Trends in Solar Inverter Warranty and Maintenance Services
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Solar Inverter Evolution and Service Goals
Solar inverter technology has undergone significant evolution since its inception, driven by the rapid growth of the solar energy industry and the increasing demand for more efficient and reliable power conversion systems. The primary goal of solar inverter development has been to enhance energy conversion efficiency, improve grid integration capabilities, and extend the operational lifespan of photovoltaic (PV) systems.
In the early stages, solar inverters were primarily focused on basic DC to AC conversion. However, as the industry matured, the emphasis shifted towards developing smart inverters with advanced features such as maximum power point tracking (MPPT), grid support functions, and remote monitoring capabilities. This evolution has been crucial in addressing the challenges posed by the intermittent nature of solar power and the need for seamless integration with existing power grids.
The service goals for solar inverters have also evolved in tandem with technological advancements. Initially, maintenance services were reactive, focusing on addressing failures and minimizing downtime. However, the industry has progressively moved towards predictive and preventive maintenance strategies, leveraging data analytics and remote monitoring to anticipate potential issues before they occur.
Warranty services have similarly transformed, reflecting the increased reliability and longevity of modern solar inverters. Early warranties typically covered shorter periods and were limited in scope. As manufacturers gained confidence in their products' performance and durability, warranty periods have extended, often reaching up to 25 years for premium models. This trend aligns with the expected lifespan of solar PV systems and provides greater assurance to investors and system owners.
The goals for future solar inverter development and associated services are multifaceted. There is a strong focus on further improving efficiency, with targets exceeding 99% conversion efficiency. Enhanced grid support features, including voltage and frequency regulation, are becoming increasingly important as the penetration of solar energy in power grids continues to grow. Additionally, there is a push towards developing more compact, modular designs that facilitate easier installation and maintenance.
In terms of service goals, the industry is moving towards comprehensive lifecycle management solutions. This includes advanced diagnostics, AI-driven predictive maintenance, and seamless integration with energy management systems. The aim is to maximize system uptime, optimize performance, and reduce the total cost of ownership over the entire lifespan of the solar PV installation.
In the early stages, solar inverters were primarily focused on basic DC to AC conversion. However, as the industry matured, the emphasis shifted towards developing smart inverters with advanced features such as maximum power point tracking (MPPT), grid support functions, and remote monitoring capabilities. This evolution has been crucial in addressing the challenges posed by the intermittent nature of solar power and the need for seamless integration with existing power grids.
The service goals for solar inverters have also evolved in tandem with technological advancements. Initially, maintenance services were reactive, focusing on addressing failures and minimizing downtime. However, the industry has progressively moved towards predictive and preventive maintenance strategies, leveraging data analytics and remote monitoring to anticipate potential issues before they occur.
Warranty services have similarly transformed, reflecting the increased reliability and longevity of modern solar inverters. Early warranties typically covered shorter periods and were limited in scope. As manufacturers gained confidence in their products' performance and durability, warranty periods have extended, often reaching up to 25 years for premium models. This trend aligns with the expected lifespan of solar PV systems and provides greater assurance to investors and system owners.
The goals for future solar inverter development and associated services are multifaceted. There is a strong focus on further improving efficiency, with targets exceeding 99% conversion efficiency. Enhanced grid support features, including voltage and frequency regulation, are becoming increasingly important as the penetration of solar energy in power grids continues to grow. Additionally, there is a push towards developing more compact, modular designs that facilitate easier installation and maintenance.
In terms of service goals, the industry is moving towards comprehensive lifecycle management solutions. This includes advanced diagnostics, AI-driven predictive maintenance, and seamless integration with energy management systems. The aim is to maximize system uptime, optimize performance, and reduce the total cost of ownership over the entire lifespan of the solar PV installation.
Market Demand Analysis for Inverter Services
The solar inverter market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing adoption of solar energy systems worldwide. This growth has led to a corresponding rise in demand for inverter warranty and maintenance services. As solar installations continue to expand, both residential and commercial customers are placing greater emphasis on the long-term reliability and performance of their systems, making warranty and maintenance services a critical factor in their purchasing decisions.
Market research indicates that the global solar inverter services market is expected to grow substantially over the next decade. This growth is attributed to several factors, including the aging of existing solar installations, the increasing complexity of inverter technology, and the growing awareness among customers about the importance of regular maintenance in maximizing system efficiency and longevity.
In the residential sector, homeowners are increasingly seeking comprehensive warranty packages that offer peace of mind and protection for their investment. This has led to a trend of extended warranty offerings from inverter manufacturers, with some providing coverage for up to 25 years. These extended warranties often include features such as parts replacement, on-site service, and performance guarantees, which are highly valued by consumers.
