Luminol in Developing Forward-Thinking Analytical Models
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luminol Analysis Background and Objectives
Luminol, a chemiluminescent compound, has been a cornerstone in forensic science and biochemical research for decades. Its ability to emit light when oxidized has made it invaluable in detecting trace amounts of blood and other biological materials. However, recent advancements in analytical techniques and data processing have opened up new possibilities for luminol beyond its traditional applications.
The evolution of luminol-based technologies has been driven by the increasing demand for more sensitive, accurate, and versatile analytical tools across various industries. From environmental monitoring to medical diagnostics, the potential applications of luminol continue to expand. This research aims to explore innovative ways to leverage luminol's unique properties in developing cutting-edge analytical models that can address complex challenges in multiple fields.
One of the primary objectives of this research is to investigate the integration of luminol-based detection systems with advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms. By combining the chemical sensitivity of luminol with the power of artificial intelligence, we aim to create predictive models that can enhance the accuracy and speed of analysis in real-time scenarios. This fusion of chemistry and computational science has the potential to revolutionize how we approach problem-solving in areas such as crime scene investigation, water quality assessment, and early disease detection.
Another key focus of this study is to explore the development of novel luminol derivatives that exhibit enhanced specificity and sensitivity. By modifying the chemical structure of luminol, we aim to create compounds that can selectively detect specific molecules or pathogens with unprecedented precision. This research direction could lead to the creation of highly targeted analytical tools for use in medical diagnostics, food safety testing, and environmental monitoring.
Furthermore, this research seeks to investigate the potential of luminol in developing non-invasive imaging techniques. By leveraging the compound's chemiluminescent properties, we aim to create new methods for visualizing biological processes in living organisms without the need for harmful radiation or invasive procedures. This could have significant implications for medical imaging, particularly in the early detection of diseases and the monitoring of treatment efficacy.
As we embark on this research journey, our ultimate goal is to push the boundaries of what is possible with luminol-based analytical models. By combining interdisciplinary approaches and cutting-edge technologies, we aim to develop forward-thinking solutions that can address some of the most pressing challenges in science, healthcare, and environmental protection. The outcomes of this research have the potential to not only advance our understanding of luminol's capabilities but also to create practical applications that can make a tangible impact on various aspects of our lives and industries.
The evolution of luminol-based technologies has been driven by the increasing demand for more sensitive, accurate, and versatile analytical tools across various industries. From environmental monitoring to medical diagnostics, the potential applications of luminol continue to expand. This research aims to explore innovative ways to leverage luminol's unique properties in developing cutting-edge analytical models that can address complex challenges in multiple fields.
One of the primary objectives of this research is to investigate the integration of luminol-based detection systems with advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms. By combining the chemical sensitivity of luminol with the power of artificial intelligence, we aim to create predictive models that can enhance the accuracy and speed of analysis in real-time scenarios. This fusion of chemistry and computational science has the potential to revolutionize how we approach problem-solving in areas such as crime scene investigation, water quality assessment, and early disease detection.
Another key focus of this study is to explore the development of novel luminol derivatives that exhibit enhanced specificity and sensitivity. By modifying the chemical structure of luminol, we aim to create compounds that can selectively detect specific molecules or pathogens with unprecedented precision. This research direction could lead to the creation of highly targeted analytical tools for use in medical diagnostics, food safety testing, and environmental monitoring.
Furthermore, this research seeks to investigate the potential of luminol in developing non-invasive imaging techniques. By leveraging the compound's chemiluminescent properties, we aim to create new methods for visualizing biological processes in living organisms without the need for harmful radiation or invasive procedures. This could have significant implications for medical imaging, particularly in the early detection of diseases and the monitoring of treatment efficacy.
As we embark on this research journey, our ultimate goal is to push the boundaries of what is possible with luminol-based analytical models. By combining interdisciplinary approaches and cutting-edge technologies, we aim to develop forward-thinking solutions that can address some of the most pressing challenges in science, healthcare, and environmental protection. The outcomes of this research have the potential to not only advance our understanding of luminol's capabilities but also to create practical applications that can make a tangible impact on various aspects of our lives and industries.
Market Demand for Advanced Analytical Models
The market demand for advanced analytical models utilizing Luminol has been steadily increasing across various industries. This growth is primarily driven by the need for more sophisticated and accurate predictive capabilities in fields such as forensic science, environmental monitoring, and biomedical research. Luminol, known for its chemiluminescent properties, has shown great potential in enhancing the sensitivity and specificity of analytical models.
