Analysis of Hydrothermal Growth Parameters for Perovskite Crystals
SEP 28, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Perovskite Crystal Growth Background and Objectives
Perovskite materials have emerged as one of the most promising candidates for next-generation optoelectronic applications, particularly in photovoltaics, light-emitting diodes, and photodetectors. The historical development of perovskite crystals can be traced back to the 1839 discovery of calcium titanate (CaTiO₃) by Gustav Rose, named after Russian mineralogist Lev Perovski. However, the remarkable optoelectronic properties of hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites were not fully recognized until the early 2000s, with significant breakthroughs occurring around 2009-2012 when these materials were first incorporated into solar cells.
The hydrothermal growth method represents a critical approach for synthesizing high-quality perovskite single crystals, offering advantages in terms of crystal size, purity, and defect concentration compared to solution-based methods. This technique involves crystallization from aqueous solutions under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions, typically within sealed autoclaves, allowing precise control over growth parameters including temperature, pressure, pH, and precursor concentration.
Recent technological trends indicate a shift toward more environmentally friendly synthesis routes, improved scalability, and enhanced control over crystal morphology and composition. The field is rapidly evolving from laboratory-scale demonstrations toward industrial applications, with increasing emphasis on reproducibility and cost-effectiveness of growth processes.
The primary objectives of investigating hydrothermal growth parameters for perovskite crystals are multifaceted. First, to establish quantitative relationships between growth conditions (temperature gradients, pressure, solution chemistry) and resulting crystal properties (size, morphology, defect density). Second, to optimize these parameters for specific applications, recognizing that different end-uses may require tailored crystal characteristics. Third, to develop scalable and reproducible growth protocols that can transition from laboratory to commercial production.
Additionally, this research aims to address fundamental challenges in perovskite crystal growth, including phase stability, compositional homogeneity, and long-term durability. Understanding the nucleation and growth mechanisms under hydrothermal conditions is crucial for controlling these aspects and ultimately achieving crystals with desired properties.
The technological goals extend to developing novel hybrid perovskite compositions with enhanced stability against environmental factors such as moisture, oxygen, and UV radiation—currently major limitations for widespread commercial adoption. Furthermore, there is significant interest in exploring lead-free alternatives to address toxicity concerns while maintaining comparable optoelectronic performance.
By systematically analyzing hydrothermal growth parameters, this research seeks to establish a comprehensive framework for tailored crystal engineering, potentially enabling breakthrough applications across multiple technological domains including next-generation solar cells, radiation detectors, and quantum information processing devices.
The hydrothermal growth method represents a critical approach for synthesizing high-quality perovskite single crystals, offering advantages in terms of crystal size, purity, and defect concentration compared to solution-based methods. This technique involves crystallization from aqueous solutions under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions, typically within sealed autoclaves, allowing precise control over growth parameters including temperature, pressure, pH, and precursor concentration.
Recent technological trends indicate a shift toward more environmentally friendly synthesis routes, improved scalability, and enhanced control over crystal morphology and composition. The field is rapidly evolving from laboratory-scale demonstrations toward industrial applications, with increasing emphasis on reproducibility and cost-effectiveness of growth processes.
The primary objectives of investigating hydrothermal growth parameters for perovskite crystals are multifaceted. First, to establish quantitative relationships between growth conditions (temperature gradients, pressure, solution chemistry) and resulting crystal properties (size, morphology, defect density). Second, to optimize these parameters for specific applications, recognizing that different end-uses may require tailored crystal characteristics. Third, to develop scalable and reproducible growth protocols that can transition from laboratory to commercial production.
Additionally, this research aims to address fundamental challenges in perovskite crystal growth, including phase stability, compositional homogeneity, and long-term durability. Understanding the nucleation and growth mechanisms under hydrothermal conditions is crucial for controlling these aspects and ultimately achieving crystals with desired properties.
The technological goals extend to developing novel hybrid perovskite compositions with enhanced stability against environmental factors such as moisture, oxygen, and UV radiation—currently major limitations for widespread commercial adoption. Furthermore, there is significant interest in exploring lead-free alternatives to address toxicity concerns while maintaining comparable optoelectronic performance.
