønsted-Lowry and Lewis acid theories, providing increasingly sophisticated frameworks for understanding acid-catalyzed reactions.
Recent technological advancements in reaction engineering have highlighted the critical importance of precise acid concentration control in various industrial processes, from pharmaceutical synthesis to petrochemical refining. The relationship between acid concentration and reaction efficiency follows complex non-linear patterns that often conform to Arrhenius equation parameters, presenting both challenges and opportunities for optimization.
The global chemical industry's increasing focus on sustainability and efficiency has accelerated research into acid concentration optimization. Historical approaches relied heavily on empirical testing and iterative adjustments, resulting in suboptimal resource utilization and inconsistent product quality. Modern computational methods and real-time monitoring technologies now offer pathways to more precise control strategies.
Current technological trends indicate a shift toward predictive modeling of acid-catalyzed reactions, with machine learning algorithms increasingly capable of identifying optimal concentration ranges for specific reaction conditions. This represents a significant departure from traditional methodologies and opens new avenues for process intensification and yield improvement.
The primary objective of this technical research is to develop systematic approaches for optimizing Arrhenius acid concentrations across diverse reaction environments. Specifically, we aim to establish quantitative relationships between acid concentration, temperature dependence, and reaction efficiency metrics including yield, selectivity, and energy consumption.
Secondary goals include identifying novel catalyst systems that can modify acid activity coefficients, thereby expanding the operational window for optimal reaction conditions. Additionally, we seek to develop real-time monitoring and control systems capable of maintaining acid concentrations within narrow optimal ranges despite process disturbances.
The long-term technological trajectory suggests potential for autonomous reaction systems that can self-optimize acid concentrations based on continuous feedback loops and predictive algorithms. This represents a convergence of chemical engineering principles with advanced data analytics and control theory, potentially revolutionizing how acid-catalyzed reactions are implemented in industrial settings.
Recent technological advancements in reaction engineering have highlighted the critical importance of precise acid concentration control in various industrial processes, from pharmaceutical synthesis to petrochemical refining. The relationship between acid concentration and reaction efficiency follows complex non-linear patterns that often conform to Arrhenius equation parameters, presenting both challenges and opportunities for optimization.
The global chemical industry's increasing focus on sustainability and efficiency has accelerated research into acid concentration optimization. Historical approaches relied heavily on empirical testing and iterative adjustments, resulting in suboptimal resource utilization and inconsistent product quality. Modern computational methods and real-time monitoring technologies now offer pathways to more precise control strategies.
Current technological trends indicate a shift toward predictive modeling of acid-catalyzed reactions, with machine learning algorithms increasingly capable of identifying optimal concentration ranges for specific reaction conditions. This represents a significant departure from traditional methodologies and opens new avenues for process intensification and yield improvement.
The primary objective of this technical research is to develop systematic approaches for optimizing Arrhenius acid concentrations across diverse reaction environments. Specifically, we aim to establish quantitative relationships between acid concentration, temperature dependence, and reaction efficiency metrics including yield, selectivity, and energy consumption.
Secondary goals include identifying novel catalyst systems that can modify acid activity coefficients, thereby expanding the operational window for optimal reaction conditions. Additionally, we seek to develop real-time monitoring and control systems capable of maintaining acid concentrations within narrow optimal ranges despite process disturbances.
The long-term technological trajectory suggests potential for autonomous reaction systems that can self-optimize acid concentrations based on continuous feedback loops and predictive algorithms. This represents a convergence of chemical engineering principles with advanced data analytics and control theory, potentially revolutionizing how acid-catalyzed reactions are implemented in industrial settings.
Industrial Applications and Market Demand Analysis
The optimization of Arrhenius acid concentrations has become increasingly critical across multiple industrial sectors, with the global specialty chemicals market valued at $630 billion in 2022 and projected to reach $950 billion by 2030. Industries including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemicals manufacturing are particularly dependent on acid-catalyzed reactions, where efficiency improvements directly translate to significant cost savings and environmental benefits.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing represents the largest demand segment, where optimized acid catalysis can reduce production costs by 15-25% for active pharmaceutical ingredients. Companies report that even a 5% improvement in reaction efficiency through optimized acid concentrations can result in millions of dollars saved annually for high-volume products.