In the forensic science sector, there is a growing demand for more reliable and non-invasive methods of crime scene investigation. Advanced analytical models incorporating Luminol technology can provide investigators with improved tools for detecting and analyzing trace evidence, particularly in cases involving blood residue detection. This has led to increased interest from law enforcement agencies and forensic laboratories worldwide.
The environmental monitoring industry has also shown significant interest in Luminol-based analytical models. With increasing concerns about water and soil contamination, there is a pressing need for more sensitive and rapid detection methods. Luminol's ability to react with certain metal ions and organic compounds makes it an attractive option for developing advanced sensors and monitoring systems. This has caught the attention of environmental agencies, water treatment facilities, and industrial plants seeking to improve their pollution detection and control measures.
In the biomedical research field, the demand for advanced analytical models is driven by the need for more precise and efficient diagnostic tools. Luminol's chemiluminescent properties can be harnessed to develop highly sensitive assays for detecting specific biomarkers or cellular activities. This has applications in early disease detection, drug discovery, and personalized medicine, attracting interest from pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and healthcare providers.
The market for these advanced analytical models is further bolstered by the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies. These technologies can enhance the interpretation of Luminol-based signals, leading to more accurate and reliable results. This convergence of chemical and computational techniques has opened up new possibilities for data-driven decision-making in various fields.
As industries continue to prioritize efficiency, accuracy, and innovation, the demand for advanced analytical models using Luminol is expected to grow. This trend is likely to drive further research and development in this area, leading to more sophisticated and versatile applications of Luminol-based technologies across multiple sectors.
In the forensic science sector, there is a growing demand for more reliable and non-invasive methods of crime scene investigation. Advanced analytical models incorporating Luminol technology can provide investigators with improved tools for detecting and analyzing trace evidence, particularly in cases involving blood residue detection. This has led to increased interest from law enforcement agencies and forensic laboratories worldwide.
The environmental monitoring industry has also shown significant interest in Luminol-based analytical models. With increasing concerns about water and soil contamination, there is a pressing need for more sensitive and rapid detection methods. Luminol's ability to react with certain metal ions and organic compounds makes it an attractive option for developing advanced sensors and monitoring systems. This has caught the attention of environmental agencies, water treatment facilities, and industrial plants seeking to improve their pollution detection and control measures.
In the biomedical research field, the demand for advanced analytical models is driven by the need for more precise and efficient diagnostic tools. Luminol's chemiluminescent properties can be harnessed to develop highly sensitive assays for detecting specific biomarkers or cellular activities. This has applications in early disease detection, drug discovery, and personalized medicine, attracting interest from pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and healthcare providers.
The market for these advanced analytical models is further bolstered by the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies. These technologies can enhance the interpretation of Luminol-based signals, leading to more accurate and reliable results. This convergence of chemical and computational techniques has opened up new possibilities for data-driven decision-making in various fields.
As industries continue to prioritize efficiency, accuracy, and innovation, the demand for advanced analytical models using Luminol is expected to grow. This trend is likely to drive further research and development in this area, leading to more sophisticated and versatile applications of Luminol-based technologies across multiple sectors.
Current Luminol Applications and Challenges
Luminol, a chemiluminescent compound, has been widely used in forensic science for blood detection. However, its applications in developing forward-thinking analytical models are still in the early stages, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Currently, luminol is primarily employed in crime scene investigations to detect trace amounts of blood, even after cleaning attempts. Its ability to react with the iron in hemoglobin, producing a blue glow, makes it an invaluable tool for forensic analysts.
In recent years, researchers have begun exploring luminol's potential in other analytical fields. One promising application is in environmental monitoring, where luminol-based systems are being developed to detect heavy metal pollutants in water sources. These systems leverage luminol's sensitivity to certain metal ions, allowing for rapid and cost-effective water quality assessments. However, challenges remain in improving the specificity and reliability of these tests in complex environmental matrices.
The medical field has also shown interest in luminol-based analytical models. Researchers are investigating its use in diagnostic tools for detecting certain biomarkers in blood samples. The high sensitivity of luminol reactions could potentially enable earlier disease detection or more accurate monitoring of treatment efficacy. However, the development of such applications faces significant hurdles, including the need for standardization and the elimination of false positives due to interfering substances in biological samples.