The commercial and utility-scale solar sectors are also driving demand for advanced maintenance services. Large-scale solar installations require more sophisticated monitoring and maintenance solutions to ensure optimal performance and minimize downtime. As a result, there is a growing market for predictive maintenance services that utilize data analytics and remote monitoring technologies to identify potential issues before they lead to system failures.
Another significant trend in the inverter services market is the shift towards proactive maintenance strategies. Rather than relying on reactive maintenance when problems occur, solar asset owners are increasingly adopting preventive maintenance programs. These programs typically include regular inspections, cleaning, and performance optimization services, which can significantly extend the lifespan of inverters and improve overall system efficiency.
The market for inverter services is also being shaped by technological advancements in inverter design. As inverters become more sophisticated, incorporating features such as advanced grid support functions and energy storage integration, there is a growing need for specialized maintenance expertise. This has created opportunities for third-party service providers who can offer specialized technical support and maintenance services for complex inverter systems.
Geographically, the demand for inverter services varies across regions, with mature solar markets such as Europe and North America showing strong growth in maintenance and aftermarket services. Emerging markets in Asia and Africa are also expected to see significant growth in demand for inverter services as their installed solar capacity increases and systems age.
Market research indicates that the global solar inverter services market is expected to grow substantially over the next decade. This growth is attributed to several factors, including the aging of existing solar installations, the increasing complexity of inverter technology, and the growing awareness among customers about the importance of regular maintenance in maximizing system efficiency and longevity.
In the residential sector, homeowners are increasingly seeking comprehensive warranty packages that offer peace of mind and protection for their investment. This has led to a trend of extended warranty offerings from inverter manufacturers, with some providing coverage for up to 25 years. These extended warranties often include features such as parts replacement, on-site service, and performance guarantees, which are highly valued by consumers.
The commercial and utility-scale solar sectors are also driving demand for advanced maintenance services. Large-scale solar installations require more sophisticated monitoring and maintenance solutions to ensure optimal performance and minimize downtime. As a result, there is a growing market for predictive maintenance services that utilize data analytics and remote monitoring technologies to identify potential issues before they lead to system failures.
Another significant trend in the inverter services market is the shift towards proactive maintenance strategies. Rather than relying on reactive maintenance when problems occur, solar asset owners are increasingly adopting preventive maintenance programs. These programs typically include regular inspections, cleaning, and performance optimization services, which can significantly extend the lifespan of inverters and improve overall system efficiency.
The market for inverter services is also being shaped by technological advancements in inverter design. As inverters become more sophisticated, incorporating features such as advanced grid support functions and energy storage integration, there is a growing need for specialized maintenance expertise. This has created opportunities for third-party service providers who can offer specialized technical support and maintenance services for complex inverter systems.
Geographically, the demand for inverter services varies across regions, with mature solar markets such as Europe and North America showing strong growth in maintenance and aftermarket services. Emerging markets in Asia and Africa are also expected to see significant growth in demand for inverter services as their installed solar capacity increases and systems age.
Current Challenges in Inverter Maintenance
Solar inverter maintenance faces several significant challenges in the current landscape. One of the primary issues is the increasing complexity of inverter technology. As inverters become more sophisticated, incorporating advanced features like smart grid integration and remote monitoring capabilities, the skill level required for maintenance and repair has risen substantially. This complexity often necessitates specialized training for technicians, which can be both time-consuming and costly for service providers.
Another challenge is the rapid pace of technological advancement in the solar industry. Inverter models are frequently updated or replaced with newer versions, making it difficult for maintenance teams to stay current with the latest hardware and software. This constant evolution can lead to issues with spare parts availability for older models and challenges in maintaining a workforce with up-to-date expertise across multiple inverter types and generations.
The growing scale of solar installations also presents logistical challenges for maintenance services. Large solar farms may have hundreds or thousands of inverters spread across vast areas, making regular inspections and preventive maintenance a significant undertaking. This scale increases the importance of efficient maintenance scheduling and remote monitoring systems to identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
Environmental factors pose another set of challenges for inverter maintenance. Inverters are often exposed to harsh conditions, including extreme temperatures, humidity, dust, and in some cases, corrosive atmospheres. These environmental stressors can accelerate wear and tear, leading to more frequent maintenance requirements and potentially shorter lifespans for the equipment. Designing maintenance protocols that account for these varied environmental conditions is crucial but complex.
Data management and analysis have become increasingly important in inverter maintenance, presenting both opportunities and challenges. The vast amount of performance data generated by modern inverters can be leveraged to predict failures and optimize maintenance schedules. However, effectively collecting, storing, and analyzing this data requires sophisticated systems and expertise, which many maintenance providers are still in the process of developing.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges related to warranty terms and service agreements. As the solar market matures, there is increasing pressure to extend warranty periods and provide more comprehensive service packages. This trend, while beneficial for system owners, places additional financial and operational burdens on inverter manufacturers and maintenance providers. Balancing these extended warranties with sustainable business models remains a significant challenge for the industry.