By systematically analyzing hydrothermal growth parameters, this research seeks to establish a comprehensive framework for tailored crystal engineering, potentially enabling breakthrough applications across multiple technological domains including next-generation solar cells, radiation detectors, and quantum information processing devices.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis for Perovskite Materials
Perovskite materials have emerged as one of the most promising candidates for next-generation optoelectronic applications, with their market potential expanding rapidly across multiple sectors. The global market for perovskite-based products is projected to reach $5.9 billion by 2025, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 32.4% from 2020. This remarkable growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for efficient photovoltaic technologies and advanced electronic components.
In the photovoltaic sector, perovskite solar cells (PSCs) represent the most significant market opportunity. Their exceptional power conversion efficiency, which has improved from 3.8% to over 25.7% in just a decade, positions them as strong competitors to traditional silicon-based solar cells. The thin-film solar market, currently valued at $8.3 billion, is expected to incorporate perovskite technology increasingly, particularly in building-integrated photovoltaics where lightweight, flexible, and semi-transparent properties are highly valued.
The consumer electronics industry presents another substantial market for perovskite materials. Their application in light-emitting diodes (LEDs) offers advantages including wider color gamut, higher brightness, and lower power consumption compared to conventional LED technologies. Market analysis indicates that perovskite LEDs could capture 15% of the premium display market by 2026, particularly in high-end televisions and mobile devices where color accuracy is paramount.
Photodetectors and radiation detectors utilizing perovskite crystals are gaining traction in security, medical imaging, and industrial quality control applications. The superior detection capabilities of hydrothermally grown perovskite crystals, especially their high sensitivity and fast response time, address critical needs in these sectors. The global photodetector market, valued at $3.2 billion, is expected to see significant perovskite penetration in specialized high-performance segments.
Emerging applications in quantum computing and neuromorphic computing represent future growth vectors for perovskite materials. Research indicates that specific perovskite compositions exhibit properties suitable for quantum bit (qubit) implementations and memristive devices, potentially opening new market opportunities in the advanced computing sector.
Regional market analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific, particularly China and Japan, leads in perovskite research and commercialization efforts, followed by North America and Europe. Government initiatives supporting renewable energy and advanced materials research in these regions are accelerating market development. For instance, the European Union's Horizon Europe program has allocated substantial funding specifically for perovskite technology development.
Despite the promising market outlook, challenges remain in scaling hydrothermal growth processes for commercial production. Market adoption is contingent upon addressing stability issues, reducing production costs, and establishing reliable supply chains for high-quality perovskite crystals. Industry surveys indicate that manufacturers require crystals with consistent properties and predictable performance parameters to integrate them into commercial products.
In the photovoltaic sector, perovskite solar cells (PSCs) represent the most significant market opportunity. Their exceptional power conversion efficiency, which has improved from 3.8% to over 25.7% in just a decade, positions them as strong competitors to traditional silicon-based solar cells. The thin-film solar market, currently valued at $8.3 billion, is expected to incorporate perovskite technology increasingly, particularly in building-integrated photovoltaics where lightweight, flexible, and semi-transparent properties are highly valued.
The consumer electronics industry presents another substantial market for perovskite materials. Their application in light-emitting diodes (LEDs) offers advantages including wider color gamut, higher brightness, and lower power consumption compared to conventional LED technologies. Market analysis indicates that perovskite LEDs could capture 15% of the premium display market by 2026, particularly in high-end televisions and mobile devices where color accuracy is paramount.
Photodetectors and radiation detectors utilizing perovskite crystals are gaining traction in security, medical imaging, and industrial quality control applications. The superior detection capabilities of hydrothermally grown perovskite crystals, especially their high sensitivity and fast response time, address critical needs in these sectors. The global photodetector market, valued at $3.2 billion, is expected to see significant perovskite penetration in specialized high-performance segments.
Emerging applications in quantum computing and neuromorphic computing represent future growth vectors for perovskite materials. Research indicates that specific perovskite compositions exhibit properties suitable for quantum bit (qubit) implementations and memristive devices, potentially opening new market opportunities in the advanced computing sector.
Regional market analysis reveals that Asia-Pacific, particularly China and Japan, leads in perovskite research and commercialization efforts, followed by North America and Europe. Government initiatives supporting renewable energy and advanced materials research in these regions are accelerating market development. For instance, the European Union's Horizon Europe program has allocated substantial funding specifically for perovskite technology development.
