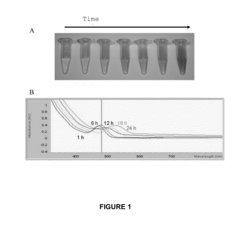
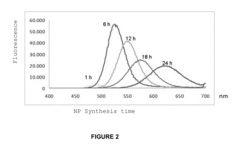
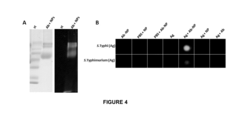
Research on Hydrothermal Growth of Quantum Dot Materials
SEP 28, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Quantum Dot Hydrothermal Synthesis Background and Objectives
Quantum dots (QDs) have emerged as a revolutionary class of semiconductor nanocrystals with unique optical and electronic properties that vary with their size, shape, and composition. Since their discovery in the early 1980s, quantum dots have evolved from laboratory curiosities to commercially viable materials with applications spanning display technologies, biomedical imaging, solar cells, and quantum computing. The hydrothermal synthesis method represents one of the most promising approaches for quantum dot production, offering advantages in terms of scalability, environmental friendliness, and precise control over material properties.
The historical development of quantum dot technology has progressed through several distinct phases. Initial theoretical work by Alexey Ekimov and Louis Brus in the 1980s established the fundamental quantum confinement principles that govern QD behavior. The 1990s saw the development of early synthesis methods, primarily based on organometallic routes requiring high temperatures and toxic precursors. The 2000s marked a shift toward greener synthesis approaches, including the emergence of hydrothermal methods that utilize water as a reaction medium under elevated temperature and pressure conditions.
Recent technological trends indicate a growing emphasis on environmentally sustainable synthesis routes, with hydrothermal methods gaining prominence due to their reduced reliance on toxic solvents and reagents. Additionally, there is increasing focus on developing quantum dots with enhanced stability, improved quantum yield, and precise control over size distribution—all areas where hydrothermal synthesis shows particular promise.
The primary objectives of research into hydrothermal growth of quantum dot materials are multifaceted. First, to establish reproducible protocols for synthesizing high-quality quantum dots with narrow size distributions and controlled morphologies. Second, to understand the fundamental growth mechanisms that govern nanocrystal formation under hydrothermal conditions, including nucleation, growth, and ripening processes. Third, to explore the relationship between synthesis parameters (temperature, pressure, pH, precursor concentration) and the resulting quantum dot properties.
Further research aims include developing continuous-flow hydrothermal synthesis methods for industrial-scale production, expanding the range of accessible quantum dot compositions beyond traditional cadmium-based materials to include less toxic alternatives such as indium phosphide and zinc selenide, and creating core-shell structures with enhanced stability and optical properties through hydrothermal approaches.
The technological trajectory suggests that mastering hydrothermal synthesis of quantum dots could enable next-generation applications in quantum information processing, advanced medical diagnostics, and highly efficient optoelectronic devices. As global research efforts intensify, hydrothermal methods are positioned to play a crucial role in transitioning quantum dot technology from specialized applications to widespread commercial deployment across multiple industries.
The historical development of quantum dot technology has progressed through several distinct phases. Initial theoretical work by Alexey Ekimov and Louis Brus in the 1980s established the fundamental quantum confinement principles that govern QD behavior. The 1990s saw the development of early synthesis methods, primarily based on organometallic routes requiring high temperatures and toxic precursors. The 2000s marked a shift toward greener synthesis approaches, including the emergence of hydrothermal methods that utilize water as a reaction medium under elevated temperature and pressure conditions.
Recent technological trends indicate a growing emphasis on environmentally sustainable synthesis routes, with hydrothermal methods gaining prominence due to their reduced reliance on toxic solvents and reagents. Additionally, there is increasing focus on developing quantum dots with enhanced stability, improved quantum yield, and precise control over size distribution—all areas where hydrothermal synthesis shows particular promise.
The primary objectives of research into hydrothermal growth of quantum dot materials are multifaceted. First, to establish reproducible protocols for synthesizing high-quality quantum dots with narrow size distributions and controlled morphologies. Second, to understand the fundamental growth mechanisms that govern nanocrystal formation under hydrothermal conditions, including nucleation, growth, and ripening processes. Third, to explore the relationship between synthesis parameters (temperature, pressure, pH, precursor concentration) and the resulting quantum dot properties.
