ULED Technology for Superior Black Levels
JUN 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ULED Technology Background and Objectives
ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology represents a significant advancement in display technology, particularly in achieving superior black levels. This innovative approach builds upon the foundation of LED technology while introducing novel techniques to enhance contrast and image quality.
The evolution of display technologies has been driven by the pursuit of more vibrant, realistic, and energy-efficient screens. From CRT to LCD, and then to LED and OLED, each iteration has brought improvements in picture quality, color reproduction, and energy efficiency. ULED technology emerges as the next step in this progression, focusing on overcoming the limitations of existing LED displays, especially in terms of black level performance.
The primary objective of ULED technology is to achieve deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios, rivaling or surpassing the performance of OLED displays. This is accomplished through a combination of advanced local dimming techniques, quantum dot technology, and sophisticated image processing algorithms. By enhancing the ability to control light output at a more granular level, ULED aims to minimize light bleed and improve overall picture quality.
Another key goal of ULED technology is to address the shortcomings of OLED displays, such as potential burn-in issues and relatively lower brightness levels, while maintaining the advantages of LED technology, including longer lifespan and higher peak brightness. This balancing act between deep blacks and high brightness is crucial for delivering HDR (High Dynamic Range) content effectively.
The development of ULED technology is also driven by the increasing demand for larger screens with higher resolutions. As 4K and 8K displays become more prevalent, the need for technologies that can maintain image quality across larger panels becomes more critical. ULED aims to provide a solution that scales well to larger screen sizes without compromising on picture quality or energy efficiency.
In the broader context of display technology trends, ULED aligns with the industry's move towards more sustainable and energy-efficient solutions. By optimizing light output and power consumption, ULED technology seeks to reduce the environmental impact of display devices while improving performance.
As we look towards the future, the continued development of ULED technology is expected to focus on further refinements in local dimming algorithms, integration with AI-driven image processing, and advancements in quantum dot materials. These improvements will aim to push the boundaries of contrast ratios, color accuracy, and overall visual fidelity, setting new standards for display quality in various applications, from home entertainment to professional monitors.
The evolution of display technologies has been driven by the pursuit of more vibrant, realistic, and energy-efficient screens. From CRT to LCD, and then to LED and OLED, each iteration has brought improvements in picture quality, color reproduction, and energy efficiency. ULED technology emerges as the next step in this progression, focusing on overcoming the limitations of existing LED displays, especially in terms of black level performance.
The primary objective of ULED technology is to achieve deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios, rivaling or surpassing the performance of OLED displays. This is accomplished through a combination of advanced local dimming techniques, quantum dot technology, and sophisticated image processing algorithms. By enhancing the ability to control light output at a more granular level, ULED aims to minimize light bleed and improve overall picture quality.
Another key goal of ULED technology is to address the shortcomings of OLED displays, such as potential burn-in issues and relatively lower brightness levels, while maintaining the advantages of LED technology, including longer lifespan and higher peak brightness. This balancing act between deep blacks and high brightness is crucial for delivering HDR (High Dynamic Range) content effectively.
The development of ULED technology is also driven by the increasing demand for larger screens with higher resolutions. As 4K and 8K displays become more prevalent, the need for technologies that can maintain image quality across larger panels becomes more critical. ULED aims to provide a solution that scales well to larger screen sizes without compromising on picture quality or energy efficiency.
In the broader context of display technology trends, ULED aligns with the industry's move towards more sustainable and energy-efficient solutions. By optimizing light output and power consumption, ULED technology seeks to reduce the environmental impact of display devices while improving performance.
As we look towards the future, the continued development of ULED technology is expected to focus on further refinements in local dimming algorithms, integration with AI-driven image processing, and advancements in quantum dot materials. These improvements will aim to push the boundaries of contrast ratios, color accuracy, and overall visual fidelity, setting new standards for display quality in various applications, from home entertainment to professional monitors.
Market Demand for Enhanced Display Technologies
The demand for enhanced display technologies has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by the growing consumer appetite for high-quality visual experiences across various devices. ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology, with its promise of superior black levels, has emerged as a potential game-changer in this landscape. The market for premium displays, particularly in the television and high-end monitor segments, has shown significant growth potential.
Consumer preferences have shifted towards larger screens with higher resolutions, creating a natural demand for technologies that can deliver deeper blacks and improved contrast ratios. This trend is particularly evident in the home entertainment sector, where consumers are increasingly investing in immersive viewing experiences. The rise of streaming services and the production of high-quality content have further fueled this demand, as viewers seek to replicate cinema-like experiences in their homes.