Another challenge is the rapid pace of technological advancement in the solar industry. Inverter models are frequently updated or replaced with newer versions, making it difficult for maintenance teams to stay current with the latest hardware and software. This constant evolution can lead to issues with spare parts availability for older models and challenges in maintaining a workforce with up-to-date expertise across multiple inverter types and generations.
The growing scale of solar installations also presents logistical challenges for maintenance services. Large solar farms may have hundreds or thousands of inverters spread across vast areas, making regular inspections and preventive maintenance a significant undertaking. This scale increases the importance of efficient maintenance scheduling and remote monitoring systems to identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
Environmental factors pose another set of challenges for inverter maintenance. Inverters are often exposed to harsh conditions, including extreme temperatures, humidity, dust, and in some cases, corrosive atmospheres. These environmental stressors can accelerate wear and tear, leading to more frequent maintenance requirements and potentially shorter lifespans for the equipment. Designing maintenance protocols that account for these varied environmental conditions is crucial but complex.
Data management and analysis have become increasingly important in inverter maintenance, presenting both opportunities and challenges. The vast amount of performance data generated by modern inverters can be leveraged to predict failures and optimize maintenance schedules. However, effectively collecting, storing, and analyzing this data requires sophisticated systems and expertise, which many maintenance providers are still in the process of developing.
Lastly, the industry faces challenges related to warranty terms and service agreements. As the solar market matures, there is increasing pressure to extend warranty periods and provide more comprehensive service packages. This trend, while beneficial for system owners, places additional financial and operational burdens on inverter manufacturers and maintenance providers. Balancing these extended warranties with sustainable business models remains a significant challenge for the industry.
Existing Warranty and Maintenance Solutions
01 Extended warranty programs for solar inverters
Solar inverter manufacturers and service providers offer extended warranty programs that go beyond standard coverage. These programs typically include longer coverage periods, enhanced support services, and may cover additional components or labor costs. Extended warranties provide peace of mind to system owners and can be customized based on specific needs and system configurations.- Extended warranty programs for solar inverters: Solar inverter manufacturers and service providers offer extended warranty programs that go beyond the standard warranty period. These programs typically cover replacement parts, labor costs, and may include additional services such as remote monitoring and performance guarantees. Extended warranties provide customers with long-term protection and peace of mind for their solar investments.
- Predictive maintenance services for solar inverters: Advanced monitoring systems and data analytics are used to predict potential issues with solar inverters before they occur. This proactive approach allows for scheduled maintenance and repairs, minimizing downtime and maximizing system performance. Predictive maintenance services may include real-time monitoring, performance analysis, and automated alerts for system operators.
- Remote diagnostics and troubleshooting: Solar inverter maintenance services increasingly utilize remote diagnostics and troubleshooting capabilities. This allows technicians to identify and resolve issues without the need for on-site visits in many cases. Remote services can include software updates, parameter adjustments, and performance optimization, reducing maintenance costs and improving response times.
- Performance-based warranty and service contracts: Some solar inverter manufacturers and service providers offer performance-based warranty and service contracts. These agreements guarantee a certain level of energy production or system uptime, with financial compensation or additional services provided if performance targets are not met. This approach aligns the interests of the service provider with the system owner's goals for energy production and reliability.
- Integrated warranty and maintenance management platforms: Digital platforms are being developed to streamline the management of solar inverter warranties and maintenance services. These platforms can track warranty status, schedule maintenance, store service records, and facilitate communication between system owners, manufacturers, and service providers. Such integrated solutions improve the efficiency of warranty claims processing and maintenance planning.
