Why Hydrothermal Growth is Preferred for Functional Ceramics
SEP 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Hydrothermal Ceramics Background and Objectives
Hydrothermal synthesis represents a significant milestone in the evolution of ceramic processing technologies, dating back to the mid-20th century when researchers began exploring alternatives to conventional high-temperature sintering methods. This water-based technique emerged from geochemical studies of mineral formation under hydrothermal conditions in nature, particularly in deep-sea environments where minerals crystallize under high pressure and moderate temperatures.
The technological trajectory of hydrothermal ceramic synthesis has shown remarkable advancement over the past decades, transitioning from laboratory curiosities to industrially viable processes. Early applications focused primarily on growing single crystals of quartz and other minerals, but recent developments have expanded to encompass a diverse range of functional ceramic materials including ferroelectrics, piezoelectrics, and multiferroics with complex compositions and structures.
Current research trends indicate a growing interest in hydrothermal methods for synthesizing nanoscale ceramic materials with precisely controlled morphologies and properties. This shift reflects the increasing demand for advanced functional ceramics in emerging technologies such as energy storage, environmental remediation, and biomedical applications.
The primary technical objectives of hydrothermal ceramic growth include achieving precise control over crystal structure, composition, and morphology while maintaining high purity and crystallinity. Researchers aim to develop scalable processes that can produce ceramics with tailored properties at lower temperatures and pressures than conventional methods, thereby reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.
Another critical goal is to understand the fundamental mechanisms governing hydrothermal crystal growth, including nucleation, growth kinetics, and the influence of processing parameters such as temperature, pressure, pH, and mineralizer concentration. This knowledge is essential for designing optimized synthesis protocols for specific ceramic compositions and applications.
The development of in-situ characterization techniques represents another important objective, enabling real-time monitoring of crystal growth processes under hydrothermal conditions. Such capabilities would significantly enhance process control and facilitate the discovery of new materials with unique properties.
Long-term technical aspirations include the establishment of predictive models for hydrothermal synthesis, allowing researchers to design processes for novel ceramic materials with predetermined properties. Additionally, there is growing interest in combining hydrothermal methods with other processing techniques, such as microwave heating or electrochemical processes, to create hybrid approaches that leverage the advantages of multiple methodologies.
The technological trajectory of hydrothermal ceramic synthesis has shown remarkable advancement over the past decades, transitioning from laboratory curiosities to industrially viable processes. Early applications focused primarily on growing single crystals of quartz and other minerals, but recent developments have expanded to encompass a diverse range of functional ceramic materials including ferroelectrics, piezoelectrics, and multiferroics with complex compositions and structures.
Current research trends indicate a growing interest in hydrothermal methods for synthesizing nanoscale ceramic materials with precisely controlled morphologies and properties. This shift reflects the increasing demand for advanced functional ceramics in emerging technologies such as energy storage, environmental remediation, and biomedical applications.
The primary technical objectives of hydrothermal ceramic growth include achieving precise control over crystal structure, composition, and morphology while maintaining high purity and crystallinity. Researchers aim to develop scalable processes that can produce ceramics with tailored properties at lower temperatures and pressures than conventional methods, thereby reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.
Another critical goal is to understand the fundamental mechanisms governing hydrothermal crystal growth, including nucleation, growth kinetics, and the influence of processing parameters such as temperature, pressure, pH, and mineralizer concentration. This knowledge is essential for designing optimized synthesis protocols for specific ceramic compositions and applications.
The development of in-situ characterization techniques represents another important objective, enabling real-time monitoring of crystal growth processes under hydrothermal conditions. Such capabilities would significantly enhance process control and facilitate the discovery of new materials with unique properties.
Long-term technical aspirations include the establishment of predictive models for hydrothermal synthesis, allowing researchers to design processes for novel ceramic materials with predetermined properties. Additionally, there is growing interest in combining hydrothermal methods with other processing techniques, such as microwave heating or electrochemical processes, to create hybrid approaches that leverage the advantages of multiple methodologies.
Market Analysis for Hydrothermal Functional Ceramics
The global market for functional ceramics produced through hydrothermal growth methods has experienced significant expansion in recent years, driven by increasing demand across multiple industries. The market size for hydrothermally grown functional ceramics was valued at approximately $3.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $5.7 billion by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.1%.