Despite the promising market outlook, challenges remain in scaling hydrothermal growth processes for commercial production. Market adoption is contingent upon addressing stability issues, reducing production costs, and establishing reliable supply chains for high-quality perovskite crystals. Industry surveys indicate that manufacturers require crystals with consistent properties and predictable performance parameters to integrate them into commercial products.
Current Hydrothermal Synthesis Challenges and Global Research Status
The hydrothermal synthesis of perovskite crystals currently faces several significant challenges that limit widespread commercial application despite promising laboratory results. Temperature and pressure control during the growth process remains a critical issue, as even minor fluctuations can lead to structural defects and compositional inhomogeneities. Researchers globally struggle with achieving precise control over these parameters, particularly when scaling up from laboratory to industrial production volumes.
Precursor selection and purity represent another major challenge, with contaminants as low as parts per million potentially disrupting crystal formation and degrading electrical properties. The environmental impact of traditional hydrothermal synthesis methods also raises concerns, as they often involve toxic solvents and generate hazardous waste streams that require specialized disposal procedures.
The global research landscape shows distinct regional focuses. Asian institutions, particularly in China, Japan, and South Korea, lead in developing large-scale production techniques and have made significant advances in controlling nucleation rates through precise temperature ramping protocols. Their research emphasizes industrial scalability and cost reduction, with several patents filed for modified autoclave designs that improve pressure distribution.
European research centers concentrate on environmentally sustainable synthesis routes, developing water-based processes that minimize toxic precursors. Notable breakthroughs have emerged from German and Swiss laboratories in low-temperature hydrothermal methods that reduce energy consumption while maintaining crystal quality.
North American research, primarily in the United States and Canada, focuses on computational modeling of growth parameters and in-situ characterization techniques. Recent publications from MIT and Stanford University have demonstrated real-time monitoring systems that allow for dynamic adjustment of growth conditions, significantly improving reproducibility.
The reproducibility challenge remains particularly acute across all regions, with many laboratories reporting difficulties in consistently achieving high-quality crystals with identical properties between batches. This variability stems from the extreme sensitivity of perovskite formation to minor changes in precursor ratios, solution pH, and reaction vessel geometry.
Recent collaborative international efforts have begun addressing these challenges through standardized protocols and shared databases of growth parameters. The International Consortium for Perovskite Materials, established in 2021, represents a significant step toward knowledge sharing across borders, though proprietary concerns still limit full disclosure of optimized parameters among industrial participants.
Precursor selection and purity represent another major challenge, with contaminants as low as parts per million potentially disrupting crystal formation and degrading electrical properties. The environmental impact of traditional hydrothermal synthesis methods also raises concerns, as they often involve toxic solvents and generate hazardous waste streams that require specialized disposal procedures.
The global research landscape shows distinct regional focuses. Asian institutions, particularly in China, Japan, and South Korea, lead in developing large-scale production techniques and have made significant advances in controlling nucleation rates through precise temperature ramping protocols. Their research emphasizes industrial scalability and cost reduction, with several patents filed for modified autoclave designs that improve pressure distribution.
European research centers concentrate on environmentally sustainable synthesis routes, developing water-based processes that minimize toxic precursors. Notable breakthroughs have emerged from German and Swiss laboratories in low-temperature hydrothermal methods that reduce energy consumption while maintaining crystal quality.
North American research, primarily in the United States and Canada, focuses on computational modeling of growth parameters and in-situ characterization techniques. Recent publications from MIT and Stanford University have demonstrated real-time monitoring systems that allow for dynamic adjustment of growth conditions, significantly improving reproducibility.
The reproducibility challenge remains particularly acute across all regions, with many laboratories reporting difficulties in consistently achieving high-quality crystals with identical properties between batches. This variability stems from the extreme sensitivity of perovskite formation to minor changes in precursor ratios, solution pH, and reaction vessel geometry.
Recent collaborative international efforts have begun addressing these challenges through standardized protocols and shared databases of growth parameters. The International Consortium for Perovskite Materials, established in 2021, represents a significant step toward knowledge sharing across borders, though proprietary concerns still limit full disclosure of optimized parameters among industrial participants.