In the realm of food safety, luminol-based methods are being explored for detecting contamination and assessing food quality. These applications aim to provide rapid, on-site testing capabilities for various contaminants, including bacterial presence and chemical adulterants. While promising, these methods still require refinement to match the accuracy of traditional laboratory techniques and to overcome limitations in complex food matrices.
One of the main challenges in expanding luminol's applications is its relative lack of specificity. While highly sensitive, luminol can react with various substances besides blood, potentially leading to false positives in forensic contexts or inaccurate results in other analytical applications. Researchers are working on developing more specific luminol derivatives or combining luminol with other detection methods to improve selectivity.
Another significant challenge is the stability and longevity of luminol-based solutions. The chemiluminescent reaction is time-sensitive, which can limit its practical use in certain analytical models, especially those requiring prolonged or repeated measurements. Efforts are underway to develop more stable formulations or to integrate luminol into systems that can generate the compound on-demand.
The integration of luminol-based detection methods with advanced technologies, such as machine learning and image analysis, represents a promising frontier. These combinations could potentially enhance the accuracy and interpretability of luminol-based tests, opening up new avenues for its application in various analytical models. However, the development of such integrated systems requires interdisciplinary collaboration and significant research investment.
In recent years, researchers have begun exploring luminol's potential in other analytical fields. One promising application is in environmental monitoring, where luminol-based systems are being developed to detect heavy metal pollutants in water sources. These systems leverage luminol's sensitivity to certain metal ions, allowing for rapid and cost-effective water quality assessments. However, challenges remain in improving the specificity and reliability of these tests in complex environmental matrices.
The medical field has also shown interest in luminol-based analytical models. Researchers are investigating its use in diagnostic tools for detecting certain biomarkers in blood samples. The high sensitivity of luminol reactions could potentially enable earlier disease detection or more accurate monitoring of treatment efficacy. However, the development of such applications faces significant hurdles, including the need for standardization and the elimination of false positives due to interfering substances in biological samples.
In the realm of food safety, luminol-based methods are being explored for detecting contamination and assessing food quality. These applications aim to provide rapid, on-site testing capabilities for various contaminants, including bacterial presence and chemical adulterants. While promising, these methods still require refinement to match the accuracy of traditional laboratory techniques and to overcome limitations in complex food matrices.
One of the main challenges in expanding luminol's applications is its relative lack of specificity. While highly sensitive, luminol can react with various substances besides blood, potentially leading to false positives in forensic contexts or inaccurate results in other analytical applications. Researchers are working on developing more specific luminol derivatives or combining luminol with other detection methods to improve selectivity.
Another significant challenge is the stability and longevity of luminol-based solutions. The chemiluminescent reaction is time-sensitive, which can limit its practical use in certain analytical models, especially those requiring prolonged or repeated measurements. Efforts are underway to develop more stable formulations or to integrate luminol into systems that can generate the compound on-demand.
The integration of luminol-based detection methods with advanced technologies, such as machine learning and image analysis, represents a promising frontier. These combinations could potentially enhance the accuracy and interpretability of luminol-based tests, opening up new avenues for its application in various analytical models. However, the development of such integrated systems requires interdisciplinary collaboration and significant research investment.
Existing Luminol-based Analytical Models
01 Analytical models for luminol chemiluminescence
Development of analytical models to predict and analyze the chemiluminescence reaction of luminol. These models aim to understand the kinetics, intensity, and duration of the light emission process, which is crucial for various applications in forensic science and biochemical analysis.- Analytical modeling for luminol-based detection systems: Analytical models are developed to optimize luminol-based detection systems. These models incorporate various parameters such as reaction kinetics, light emission characteristics, and detection sensitivity to improve the accuracy and efficiency of luminol-based analytical techniques.
- Machine learning approaches for luminol data analysis: Machine learning algorithms are applied to analyze and interpret data from luminol-based experiments. These approaches can enhance pattern recognition, anomaly detection, and predictive modeling in luminol analytical applications, improving the overall performance of the analytical process.
- Simulation and modeling of luminol chemiluminescence: Computational models are developed to simulate the chemiluminescence process of luminol reactions. These simulations help in understanding the underlying mechanisms, predicting reaction outcomes, and optimizing experimental conditions for luminol-based analytical techniques.
- Integration of luminol models in forensic analysis systems: Analytical models for luminol reactions are integrated into comprehensive forensic analysis systems. These integrated models enhance the accuracy and reliability of crime scene investigations by providing more precise interpretations of luminol-based evidence detection.
