Sodium Percarbonate's Application in Dairy Equipment Sterilization
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Percarbonate Sterilization Background
Sodium percarbonate, a white crystalline compound with the chemical formula 2Na2CO3·3H2O2, has emerged as a promising alternative in the field of dairy equipment sterilization. This adduct of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide has gained attention due to its effective oxidizing properties and environmentally friendly nature.
The use of sodium percarbonate in dairy equipment sterilization is rooted in the industry's ongoing quest for more efficient and sustainable cleaning methods. Traditionally, dairy processing facilities have relied on chlorine-based sanitizers and other harsh chemicals to maintain hygiene standards. However, these methods often pose environmental concerns and can leave residues that may affect product quality.
Sodium percarbonate's application in this context stems from its ability to release hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water. This reaction produces a potent oxidizing agent that effectively eliminates a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, yeasts, and molds commonly found in dairy processing environments. The compound's efficacy against biofilms, which are notoriously difficult to remove from dairy equipment surfaces, has made it particularly attractive to the industry.
The historical development of sodium percarbonate as a sterilizing agent can be traced back to the early 20th century when it was first synthesized. However, its widespread use in industrial applications, including dairy equipment sterilization, has gained momentum in recent decades. This shift has been driven by increasing awareness of environmental issues and the need for more sustainable practices in food processing.
In the dairy industry, the adoption of sodium percarbonate aligns with the broader trend towards "green chemistry" and sustainable manufacturing processes. Its decomposition into harmless byproducts – water and sodium carbonate – addresses concerns about chemical residues and environmental impact. This characteristic has positioned sodium percarbonate as a key player in the industry's efforts to meet stringent regulatory requirements and consumer demands for cleaner, more natural food processing methods.
The technology behind sodium percarbonate's application in dairy equipment sterilization continues to evolve. Research focuses on optimizing its use in various dairy processing environments, from small-scale operations to large industrial facilities. Current efforts aim to enhance its effectiveness, improve its stability in different conditions, and develop innovative delivery systems for more efficient application.
As the dairy industry faces increasing pressure to maintain high hygiene standards while reducing its environmental footprint, the role of sodium percarbonate in equipment sterilization is likely to expand. This background sets the stage for further exploration of its potential, challenges, and future developments in the context of dairy processing technology.
The use of sodium percarbonate in dairy equipment sterilization is rooted in the industry's ongoing quest for more efficient and sustainable cleaning methods. Traditionally, dairy processing facilities have relied on chlorine-based sanitizers and other harsh chemicals to maintain hygiene standards. However, these methods often pose environmental concerns and can leave residues that may affect product quality.
Sodium percarbonate's application in this context stems from its ability to release hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water. This reaction produces a potent oxidizing agent that effectively eliminates a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, yeasts, and molds commonly found in dairy processing environments. The compound's efficacy against biofilms, which are notoriously difficult to remove from dairy equipment surfaces, has made it particularly attractive to the industry.
The historical development of sodium percarbonate as a sterilizing agent can be traced back to the early 20th century when it was first synthesized. However, its widespread use in industrial applications, including dairy equipment sterilization, has gained momentum in recent decades. This shift has been driven by increasing awareness of environmental issues and the need for more sustainable practices in food processing.
In the dairy industry, the adoption of sodium percarbonate aligns with the broader trend towards "green chemistry" and sustainable manufacturing processes. Its decomposition into harmless byproducts – water and sodium carbonate – addresses concerns about chemical residues and environmental impact. This characteristic has positioned sodium percarbonate as a key player in the industry's efforts to meet stringent regulatory requirements and consumer demands for cleaner, more natural food processing methods.
The technology behind sodium percarbonate's application in dairy equipment sterilization continues to evolve. Research focuses on optimizing its use in various dairy processing environments, from small-scale operations to large industrial facilities. Current efforts aim to enhance its effectiveness, improve its stability in different conditions, and develop innovative delivery systems for more efficient application.
As the dairy industry faces increasing pressure to maintain high hygiene standards while reducing its environmental footprint, the role of sodium percarbonate in equipment sterilization is likely to expand. This background sets the stage for further exploration of its potential, challenges, and future developments in the context of dairy processing technology.
Dairy Industry Demand
The dairy industry has witnessed a growing demand for effective and efficient sterilization methods, particularly for dairy equipment. This demand is driven by several factors, including stringent food safety regulations, increasing consumer awareness about hygiene, and the need for cost-effective solutions in dairy processing.