The agrochemical sector has demonstrated growing interest in precision acid catalysis, with market research indicating a 12% annual increase in R&D investments specifically targeting reaction optimization technologies. This trend is driven by increasingly stringent environmental regulations and the need to reduce waste streams containing residual acids.
Fine chemical manufacturers face mounting pressure to improve sustainability metrics while maintaining competitive pricing. Survey data from industry associations reveals that 78% of specialty chemical producers consider reaction efficiency optimization a "high priority" investment area, with acid concentration management identified as a key focus.
Geographically, demand is strongest in regions with established chemical manufacturing infrastructure. North America and Europe lead in technology adoption, while the Asia-Pacific region shows the fastest growth rate at 14% annually for acid catalysis optimization solutions.
The market for analytical instruments and software specifically designed for acid concentration monitoring and optimization has emerged as a distinct segment, valued at $3.2 billion globally. This includes in-line monitoring systems, predictive modeling software, and automated dosing equipment.
Energy-intensive industries are increasingly recognizing the potential of optimized acid reactions to reduce their carbon footprint. Data indicates that properly optimized acid concentrations can reduce energy requirements by 10-30% compared to traditional approaches, aligning with corporate sustainability goals and regulatory compliance requirements.
Customer demand increasingly focuses on solutions that offer real-time monitoring and adjustment capabilities rather than static optimization models. This shift reflects the industry's movement toward more agile and responsive manufacturing processes capable of adapting to variable input conditions while maintaining optimal efficiency.
Pharmaceutical manufacturing represents the largest demand segment, where optimized acid catalysis can reduce production costs by 15-25% for active pharmaceutical ingredients. Companies report that even a 5% improvement in reaction efficiency through optimized acid concentrations can result in millions of dollars saved annually for high-volume products.
The agrochemical sector has demonstrated growing interest in precision acid catalysis, with market research indicating a 12% annual increase in R&D investments specifically targeting reaction optimization technologies. This trend is driven by increasingly stringent environmental regulations and the need to reduce waste streams containing residual acids.
Fine chemical manufacturers face mounting pressure to improve sustainability metrics while maintaining competitive pricing. Survey data from industry associations reveals that 78% of specialty chemical producers consider reaction efficiency optimization a "high priority" investment area, with acid concentration management identified as a key focus.
Geographically, demand is strongest in regions with established chemical manufacturing infrastructure. North America and Europe lead in technology adoption, while the Asia-Pacific region shows the fastest growth rate at 14% annually for acid catalysis optimization solutions.
The market for analytical instruments and software specifically designed for acid concentration monitoring and optimization has emerged as a distinct segment, valued at $3.2 billion globally. This includes in-line monitoring systems, predictive modeling software, and automated dosing equipment.
Energy-intensive industries are increasingly recognizing the potential of optimized acid reactions to reduce their carbon footprint. Data indicates that properly optimized acid concentrations can reduce energy requirements by 10-30% compared to traditional approaches, aligning with corporate sustainability goals and regulatory compliance requirements.
Customer demand increasingly focuses on solutions that offer real-time monitoring and adjustment capabilities rather than static optimization models. This shift reflects the industry's movement toward more agile and responsive manufacturing processes capable of adapting to variable input conditions while maintaining optimal efficiency.
Current Challenges in Acid Concentration Control
The control of acid concentration in Arrhenius reactions presents significant challenges that impact both reaction efficiency and product quality. Current industrial processes struggle with maintaining precise acid concentration levels due to several interrelated factors. Temperature fluctuations during reactions cause substantial variations in acid concentration, as higher temperatures accelerate evaporation rates of volatile acids and can lead to concentration instability. This is particularly problematic in exothermic reactions where temperature control systems often lag behind rapid thermal changes.
Real-time monitoring capabilities remain inadequate across many production environments. Traditional sampling methods introduce delays between measurement and adjustment, creating inefficient control loops. While some advanced spectroscopic techniques offer promising solutions, their implementation is hindered by high costs and integration difficulties with existing production infrastructure.
Equipment limitations further exacerbate concentration control issues. Conventional reactors often exhibit poor mixing characteristics, resulting in concentration gradients throughout the reaction vessel. These non-uniform conditions lead to inconsistent reaction rates and unpredictable product quality. Additionally, material compatibility concerns restrict equipment options, as highly concentrated acids rapidly degrade many common construction materials.