02 Predictive maintenance and remote monitoring
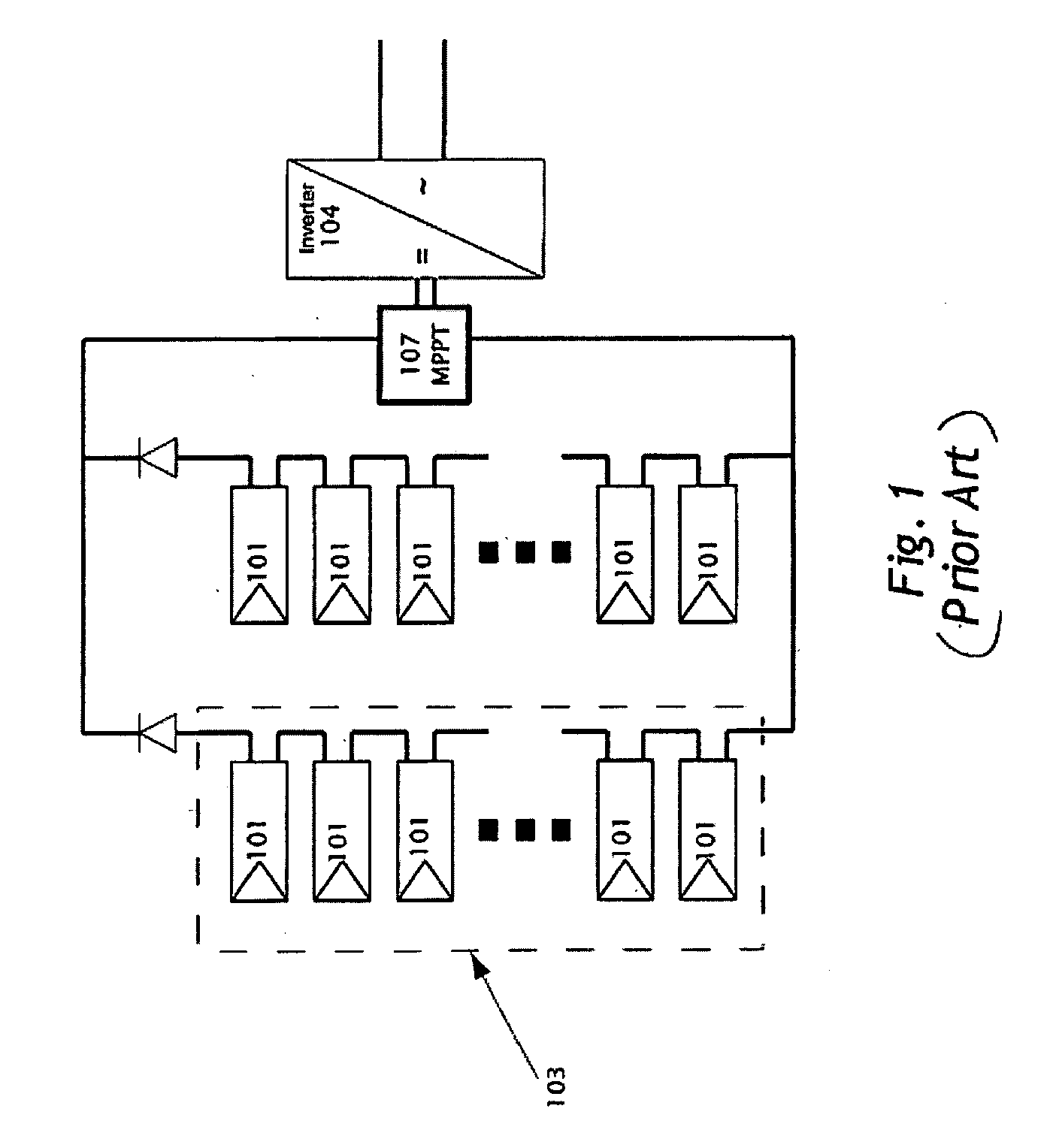
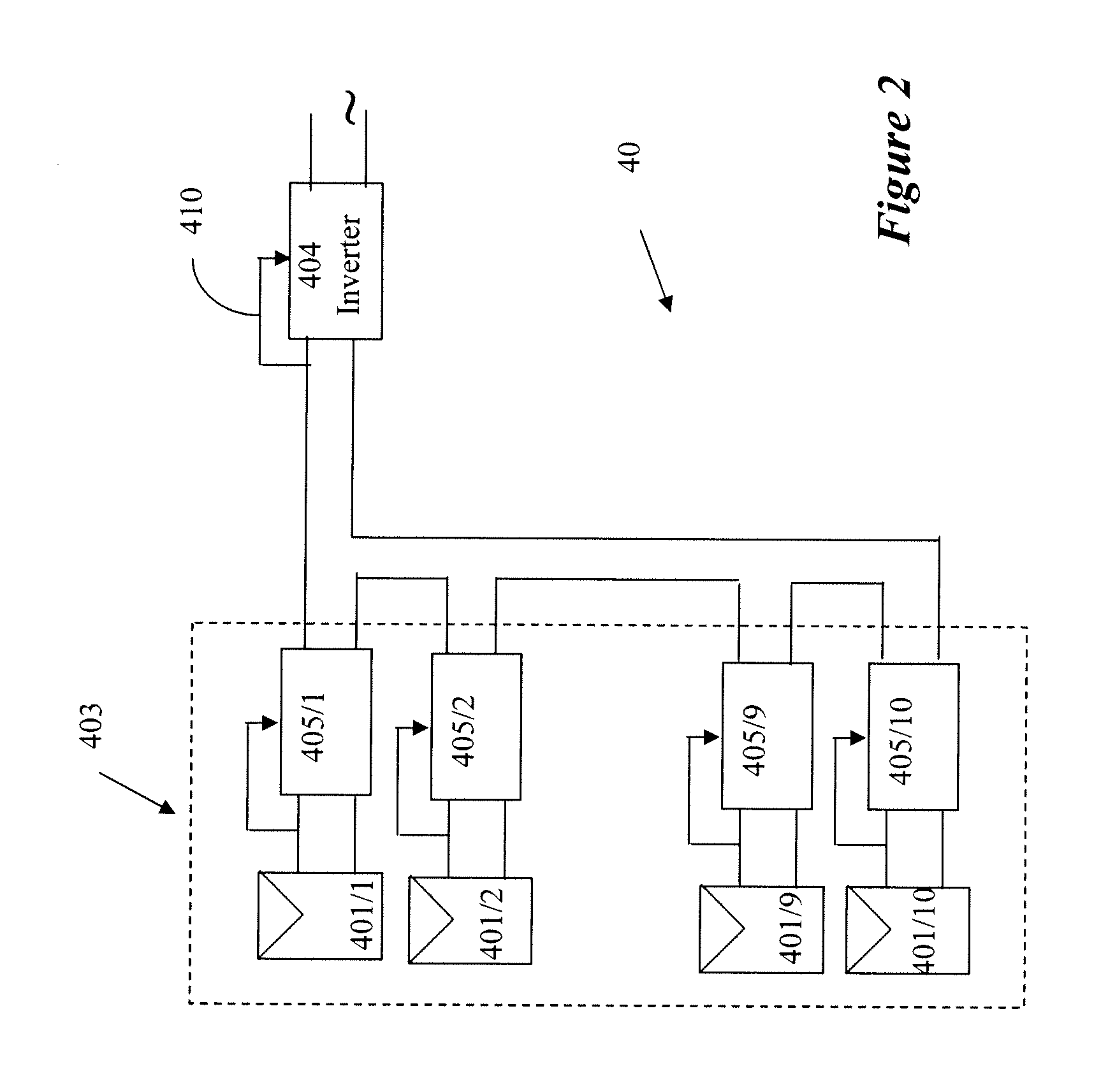
Advanced monitoring systems are employed to track solar inverter performance and predict potential issues before they occur. These systems use data analytics and machine learning algorithms to analyze inverter data in real-time, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime. Remote monitoring capabilities enable service providers to diagnose and sometimes resolve issues without on-site visits.Expand Specific Solutions03 Performance-based warranty and service contracts
Some solar inverter manufacturers and service providers offer performance-based warranties or service contracts. These agreements guarantee a certain level of energy production or system uptime, with compensation or additional services provided if performance falls below the agreed-upon threshold. This approach aligns the interests of the service provider with the system owner's goal of maximizing energy production.Expand Specific Solutions04 Modular design and rapid replacement services
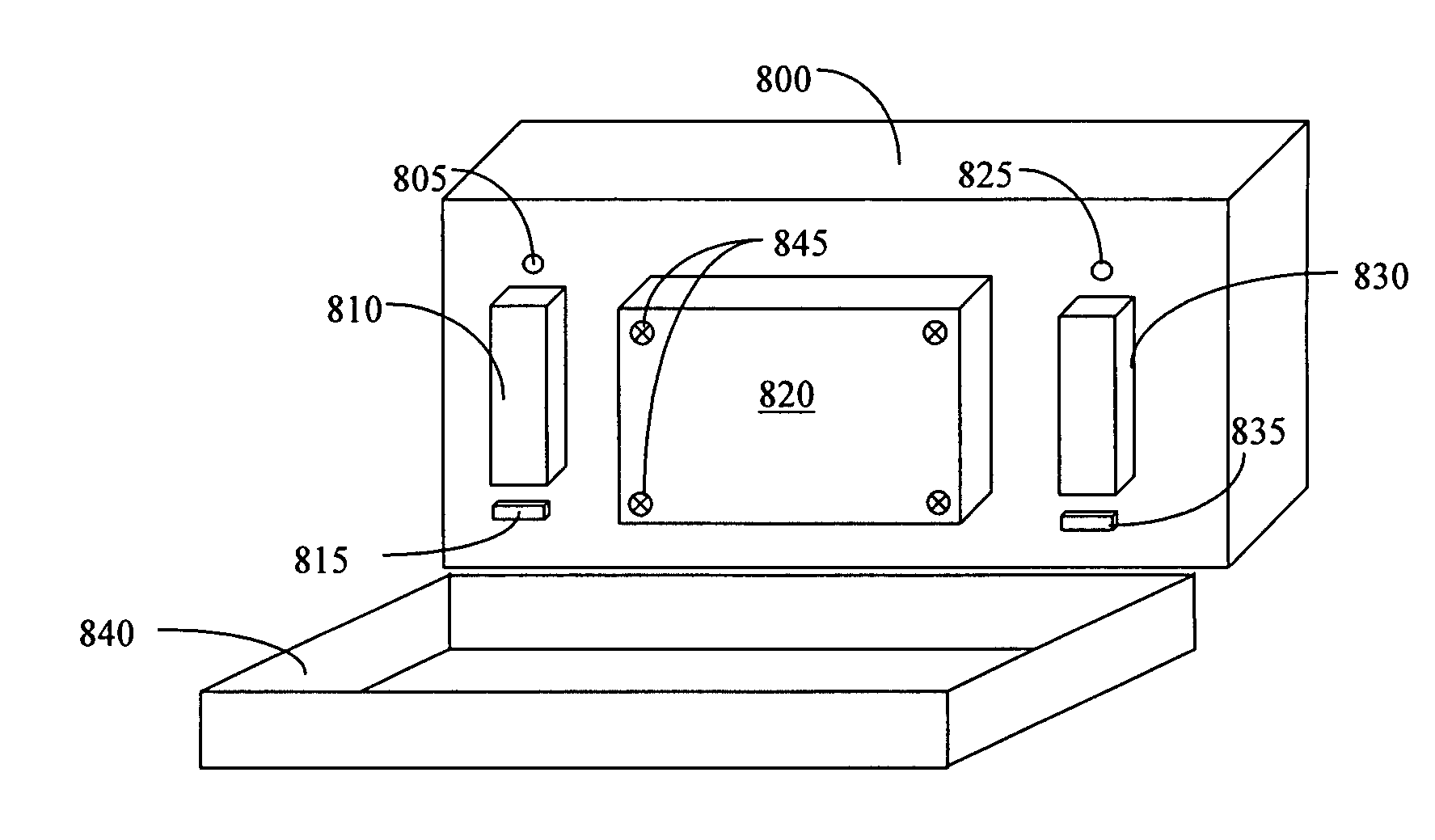
Solar inverters with modular designs allow for easier and quicker component replacement. Service providers offer rapid replacement services where faulty components or entire inverter units can be swapped out quickly, minimizing system downtime. This approach is often combined with inventory management systems to ensure replacement parts are readily available when needed.Expand Specific Solutions05 Comprehensive maintenance plans and training programs