Dairy equipment sterilization is crucial for maintaining product quality and safety. Contaminated equipment can lead to bacterial growth, spoilage, and potential health hazards. As a result, dairy processors are constantly seeking innovative sterilization methods that can effectively eliminate harmful microorganisms while being environmentally friendly and economically viable.
Sodium percarbonate has emerged as a promising candidate for dairy equipment sterilization due to its unique properties. It is a stable, solid form of hydrogen peroxide that releases oxygen when dissolved in water, providing powerful oxidizing and bleaching capabilities. This characteristic makes it particularly attractive for the dairy industry, as it offers a potentially safer and more sustainable alternative to traditional chlorine-based sanitizers.
The market demand for sodium percarbonate in dairy equipment sterilization is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of eco-friendly cleaning solutions and the rising emphasis on sustainable practices in the dairy industry. Additionally, the versatility of sodium percarbonate, which can be used for both cleaning and sanitizing purposes, makes it an attractive option for dairy processors looking to streamline their sanitation processes.
Furthermore, the global trend towards organic and natural food products has created a niche market for chemical-free or reduced-chemical processing methods. Sodium percarbonate, being a more natural alternative to harsh chemicals, aligns well with this consumer preference. This trend is likely to drive further demand for sodium percarbonate-based sterilization solutions in the dairy industry.
The dairy equipment sterilization market is also influenced by technological advancements in cleaning and sanitizing systems. Automated cleaning-in-place (CIP) systems, which are widely used in modern dairy processing facilities, require effective and compatible sterilization agents. Sodium percarbonate's potential compatibility with these systems could further boost its demand in the industry.
In conclusion, the dairy industry's demand for sodium percarbonate as a sterilization agent is driven by a combination of factors including food safety requirements, environmental concerns, cost-effectiveness, and consumer preferences. As research continues to explore and validate its efficacy in dairy equipment sterilization, the market potential for sodium percarbonate in this application is expected to expand significantly.
Dairy equipment sterilization is crucial for maintaining product quality and safety. Contaminated equipment can lead to bacterial growth, spoilage, and potential health hazards. As a result, dairy processors are constantly seeking innovative sterilization methods that can effectively eliminate harmful microorganisms while being environmentally friendly and economically viable.
Sodium percarbonate has emerged as a promising candidate for dairy equipment sterilization due to its unique properties. It is a stable, solid form of hydrogen peroxide that releases oxygen when dissolved in water, providing powerful oxidizing and bleaching capabilities. This characteristic makes it particularly attractive for the dairy industry, as it offers a potentially safer and more sustainable alternative to traditional chlorine-based sanitizers.
The market demand for sodium percarbonate in dairy equipment sterilization is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of eco-friendly cleaning solutions and the rising emphasis on sustainable practices in the dairy industry. Additionally, the versatility of sodium percarbonate, which can be used for both cleaning and sanitizing purposes, makes it an attractive option for dairy processors looking to streamline their sanitation processes.
Furthermore, the global trend towards organic and natural food products has created a niche market for chemical-free or reduced-chemical processing methods. Sodium percarbonate, being a more natural alternative to harsh chemicals, aligns well with this consumer preference. This trend is likely to drive further demand for sodium percarbonate-based sterilization solutions in the dairy industry.
The dairy equipment sterilization market is also influenced by technological advancements in cleaning and sanitizing systems. Automated cleaning-in-place (CIP) systems, which are widely used in modern dairy processing facilities, require effective and compatible sterilization agents. Sodium percarbonate's potential compatibility with these systems could further boost its demand in the industry.
In conclusion, the dairy industry's demand for sodium percarbonate as a sterilization agent is driven by a combination of factors including food safety requirements, environmental concerns, cost-effectiveness, and consumer preferences. As research continues to explore and validate its efficacy in dairy equipment sterilization, the market potential for sodium percarbonate in this application is expected to expand significantly.
Current Challenges
The application of sodium percarbonate in dairy equipment sterilization faces several significant challenges that need to be addressed for its widespread adoption. One of the primary concerns is the potential for residual chemical contamination in dairy products. While sodium percarbonate is generally considered safe, there is a need for comprehensive studies to ensure that its use does not lead to any chemical residues that could affect the quality or safety of dairy products.
Another challenge lies in the optimization of the sterilization process. The effectiveness of sodium percarbonate as a sterilizing agent can vary depending on factors such as temperature, concentration, and contact time. Determining the optimal parameters for different types of dairy equipment and various microbial contaminants requires extensive research and testing. This variability in effectiveness can lead to inconsistent sterilization results, potentially compromising food safety standards.