Process scaling presents another significant challenge. Laboratory-optimized acid concentrations frequently fail to translate effectively to industrial-scale operations due to differences in heat transfer dynamics, mixing efficiency, and residence time distributions. This scaling gap necessitates extensive re-optimization at each production level, consuming valuable resources and delaying market entry.
Environmental and safety regulations impose strict limitations on acid handling and waste management. These constraints often force compromises in concentration optimization, as ideal reaction conditions may conflict with permissible emission levels or waste treatment capabilities. The resulting operational adjustments frequently lead to suboptimal reaction efficiency.
Feedstock variability introduces additional complexity to concentration control. Raw material inconsistencies, particularly in water content and impurity profiles, require continuous adjustment of acid dosing protocols. Many production facilities lack the analytical capabilities to detect these variations promptly, resulting in reactive rather than proactive concentration management.
Economic considerations further complicate optimization efforts. The cost of high-purity acids drives many manufacturers to use lower-grade alternatives, introducing additional variables that affect reaction kinetics. Meanwhile, the capital investment required for advanced concentration control systems often faces resistance from management, despite potential long-term efficiency gains.
Real-time monitoring capabilities remain inadequate across many production environments. Traditional sampling methods introduce delays between measurement and adjustment, creating inefficient control loops. While some advanced spectroscopic techniques offer promising solutions, their implementation is hindered by high costs and integration difficulties with existing production infrastructure.
Equipment limitations further exacerbate concentration control issues. Conventional reactors often exhibit poor mixing characteristics, resulting in concentration gradients throughout the reaction vessel. These non-uniform conditions lead to inconsistent reaction rates and unpredictable product quality. Additionally, material compatibility concerns restrict equipment options, as highly concentrated acids rapidly degrade many common construction materials.
Process scaling presents another significant challenge. Laboratory-optimized acid concentrations frequently fail to translate effectively to industrial-scale operations due to differences in heat transfer dynamics, mixing efficiency, and residence time distributions. This scaling gap necessitates extensive re-optimization at each production level, consuming valuable resources and delaying market entry.
Environmental and safety regulations impose strict limitations on acid handling and waste management. These constraints often force compromises in concentration optimization, as ideal reaction conditions may conflict with permissible emission levels or waste treatment capabilities. The resulting operational adjustments frequently lead to suboptimal reaction efficiency.
Feedstock variability introduces additional complexity to concentration control. Raw material inconsistencies, particularly in water content and impurity profiles, require continuous adjustment of acid dosing protocols. Many production facilities lack the analytical capabilities to detect these variations promptly, resulting in reactive rather than proactive concentration management.
Economic considerations further complicate optimization efforts. The cost of high-purity acids drives many manufacturers to use lower-grade alternatives, introducing additional variables that affect reaction kinetics. Meanwhile, the capital investment required for advanced concentration control systems often faces resistance from management, despite potential long-term efficiency gains.
Established Methodologies for Concentration Optimization
01 Catalytic enhancement of Arrhenius acid reactions
Various catalysts can significantly improve the efficiency of Arrhenius acid reactions. These catalysts work by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction, thereby increasing reaction rates and yields. Metal-based catalysts, particularly transition metals, have shown promising results in enhancing acid-catalyzed reactions. The catalytic systems can be optimized for specific reaction conditions to maximize efficiency while minimizing side reactions.- Catalytic enhancement of Arrhenius acid reactions: Catalysts can significantly improve the efficiency of Arrhenius acid reactions by lowering activation energy and increasing reaction rates. Various catalytic materials including transition metals, metal oxides, and supported catalysts have been developed to enhance acid-catalyzed processes. These catalysts provide alternative reaction pathways, allowing reactions to proceed under milder conditions with improved yields and selectivity, while reducing energy requirements and waste production.
- Temperature and concentration effects on acid reaction kinetics: The efficiency of Arrhenius acid reactions is significantly influenced by temperature and concentration parameters. According to the Arrhenius equation, reaction rates increase exponentially with temperature, allowing for optimization of reaction conditions. Concentration adjustments can shift equilibrium positions and reaction rates, while proper temperature control prevents unwanted side reactions and degradation. Optimizing these parameters enables improved yields, selectivity, and energy efficiency in acid-catalyzed processes.