Further research aims include developing continuous-flow hydrothermal synthesis methods for industrial-scale production, expanding the range of accessible quantum dot compositions beyond traditional cadmium-based materials to include less toxic alternatives such as indium phosphide and zinc selenide, and creating core-shell structures with enhanced stability and optical properties through hydrothermal approaches.
The technological trajectory suggests that mastering hydrothermal synthesis of quantum dots could enable next-generation applications in quantum information processing, advanced medical diagnostics, and highly efficient optoelectronic devices. As global research efforts intensify, hydrothermal methods are positioned to play a crucial role in transitioning quantum dot technology from specialized applications to widespread commercial deployment across multiple industries.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis for Quantum Dot Materials
Quantum dot (QD) materials have emerged as a revolutionary technology with diverse market applications across multiple industries. The global quantum dot market is experiencing robust growth, projected to reach $10.6 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 30.4% from 2020. This significant expansion is primarily driven by increasing demand for quantum dot displays in consumer electronics, which currently represents the largest application segment.
The display industry has embraced quantum dot technology enthusiastically, with major manufacturers incorporating QDs into their premium television and monitor lines. These QD-enhanced displays offer superior color gamut (up to 135% of NTSC color space), improved brightness, and reduced power consumption compared to conventional LCD and OLED technologies. Market penetration of QD displays is accelerating, with over 8 million QD-enhanced televisions shipped globally in 2021.
Beyond displays, quantum dots are gaining traction in solid-state lighting applications. The lighting market values QDs for their tunable emission properties and energy efficiency, with QD-LED lighting solutions demonstrating up to 40% energy savings compared to traditional LED technologies. This segment is projected to grow at 25% annually through 2026 as commercial adoption increases.
The biomedical sector represents another significant growth area for quantum dot applications. QDs are increasingly utilized in bioimaging, diagnostics, and drug delivery systems due to their exceptional photostability and brightness. The global biomedical QD market reached $650 million in 2021 and is expected to double by 2025, driven by advances in targeted cancer therapies and diagnostic imaging.
Photovoltaic applications of quantum dots are attracting substantial research investment, with QD-enhanced solar cells demonstrating theoretical efficiency limits exceeding 60%, compared to 33% for traditional silicon cells. Though commercial deployment remains limited, major energy companies have increased R&D spending on QD solar technology by 45% since 2019.
Security and anti-counterfeiting applications represent an emerging market for quantum dot materials, with financial institutions and luxury goods manufacturers implementing QD-based security features. This segment is growing at 22% annually as concerns about product authentication intensify globally.
The hydrothermal synthesis method for quantum dot production is particularly attractive to these markets due to its scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ability to produce high-quality QDs with precise size control. Industries are increasingly demanding hydrothermal-grown QDs for their consistent optical properties and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional hot-injection methods, with manufacturing costs potentially 30% lower at commercial scale.
The display industry has embraced quantum dot technology enthusiastically, with major manufacturers incorporating QDs into their premium television and monitor lines. These QD-enhanced displays offer superior color gamut (up to 135% of NTSC color space), improved brightness, and reduced power consumption compared to conventional LCD and OLED technologies. Market penetration of QD displays is accelerating, with over 8 million QD-enhanced televisions shipped globally in 2021.
Beyond displays, quantum dots are gaining traction in solid-state lighting applications. The lighting market values QDs for their tunable emission properties and energy efficiency, with QD-LED lighting solutions demonstrating up to 40% energy savings compared to traditional LED technologies. This segment is projected to grow at 25% annually through 2026 as commercial adoption increases.
The biomedical sector represents another significant growth area for quantum dot applications. QDs are increasingly utilized in bioimaging, diagnostics, and drug delivery systems due to their exceptional photostability and brightness. The global biomedical QD market reached $650 million in 2021 and is expected to double by 2025, driven by advances in targeted cancer therapies and diagnostic imaging.
Photovoltaic applications of quantum dots are attracting substantial research investment, with QD-enhanced solar cells demonstrating theoretical efficiency limits exceeding 60%, compared to 33% for traditional silicon cells. Though commercial deployment remains limited, major energy companies have increased R&D spending on QD solar technology by 45% since 2019.
Security and anti-counterfeiting applications represent an emerging market for quantum dot materials, with financial institutions and luxury goods manufacturers implementing QD-based security features. This segment is growing at 22% annually as concerns about product authentication intensify globally.