The stability of sodium percarbonate solutions is also a concern. When dissolved in water, sodium percarbonate releases hydrogen peroxide, which is the active sterilizing agent. However, the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide can be affected by various environmental factors, including temperature, pH, and the presence of metal ions. This instability can lead to a reduction in sterilization efficacy over time, necessitating careful monitoring and control of the sterilization process.
Compatibility with different materials used in dairy equipment is another challenge. While sodium percarbonate is generally less corrosive than some traditional sterilizing agents, its oxidizing properties may still cause damage to certain materials, particularly over prolonged use. This necessitates thorough testing and potentially the development of new, compatible materials for dairy equipment construction.
The environmental impact of using sodium percarbonate for sterilization also needs to be considered. Although it breaks down into environmentally friendly components (sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide), the large-scale use in dairy industries could potentially affect local ecosystems if not properly managed. This requires the development of effective waste management strategies and the assessment of long-term environmental effects.
Regulatory compliance presents another significant challenge. The use of sodium percarbonate as a sterilizing agent in the dairy industry must meet stringent food safety regulations in different countries. Obtaining necessary approvals and certifications can be a time-consuming and costly process, potentially slowing down the adoption of this technology.
Lastly, there is a need for comprehensive training and education within the dairy industry. The proper handling and application of sodium percarbonate for sterilization requires specific knowledge and skills. Developing effective training programs and ensuring widespread adoption of best practices is crucial for the safe and effective implementation of this sterilization method.
Another challenge lies in the optimization of the sterilization process. The effectiveness of sodium percarbonate as a sterilizing agent can vary depending on factors such as temperature, concentration, and contact time. Determining the optimal parameters for different types of dairy equipment and various microbial contaminants requires extensive research and testing. This variability in effectiveness can lead to inconsistent sterilization results, potentially compromising food safety standards.
The stability of sodium percarbonate solutions is also a concern. When dissolved in water, sodium percarbonate releases hydrogen peroxide, which is the active sterilizing agent. However, the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide can be affected by various environmental factors, including temperature, pH, and the presence of metal ions. This instability can lead to a reduction in sterilization efficacy over time, necessitating careful monitoring and control of the sterilization process.
Compatibility with different materials used in dairy equipment is another challenge. While sodium percarbonate is generally less corrosive than some traditional sterilizing agents, its oxidizing properties may still cause damage to certain materials, particularly over prolonged use. This necessitates thorough testing and potentially the development of new, compatible materials for dairy equipment construction.
The environmental impact of using sodium percarbonate for sterilization also needs to be considered. Although it breaks down into environmentally friendly components (sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide), the large-scale use in dairy industries could potentially affect local ecosystems if not properly managed. This requires the development of effective waste management strategies and the assessment of long-term environmental effects.
Regulatory compliance presents another significant challenge. The use of sodium percarbonate as a sterilizing agent in the dairy industry must meet stringent food safety regulations in different countries. Obtaining necessary approvals and certifications can be a time-consuming and costly process, potentially slowing down the adoption of this technology.
Lastly, there is a need for comprehensive training and education within the dairy industry. The proper handling and application of sodium percarbonate for sterilization requires specific knowledge and skills. Developing effective training programs and ensuring widespread adoption of best practices is crucial for the safe and effective implementation of this sterilization method.
Existing Solutions
01 Sodium percarbonate as a sterilizing agent
Sodium percarbonate is used as an effective sterilizing agent due to its ability to release hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water. This property makes it suitable for various disinfection and sterilization applications, including water treatment, surface cleaning, and medical instrument sterilization.- Sodium percarbonate as a sterilizing agent: Sodium percarbonate is used as an effective sterilizing agent due to its ability to release hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water. This property makes it suitable for various disinfection and sterilization applications, including water treatment, surface cleaning, and medical instrument sterilization.
- Formulation of sodium percarbonate-based sterilizing compositions: Various formulations of sodium percarbonate-based sterilizing compositions have been developed to enhance stability, efficacy, and ease of use. These formulations may include additives such as stabilizers, activators, and pH regulators to optimize the sterilization performance and shelf life of the product.
- Application methods for sodium percarbonate sterilization: Different application methods have been developed for sodium percarbonate sterilization, including liquid solutions, powders, tablets, and controlled-release systems. These methods are designed to suit various sterilization needs in different industries and environments, such as healthcare, food processing, and water treatment.