Service providers offer comprehensive maintenance plans that include regular inspections, cleaning, firmware updates, and preventive maintenance tasks. These plans often come with detailed documentation and reporting. Additionally, training programs are provided for system owners or local technicians to perform basic maintenance tasks and troubleshooting, reducing the need for specialist interventions and improving overall system reliability.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Solar Inverter Services
The solar inverter warranty and maintenance services market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing solar installations globally. The market size is expanding rapidly, with key players like Enphase Energy, SolarEdge Technologies, and SMA Solar Technology competing for market share. Technological advancements are improving inverter reliability and efficiency, leading to longer warranty periods and more comprehensive maintenance services. Companies are differentiating themselves through smart monitoring systems, remote diagnostics, and predictive maintenance capabilities. The market is becoming more mature, with established players like ABB and emerging companies like Sungrow Power Supply offering innovative solutions to meet evolving customer needs and regulatory requirements.
Enphase Energy, Inc.
Technical Solution: Enphase Energy has pioneered a comprehensive approach to solar inverter warranty and maintenance services. Their microinverter technology allows for individual panel monitoring and optimization, enhancing system reliability. Enphase offers a 25-year warranty on their microinverters, which is among the longest in the industry [1]. They have implemented a proactive monitoring system that can detect and diagnose issues remotely, often before the customer is aware of any problem. This system, combined with their Enlighten software platform, provides real-time performance data and alerts, enabling swift response to potential issues [2]. Enphase has also introduced the Enphase Upgrade Program, allowing customers to easily upgrade to newer, more efficient microinverter models, ensuring long-term system performance and value [3].
Strengths: Long warranty period, individual panel monitoring, proactive maintenance. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost compared to string inverters, potential for more points of failure due to multiple microinverters.
SolarEdge Technologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: SolarEdge has developed a unique power optimizer and inverter solution that offers module-level monitoring and management. They provide a 12-year warranty on their inverters, extendable to 20 or 25 years, and a 25-year warranty on power optimizers [4]. SolarEdge's monitoring platform offers comprehensive system visibility and remote troubleshooting capabilities. They have introduced predictive maintenance features that use machine learning algorithms to detect potential issues before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs [5]. SolarEdge also offers a StorEdge solution that integrates battery storage with inverter technology, providing backup power and increasing self-consumption of solar energy [6].
Strengths: Module-level optimization, advanced monitoring capabilities, integrated storage solutions. Weaknesses: Reliance on proprietary components, potentially higher replacement costs for specialized parts.