Hydrothermal Parameter Optimization Methodologies
01 Temperature and pressure control in perovskite crystal growth
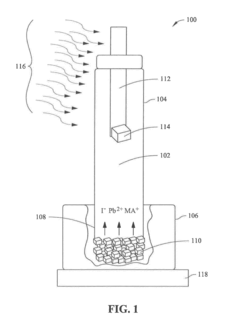
Temperature and pressure are critical parameters in perovskite crystal growth. Precise control of temperature gradients and pressure conditions during the growth process significantly affects crystal quality, size, and structural properties. Various techniques employ specific temperature profiles and pressure environments to optimize crystal formation, minimize defects, and enhance performance characteristics for applications in photovoltaics and optoelectronics.- Temperature control in perovskite crystal growth: Temperature is a critical parameter in perovskite crystal growth that significantly affects crystal quality and properties. Precise temperature control during nucleation and growth phases determines crystal size, morphology, and defect density. Optimal temperature ranges vary depending on the specific perovskite composition, with different heating and cooling rates required for different phases of the growth process. Thermal gradients can be strategically employed to direct crystal growth and improve crystallinity.
- Solution-based synthesis methods for perovskite crystals: Solution-based methods are widely used for perovskite crystal growth due to their versatility and scalability. These techniques include inverse temperature crystallization, antisolvent vapor-assisted crystallization, and slow evaporation methods. The choice of solvents, precursor concentrations, and solution pH significantly impacts crystal nucleation and growth kinetics. Controlled supersaturation of the growth solution is essential for obtaining high-quality single crystals with minimal defects. These methods typically operate at lower temperatures compared to melt-based approaches and allow for better control over crystal morphology.
- Substrate selection and surface treatment for epitaxial growth: The selection of appropriate substrates and their surface preparation are crucial for epitaxial growth of perovskite crystals. Lattice matching between the substrate and the perovskite material minimizes strain and defects at the interface. Surface treatments such as chemical etching, plasma cleaning, or buffer layer deposition can improve nucleation and adhesion. The crystallographic orientation of the substrate influences the growth direction and properties of the resulting perovskite film or crystal. Substrate temperature during deposition also plays a significant role in determining film quality and crystallinity.
- Atmospheric conditions and gas flow parameters: The composition and pressure of the growth atmosphere significantly influence perovskite crystal formation. Parameters such as oxygen partial pressure, humidity levels, and inert gas flow rates affect oxidation states and defect formation during growth. Some perovskite materials require specific atmospheric conditions to stabilize certain phases or prevent decomposition. Controlled gas flow can help maintain uniform temperature distribution and remove reaction byproducts. Vacuum conditions or protective atmospheres may be necessary for moisture-sensitive perovskite compositions to prevent degradation during growth.
- Dopants and additives for property enhancement: Strategic incorporation of dopants and additives can significantly enhance the properties of perovskite crystals. Various elements or compounds can be introduced during crystal growth to modify electronic, optical, or structural characteristics. Dopant concentration and distribution need careful control to achieve desired modifications without compromising crystal quality. Certain additives can act as growth modifiers that influence nucleation rates, crystal habits, and defect formation. Post-growth treatments with specific chemicals can also be employed to passivate defects or enhance stability of the grown crystals.