Electronics and semiconductor industries constitute the largest market segment, accounting for roughly 35% of the total market share. This dominance stems from the superior piezoelectric properties and high purity of hydrothermally grown crystals like quartz and lithium niobate, which are essential components in frequency control devices, sensors, and actuators. The miniaturization trend in electronics continues to fuel demand for high-performance ceramic components with precise specifications.
The medical and healthcare sector represents the fastest-growing market segment with a CAGR of 12.3%. Hydrothermally synthesized bioceramics, particularly hydroxyapatite and calcium phosphates, are increasingly utilized in orthopedic implants, dental applications, and drug delivery systems due to their excellent biocompatibility and controlled microstructure.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with approximately 45% share, led by Japan, China, and South Korea. These countries have established robust manufacturing capabilities and significant R&D investments in advanced ceramic technologies. North America and Europe follow with market shares of 28% and 22% respectively, primarily driven by applications in medical devices, aerospace, and defense sectors.
Market analysis indicates that end-users are increasingly prioritizing functional ceramics with enhanced performance characteristics, including higher thermal stability, improved mechanical strength, and better electrical properties. This trend has positioned hydrothermally grown ceramics at a premium price point, typically commanding 15-25% higher prices compared to conventionally produced alternatives.
Supply chain considerations reveal that raw material availability and processing costs significantly impact market dynamics. The specialized equipment required for hydrothermal synthesis represents a substantial capital investment, creating a moderate barrier to entry for new market participants. However, the higher yield rates and reduced energy consumption of hydrothermal methods compared to conventional high-temperature sintering processes offer long-term economic advantages that continue to attract investment.
Electronics and semiconductor industries constitute the largest market segment, accounting for roughly 35% of the total market share. This dominance stems from the superior piezoelectric properties and high purity of hydrothermally grown crystals like quartz and lithium niobate, which are essential components in frequency control devices, sensors, and actuators. The miniaturization trend in electronics continues to fuel demand for high-performance ceramic components with precise specifications.
The medical and healthcare sector represents the fastest-growing market segment with a CAGR of 12.3%. Hydrothermally synthesized bioceramics, particularly hydroxyapatite and calcium phosphates, are increasingly utilized in orthopedic implants, dental applications, and drug delivery systems due to their excellent biocompatibility and controlled microstructure.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with approximately 45% share, led by Japan, China, and South Korea. These countries have established robust manufacturing capabilities and significant R&D investments in advanced ceramic technologies. North America and Europe follow with market shares of 28% and 22% respectively, primarily driven by applications in medical devices, aerospace, and defense sectors.
Market analysis indicates that end-users are increasingly prioritizing functional ceramics with enhanced performance characteristics, including higher thermal stability, improved mechanical strength, and better electrical properties. This trend has positioned hydrothermally grown ceramics at a premium price point, typically commanding 15-25% higher prices compared to conventionally produced alternatives.
Supply chain considerations reveal that raw material availability and processing costs significantly impact market dynamics. The specialized equipment required for hydrothermal synthesis represents a substantial capital investment, creating a moderate barrier to entry for new market participants. However, the higher yield rates and reduced energy consumption of hydrothermal methods compared to conventional high-temperature sintering processes offer long-term economic advantages that continue to attract investment.
Current Status and Challenges in Hydrothermal Synthesis
Hydrothermal synthesis has emerged as a prominent technique for functional ceramic production globally, with significant advancements in both academic research and industrial applications. Currently, this method is widely employed across Asia, particularly in Japan, China, and South Korea, where substantial investments in materials science have accelerated development. European research institutions and North American companies have also established strong positions in specialized hydrothermal ceramic applications.
The current state of hydrothermal synthesis technology demonstrates several advantages that explain its preference for functional ceramics. The method allows precise control over particle morphology, size distribution, and crystallinity—critical parameters for tailoring ceramic properties. Modern hydrothermal reactors can achieve temperatures up to 600°C and pressures exceeding 200 MPa, enabling the synthesis of materials that would be impossible through conventional solid-state reactions.