- Synergistic effects with other sterilizing agents: Sodium percarbonate has been found to exhibit synergistic effects when combined with other sterilizing agents or additives. These combinations can enhance the overall sterilization efficacy, broaden the spectrum of antimicrobial activity, or reduce the required concentration of individual components.
- Environmental and safety considerations: The use of sodium percarbonate for sterilization has been studied with regard to its environmental impact and safety profile. Research has focused on developing eco-friendly formulations, assessing biodegradability, and ensuring safe handling and disposal practices for sodium percarbonate-based sterilizing products.
02 Formulation of sodium percarbonate-based sterilizing compositions
Sterilizing compositions containing sodium percarbonate are formulated with additional components to enhance stability, efficacy, and ease of use. These formulations may include stabilizers, activators, surfactants, and pH adjusters to optimize the sterilizing performance of sodium percarbonate in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Sodium percarbonate sterilization in water treatment
Sodium percarbonate is utilized in water treatment processes for sterilization and disinfection purposes. It is effective in eliminating harmful microorganisms, algae, and other contaminants in various water sources, including swimming pools, industrial water systems, and drinking water supplies.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sodium percarbonate in medical and dental sterilization
The sterilizing properties of sodium percarbonate are applied in medical and dental settings for disinfecting instruments, surfaces, and equipment. Its effectiveness against a wide range of pathogens makes it suitable for maintaining hygiene standards in healthcare environments.Expand Specific Solutions05 Controlled release of sodium percarbonate for prolonged sterilization
Techniques for controlled release of sodium percarbonate have been developed to provide sustained sterilization effects. These methods involve encapsulation, coating, or incorporation into matrices to regulate the release of the active sterilizing agent over time, enhancing its long-term effectiveness in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The research on sodium percarbonate's application in dairy equipment sterilization is in a developing stage, with growing market potential due to increasing demand for effective and environmentally friendly sterilization methods in the dairy industry. The market size is expanding as more dairy companies adopt advanced sterilization techniques. Technologically, the field is moderately mature, with established players like Solvay SA, DuPont de Nemours, Inc., and Henkel AG & Co. KGaA leading innovation. These companies are investing in R&D to enhance sodium percarbonate's efficacy and safety for dairy applications. Emerging players such as Henan Jindan Lactic Acid Technology Co., Ltd. and Jiangsu Xinshenao Biotechnology Co., Ltd. are also contributing to technological advancements, intensifying competition in this niche market.
Solvay SA
Technical Solution: Solvay SA has developed advanced sodium percarbonate formulations specifically tailored for dairy equipment sterilization. Their technology focuses on enhancing the stability and efficacy of sodium percarbonate in dairy environments. The company has engineered a proprietary coating process that protects sodium percarbonate particles, allowing for prolonged release of active oxygen[1]. This controlled release mechanism ensures sustained antimicrobial activity throughout the cleaning cycle. Solvay's formulation also incorporates surfactants and chelating agents to improve the penetration of the sterilizing solution into hard-to-reach areas of dairy equipment[3]. The company has conducted extensive studies on the effectiveness of their sodium percarbonate products against common dairy pathogens, demonstrating a 99.99% reduction in bacterial load within standard cleaning times[5].
Strengths: Enhanced stability and controlled release of active oxygen, improved penetration into complex dairy equipment geometries. Weaknesses: May require higher initial investment compared to traditional chlorine-based sanitizers.
DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
Technical Solution: DuPont has innovated in the field of dairy equipment sterilization by developing a sodium percarbonate-based system that integrates with their broader clean-in-place (CIP) solutions. Their approach combines sodium percarbonate with proprietary enzymes and surfactants to create a synergistic cleaning and sterilization effect[2]. The company's research has shown that this combination can effectively remove protein and fat residues while simultaneously achieving high-level disinfection. DuPont's system utilizes a smart dosing technology that optimizes the concentration of sodium percarbonate based on real-time monitoring of organic load and water quality[4]. This adaptive approach ensures consistent sterilization results while minimizing chemical usage and environmental impact. The company has also developed specialized nozzle designs that enhance the distribution of the sodium percarbonate solution across complex dairy equipment surfaces[6].
Strengths: Integrated CIP solution with smart dosing technology, effective against both organic residues and microorganisms. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for optimal performance, potentially increasing implementation costs.