- Solvent selection for optimizing acid reaction efficiency: Solvent choice plays a crucial role in Arrhenius acid reaction efficiency by affecting reactant solubility, stabilizing transition states, and influencing reaction rates. Protic solvents can facilitate proton transfer in acid-catalyzed reactions, while aprotic solvents may enhance nucleophilic substitutions. Solvent polarity affects reactant and intermediate stabilization, and some specialized solvent systems can dramatically improve reaction efficiency through enhanced mass transfer or by suppressing side reactions. Proper solvent selection can significantly improve yield, selectivity, and reaction rate.
- pH control and buffering systems in acid reactions: Maintaining optimal pH conditions through buffering systems is essential for maximizing Arrhenius acid reaction efficiency. Precise pH control ensures consistent protonation states of reactants and intermediates, directly affecting reaction rates and pathways. Buffer solutions help maintain stable pH despite acid consumption or generation during reactions. Advanced pH monitoring and control systems allow for dynamic adjustment throughout reaction processes, preventing unwanted side reactions and improving product quality, yield, and reproducibility in acid-catalyzed transformations.
- Reactor design and mixing techniques for acid reactions: Innovative reactor designs and mixing techniques significantly enhance Arrhenius acid reaction efficiency through improved mass and heat transfer. Continuous flow reactors offer precise residence time control and enhanced safety for handling strong acids. Microreactors provide excellent surface-to-volume ratios for better heat management and mixing. Advanced mixing technologies ensure uniform reactant distribution and prevent localized concentration gradients. Specialized materials resistant to acid corrosion extend equipment lifespan, while process intensification approaches combine multiple operations to reduce energy consumption and improve overall reaction efficiency.
02 Temperature and concentration effects on reaction kinetics
The efficiency of Arrhenius acid reactions is significantly influenced by temperature and concentration parameters. According to the Arrhenius equation, reaction rates increase exponentially with temperature, allowing for optimization of reaction conditions. Concentration adjustments can shift equilibrium positions and reaction rates, with higher acid concentrations generally accelerating reactions up to certain thresholds. Careful control of these parameters enables fine-tuning of reaction efficiency while managing potential side reactions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Solvent systems for optimizing acid reaction efficiency
The choice of solvent system plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency of Arrhenius acid reactions. Protic solvents can stabilize ionic intermediates, while aprotic solvents may enhance nucleophilic reactions. Mixed solvent systems can be designed to optimize solubility, reactivity, and stability of reactants and products. Solvent polarity affects the dissociation of acids and the stabilization of transition states, directly impacting reaction rates and selectivity.Expand Specific Solutions04 pH control and buffering systems
Maintaining optimal pH conditions through buffering systems can significantly enhance the efficiency of Arrhenius acid reactions. Precise pH control allows for selective activation of acid-catalyzed pathways while suppressing unwanted side reactions. Buffer solutions help maintain steady reaction conditions even as acids are consumed or produced during the reaction process. Advanced pH monitoring and control systems enable dynamic adjustment of reaction conditions to maintain optimal efficiency throughout the reaction timeline.Expand Specific Solutions05 Innovative reactor designs for acid reaction processes
Specialized reactor designs can substantially improve the efficiency of Arrhenius acid reactions. Continuous flow reactors allow for precise control of reaction parameters and improved heat transfer. Microreactors provide enhanced surface-to-volume ratios, facilitating better mixing and temperature control. Advanced materials resistant to acid corrosion extend reactor lifespan while maintaining reaction integrity. Reactor configurations that enable controlled addition of reactants can optimize reaction kinetics and product selectivity.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Institutions and Chemical Companies
The Arrhenius acid concentration optimization market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand for efficient chemical processes across industries. The market size is expanding due to applications in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and industrial manufacturing. Technologically, companies are at varying maturity levels: established chemical giants like BASF, Bayer AG, and Daicel Corp. lead with comprehensive acid optimization platforms, while specialized firms such as Takara Bio and Crown Bioscience focus on niche applications. Research organizations including TNO and University of Florida are advancing fundamental understanding of reaction kinetics. Automotive players like Toyota Motor Europe are exploring applications for sustainable manufacturing processes, indicating cross-industry adoption potential. The competitive landscape shows a mix of traditional chemical companies and emerging biotechnology firms driving innovation.