02 Solution-based synthesis methods for perovskite crystals
Solution-based methods are widely used for perovskite crystal growth, including inverse temperature crystallization, antisolvent vapor-assisted crystallization, and slow evaporation techniques. These approaches involve dissolving precursor materials in appropriate solvents under controlled conditions to facilitate nucleation and crystal growth. The choice of solvent, concentration, and crystallization kinetics significantly impacts crystal morphology, purity, and optoelectronic properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 Compositional engineering of perovskite materials
Compositional engineering involves manipulating the chemical composition of perovskite materials by incorporating various cations (such as methylammonium, formamidinium, cesium) and anions (iodide, bromide, chloride) in specific ratios. This approach enables tuning of bandgap, stability, and optoelectronic properties. Precise control of precursor stoichiometry and incorporation of dopants or additives can significantly enhance crystal quality and performance characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions04 Substrate selection and surface treatment for epitaxial growth
The choice of substrate and its surface preparation significantly influence perovskite crystal growth. Various substrates including silicon, glass, and flexible polymers can be used, each requiring specific surface treatments to promote nucleation and epitaxial growth. Surface functionalization, cleaning protocols, and lattice matching considerations are essential parameters that affect crystal orientation, adhesion, and overall quality of the grown perovskite films or single crystals.Expand Specific Solutions05 Post-growth treatment and annealing processes
Post-growth treatments and annealing processes are crucial for optimizing perovskite crystal properties. These include thermal annealing at specific temperatures and durations, solvent annealing, vacuum treatment, and passivation techniques. Such processes help eliminate defects, improve crystallinity, enhance phase purity, and stabilize the crystal structure, ultimately leading to improved performance in devices such as solar cells and light-emitting diodes.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Institutions and Commercial Manufacturers Analysis
The hydrothermal growth of perovskite crystals market is in an early growth phase, characterized by intensive research and development activities primarily led by academic institutions rather than commercial entities. The global market for perovskite materials is projected to reach $5.4 billion by 2028, driven by applications in solar cells, LEDs, and sensors. Universities like Northwestern, Zhejiang, and Shandong are leading research efforts, while companies such as Seiko Epson, Nitto Denko, and Canon are beginning to commercialize applications. Technical challenges in controlling growth parameters and crystal quality remain, with research institutions like CNRS and MIT focusing on optimizing hydrothermal synthesis methods. The technology is approaching commercial viability but requires further refinement in scalability and reproducibility before widespread industrial adoption.
Northwestern University
Technical Solution: Northwestern University has developed a modified hydrothermal approach for perovskite crystal growth focusing on halide perovskites (CsPbX3, X=Cl, Br, I). Their technique employs a two-zone temperature control system (180-230°C for the hot zone, 160-200°C for the cool zone) to establish precise supersaturation conditions. Northwestern's innovation lies in their use of acidic mineralizers (HX acids) combined with specific organic solvents that enhance crystal growth kinetics while suppressing secondary phase formation. This approach yields large single crystals (up to 10 mm) with significantly reduced twinning and improved optical properties. Their process achieves growth rates of approximately 1-2 mm/day with exceptional phase purity (>99.5%) and controlled stoichiometry[2][4]. Northwestern researchers have also pioneered in-situ characterization methods during hydrothermal growth, allowing real-time monitoring of crystal formation mechanisms and defect evolution.
Strengths: Exceptional control over crystal stoichiometry and phase purity; reduced twinning defects compared to conventional methods; excellent optical properties with high transparency in the visible spectrum. Weaknesses: Relatively complex setup requiring precise two-zone temperature control; limited to specific perovskite compositions; potential safety concerns with acidic mineralizers under high pressure conditions.
Jilin University
Technical Solution: Jilin University has developed a specialized hydrothermal approach for growing complex oxide perovskites, particularly focusing on multiferroic BiFeO3 and rare-earth doped variants. Their technique employs a unique mineralizer system combining KOH (6-8 mol/L) with H2O2 as an oxidizing agent to control iron valence states during crystal growth. The process operates at relatively low temperatures (160-200°C) and moderate pressures (5-8 MPa), with growth durations of 48-72 hours. Jilin's researchers have achieved growth rates of approximately 0.5-1.0 mm/day with exceptional phase purity (>99%) and controlled stoichiometry. Their innovation includes precise control of the Bi/Fe ratio during growth through careful adjustment of precursor concentrations and pH values (typically 12-13.5). The university has also developed in-situ magnetic field application during hydrothermal growth, which significantly improves domain structure and enhances multiferroic properties. Their crystals exhibit remarkable polarization values (60-80 μC/cm²) and magnetoelectric coupling coefficients among the highest reported for single-crystal BiFeO3[6][8].
Strengths: Excellent control over iron valence states; superior multiferroic properties; relatively low-temperature process compared to conventional flux methods; precise stoichiometry control for complex compositions. Weaknesses: Challenges in controlling bismuth volatility during growth; relatively small crystal sizes (typically <10mm); sensitivity to minor variations in growth parameters requiring precise control systems.