Core Innovations
Sterilization method
PatentInactiveJP2012101825A
Innovation
- Sodium percarbonate, a stable alkaline granular powder, is used as a sterilizing agent, which is dissolved in sterile water to generate hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate, allowing for stable storage and reduced transportation costs, while maintaining effective sterilization performance.
Method for preparing aqueous composition for sterilization
PatentInactiveEP1803350A3
Innovation
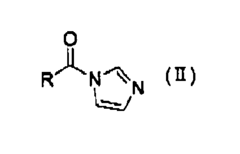
- A method involving the mixing of an acyl compound, such as N-acylimidazole, with hydrogen peroxide under acidic conditions to quickly generate peroxycarboxylic acid, creating an aqueous composition that effectively kills bacterial spores and maintains sterilization activity for repeated use.
Regulatory Compliance
The application of sodium percarbonate in dairy equipment sterilization must adhere to strict regulatory compliance standards to ensure food safety and public health. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the use of sanitizers and disinfectants in food processing facilities, including dairy operations. The FDA's Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21, Part 178 specifically addresses the use of sanitizing solutions in food processing environments.
For sodium percarbonate to be used as a sanitizer in dairy equipment, it must meet the requirements set forth in 21 CFR 178.1010, which outlines the conditions for sanitizing solutions to be safely used on food-contact surfaces. This regulation specifies the maximum concentration levels, contact times, and rinsing procedures for various sanitizing agents. Manufacturers and dairy processors must ensure that their use of sodium percarbonate aligns with these guidelines.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a role in regulating sanitizers and disinfectants through its pesticide registration program. Sodium percarbonate-based products intended for use in dairy equipment sterilization must be registered with the EPA and carry appropriate labeling that includes specific use instructions and safety precautions.
In the European Union, the use of sodium percarbonate in dairy equipment sterilization falls under the purview of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and must comply with Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 on the hygiene of foodstuffs. This regulation sets out general rules for food business operators, including those in the dairy industry, regarding the cleaning and disinfection of facilities and equipment.
Additionally, the EU Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR, Regulation (EU) 528/2012) governs the use of biocidal products, which includes disinfectants used in food and feed areas. Sodium percarbonate-based sterilization products must be authorized under this regulation before they can be placed on the EU market.
Globally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides international food standards that many countries use as a basis for their national regulations. The Codex General Principles of Food Hygiene (CXC 1-1969) includes guidelines on cleaning and sanitizing that are relevant to the use of sodium percarbonate in dairy equipment sterilization.
Compliance with these regulatory frameworks is essential for dairy processors and equipment manufacturers. They must maintain detailed records of sanitization procedures, including the concentration of sodium percarbonate used, contact times, and frequency of application. Regular audits and inspections by regulatory authorities may be conducted to ensure ongoing compliance with these standards.
For sodium percarbonate to be used as a sanitizer in dairy equipment, it must meet the requirements set forth in 21 CFR 178.1010, which outlines the conditions for sanitizing solutions to be safely used on food-contact surfaces. This regulation specifies the maximum concentration levels, contact times, and rinsing procedures for various sanitizing agents. Manufacturers and dairy processors must ensure that their use of sodium percarbonate aligns with these guidelines.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a role in regulating sanitizers and disinfectants through its pesticide registration program. Sodium percarbonate-based products intended for use in dairy equipment sterilization must be registered with the EPA and carry appropriate labeling that includes specific use instructions and safety precautions.
In the European Union, the use of sodium percarbonate in dairy equipment sterilization falls under the purview of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and must comply with Regulation (EC) No 852/2004 on the hygiene of foodstuffs. This regulation sets out general rules for food business operators, including those in the dairy industry, regarding the cleaning and disinfection of facilities and equipment.
Additionally, the EU Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR, Regulation (EU) 528/2012) governs the use of biocidal products, which includes disinfectants used in food and feed areas. Sodium percarbonate-based sterilization products must be authorized under this regulation before they can be placed on the EU market.
Globally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides international food standards that many countries use as a basis for their national regulations. The Codex General Principles of Food Hygiene (CXC 1-1969) includes guidelines on cleaning and sanitizing that are relevant to the use of sodium percarbonate in dairy equipment sterilization.
Compliance with these regulatory frameworks is essential for dairy processors and equipment manufacturers. They must maintain detailed records of sanitization procedures, including the concentration of sodium percarbonate used, contact times, and frequency of application. Regular audits and inspections by regulatory authorities may be conducted to ensure ongoing compliance with these standards.