In the professional sector, there is a growing need for displays with superior black levels in industries such as graphic design, video editing, and medical imaging. These fields require precise color reproduction and high contrast ratios to ensure accuracy in their work. The adoption of ULED technology in these professional markets could potentially lead to improved workflow efficiency and output quality.
The gaming industry represents another significant market segment driving the demand for enhanced display technologies. Gamers are constantly seeking displays that can offer faster response times, higher refresh rates, and better contrast ratios to gain a competitive edge. ULED technology's potential to deliver superior black levels could greatly enhance the gaming experience, particularly in titles with dark or atmospheric settings.
Mobile devices, including smartphones and tablets, are also potential beneficiaries of ULED technology. As mobile content consumption continues to rise, there is an increasing demand for displays that can deliver high-quality visuals while maintaining energy efficiency. ULED's ability to provide deep blacks could contribute to improved battery life in mobile devices, addressing a key consumer concern.
The automotive industry is another sector showing interest in advanced display technologies. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, the role of in-car displays is expanding. ULED technology could potentially enhance the visibility and clarity of instrument clusters, infotainment systems, and heads-up displays, contributing to both safety and user experience.
Consumer preferences have shifted towards larger screens with higher resolutions, creating a natural demand for technologies that can deliver deeper blacks and improved contrast ratios. This trend is particularly evident in the home entertainment sector, where consumers are increasingly investing in immersive viewing experiences. The rise of streaming services and the production of high-quality content have further fueled this demand, as viewers seek to replicate cinema-like experiences in their homes.
In the professional sector, there is a growing need for displays with superior black levels in industries such as graphic design, video editing, and medical imaging. These fields require precise color reproduction and high contrast ratios to ensure accuracy in their work. The adoption of ULED technology in these professional markets could potentially lead to improved workflow efficiency and output quality.
The gaming industry represents another significant market segment driving the demand for enhanced display technologies. Gamers are constantly seeking displays that can offer faster response times, higher refresh rates, and better contrast ratios to gain a competitive edge. ULED technology's potential to deliver superior black levels could greatly enhance the gaming experience, particularly in titles with dark or atmospheric settings.
Mobile devices, including smartphones and tablets, are also potential beneficiaries of ULED technology. As mobile content consumption continues to rise, there is an increasing demand for displays that can deliver high-quality visuals while maintaining energy efficiency. ULED's ability to provide deep blacks could contribute to improved battery life in mobile devices, addressing a key consumer concern.
The automotive industry is another sector showing interest in advanced display technologies. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, the role of in-car displays is expanding. ULED technology could potentially enhance the visibility and clarity of instrument clusters, infotainment systems, and heads-up displays, contributing to both safety and user experience.
Current ULED Challenges and Limitations
ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology has made significant strides in enhancing display quality, particularly in achieving superior black levels. However, several challenges and limitations persist in the current state of ULED technology, hindering its widespread adoption and optimal performance.
One of the primary challenges facing ULED technology is the issue of light leakage. Despite advancements in local dimming techniques, ULED displays still struggle to completely eliminate light bleed in dark scenes. This results in a slight halo effect around bright objects on dark backgrounds, compromising the overall contrast and black level performance.
Another limitation is the complexity and cost associated with manufacturing high-quality ULED panels. The intricate process of precisely controlling thousands of individual LED zones requires advanced manufacturing techniques and quality control measures. This complexity translates to higher production costs, making ULED displays less accessible to the mass market.
Power consumption remains a concern for ULED technology, especially in larger display sizes. While more energy-efficient than traditional LED-LCD displays, ULED still consumes more power than OLED alternatives, particularly when displaying bright content. This limitation becomes more pronounced in applications where energy efficiency is crucial, such as portable devices or eco-friendly home entertainment systems.
The response time of ULED displays, while improved from earlier LED technologies, still lags behind OLED in terms of pixel transition speed. This can result in slight motion blur during fast-moving scenes, which may be noticeable to discerning viewers, especially in gaming or sports content.
Uniformity issues across the display panel pose another challenge for ULED technology. Achieving consistent brightness and color accuracy across the entire screen, particularly in larger sizes, remains difficult. This can lead to visible variations in image quality, especially in scenes with uniform colors or gradients.
The limited viewing angles of ULED displays compared to OLED technology is another area of concern. While improvements have been made, off-axis viewing can still result in color shift and reduced contrast, impacting the overall viewing experience in scenarios where wide viewing angles are essential.