Akzo Nobel Chemicals International BV
Technical Solution: Akzo Nobel has developed the "AcidMaster" platform specifically designed for optimizing Arrhenius acid concentrations across various industrial chemical processes. Their approach combines thermodynamic modeling with kinetic analysis to predict optimal acid concentration ranges for maximum reaction efficiency. The system incorporates advanced calorimetry to precisely measure reaction enthalpies at different acid concentrations, allowing for both yield optimization and safety parameter determination. Akzo Nobel's technology includes specialized corrosion-resistant reactor designs that enable testing of highly concentrated acid conditions without equipment degradation. Their methodology also features a sustainability assessment module that evaluates the environmental impact of different acid concentration scenarios, helping to balance efficiency with environmental considerations. The platform has been successfully implemented in their coating resin production facilities, demonstrating significant yield improvements and reduction in waste acid streams.
Strengths: Comprehensive approach that addresses both efficiency and sustainability concerns. Their specialized reactor designs allow for testing extreme concentration conditions safely. Weaknesses: System requires significant expertise to operate effectively and interpret results. Initial calibration for new reaction types can be time-consuming.
Celanese Chemicals Europe GmbH
Technical Solution: Celanese Chemicals Europe has implemented an advanced acid concentration optimization system called "AcidEfficient" that builds upon the parent company's technology but with specific adaptations for European manufacturing facilities. Their approach focuses on precise temperature control coupled with acid concentration optimization, recognizing the interdependence of these parameters in Arrhenius equations. The system incorporates advanced process analytical technology (PAT) tools including online HPLC and mass spectrometry to monitor reaction intermediates and products in real-time. Celanese Europe has developed specialized mixing technologies that ensure homogeneous acid distribution throughout reaction vessels, eliminating concentration gradients that can reduce efficiency. Their methodology includes detailed kinetic modeling that predicts optimal concentration profiles throughout reaction progression, allowing for programmed concentration adjustments at key reaction stages.
Strengths: Exceptional analytical capabilities allow for detailed understanding of reaction mechanisms and intermediates. Their temperature-acid concentration coupled optimization approach often yields better results than optimizing either parameter independently. Weaknesses: Implementation requires significant capital investment in analytical equipment. The system is most effective for batch processes and less optimized for continuous flow applications.
Key Patents in Acid Reaction Efficiency Enhancement
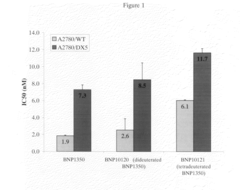
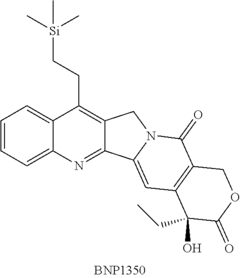
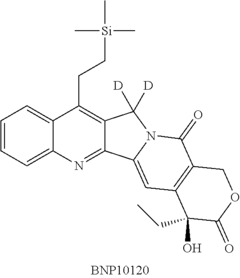
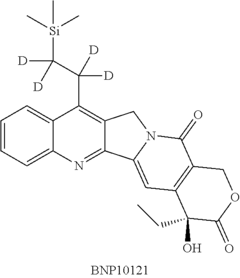
Deuterated analogs of (4S)-4-Ethyl-4-hydroxy-11-[2- (trimethylsilyl)ethyl]-1H-pyrano[3', 4':6,7] indolizino [1,2-b]quinoline-3,14(4H, 12H)-dione and methods of use thereof
PatentInactiveUS20120282261A1
Innovation
- Development of deuterated analogs of (4S)-4-Ethyl-4-hydroxy-11-[2-(trimethylsilyl)ethyl]-1H-pyrano[3′,4′:6,7]indolizino[1,2-b]quinoline-3,14(4H,12H)-dione, such as BNP10120 and BNP10121, and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and derivatives, which are synthesized to improve metabolic profiles and reduce toxicity.