Innovative Approaches in Inverter Servicing
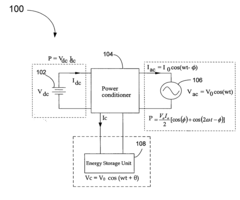
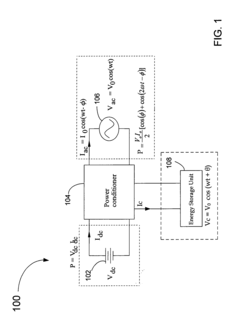
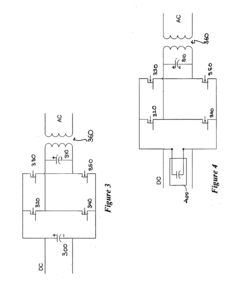
Methods for minimizing double-frequency ripple power in single-phase power conditioners
PatentActiveUS20110305050A1
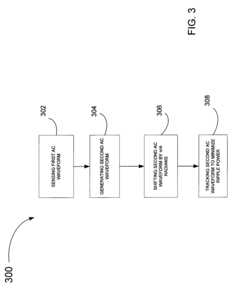
Innovation
- A method that senses the AC waveform at the output of the power conditioner and generates a second AC waveform with the same frequency but shifted by n/4 radians, minimizing double-frequency ripple power by controlling the flow of electrical power through an energy storage device, allowing for the use of smaller, more reliable film capacitors or inductors.
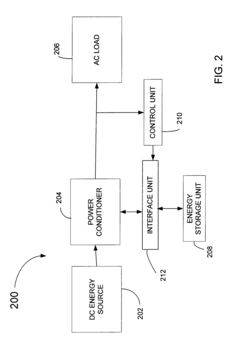
Removal component cartridge for increasing reliability in power harvesting systems
PatentInactiveUS20080144294A1
Innovation
- A power harvesting system with a DC-AC inverter featuring removable cartridges for replaceable components, such as capacitors, and a controller that indicates when replacement is necessary, allowing for easy diagnosis and maintenance by users, including a timer for preventative replacement.
Regulatory Framework for Solar Warranties
The regulatory framework for solar warranties plays a crucial role in shaping the landscape of solar inverter warranty and maintenance services. As the solar industry continues to grow, governments and regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented various policies and standards to protect consumers and ensure the quality of solar installations.
In many countries, solar warranties are subject to consumer protection laws that mandate minimum warranty periods for solar equipment. For instance, in the United States, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) enforces regulations that require manufacturers to honor their written warranties. Additionally, some states have enacted specific solar consumer protection laws, such as California's Solar Rights Act, which provides additional safeguards for solar system owners.
The European Union has established the Ecodesign Directive, which sets minimum performance and durability requirements for various products, including solar inverters. This directive influences warranty terms by ensuring that manufacturers meet certain quality standards before bringing their products to market.
In Australia, the Clean Energy Council (CEC) has implemented a Solar Retailer Code of Conduct, which includes guidelines for warranty provisions. Accredited solar retailers must adhere to these guidelines, providing consumers with added protection and confidence in their solar investments.
International standards, such as IEC 62109 for safety of power converters in photovoltaic systems, also impact warranty regulations by setting benchmarks for product quality and reliability. Compliance with these standards often forms the basis for warranty terms and conditions.
Many countries have introduced renewable energy targets and incentive programs, which indirectly affect warranty regulations. These programs often require solar equipment to meet specific quality and performance standards to be eligible for incentives, thereby influencing warranty offerings.
The regulatory landscape also addresses issues related to warranty transferability, particularly in cases of property sales or changes in system ownership. Some jurisdictions mandate that warranties remain valid even after a change in property ownership, ensuring long-term protection for solar investments.
As the solar industry matures, regulators are increasingly focusing on the end-of-life management of solar equipment. This has led to the development of regulations concerning the disposal and recycling of solar inverters, which may impact future warranty and maintenance service offerings.
The dynamic nature of solar technology and market conditions necessitates ongoing updates to regulatory frameworks. Policymakers and industry stakeholders collaborate to refine warranty regulations, addressing emerging challenges such as cybersecurity risks in smart inverters and the integration of energy storage systems.
In many countries, solar warranties are subject to consumer protection laws that mandate minimum warranty periods for solar equipment. For instance, in the United States, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) enforces regulations that require manufacturers to honor their written warranties. Additionally, some states have enacted specific solar consumer protection laws, such as California's Solar Rights Act, which provides additional safeguards for solar system owners.
The European Union has established the Ecodesign Directive, which sets minimum performance and durability requirements for various products, including solar inverters. This directive influences warranty terms by ensuring that manufacturers meet certain quality standards before bringing their products to market.
In Australia, the Clean Energy Council (CEC) has implemented a Solar Retailer Code of Conduct, which includes guidelines for warranty provisions. Accredited solar retailers must adhere to these guidelines, providing consumers with added protection and confidence in their solar investments.