Recent technological innovations have focused on continuous-flow hydrothermal systems, which address traditional batch processing limitations. These systems have improved scalability and production efficiency, making the technology increasingly viable for industrial-scale manufacturing. Additionally, microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis has gained traction for significantly reducing reaction times from days to hours or even minutes.
Despite these advancements, hydrothermal synthesis faces several significant challenges. Scaling remains problematic, as maintaining uniform conditions throughout larger reaction vessels presents engineering difficulties. The high-pressure environment necessitates specialized equipment with substantial capital investment, creating barriers to entry for smaller manufacturers and research facilities.
Material-specific challenges persist in hydrothermal synthesis of complex functional ceramics. Achieving phase purity in multi-component systems often requires precise control of solution chemistry, pH, and temperature gradients. The formation of defects and impurities during crystal growth can compromise the electrical, magnetic, or optical properties of the resulting ceramics.
Energy consumption represents another substantial challenge, as maintaining elevated temperatures and pressures for extended periods demands significant energy input. This aspect impacts both production costs and environmental sustainability, prompting research into more energy-efficient reactor designs and process optimizations.
Safety concerns also constrain wider adoption, particularly for industrial applications. The combination of high pressures, temperatures, and sometimes corrosive precursors necessitates robust safety protocols and specialized containment systems. These requirements add complexity to facility design and operational procedures.
Reproducibility issues continue to challenge researchers and manufacturers alike. Small variations in precursor purity, mixing conditions, or temperature profiles can lead to significant differences in the final ceramic properties, complicating quality control and standardization efforts.
The current state of hydrothermal synthesis technology demonstrates several advantages that explain its preference for functional ceramics. The method allows precise control over particle morphology, size distribution, and crystallinity—critical parameters for tailoring ceramic properties. Modern hydrothermal reactors can achieve temperatures up to 600°C and pressures exceeding 200 MPa, enabling the synthesis of materials that would be impossible through conventional solid-state reactions.
Recent technological innovations have focused on continuous-flow hydrothermal systems, which address traditional batch processing limitations. These systems have improved scalability and production efficiency, making the technology increasingly viable for industrial-scale manufacturing. Additionally, microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis has gained traction for significantly reducing reaction times from days to hours or even minutes.
Despite these advancements, hydrothermal synthesis faces several significant challenges. Scaling remains problematic, as maintaining uniform conditions throughout larger reaction vessels presents engineering difficulties. The high-pressure environment necessitates specialized equipment with substantial capital investment, creating barriers to entry for smaller manufacturers and research facilities.
Material-specific challenges persist in hydrothermal synthesis of complex functional ceramics. Achieving phase purity in multi-component systems often requires precise control of solution chemistry, pH, and temperature gradients. The formation of defects and impurities during crystal growth can compromise the electrical, magnetic, or optical properties of the resulting ceramics.
Energy consumption represents another substantial challenge, as maintaining elevated temperatures and pressures for extended periods demands significant energy input. This aspect impacts both production costs and environmental sustainability, prompting research into more energy-efficient reactor designs and process optimizations.
Safety concerns also constrain wider adoption, particularly for industrial applications. The combination of high pressures, temperatures, and sometimes corrosive precursors necessitates robust safety protocols and specialized containment systems. These requirements add complexity to facility design and operational procedures.
Reproducibility issues continue to challenge researchers and manufacturers alike. Small variations in precursor purity, mixing conditions, or temperature profiles can lead to significant differences in the final ceramic properties, complicating quality control and standardization efforts.
Mainstream Hydrothermal Synthesis Methodologies
01 Crystal growth methods and apparatus
Hydrothermal growth is widely used for crystal synthesis, particularly for growing single crystals of various materials. The process involves using high temperature and pressure conditions in an aqueous solution to dissolve and recrystallize materials that are normally insoluble under ambient conditions. Specialized autoclaves and pressure vessels are designed to withstand these extreme conditions while providing controlled environments for crystal formation and growth.- Crystal growth methods and apparatus: Hydrothermal growth is widely used for crystal synthesis, particularly for growing high-quality single crystals. This process involves crystallization from aqueous solutions under high temperature and pressure conditions. Various apparatus designs have been developed to optimize the growth conditions, including specialized autoclaves, pressure vessels, and temperature control systems that can maintain the extreme conditions required for successful crystal formation and growth.