Process for poly (bisphenol A/terephthalate/carbonate) using pyridine reaction medium
PatentInactiveUS4219635A
Innovation
- The process involves adding phosgene to a reaction mixture of bisphenol A and terephthalic acid in pyridine, maintaining a temperature between 50°C and 115°C, and controlling the phosgene feed rate according to the relation lnU=C-E/RT, where U is the phosgene feed rate, C is approximately 10, E is 12 kilocalories/gram-mole, R is the gas constant, and T is the absolute temperature, to achieve good agitation and specific reaction conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The optimization of Arrhenius acid concentrations in chemical reactions carries significant environmental implications that must be carefully considered in modern industrial processes. Acid-catalyzed reactions, while efficient from a production standpoint, often generate waste streams with high acidity levels that require neutralization before discharge. This neutralization process typically consumes additional chemicals such as bases, contributing to the overall environmental footprint of the manufacturing process.
When optimizing acid concentrations for reaction efficiency, a life cycle assessment approach reveals that lower acid concentrations, even if requiring slightly longer reaction times, may result in substantially reduced environmental impact. The production, transportation, and storage of concentrated acids themselves represent significant environmental hazards, including potential for accidental spills, atmospheric emissions during manufacturing, and energy consumption associated with acid production.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental consideration. Higher acid concentrations often necessitate larger volumes of water for dilution, washing, and neutralization processes. In regions facing water scarcity, this additional demand can strain local resources and ecosystems. Implementing closed-loop water systems and acid recovery technologies can significantly mitigate these impacts while simultaneously reducing operational costs.
Greenhouse gas emissions associated with acid production and use must also be factored into optimization strategies. The carbon footprint of producing common industrial acids like sulfuric and hydrochloric acid is substantial, with emissions occurring throughout their supply chain. By precisely optimizing acid concentrations to the minimum effective level, organizations can achieve meaningful reductions in their scope 3 emissions while maintaining reaction efficiency.
Regulatory compliance represents an increasingly important driver for sustainable acid use. Many jurisdictions have implemented stringent regulations regarding acidic waste disposal, with compliance costs rising steadily. Forward-thinking organizations are adopting green chemistry principles that emphasize atom economy and waste prevention, designing reaction systems that minimize acid requirements from the outset rather than treating waste streams afterward.
Emerging technologies offer promising pathways for more sustainable acid utilization. These include heterogeneous catalysts that can replace homogeneous acid catalysts, continuous flow reactors that enable precise acid dosing, and novel separation technologies that facilitate acid recovery and reuse. When evaluating the optimization of Arrhenius acid concentrations, these technologies should be considered as part of a comprehensive sustainability strategy that balances reaction efficiency with environmental responsibility.
When optimizing acid concentrations for reaction efficiency, a life cycle assessment approach reveals that lower acid concentrations, even if requiring slightly longer reaction times, may result in substantially reduced environmental impact. The production, transportation, and storage of concentrated acids themselves represent significant environmental hazards, including potential for accidental spills, atmospheric emissions during manufacturing, and energy consumption associated with acid production.
Water consumption represents another critical environmental consideration. Higher acid concentrations often necessitate larger volumes of water for dilution, washing, and neutralization processes. In regions facing water scarcity, this additional demand can strain local resources and ecosystems. Implementing closed-loop water systems and acid recovery technologies can significantly mitigate these impacts while simultaneously reducing operational costs.
Greenhouse gas emissions associated with acid production and use must also be factored into optimization strategies. The carbon footprint of producing common industrial acids like sulfuric and hydrochloric acid is substantial, with emissions occurring throughout their supply chain. By precisely optimizing acid concentrations to the minimum effective level, organizations can achieve meaningful reductions in their scope 3 emissions while maintaining reaction efficiency.
Regulatory compliance represents an increasingly important driver for sustainable acid use. Many jurisdictions have implemented stringent regulations regarding acidic waste disposal, with compliance costs rising steadily. Forward-thinking organizations are adopting green chemistry principles that emphasize atom economy and waste prevention, designing reaction systems that minimize acid requirements from the outset rather than treating waste streams afterward.
Emerging technologies offer promising pathways for more sustainable acid utilization. These include heterogeneous catalysts that can replace homogeneous acid catalysts, continuous flow reactors that enable precise acid dosing, and novel separation technologies that facilitate acid recovery and reuse. When evaluating the optimization of Arrhenius acid concentrations, these technologies should be considered as part of a comprehensive sustainability strategy that balances reaction efficiency with environmental responsibility.