- Optimization of luminol reaction parameters through modeling: Mathematical models are used to optimize various parameters in luminol reactions, such as reagent concentrations, pH levels, and reaction time. These optimizations lead to improved sensitivity, specificity, and reproducibility in luminol-based analytical methods.
02 Machine learning approaches for luminol analysis
Application of machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence techniques to improve the accuracy and efficiency of luminol-based analytical models. These approaches can help in pattern recognition, data interpretation, and predictive analysis of luminol reactions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Simulation and modeling of luminol reactions
Creation of computer simulations and mathematical models to replicate and study luminol reactions in various conditions. These models can help in optimizing experimental parameters, predicting outcomes, and understanding complex reaction mechanisms without the need for extensive physical experiments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of luminol models with analytical instruments
Development of analytical models that can be integrated with spectrophotometers, fluorometers, and other analytical instruments to enhance the detection and quantification of luminol-based reactions. This integration aims to improve sensitivity, accuracy, and real-time analysis capabilities.Expand Specific Solutions05 Data analysis and interpretation for luminol experiments
Creation of specialized analytical models for processing and interpreting data obtained from luminol experiments. These models focus on signal processing, noise reduction, and statistical analysis to extract meaningful information from raw experimental data and improve the overall reliability of luminol-based analytical techniques.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Luminol Research and Development
The research on using Luminol in developing forward-thinking analytical models is in an early stage of development, with a growing market potential as the technology matures. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of academic institutions, research centers, and private companies exploring innovative applications. Key players like MetrioPharm AG, Alverix, Inc., and Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics are investing in R&D to leverage Luminol's chemiluminescent properties for advanced analytical techniques. While the market size is currently modest, it is expected to expand as the technology demonstrates its utility in various fields, including medical diagnostics, forensic science, and environmental monitoring.
Washington University in St. Louis
Technical Solution: Washington University in St. Louis has made significant strides in developing forward-thinking analytical models using Luminol. Their research focuses on enhancing the sensitivity and specificity of Luminol-based detection systems through advanced signal processing and machine learning techniques. The university's team has developed a novel approach that combines Luminol's chemiluminescent properties with spectral analysis and pattern recognition algorithms[4]. This innovative method allows for the differentiation of various biological materials and contaminants with unprecedented accuracy. The model utilizes a multi-layered neural network to analyze the spectral signatures produced by Luminol reactions, enabling the identification of specific compounds even in complex mixtures[5]. Additionally, the research incorporates predictive modeling to anticipate potential interferences and adjust the analysis accordingly, further improving the robustness of the system[6].
Strengths: High specificity in complex mixtures, advanced pattern recognition capabilities, and predictive modeling for improved accuracy. Weaknesses: May require substantial computational resources and specialized knowledge for optimal performance.
South China University of Technology
Technical Solution: South China University of Technology has made significant advancements in using Luminol for developing forward-thinking analytical models. Their research focuses on combining Luminol-based detection with nanotechnology and microfluidics to create highly sensitive and miniaturized analytical systems. The university's team has developed a novel microfluidic chip that incorporates Luminol-functionalized nanoparticles for enhanced chemiluminescence detection[10]. This innovative approach allows for the analysis of extremely small sample volumes with high sensitivity and specificity. The analytical model utilizes advanced image processing algorithms to analyze the spatial and temporal patterns of chemiluminescence within the microfluidic channels, enabling multi-analyte detection in a single assay[11]. Additionally, the research team has implemented machine learning techniques to optimize the flow conditions and reaction parameters in real-time, further improving the system's performance and adaptability to various sample types[12].
Strengths: Miniaturization for portable applications, high sensitivity with small sample volumes, and multi-analyte detection capabilities. Weaknesses: May face challenges in scaling up for high-throughput applications and potential issues with nanoparticle stability over time.
Innovative Approaches in Luminol Analysis
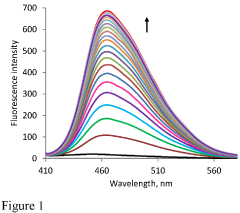
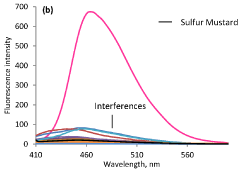
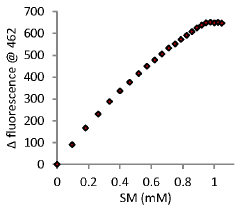
A rapid method for naked-eye detection of sulfur mustard at room temperature
PatentActiveIN202111056218A
Innovation
- A novel chemosensing system utilizing luminol and ionic liquid (l-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium dicyanamide) at pH 8.5, which enables rapid, selective, and sensitive detection of sulfur mustard through turn-on fluorescence and chromogenic methods, allowing for detection within seconds at room temperature.