Lastly, the challenge of managing heat dissipation in ULED displays, especially in high-brightness scenarios, persists. Excessive heat can affect the longevity of the LEDs and potentially impact the display's performance over time, necessitating advanced cooling solutions that add to the complexity and cost of the technology.
One of the primary challenges facing ULED technology is the issue of light leakage. Despite advancements in local dimming techniques, ULED displays still struggle to completely eliminate light bleed in dark scenes. This results in a slight halo effect around bright objects on dark backgrounds, compromising the overall contrast and black level performance.
Another limitation is the complexity and cost associated with manufacturing high-quality ULED panels. The intricate process of precisely controlling thousands of individual LED zones requires advanced manufacturing techniques and quality control measures. This complexity translates to higher production costs, making ULED displays less accessible to the mass market.
Power consumption remains a concern for ULED technology, especially in larger display sizes. While more energy-efficient than traditional LED-LCD displays, ULED still consumes more power than OLED alternatives, particularly when displaying bright content. This limitation becomes more pronounced in applications where energy efficiency is crucial, such as portable devices or eco-friendly home entertainment systems.
The response time of ULED displays, while improved from earlier LED technologies, still lags behind OLED in terms of pixel transition speed. This can result in slight motion blur during fast-moving scenes, which may be noticeable to discerning viewers, especially in gaming or sports content.
Uniformity issues across the display panel pose another challenge for ULED technology. Achieving consistent brightness and color accuracy across the entire screen, particularly in larger sizes, remains difficult. This can lead to visible variations in image quality, especially in scenes with uniform colors or gradients.
The limited viewing angles of ULED displays compared to OLED technology is another area of concern. While improvements have been made, off-axis viewing can still result in color shift and reduced contrast, impacting the overall viewing experience in scenarios where wide viewing angles are essential.
Lastly, the challenge of managing heat dissipation in ULED displays, especially in high-brightness scenarios, persists. Excessive heat can affect the longevity of the LEDs and potentially impact the display's performance over time, necessitating advanced cooling solutions that add to the complexity and cost of the technology.
Existing ULED Black Level Enhancement Solutions
01 ULED backlight control for improved black levels
ULED technology employs advanced backlight control techniques to enhance black levels in displays. This involves precise dimming of LED zones behind the screen, allowing for deeper blacks and improved contrast ratios. The technology can dynamically adjust backlight intensity based on image content, resulting in more vibrant and realistic picture quality.- ULED backlight control for improved black levels: ULED technology employs advanced backlight control techniques to enhance black levels in displays. This involves precise dimming of LED zones behind the screen, allowing for deeper blacks and improved contrast ratios. The technology can dynamically adjust the backlight based on image content, resulting in more vibrant and realistic picture quality.
- Quantum dot enhancement for color accuracy: ULED displays often incorporate quantum dot technology to improve color accuracy and expand the color gamut. This combination allows for more precise control over color reproduction, particularly in darker scenes, contributing to better overall black levels and image quality. The quantum dots enhance the purity of colors, resulting in more lifelike and saturated images.
- Local dimming algorithms for contrast enhancement: Advanced local dimming algorithms are employed in ULED technology to optimize contrast and black levels. These algorithms analyze incoming video signals and selectively dim or brighten specific areas of the screen. This results in improved perceived contrast ratios and deeper blacks, especially in high dynamic range (HDR) content.
- Panel design optimization for black level performance: ULED technology incorporates optimized panel designs to enhance black level performance. This includes improvements in LCD panel structure, light-blocking layers, and pixel arrangements. These design enhancements work in conjunction with the backlight control to minimize light leakage and achieve deeper blacks across the entire display.
- Image processing techniques for black level enhancement: ULED displays utilize advanced image processing techniques to further improve black levels and overall picture quality. These may include adaptive contrast enhancement, shadow detail preservation, and noise reduction algorithms. The processing helps to maintain deep blacks while preserving detail in dark scenes, resulting in a more immersive viewing experience.