Scale-up Challenges and Industrial Implementation
The transition from laboratory-scale optimization of Arrhenius acid concentrations to industrial implementation presents significant engineering challenges. When scaling up acid-catalyzed reactions, the heat transfer dynamics change dramatically, potentially leading to hotspots, runaway reactions, or insufficient mixing. Industrial reactors typically operate at volumes 1,000-10,000 times larger than laboratory equipment, requiring redesigned cooling systems and precise temperature control mechanisms to maintain the optimal Arrhenius parameters established in smaller settings.
Material compatibility becomes increasingly critical at scale, as higher acid concentrations accelerate corrosion rates in industrial equipment. This necessitates investment in specialized acid-resistant materials such as high-grade stainless steel, tantalum-lined vessels, or fluoropolymer coatings, significantly impacting capital expenditure calculations. Many facilities must retrofit existing infrastructure rather than building purpose-designed systems, creating additional engineering constraints.
Mixing efficiency represents another major challenge, as maintaining homogeneous acid distribution throughout large reaction volumes requires sophisticated impeller designs and flow modeling. Computational fluid dynamics simulations have become essential tools for predicting acid concentration gradients in scaled-up processes, helping engineers optimize reactor geometry and agitation parameters to ensure consistent reaction conditions throughout the vessel.
Safety considerations multiply exponentially during scale-up, particularly regarding acid handling, storage, and emergency neutralization capabilities. Industrial implementation requires comprehensive hazard assessments, specialized training programs, and robust containment systems to mitigate risks associated with large acid volumes. Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity, with different jurisdictions imposing varying requirements for emissions control, waste management, and worker protection.
Economic viability ultimately determines successful implementation, balancing increased efficiency against higher capital and operational costs. While optimized acid concentrations may improve reaction yields and reduce cycle times, the associated equipment modifications and safety measures require careful cost-benefit analysis. Many companies implement staged scale-up approaches, utilizing pilot plants at intermediate scales (100-1000L) to identify and address challenges before committing to full industrial implementation.
Recent innovations in process intensification technologies, such as continuous flow reactors and microreactor systems, offer alternative scale-up pathways that maintain precise control over acid concentrations while minimizing safety risks and capital requirements. These approaches represent promising directions for bridging the laboratory-industrial divide in Arrhenius acid optimization.
Material compatibility becomes increasingly critical at scale, as higher acid concentrations accelerate corrosion rates in industrial equipment. This necessitates investment in specialized acid-resistant materials such as high-grade stainless steel, tantalum-lined vessels, or fluoropolymer coatings, significantly impacting capital expenditure calculations. Many facilities must retrofit existing infrastructure rather than building purpose-designed systems, creating additional engineering constraints.
Mixing efficiency represents another major challenge, as maintaining homogeneous acid distribution throughout large reaction volumes requires sophisticated impeller designs and flow modeling. Computational fluid dynamics simulations have become essential tools for predicting acid concentration gradients in scaled-up processes, helping engineers optimize reactor geometry and agitation parameters to ensure consistent reaction conditions throughout the vessel.
Safety considerations multiply exponentially during scale-up, particularly regarding acid handling, storage, and emergency neutralization capabilities. Industrial implementation requires comprehensive hazard assessments, specialized training programs, and robust containment systems to mitigate risks associated with large acid volumes. Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity, with different jurisdictions imposing varying requirements for emissions control, waste management, and worker protection.
Economic viability ultimately determines successful implementation, balancing increased efficiency against higher capital and operational costs. While optimized acid concentrations may improve reaction yields and reduce cycle times, the associated equipment modifications and safety measures require careful cost-benefit analysis. Many companies implement staged scale-up approaches, utilizing pilot plants at intermediate scales (100-1000L) to identify and address challenges before committing to full industrial implementation.
Recent innovations in process intensification technologies, such as continuous flow reactors and microreactor systems, offer alternative scale-up pathways that maintain precise control over acid concentrations while minimizing safety risks and capital requirements. These approaches represent promising directions for bridging the laboratory-industrial divide in Arrhenius acid optimization.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!