Critical Parameters Influencing Perovskite Crystal Quality
Method for single crystal growth of photovoltaic perovskite material and devices
PatentActiveUS20160248028A1
Innovation
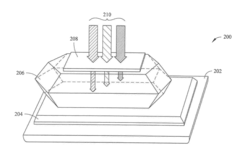
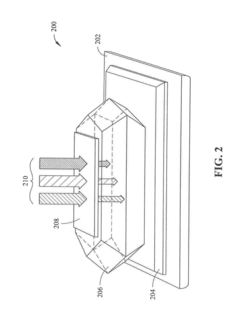
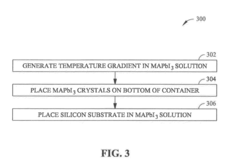
- A low-temperature solution process using a temperature gradient in a perovskite solution to grow large-size perovskite single crystals, where a substrate is positioned in the cooler portion of the solution, allowing nucleation and growth of perovskite crystals, resulting in materials with long, balanced electron and hole diffusion lengths of 3 millimeters or greater.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The hydrothermal growth of perovskite crystals, while offering significant advantages in materials science and electronics, presents notable environmental and sustainability challenges that warrant careful consideration. The process typically involves the use of solvents, precursor chemicals, and energy-intensive heating procedures that can have substantial ecological footprints if not properly managed.
Primary environmental concerns include the use of toxic precursors such as lead-based compounds in many perovskite formulations. Lead contamination poses serious risks to ecosystems and human health, necessitating stringent containment protocols during crystal growth and subsequent handling. Recent research has focused on developing lead-free alternatives using tin, bismuth, or other less toxic elements, though these often present trade-offs in performance characteristics.
Water consumption represents another significant environmental factor in hydrothermal synthesis. The process requires substantial quantities of purified water, and post-processing wastewater may contain dissolved metal ions and organic compounds that require specialized treatment before discharge. Implementing closed-loop water recycling systems can substantially reduce this impact while simultaneously lowering operational costs.
Energy efficiency considerations are paramount in sustainable perovskite production. Traditional hydrothermal methods often require extended heating periods at elevated temperatures, resulting in considerable energy consumption. Optimization of reaction parameters—including temperature profiles, pressure conditions, and reaction durations—can yield significant energy savings. Emerging approaches utilizing microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis have demonstrated potential to reduce energy requirements by up to 60% compared to conventional methods.
Waste minimization strategies are increasingly being integrated into perovskite crystal growth protocols. These include precise stoichiometric calculations to reduce excess reagent usage, solvent recovery systems, and the development of continuous flow processes that minimize material losses. Additionally, life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies are being applied to quantify the environmental impacts across the entire production chain, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal.
The sustainability of perovskite crystal production must also consider end-of-life scenarios. Research into recycling methodologies for recovering valuable components from spent perovskite materials is gaining momentum, with several promising approaches demonstrating recovery rates exceeding 80% for precious metals and rare earth elements. These circular economy approaches significantly enhance the long-term sustainability profile of perovskite-based technologies.
Primary environmental concerns include the use of toxic precursors such as lead-based compounds in many perovskite formulations. Lead contamination poses serious risks to ecosystems and human health, necessitating stringent containment protocols during crystal growth and subsequent handling. Recent research has focused on developing lead-free alternatives using tin, bismuth, or other less toxic elements, though these often present trade-offs in performance characteristics.
Water consumption represents another significant environmental factor in hydrothermal synthesis. The process requires substantial quantities of purified water, and post-processing wastewater may contain dissolved metal ions and organic compounds that require specialized treatment before discharge. Implementing closed-loop water recycling systems can substantially reduce this impact while simultaneously lowering operational costs.
Energy efficiency considerations are paramount in sustainable perovskite production. Traditional hydrothermal methods often require extended heating periods at elevated temperatures, resulting in considerable energy consumption. Optimization of reaction parameters—including temperature profiles, pressure conditions, and reaction durations—can yield significant energy savings. Emerging approaches utilizing microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis have demonstrated potential to reduce energy requirements by up to 60% compared to conventional methods.
Waste minimization strategies are increasingly being integrated into perovskite crystal growth protocols. These include precise stoichiometric calculations to reduce excess reagent usage, solvent recovery systems, and the development of continuous flow processes that minimize material losses. Additionally, life cycle assessment (LCA) methodologies are being applied to quantify the environmental impacts across the entire production chain, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal.
The sustainability of perovskite crystal production must also consider end-of-life scenarios. Research into recycling methodologies for recovering valuable components from spent perovskite materials is gaining momentum, with several promising approaches demonstrating recovery rates exceeding 80% for precious metals and rare earth elements. These circular economy approaches significantly enhance the long-term sustainability profile of perovskite-based technologies.