02 Quantum dot enhancement for color accuracy
ULED displays often incorporate quantum dot technology to improve color accuracy and expand the color gamut. This combination allows for more precise control over color reproduction, particularly in dark scenes, contributing to better overall black levels and image quality. The quantum dots enhance the purity of colors, resulting in more lifelike and saturated images.Expand Specific Solutions03 Local dimming algorithms for contrast enhancement
Advanced local dimming algorithms are implemented in ULED displays to optimize contrast and black levels. These algorithms analyze incoming video signals and selectively dim or brighten specific areas of the screen. This results in improved perceived contrast ratios and deeper blacks, especially in high dynamic range (HDR) content.Expand Specific Solutions04 Panel technology optimization for black level performance
ULED technology incorporates optimized panel designs to enhance black level performance. This includes improvements in liquid crystal alignment, pixel structure, and light-blocking layers. These enhancements work in conjunction with the backlight control to minimize light leakage and achieve deeper blacks across the entire display surface.Expand Specific Solutions05 Image processing techniques for black level enhancement
ULED displays employ sophisticated image processing algorithms to further improve black levels and overall picture quality. These techniques may include adaptive contrast enhancement, shadow detail preservation, and noise reduction in dark areas. The processing helps to maintain deep blacks while preserving detail in shadowy regions of the image.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ULED Development
The research on ULED technology for superior black levels is currently in a competitive and rapidly evolving phase. The market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for high-quality displays in various sectors. While the technology is advancing, it is not yet fully mature, with several key players pushing the boundaries of innovation. Companies like Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE Technology Group are at the forefront, investing heavily in R&D to enhance ULED performance. Other notable contributors include TCL, Hisense, and emerging players like Appotronics. The competition is fierce, with each company striving to achieve deeper blacks, improved contrast ratios, and overall superior image quality, indicating a dynamic and promising future for ULED technology.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed Quantum Dot OLED (QD-OLED) technology for superior black levels in ULED displays. This innovative approach combines the benefits of OLED's self-emitting pixels with quantum dot color conversion. The result is a display that can achieve perfect blacks by turning off individual pixels, while also delivering enhanced color volume and brightness. Samsung's QD-OLED panels use blue OLED as the light source, with red and green quantum dots for color conversion, allowing for more efficient energy usage and potentially longer panel lifespan compared to traditional OLED.
Strengths: Exceptional contrast ratios, wider color gamut, and improved energy efficiency. Weaknesses: Higher production costs and potential for blue OLED degradation over time.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed advanced Mini-LED backlight technology for their ULED displays to achieve superior black levels. This approach uses thousands of miniature LED chips as the backlight source, allowing for precise local dimming control. BOE's Mini-LED ULED displays can have up to thousands of local dimming zones, significantly reducing light blooming and enhancing contrast. The company has also implemented sophisticated algorithms to optimize the dimming process, ensuring smooth transitions between bright and dark areas of the image. Additionally, BOE is exploring the integration of quantum dot technology with their Mini-LED backlight to further improve color performance.
Strengths: High brightness capabilities, improved contrast over traditional LED-LCD, and lower cost than OLED. Weaknesses: Not as perfect black levels as OLED and potential for visible blooming in some scenarios.
Core Innovations in ULED Black Level Technology
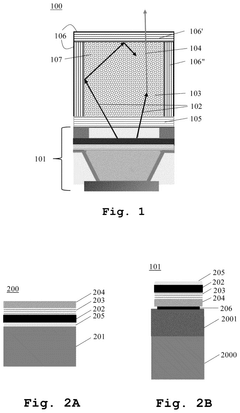
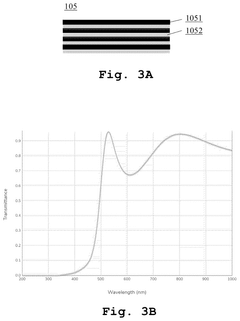
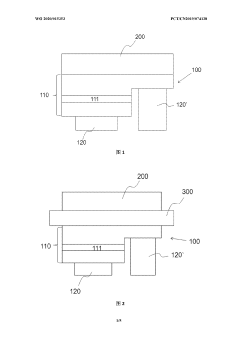
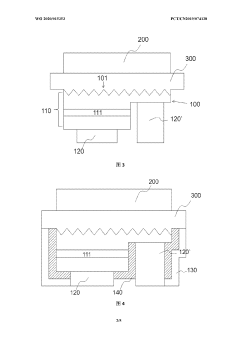
An optoelectronic device with color conversion and with conformal DBR and an associated fabrication method
PatentPendingUS20250151479A1
Innovation
- The proposed optoelectronic device incorporates a semiconductor light-emitting component with a cavity filled with wavelength conversion material, surrounded by multilayer interference reflectors that enhance light conversion and isolation, allowing for improved light emission efficiency and longer device lifetime.