Environmental Impact
The application of sodium percarbonate in dairy equipment sterilization presents both advantages and challenges from an environmental perspective. This compound, when dissolved in water, releases hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate, providing an effective and relatively eco-friendly sterilization solution. Unlike traditional chlorine-based disinfectants, sodium percarbonate does not produce harmful chlorinated byproducts, reducing the potential for environmental contamination.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using sodium percarbonate is its biodegradability. After use, it breaks down into water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate, leaving no persistent toxic residues in the environment. This characteristic makes it particularly suitable for dairy operations, where effluent management is a critical concern. The reduced chemical load in wastewater streams can lead to lower treatment costs and minimized environmental impact on aquatic ecosystems.
However, the environmental impact of sodium percarbonate production must also be considered. The manufacturing process typically involves the reaction of sodium carbonate with hydrogen peroxide, which requires energy input and may contribute to carbon emissions depending on the energy source. Efforts to optimize production efficiency and utilize renewable energy sources can help mitigate these environmental concerns.
In terms of resource conservation, sodium percarbonate offers advantages over traditional sterilization methods. Its concentrated form allows for reduced packaging and transportation requirements, potentially lowering the carbon footprint associated with product distribution. Additionally, the ability to use sodium percarbonate at lower temperatures compared to some other sterilization methods can result in energy savings during the cleaning process.
The impact on water quality is another important environmental consideration. While sodium percarbonate itself is not harmful to aquatic life at typical use concentrations, the release of oxygen during decomposition can temporarily affect dissolved oxygen levels in water bodies if large quantities of untreated effluent are discharged. Proper wastewater management practices are essential to prevent any adverse effects on local ecosystems.
From a lifecycle perspective, the use of sodium percarbonate in dairy equipment sterilization aligns well with principles of green chemistry. Its dual functionality as both a cleaning agent and disinfectant can reduce the overall chemical consumption in dairy operations. This streamlined approach not only simplifies the cleaning process but also minimizes the environmental footprint associated with multiple chemical products.
In conclusion, while sodium percarbonate offers several environmental advantages for dairy equipment sterilization, a holistic approach to its application is necessary to maximize its eco-friendly potential. This includes optimizing production processes, implementing efficient wastewater treatment systems, and considering the entire lifecycle of the product from manufacture to disposal. By addressing these aspects, the dairy industry can leverage sodium percarbonate as a tool for enhancing both operational efficiency and environmental sustainability.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using sodium percarbonate is its biodegradability. After use, it breaks down into water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate, leaving no persistent toxic residues in the environment. This characteristic makes it particularly suitable for dairy operations, where effluent management is a critical concern. The reduced chemical load in wastewater streams can lead to lower treatment costs and minimized environmental impact on aquatic ecosystems.
However, the environmental impact of sodium percarbonate production must also be considered. The manufacturing process typically involves the reaction of sodium carbonate with hydrogen peroxide, which requires energy input and may contribute to carbon emissions depending on the energy source. Efforts to optimize production efficiency and utilize renewable energy sources can help mitigate these environmental concerns.
In terms of resource conservation, sodium percarbonate offers advantages over traditional sterilization methods. Its concentrated form allows for reduced packaging and transportation requirements, potentially lowering the carbon footprint associated with product distribution. Additionally, the ability to use sodium percarbonate at lower temperatures compared to some other sterilization methods can result in energy savings during the cleaning process.
The impact on water quality is another important environmental consideration. While sodium percarbonate itself is not harmful to aquatic life at typical use concentrations, the release of oxygen during decomposition can temporarily affect dissolved oxygen levels in water bodies if large quantities of untreated effluent are discharged. Proper wastewater management practices are essential to prevent any adverse effects on local ecosystems.
From a lifecycle perspective, the use of sodium percarbonate in dairy equipment sterilization aligns well with principles of green chemistry. Its dual functionality as both a cleaning agent and disinfectant can reduce the overall chemical consumption in dairy operations. This streamlined approach not only simplifies the cleaning process but also minimizes the environmental footprint associated with multiple chemical products.
In conclusion, while sodium percarbonate offers several environmental advantages for dairy equipment sterilization, a holistic approach to its application is necessary to maximize its eco-friendly potential. This includes optimizing production processes, implementing efficient wastewater treatment systems, and considering the entire lifecycle of the product from manufacture to disposal. By addressing these aspects, the dairy industry can leverage sodium percarbonate as a tool for enhancing both operational efficiency and environmental sustainability.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!