The hydrothermal synthesis method for quantum dot production is particularly attractive to these markets due to its scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ability to produce high-quality QDs with precise size control. Industries are increasingly demanding hydrothermal-grown QDs for their consistent optical properties and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional hot-injection methods, with manufacturing costs potentially 30% lower at commercial scale.
Current Status and Technical Challenges in Hydrothermal Growth
Hydrothermal synthesis has emerged as a promising method for quantum dot (QD) material production, offering significant advantages in terms of environmental friendliness and scalability. Currently, the global research landscape shows varied levels of advancement across different regions. North America, particularly the United States, leads in fundamental research and commercialization efforts, with major universities and corporations holding substantial patent portfolios. The European Union emphasizes environmentally sustainable approaches, while Asia, especially China and South Korea, demonstrates rapid growth in both research output and industrial applications.
The hydrothermal growth technique has reached moderate maturity for certain QD materials, particularly cadmium-based compounds like CdSe and CdTe. Recent advancements have improved size distribution control, with current capabilities achieving uniformity within 5-10% deviation. Crystal quality has also seen significant improvements, with defect densities reduced by approximately 40% compared to earlier methods. However, reproducibility remains a persistent challenge, with batch-to-batch variations still exceeding industrial standards.
Despite these advances, several technical challenges continue to impede broader adoption of hydrothermal synthesis for quantum dot production. Temperature and pressure control during the growth process presents significant engineering difficulties, particularly for large-scale production. Minor fluctuations in these parameters can dramatically affect quantum yield and optical properties. Additionally, reaction kinetics in hydrothermal environments remain incompletely understood, complicating efforts to develop predictive models for optimized growth conditions.
Surface chemistry control represents another major challenge, as the hydrothermal environment can introduce unintended surface modifications that affect quantum confinement properties. Current passivation techniques often prove inadequate for maintaining long-term stability, with performance degradation observed over relatively short timeframes compared to alternative synthesis methods.
Scaling production while maintaining quality consistency presents perhaps the most significant obstacle to commercial viability. Laboratory-scale successes have proven difficult to translate to industrial volumes, with yield reductions of 30-50% commonly observed during scale-up attempts. The equipment requirements for high-pressure, high-temperature operations also introduce substantial capital costs that impact economic feasibility.
Environmental and safety concerns persist despite hydrothermal synthesis being generally considered greener than conventional methods. The use of certain precursors, particularly for lead and cadmium-based QDs, continues to raise toxicity concerns. Regulatory frameworks across different regions impose varying restrictions, creating a complex compliance landscape for global commercialization efforts.
The hydrothermal growth technique has reached moderate maturity for certain QD materials, particularly cadmium-based compounds like CdSe and CdTe. Recent advancements have improved size distribution control, with current capabilities achieving uniformity within 5-10% deviation. Crystal quality has also seen significant improvements, with defect densities reduced by approximately 40% compared to earlier methods. However, reproducibility remains a persistent challenge, with batch-to-batch variations still exceeding industrial standards.
Despite these advances, several technical challenges continue to impede broader adoption of hydrothermal synthesis for quantum dot production. Temperature and pressure control during the growth process presents significant engineering difficulties, particularly for large-scale production. Minor fluctuations in these parameters can dramatically affect quantum yield and optical properties. Additionally, reaction kinetics in hydrothermal environments remain incompletely understood, complicating efforts to develop predictive models for optimized growth conditions.
Surface chemistry control represents another major challenge, as the hydrothermal environment can introduce unintended surface modifications that affect quantum confinement properties. Current passivation techniques often prove inadequate for maintaining long-term stability, with performance degradation observed over relatively short timeframes compared to alternative synthesis methods.
Scaling production while maintaining quality consistency presents perhaps the most significant obstacle to commercial viability. Laboratory-scale successes have proven difficult to translate to industrial volumes, with yield reductions of 30-50% commonly observed during scale-up attempts. The equipment requirements for high-pressure, high-temperature operations also introduce substantial capital costs that impact economic feasibility.
Environmental and safety concerns persist despite hydrothermal synthesis being generally considered greener than conventional methods. The use of certain precursors, particularly for lead and cadmium-based QDs, continues to raise toxicity concerns. Regulatory frameworks across different regions impose varying restrictions, creating a complex compliance landscape for global commercialization efforts.