International standards, such as IEC 62109 for safety of power converters in photovoltaic systems, also impact warranty regulations by setting benchmarks for product quality and reliability. Compliance with these standards often forms the basis for warranty terms and conditions.
Many countries have introduced renewable energy targets and incentive programs, which indirectly affect warranty regulations. These programs often require solar equipment to meet specific quality and performance standards to be eligible for incentives, thereby influencing warranty offerings.
The regulatory landscape also addresses issues related to warranty transferability, particularly in cases of property sales or changes in system ownership. Some jurisdictions mandate that warranties remain valid even after a change in property ownership, ensuring long-term protection for solar investments.
As the solar industry matures, regulators are increasingly focusing on the end-of-life management of solar equipment. This has led to the development of regulations concerning the disposal and recycling of solar inverters, which may impact future warranty and maintenance service offerings.
The dynamic nature of solar technology and market conditions necessitates ongoing updates to regulatory frameworks. Policymakers and industry stakeholders collaborate to refine warranty regulations, addressing emerging challenges such as cybersecurity risks in smart inverters and the integration of energy storage systems.
Environmental Impact of Inverter Lifecycles
The environmental impact of solar inverter lifecycles is a critical consideration in the broader context of sustainable energy solutions. As the solar industry continues to grow, the production, use, and disposal of inverters play a significant role in determining the overall ecological footprint of solar energy systems.
Manufacturing processes for solar inverters involve the use of various materials, including metals, plastics, and electronic components. The extraction and processing of these raw materials contribute to resource depletion and energy consumption. Additionally, the production phase often involves the use of potentially harmful chemicals and generates waste that requires proper management to minimize environmental harm.
During their operational lifespan, solar inverters generally have a minimal direct environmental impact. However, their efficiency and reliability directly affect the overall performance of solar energy systems. More efficient inverters can maximize energy output, thereby reducing the need for additional solar panels and associated resources.
The end-of-life phase of solar inverters presents both challenges and opportunities from an environmental perspective. Proper recycling and disposal of inverters are crucial to prevent the release of hazardous materials into the environment. Many inverter components, such as metals and certain electronic parts, can be recycled and reused, contributing to a circular economy approach.
Recent trends in inverter design have focused on improving durability and extending operational lifespans. This shift not only enhances the economic value for consumers but also reduces the frequency of replacements, thereby minimizing waste generation and resource consumption associated with manufacturing new units.
The development of more environmentally friendly materials and manufacturing processes for inverters is an ongoing area of research and innovation. Some manufacturers are exploring the use of biodegradable components or designing inverters with easier disassembly for recycling purposes.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, life cycle assessments (LCAs) are becoming increasingly important. These assessments help quantify the environmental impacts of inverters from cradle to grave, enabling manufacturers to identify areas for improvement and optimize their products for reduced ecological impact.
The environmental impact of inverter lifecycles is intrinsically linked to the broader sustainability goals of the solar energy sector. As such, addressing these impacts is crucial for maintaining the green credentials of solar power and ensuring its role in a sustainable energy future.
Manufacturing processes for solar inverters involve the use of various materials, including metals, plastics, and electronic components. The extraction and processing of these raw materials contribute to resource depletion and energy consumption. Additionally, the production phase often involves the use of potentially harmful chemicals and generates waste that requires proper management to minimize environmental harm.
During their operational lifespan, solar inverters generally have a minimal direct environmental impact. However, their efficiency and reliability directly affect the overall performance of solar energy systems. More efficient inverters can maximize energy output, thereby reducing the need for additional solar panels and associated resources.
The end-of-life phase of solar inverters presents both challenges and opportunities from an environmental perspective. Proper recycling and disposal of inverters are crucial to prevent the release of hazardous materials into the environment. Many inverter components, such as metals and certain electronic parts, can be recycled and reused, contributing to a circular economy approach.
Recent trends in inverter design have focused on improving durability and extending operational lifespans. This shift not only enhances the economic value for consumers but also reduces the frequency of replacements, thereby minimizing waste generation and resource consumption associated with manufacturing new units.
The development of more environmentally friendly materials and manufacturing processes for inverters is an ongoing area of research and innovation. Some manufacturers are exploring the use of biodegradable components or designing inverters with easier disassembly for recycling purposes.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, life cycle assessments (LCAs) are becoming increasingly important. These assessments help quantify the environmental impacts of inverters from cradle to grave, enabling manufacturers to identify areas for improvement and optimize their products for reduced ecological impact.
The environmental impact of inverter lifecycles is intrinsically linked to the broader sustainability goals of the solar energy sector. As such, addressing these impacts is crucial for maintaining the green credentials of solar power and ensuring its role in a sustainable energy future.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!