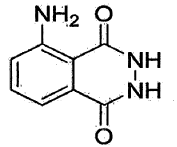
Method for producing a crystalline form of 5-amino-2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione
PatentWO2017140422A1
Innovation
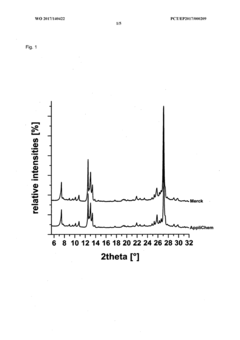
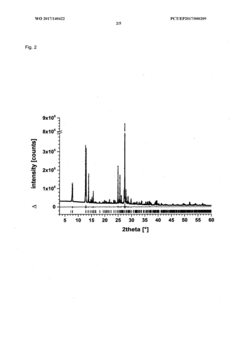
- A method involving dissolving 5-amino-2,3-dihydrophthalazine-1,4-dione in a refluxing ethanol-water solution, cooling, separating the precipitated crystals, and drying to produce a phase-pure crystalline form of luminol, which can be resuspended and washed for enhanced purity.
Regulatory Considerations for Luminol Use
The use of luminol in developing forward-thinking analytical models must adhere to strict regulatory guidelines to ensure safety, reliability, and ethical considerations. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) play crucial roles in regulating the use of luminol and similar chemiluminescent compounds. These agencies establish exposure limits, handling protocols, and disposal procedures to protect both workers and the environment.
Internationally, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) under the REACH regulation (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) governs the use of luminol in European Union member states. Researchers and manufacturers must comply with REACH requirements for registration, safety data sheets, and risk assessments when developing analytical models using luminol.
In the context of forensic applications, the use of luminol must align with legal standards for evidence collection and preservation. The admissibility of luminol-based evidence in court proceedings varies by jurisdiction, necessitating careful consideration of local laws and precedents. Researchers developing analytical models must work closely with legal experts to ensure their methodologies meet evidentiary standards.
Ethical considerations also play a significant role in the regulatory landscape. Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) or Ethics Committees must approve research protocols involving luminol, particularly when human subjects or sensitive information are involved. These bodies ensure that the research adheres to principles of informed consent, privacy protection, and minimization of potential harm.
As luminol-based analytical models advance, regulatory frameworks may need to evolve to address emerging applications and potential risks. Researchers and developers should actively engage with regulatory bodies to help shape future guidelines that balance innovation with safety and ethical concerns. This proactive approach can help streamline the approval process for new luminol-based technologies and ensure their responsible implementation across various sectors.
Compliance with Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is essential for the development and production of luminol-based analytical tools. These standards, enforced by agencies such as the FDA in the United States, ensure the quality, consistency, and reliability of research outcomes and manufactured products. Adherence to these practices is crucial for gaining regulatory approval and maintaining public trust in luminol-based technologies.
Internationally, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) under the REACH regulation (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) governs the use of luminol in European Union member states. Researchers and manufacturers must comply with REACH requirements for registration, safety data sheets, and risk assessments when developing analytical models using luminol.
In the context of forensic applications, the use of luminol must align with legal standards for evidence collection and preservation. The admissibility of luminol-based evidence in court proceedings varies by jurisdiction, necessitating careful consideration of local laws and precedents. Researchers developing analytical models must work closely with legal experts to ensure their methodologies meet evidentiary standards.
Ethical considerations also play a significant role in the regulatory landscape. Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) or Ethics Committees must approve research protocols involving luminol, particularly when human subjects or sensitive information are involved. These bodies ensure that the research adheres to principles of informed consent, privacy protection, and minimization of potential harm.
As luminol-based analytical models advance, regulatory frameworks may need to evolve to address emerging applications and potential risks. Researchers and developers should actively engage with regulatory bodies to help shape future guidelines that balance innovation with safety and ethical concerns. This proactive approach can help streamline the approval process for new luminol-based technologies and ensure their responsible implementation across various sectors.
Compliance with Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is essential for the development and production of luminol-based analytical tools. These standards, enforced by agencies such as the FDA in the United States, ensure the quality, consistency, and reliability of research outcomes and manufactured products. Adherence to these practices is crucial for gaining regulatory approval and maintaining public trust in luminol-based technologies.