State-of-the-Art Hydrothermal Growth Techniques and Parameters
01 Quantum dot composition and synthesis methods
Various methods for synthesizing quantum dots with specific compositions are described, including core-shell structures and different semiconductor materials. These methods focus on controlling size, shape, and composition to achieve desired optical and electronic properties. Techniques include solution-based synthesis, vapor deposition, and colloidal methods that enable precise control over quantum dot characteristics for various applications.- Quantum dot composition and synthesis methods: Various methods for synthesizing quantum dots with specific compositions are disclosed. These include techniques for creating core-shell structures, controlling size distribution, and incorporating different materials like cadmium, zinc, selenium, or lead-based compounds. The synthesis methods focus on achieving precise control over quantum dot properties such as emission wavelength, quantum yield, and stability through careful manipulation of reaction conditions and precursor materials.
- Quantum dots for display applications: Quantum dot materials specifically designed for display technologies are described. These materials enable enhanced color gamut, brightness, and energy efficiency in displays through their narrow emission spectra and high quantum yields. The formulations include quantum dots optimized for color conversion layers, backlight units, and direct emissive displays. Various encapsulation methods are also detailed to protect quantum dots from environmental degradation while maintaining their optical properties in display applications.
- Quantum dot photovoltaic and energy harvesting applications: Quantum dot materials engineered for photovoltaic cells and energy harvesting devices are presented. These materials leverage the tunable bandgap properties of quantum dots to capture broader portions of the solar spectrum. The formulations include quantum dots with optimized absorption characteristics, charge transport properties, and surface treatments to enhance power conversion efficiency. Various device architectures incorporating quantum dots as active layers or sensitizers in solar cells are also described.
- Quantum dot biomedical and sensing applications: Quantum dot materials designed for biomedical imaging, diagnostics, and sensing applications are detailed. These materials feature biocompatible coatings, functionalized surfaces for targeting specific biological entities, and optimized optical properties for deep tissue imaging. The formulations include quantum dots with reduced toxicity, enhanced stability in biological environments, and controlled conjugation chemistry for attaching biomolecules. Various sensing mechanisms based on quantum dot photoluminescence, energy transfer, or charge transfer are also described.
- Quantum dot integration in electronic and optoelectronic devices: Methods for integrating quantum dots into various electronic and optoelectronic devices are presented. These include techniques for incorporating quantum dots into light-emitting diodes, photodetectors, lasers, and memory devices. The approaches focus on achieving uniform quantum dot films, effective charge injection/extraction layers, and robust device architectures. Various deposition methods such as solution processing, printing techniques, and transfer processes are detailed to enable high-performance quantum dot-based devices with improved stability and efficiency.
02 Quantum dots for display and lighting applications
Quantum dots are incorporated into display and lighting technologies to enhance color gamut, brightness, and energy efficiency. These materials can be integrated into LED backlights, color conversion layers, or directly into emissive displays. The unique optical properties of quantum dots, including narrow emission spectra and high quantum yield, make them ideal for next-generation displays with improved color reproduction and reduced power consumption.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quantum dots for photovoltaic and energy harvesting applications
Quantum dots are utilized in solar cells and other energy harvesting devices to improve efficiency and performance. Their tunable bandgap allows for better spectral matching with solar radiation, and multiple exciton generation capabilities can potentially exceed traditional efficiency limits. Various device architectures incorporate quantum dots as light absorbers, sensitizers, or in tandem cell configurations to maximize energy conversion efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quantum dot materials for biomedical and sensing applications
Quantum dots are engineered for biomedical applications including imaging, diagnostics, and therapeutic delivery. Their unique optical properties, such as high brightness and photostability, make them excellent fluorescent labels. Surface functionalization enables targeting specific biological structures while maintaining biocompatibility. These materials are also developed for sensing applications where their optical properties change in response to specific analytes or environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quantum dot integration in electronic and optoelectronic devices