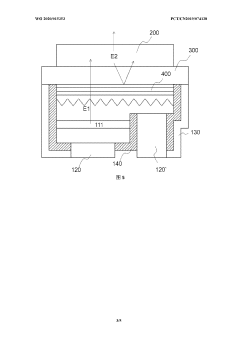
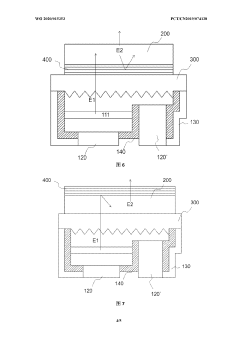
Micro light emitting device and display thereof
PatentWO2020015353A1
Innovation
- Using a micro-light-emitting diode structure with a transparent adhesive layer, the blue/green light is converted into red light through photon conversion technology, the AlInGaP-based quantum well layer is used to achieve efficient photon conversion, and anti-reflection and anti-reflection are set on the micro-light-emitting diode. The film layer and light reflective layer optimize the light emission efficiency.
Environmental Impact of ULED Manufacturing
The environmental impact of ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) manufacturing is a critical consideration in the development and adoption of this advanced display technology. As ULED production scales up to meet growing market demand, it is essential to assess and mitigate potential environmental consequences throughout the manufacturing process.
ULED manufacturing involves several stages that can have significant environmental implications. The production of ultra-thin quantum dot layers, a key component of ULED displays, requires the use of rare earth elements and heavy metals. The extraction and processing of these materials can lead to soil degradation, water pollution, and ecosystem disruption in mining areas. Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of ULED production contributes to increased carbon emissions, particularly in regions where manufacturing facilities rely on fossil fuel-based energy sources.
The use of hazardous chemicals in ULED manufacturing processes poses another environmental concern. Solvents, etching agents, and other potentially toxic substances are employed in various stages of production, necessitating stringent waste management protocols to prevent contamination of local water sources and soil. Proper disposal and recycling of these materials are crucial to minimizing their environmental impact.
Water consumption is another significant factor in ULED manufacturing. The production process requires large volumes of ultra-pure water for cleaning and cooling purposes. In water-stressed regions, this demand can exacerbate existing water scarcity issues and potentially lead to conflicts with local communities over water resources.
However, it is important to note that ULED technology also offers potential environmental benefits. The superior energy efficiency of ULED displays compared to traditional LED and OLED technologies can lead to reduced power consumption during the use phase of the product lifecycle. This efficiency gain may partially offset the environmental impact of the manufacturing process over the long term.
To address these environmental challenges, manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices in ULED production. These include implementing closed-loop water recycling systems, investing in renewable energy sources for manufacturing facilities, and developing more efficient production techniques that reduce material waste and energy consumption. Additionally, research into alternative materials and production methods that minimize the use of rare earth elements and hazardous chemicals is ongoing.
As ULED technology continues to evolve, it is crucial for manufacturers to prioritize environmental sustainability alongside performance improvements. This approach will not only help mitigate the ecological footprint of ULED production but also enhance the technology's overall value proposition in an increasingly environmentally conscious market.
ULED manufacturing involves several stages that can have significant environmental implications. The production of ultra-thin quantum dot layers, a key component of ULED displays, requires the use of rare earth elements and heavy metals. The extraction and processing of these materials can lead to soil degradation, water pollution, and ecosystem disruption in mining areas. Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of ULED production contributes to increased carbon emissions, particularly in regions where manufacturing facilities rely on fossil fuel-based energy sources.
The use of hazardous chemicals in ULED manufacturing processes poses another environmental concern. Solvents, etching agents, and other potentially toxic substances are employed in various stages of production, necessitating stringent waste management protocols to prevent contamination of local water sources and soil. Proper disposal and recycling of these materials are crucial to minimizing their environmental impact.
Water consumption is another significant factor in ULED manufacturing. The production process requires large volumes of ultra-pure water for cleaning and cooling purposes. In water-stressed regions, this demand can exacerbate existing water scarcity issues and potentially lead to conflicts with local communities over water resources.
However, it is important to note that ULED technology also offers potential environmental benefits. The superior energy efficiency of ULED displays compared to traditional LED and OLED technologies can lead to reduced power consumption during the use phase of the product lifecycle. This efficiency gain may partially offset the environmental impact of the manufacturing process over the long term.
To address these environmental challenges, manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices in ULED production. These include implementing closed-loop water recycling systems, investing in renewable energy sources for manufacturing facilities, and developing more efficient production techniques that reduce material waste and energy consumption. Additionally, research into alternative materials and production methods that minimize the use of rare earth elements and hazardous chemicals is ongoing.