Environmental Impact of Luminol Applications
The use of luminol in analytical models has raised significant environmental concerns that warrant careful consideration. Luminol, a chemiluminescent compound widely used in forensic science and biomedical research, can have both direct and indirect impacts on the environment when applied in large-scale analytical processes.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential for luminol and its byproducts to contaminate water systems. When luminol reacts with oxidizing agents, it produces aminophthalate ions and nitrogen gas. While these byproducts are generally considered non-toxic, their accumulation in aquatic ecosystems could potentially disrupt the delicate balance of microbial communities and affect water quality. Furthermore, the presence of luminol in wastewater may interfere with conventional water treatment processes, necessitating additional purification steps.
The production and disposal of luminol-based analytical kits also contribute to environmental impact. The manufacturing process involves various chemical precursors and solvents, some of which may be harmful if released into the environment. Proper disposal of used luminol solutions and contaminated materials is crucial to prevent soil and groundwater contamination. Inadequate handling and disposal practices could lead to the accumulation of luminol and its derivatives in landfills, potentially leaching into surrounding ecosystems.
Another aspect to consider is the energy consumption associated with luminol-based analytical techniques. The equipment required for detecting and measuring luminol chemiluminescence often demands significant power, contributing to increased energy usage and associated carbon emissions. As analytical models become more sophisticated and widely adopted, the cumulative energy footprint of luminol applications could become substantial.
The environmental impact of luminol extends to its potential effects on wildlife. While direct toxicity to most organisms is low, the introduction of luminol into natural habitats could disrupt bioluminescent organisms that rely on light-producing chemical reactions for communication, defense, or prey attraction. This interference could have cascading effects on ecosystem dynamics and biodiversity in affected areas.
Moreover, the increased use of luminol in analytical models may lead to greater demand for its production, potentially resulting in expanded mining and processing of raw materials needed for luminol synthesis. This could contribute to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and other environmental issues associated with resource extraction activities.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, researchers and industries employing luminol-based analytical models must prioritize sustainable practices. This includes developing more efficient luminol formulations that require smaller quantities, implementing closed-loop systems for luminol recycling, and investing in energy-efficient detection technologies. Additionally, exploring bio-based alternatives to synthetic luminol could reduce the overall environmental footprint of these analytical techniques.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the potential for luminol and its byproducts to contaminate water systems. When luminol reacts with oxidizing agents, it produces aminophthalate ions and nitrogen gas. While these byproducts are generally considered non-toxic, their accumulation in aquatic ecosystems could potentially disrupt the delicate balance of microbial communities and affect water quality. Furthermore, the presence of luminol in wastewater may interfere with conventional water treatment processes, necessitating additional purification steps.
The production and disposal of luminol-based analytical kits also contribute to environmental impact. The manufacturing process involves various chemical precursors and solvents, some of which may be harmful if released into the environment. Proper disposal of used luminol solutions and contaminated materials is crucial to prevent soil and groundwater contamination. Inadequate handling and disposal practices could lead to the accumulation of luminol and its derivatives in landfills, potentially leaching into surrounding ecosystems.
Another aspect to consider is the energy consumption associated with luminol-based analytical techniques. The equipment required for detecting and measuring luminol chemiluminescence often demands significant power, contributing to increased energy usage and associated carbon emissions. As analytical models become more sophisticated and widely adopted, the cumulative energy footprint of luminol applications could become substantial.
The environmental impact of luminol extends to its potential effects on wildlife. While direct toxicity to most organisms is low, the introduction of luminol into natural habitats could disrupt bioluminescent organisms that rely on light-producing chemical reactions for communication, defense, or prey attraction. This interference could have cascading effects on ecosystem dynamics and biodiversity in affected areas.
Moreover, the increased use of luminol in analytical models may lead to greater demand for its production, potentially resulting in expanded mining and processing of raw materials needed for luminol synthesis. This could contribute to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and other environmental issues associated with resource extraction activities.
To mitigate these environmental concerns, researchers and industries employing luminol-based analytical models must prioritize sustainable practices. This includes developing more efficient luminol formulations that require smaller quantities, implementing closed-loop systems for luminol recycling, and investing in energy-efficient detection technologies. Additionally, exploring bio-based alternatives to synthetic luminol could reduce the overall environmental footprint of these analytical techniques.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!