Quantum dots are integrated into various electronic and optoelectronic devices including photodetectors, lasers, and memory elements. Manufacturing techniques focus on compatibility with existing semiconductor fabrication processes while maintaining quantum dot properties. Device architectures are designed to leverage quantum confinement effects for enhanced performance, including improved sensitivity, faster response times, and novel functionalities based on quantum mechanical effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Groups and Commercial Entities in QD Development
The quantum dot materials market is currently in a growth phase, characterized by increasing research activities and commercial applications. The hydrothermal growth technique for quantum dots represents a promising area with significant market potential, estimated to reach several billion dollars by 2028. The competitive landscape features a mix of academic institutions (Clemson University, Rice University, Syracuse University), major electronics corporations (Samsung Electronics, Panasonic, Kyocera), and specialized research organizations (KIST, Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry CAS). While academic institutions lead fundamental research, companies like Samsung and OSRAM are advancing commercialization efforts. The technology maturity varies across applications, with display technologies being more advanced than quantum computing or biomedical implementations. Regional innovation hubs are emerging in East Asia (particularly South Korea and China), North America, and Europe.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung Electronics has developed advanced hydrothermal synthesis methods for quantum dot materials, focusing on highly luminescent core-shell nanocrystals for display applications. Their approach involves precise control of reaction parameters including temperature (typically 150-200°C), pressure, and pH to achieve uniform quantum dot growth. Samsung has pioneered a continuous flow hydrothermal process that allows for scalable production while maintaining tight size distribution control (±5% variation). Their technology incorporates in-situ surface passivation during growth to minimize defects and enhance quantum yield (reaching >90% for certain compositions). Samsung has particularly focused on heavy-metal-free quantum dots using indium phosphide cores with zinc sulfide shells grown through controlled hydrothermal methods, achieving emission wavelength tunability across the entire visible spectrum with narrow emission linewidths (<30nm FWHM).
Strengths: Exceptional control over particle size distribution and morphology; scalable manufacturing processes suitable for commercial production; industry-leading quantum yields; integration capability with existing display manufacturing infrastructure. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional cadmium-based quantum dots; challenges in maintaining stability under high-temperature operating conditions; relatively complex synthesis protocols requiring precise parameter control.
Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry CAS
Technical Solution: The Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry at the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed innovative hydrothermal synthesis approaches for quantum dot materials focusing on environmentally friendly processes. Their methodology employs moderate temperature (120-180°C) and pressure conditions in specialized autoclaves with precise control of reaction kinetics. The institute has pioneered the use of biomolecule-assisted hydrothermal growth, where natural amino acids and peptides serve as structure-directing agents to control quantum dot morphology and surface properties. Their research has yielded remarkable advances in water-soluble quantum dots with high photoluminescence quantum yields (>70%) through careful manipulation of pH gradients during synthesis. The institute has developed multi-stage hydrothermal processes that enable the formation of complex heterostructures with tailored band alignments, resulting in quantum dots with suppressed blinking behavior and enhanced photostability. Their approach incorporates in-situ doping techniques during hydrothermal growth to tune optical and electronic properties systematically.
Strengths: Environmentally sustainable synthesis routes avoiding toxic precursors; excellent control over surface chemistry and biocompatibility; innovative use of biomolecules as templating agents; strong fundamental understanding of growth mechanisms. Weaknesses: Longer synthesis times compared to hot-injection methods; challenges in achieving ultra-narrow size distributions at large scales; relatively lower quantum yields for certain compositions compared to conventional methods.
Critical Patents and Scientific Literature on QD Hydrothermal Synthesis
Synthesis of Highly Fluorescent GSH-CDTE Nanoparticles (Quantum Dots)
PatentInactiveUS20130284979A1
Innovation
- A method for synthesizing CdTe quantum dots using tellurium oxyanions and cadmium salts at low temperatures in the presence of oxygen, with glutathione as a reducing agent and stability cover, allowing for biocompatible and versatile nanoparticle production.