As ULED technology continues to evolve, it is crucial for manufacturers to prioritize environmental sustainability alongside performance improvements. This approach will not only help mitigate the ecological footprint of ULED production but also enhance the technology's overall value proposition in an increasingly environmentally conscious market.
ULED Integration in Consumer Electronics
The integration of ULED (Ultra Light Emitting Diode) technology in consumer electronics represents a significant advancement in display technology, particularly in achieving superior black levels. This integration has been driven by the increasing demand for high-quality visual experiences in various consumer devices, including televisions, smartphones, and tablets.
ULED technology leverages advanced local dimming techniques, which allow for precise control of backlight zones. This enables the display to achieve deeper blacks by selectively dimming or turning off LEDs in darker areas of the image. The result is a significant improvement in contrast ratio and overall picture quality, rivaling that of OLED displays while potentially offering advantages in terms of cost and longevity.
In the television market, ULED integration has been particularly impactful. Major manufacturers have introduced ULED-equipped models that offer enhanced HDR performance and improved color accuracy. These televisions typically feature thousands of local dimming zones, allowing for granular control of brightness across the screen. This level of control not only enhances black levels but also reduces blooming effects, where light from bright areas bleeds into adjacent dark areas.
The smartphone industry has also begun to adopt ULED technology, albeit at a slower pace. The integration of ULED in mobile devices presents unique challenges due to size and power constraints. However, some manufacturers have successfully implemented ULED backlighting in their flagship models, offering improved display quality and energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD screens.
Beyond televisions and smartphones, ULED technology is finding applications in other consumer electronics sectors. High-end computer monitors, particularly those targeted at gaming and professional content creation, are incorporating ULED backlighting to deliver superior image quality and responsiveness. Additionally, automotive displays are beginning to utilize ULED technology to enhance visibility and reduce power consumption in vehicle infotainment systems.
The integration of ULED technology in consumer electronics has also spurred advancements in related areas. For instance, improvements in LED manufacturing processes have led to more efficient and smaller LEDs, enabling even finer control of local dimming zones. Furthermore, the development of sophisticated algorithms for managing ULED backlighting has become a key area of research and development for display manufacturers.
As ULED technology continues to evolve, its integration in consumer electronics is expected to expand further. Future developments may include the incorporation of mini-LED and micro-LED technologies, which could offer even greater control over local dimming and potentially rival the pixel-level control of OLED displays. This ongoing innovation in ULED technology promises to deliver increasingly immersive and high-quality visual experiences across a wide range of consumer electronic devices.
ULED technology leverages advanced local dimming techniques, which allow for precise control of backlight zones. This enables the display to achieve deeper blacks by selectively dimming or turning off LEDs in darker areas of the image. The result is a significant improvement in contrast ratio and overall picture quality, rivaling that of OLED displays while potentially offering advantages in terms of cost and longevity.
In the television market, ULED integration has been particularly impactful. Major manufacturers have introduced ULED-equipped models that offer enhanced HDR performance and improved color accuracy. These televisions typically feature thousands of local dimming zones, allowing for granular control of brightness across the screen. This level of control not only enhances black levels but also reduces blooming effects, where light from bright areas bleeds into adjacent dark areas.
The smartphone industry has also begun to adopt ULED technology, albeit at a slower pace. The integration of ULED in mobile devices presents unique challenges due to size and power constraints. However, some manufacturers have successfully implemented ULED backlighting in their flagship models, offering improved display quality and energy efficiency compared to traditional LCD screens.
Beyond televisions and smartphones, ULED technology is finding applications in other consumer electronics sectors. High-end computer monitors, particularly those targeted at gaming and professional content creation, are incorporating ULED backlighting to deliver superior image quality and responsiveness. Additionally, automotive displays are beginning to utilize ULED technology to enhance visibility and reduce power consumption in vehicle infotainment systems.
The integration of ULED technology in consumer electronics has also spurred advancements in related areas. For instance, improvements in LED manufacturing processes have led to more efficient and smaller LEDs, enabling even finer control of local dimming zones. Furthermore, the development of sophisticated algorithms for managing ULED backlighting has become a key area of research and development for display manufacturers.
As ULED technology continues to evolve, its integration in consumer electronics is expected to expand further. Future developments may include the incorporation of mini-LED and micro-LED technologies, which could offer even greater control over local dimming and potentially rival the pixel-level control of OLED displays. This ongoing innovation in ULED technology promises to deliver increasingly immersive and high-quality visual experiences across a wide range of consumer electronic devices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!