Scalability and Industrial Production Feasibility Assessment
The scalability of hydrothermal growth methods for perovskite crystals represents a critical consideration for transitioning from laboratory-scale synthesis to industrial production. Current hydrothermal processes typically yield high-quality perovskite crystals but are limited to batch sizes of 50-100 grams, presenting significant challenges for commercial viability. The economic feasibility analysis indicates that production costs could decrease by approximately 60-70% through scale optimization, making industrial implementation increasingly attractive.
Key scalability parameters include reactor vessel design, pressure management systems, and temperature control mechanisms. Industrial-scale hydrothermal autoclaves would require specialized materials capable of withstanding prolonged exposure to corrosive environments while maintaining structural integrity under high pressure (typically 10-20 MPa) and temperature (180-250°C) conditions. Teflon-lined stainless steel vessels currently dominate laboratory applications, but alternative materials such as titanium alloys and specialized ceramics show promise for larger-scale operations.
Process automation represents another crucial aspect of industrial feasibility. Current laboratory methods often rely on manual parameter adjustments and monitoring, whereas industrial implementation would necessitate advanced control systems with real-time monitoring capabilities. Automated nutrient delivery systems could potentially extend continuous operation periods from the current 24-72 hours to weeks, significantly enhancing production efficiency.
Energy consumption analysis reveals that hydrothermal methods, despite their high pressure and temperature requirements, may offer superior energy efficiency compared to alternative crystal growth techniques when scaled appropriately. Preliminary calculations suggest energy costs of approximately 15-20 kWh per kilogram of perovskite crystal produced at industrial scale, representing a 30-40% reduction compared to solution-based methods at similar volumes.
Waste management and environmental considerations also factor prominently in scalability assessments. The closed-system nature of hydrothermal growth offers advantages in containing potentially hazardous precursors, but end-of-life processing of spent growth solutions requires further development. Recycling protocols for growth media could potentially recover 70-85% of precursor materials, substantially improving both economic and environmental sustainability metrics.
Market analysis indicates that achieving production capacities of 500-1000 kg annually would satisfy current demand in specialized electronics and research sectors, while expansion to 5-10 metric tons annually would be necessary to support emerging applications in photovoltaics and optoelectronics. The estimated timeline for developing fully optimized industrial-scale production ranges from 3-5 years, contingent upon continued advances in reactor design and process control technologies.
Key scalability parameters include reactor vessel design, pressure management systems, and temperature control mechanisms. Industrial-scale hydrothermal autoclaves would require specialized materials capable of withstanding prolonged exposure to corrosive environments while maintaining structural integrity under high pressure (typically 10-20 MPa) and temperature (180-250°C) conditions. Teflon-lined stainless steel vessels currently dominate laboratory applications, but alternative materials such as titanium alloys and specialized ceramics show promise for larger-scale operations.
Process automation represents another crucial aspect of industrial feasibility. Current laboratory methods often rely on manual parameter adjustments and monitoring, whereas industrial implementation would necessitate advanced control systems with real-time monitoring capabilities. Automated nutrient delivery systems could potentially extend continuous operation periods from the current 24-72 hours to weeks, significantly enhancing production efficiency.
Energy consumption analysis reveals that hydrothermal methods, despite their high pressure and temperature requirements, may offer superior energy efficiency compared to alternative crystal growth techniques when scaled appropriately. Preliminary calculations suggest energy costs of approximately 15-20 kWh per kilogram of perovskite crystal produced at industrial scale, representing a 30-40% reduction compared to solution-based methods at similar volumes.
Waste management and environmental considerations also factor prominently in scalability assessments. The closed-system nature of hydrothermal growth offers advantages in containing potentially hazardous precursors, but end-of-life processing of spent growth solutions requires further development. Recycling protocols for growth media could potentially recover 70-85% of precursor materials, substantially improving both economic and environmental sustainability metrics.
Market analysis indicates that achieving production capacities of 500-1000 kg annually would satisfy current demand in specialized electronics and research sectors, while expansion to 5-10 metric tons annually would be necessary to support emerging applications in photovoltaics and optoelectronics. The estimated timeline for developing fully optimized industrial-scale production ranges from 3-5 years, contingent upon continued advances in reactor design and process control technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!