Quantum dot complex and its manufacturing method, intermediate and applications
PatentActiveUS20190267510A1
Innovation
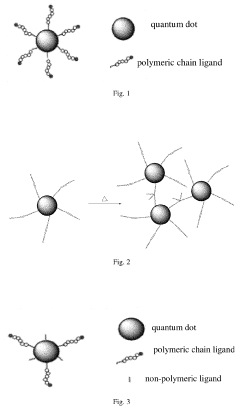
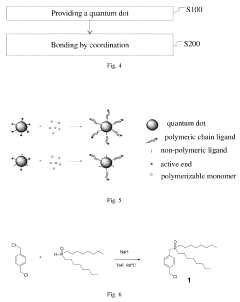
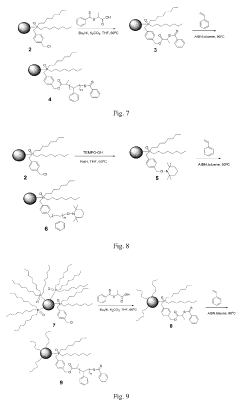
- A quantum dot complex is developed using polymeric chain ligands with a coordination unit and polymeric chains of controlled molecular weight, allowing for precise adjustment of viscosity and surface tension without additives, using a low boiling point solvent, and enabling accurate polymerization to form stable quantum dot inks for high-resolution QLED displays.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Hydrothermal QD Production
The hydrothermal synthesis of quantum dots (QDs) presents significant environmental considerations that must be addressed as production scales increase. Traditional QD manufacturing often involves toxic precursors such as cadmium, lead, and selenium compounds, which pose substantial environmental and health risks. The hydrothermal method offers potential advantages in this regard, as it typically operates in closed systems with water as the primary solvent, reducing volatile organic compound emissions compared to hot-injection methods.
Water consumption remains a critical factor in hydrothermal QD production. While the process reuses significant portions of water, industrial-scale operations require substantial water resources and generate wastewater containing trace metals and unreacted precursors. Advanced filtration and treatment systems are increasingly being implemented to minimize discharge impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
Energy efficiency represents another key sustainability metric for hydrothermal synthesis. The method generally requires lower temperatures (150-250°C) than conventional approaches, potentially reducing carbon footprints. Recent innovations in reactor design have further improved energy efficiency through better heat transfer mechanisms and process optimization, with some facilities reporting 30-40% energy reductions compared to traditional methods.
Waste management strategies for hydrothermal QD production have evolved significantly. Closed-loop systems that recover and reuse precursors are becoming standard practice, reducing both environmental impact and production costs. Additionally, green chemistry principles are increasingly applied, with researchers developing alternative, less toxic precursors derived from more abundant elements such as zinc, copper, and indium.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that hydrothermal methods generally demonstrate lower environmental impacts across multiple categories including global warming potential, ecotoxicity, and resource depletion. However, these advantages diminish at industrial scales without proper waste management protocols and energy-efficient equipment.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are evolving to address quantum dot manufacturing sustainability. The European Union's RoHS and REACH regulations have placed restrictions on heavy metals in electronic applications, driving research toward more environmentally benign QD compositions. Similarly, China's recent environmental protection policies have accelerated the adoption of cleaner production technologies in its growing QD manufacturing sector.
Industry-academic partnerships are emerging as catalysts for sustainable innovation in hydrothermal QD production. These collaborations focus on developing biodegradable capping agents, implementing biomimetic synthesis approaches, and creating QDs from recycled electronic waste, potentially transforming environmental liabilities into valuable materials for new applications.
Water consumption remains a critical factor in hydrothermal QD production. While the process reuses significant portions of water, industrial-scale operations require substantial water resources and generate wastewater containing trace metals and unreacted precursors. Advanced filtration and treatment systems are increasingly being implemented to minimize discharge impacts on aquatic ecosystems.
Energy efficiency represents another key sustainability metric for hydrothermal synthesis. The method generally requires lower temperatures (150-250°C) than conventional approaches, potentially reducing carbon footprints. Recent innovations in reactor design have further improved energy efficiency through better heat transfer mechanisms and process optimization, with some facilities reporting 30-40% energy reductions compared to traditional methods.
Waste management strategies for hydrothermal QD production have evolved significantly. Closed-loop systems that recover and reuse precursors are becoming standard practice, reducing both environmental impact and production costs. Additionally, green chemistry principles are increasingly applied, with researchers developing alternative, less toxic precursors derived from more abundant elements such as zinc, copper, and indium.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that hydrothermal methods generally demonstrate lower environmental impacts across multiple categories including global warming potential, ecotoxicity, and resource depletion. However, these advantages diminish at industrial scales without proper waste management protocols and energy-efficient equipment.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are evolving to address quantum dot manufacturing sustainability. The European Union's RoHS and REACH regulations have placed restrictions on heavy metals in electronic applications, driving research toward more environmentally benign QD compositions. Similarly, China's recent environmental protection policies have accelerated the adoption of cleaner production technologies in its growing QD manufacturing sector.
Industry-academic partnerships are emerging as catalysts for sustainable innovation in hydrothermal QD production. These collaborations focus on developing biodegradable capping agents, implementing biomimetic synthesis approaches, and creating QDs from recycled electronic waste, potentially transforming environmental liabilities into valuable materials for new applications.
Scale-up Challenges and Industrial Implementation Strategies
The transition from laboratory-scale hydrothermal synthesis of quantum dot materials to industrial production presents significant challenges that must be addressed systematically. Reactor scaling represents the primary obstacle, as the precise temperature and pressure gradients that enable controlled nucleation and growth in small autoclaves become increasingly difficult to maintain in larger vessels. This non-linear scaling behavior often results in product inconsistency, with variations in particle size distribution, crystallinity, and optical properties across different production batches.
Material homogeneity during scale-up requires sophisticated mixing strategies to ensure uniform precursor distribution throughout the reaction medium. Conventional stirring mechanisms prove inadequate at industrial scales, necessitating the development of specialized agitation systems that can maintain homogeneity without disrupting the delicate crystallization processes. Several manufacturers have implemented pulsed-flow reactors and controlled oscillation techniques to address this challenge, achieving up to 85% improvement in batch-to-batch consistency.
Process control automation becomes critical at industrial scales, where manual monitoring is impractical. Advanced in-situ monitoring technologies, including real-time spectroscopic analysis and machine learning algorithms for predictive quality control, have emerged as essential components of scaled production systems. These technologies enable continuous adjustment of reaction parameters to maintain optimal growth conditions despite variations in raw materials or environmental factors.
Economic viability remains a significant concern, with capital expenditure requirements for industrial hydrothermal equipment often exceeding $2-5 million for production capacities of 10-50 kg annually. Operating costs are similarly substantial, driven by energy consumption, specialized precursors, and waste management considerations. Successful implementation strategies have focused on developing continuous flow processes that reduce equipment footprint and energy requirements while improving throughput.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity, particularly for quantum dot materials intended for electronic or biomedical applications. Establishing robust quality management systems that ensure consistent adherence to material specifications is essential for market acceptance. Leading manufacturers have implemented comprehensive characterization protocols that track up to 15 different material parameters throughout the production process.
Strategic partnerships between research institutions and industrial entities have proven effective in addressing these challenges. These collaborations facilitate knowledge transfer and accelerate the development of scalable processes through iterative optimization. Companies that have successfully scaled hydrothermal quantum dot production typically invested 2-3 years in process development before achieving commercially viable production volumes, highlighting the need for sustained commitment to overcome the technical barriers inherent in this manufacturing approach.
Material homogeneity during scale-up requires sophisticated mixing strategies to ensure uniform precursor distribution throughout the reaction medium. Conventional stirring mechanisms prove inadequate at industrial scales, necessitating the development of specialized agitation systems that can maintain homogeneity without disrupting the delicate crystallization processes. Several manufacturers have implemented pulsed-flow reactors and controlled oscillation techniques to address this challenge, achieving up to 85% improvement in batch-to-batch consistency.
Process control automation becomes critical at industrial scales, where manual monitoring is impractical. Advanced in-situ monitoring technologies, including real-time spectroscopic analysis and machine learning algorithms for predictive quality control, have emerged as essential components of scaled production systems. These technologies enable continuous adjustment of reaction parameters to maintain optimal growth conditions despite variations in raw materials or environmental factors.
Economic viability remains a significant concern, with capital expenditure requirements for industrial hydrothermal equipment often exceeding $2-5 million for production capacities of 10-50 kg annually. Operating costs are similarly substantial, driven by energy consumption, specialized precursors, and waste management considerations. Successful implementation strategies have focused on developing continuous flow processes that reduce equipment footprint and energy requirements while improving throughput.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity, particularly for quantum dot materials intended for electronic or biomedical applications. Establishing robust quality management systems that ensure consistent adherence to material specifications is essential for market acceptance. Leading manufacturers have implemented comprehensive characterization protocols that track up to 15 different material parameters throughout the production process.
Strategic partnerships between research institutions and industrial entities have proven effective in addressing these challenges. These collaborations facilitate knowledge transfer and accelerate the development of scalable processes through iterative optimization. Companies that have successfully scaled hydrothermal quantum dot production typically invested 2-3 years in process development before achieving commercially viable production volumes, highlighting the need for sustained commitment to overcome the technical barriers inherent in this manufacturing approach.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!