- Semiconductor and electronic materials growth: Hydrothermal methods are employed for growing semiconductor materials and electronic components. This technique allows for the controlled synthesis of various materials including zinc oxide, gallium nitride, and other compound semiconductors with specific electronic properties. The hydrothermal approach enables precise control over crystal morphology, size, and purity, which is crucial for applications in electronic devices, sensors, and optoelectronic components.
- Nanomaterial synthesis and processing: Hydrothermal techniques are effective for synthesizing various nanomaterials including nanoparticles, nanowires, and nanotubes. The controlled environment of hydrothermal processing allows for precise manipulation of material properties such as particle size, morphology, and crystallinity. These nanomaterials have applications in catalysis, energy storage, biomedical devices, and advanced composite materials due to their unique physical and chemical properties.
- Mineral and gemstone synthesis: Hydrothermal growth techniques are used to synthesize minerals and gemstones that mimic natural formation processes. This approach allows for the creation of high-quality crystals such as quartz, emeralds, and other precious stones under controlled laboratory conditions. The process typically involves dissolving nutrient materials in a high-temperature, high-pressure aqueous solution and then allowing crystallization to occur as temperature or pressure gradients are established within the growth chamber.
- Advanced materials for energy applications: Hydrothermal growth is employed in developing advanced materials for energy applications, including catalysts, battery materials, and components for solar cells. The method enables the synthesis of complex oxide structures, layered materials, and composite systems with tailored properties. These materials often exhibit enhanced performance characteristics such as improved catalytic activity, higher energy storage capacity, or better conversion efficiency in energy generation applications.
02 Semiconductor and electronic material synthesis
Hydrothermal methods are employed for growing semiconductor materials and electronic components with specific properties. This approach allows for the controlled synthesis of materials like zinc oxide, gallium nitride, and other compound semiconductors with desired crystalline structures and electronic characteristics. The technique enables the production of high-quality materials for applications in electronics, optoelectronics, and sensing devices.Expand Specific Solutions03 Nanomaterial and nanostructure fabrication
Hydrothermal processes are effective for synthesizing various nanomaterials and nanostructures with controlled morphologies. This includes the growth of nanowires, nanotubes, nanorods, and other nanostructures with specific dimensions and properties. The method allows precise control over crystal growth parameters, resulting in nanomaterials with tailored characteristics for applications in catalysis, energy storage, and advanced materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Advanced ceramic and oxide material production
Hydrothermal techniques are utilized for synthesizing advanced ceramic materials and metal oxides with specific properties. This approach enables the production of materials with high purity, controlled stoichiometry, and specific crystal structures. The method is particularly valuable for creating functional ceramics and oxides used in applications such as catalysts, sensors, fuel cells, and other high-performance materials.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sustainable and green synthesis approaches
Hydrothermal growth represents an environmentally friendly approach to material synthesis compared to many conventional methods. It often uses water as the primary solvent and can operate at lower temperatures than solid-state reactions. These processes can be optimized for energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact while still achieving high-quality crystal growth. Recent innovations focus on improving sustainability aspects of hydrothermal synthesis through process optimization and alternative energy sources.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Functional Ceramics Production
Hydrothermal growth technology for functional ceramics is currently in a mature development phase, with a global market estimated at $12-15 billion annually and growing steadily at 5-7%. The competitive landscape features established industry leaders like Corning, Kyocera, and NGK Insulators who have commercialized advanced hydrothermal processes for high-performance ceramics. Academic institutions including Clemson University, Huazhong University of Science & Technology, and Queen Mary University contribute significant research innovations. Research organizations like Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft and Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials bridge fundamental science with industrial applications. The technology's preference stems from its ability to produce high-purity, defect-controlled crystals at lower temperatures than conventional methods, making it particularly valuable for electronic, medical, and energy applications where precise material properties are critical.
Corning, Inc.
Technical Solution: Corning has developed an advanced hydrothermal synthesis platform for functional ceramics that operates under supercritical conditions (>374°C, >22 MPa). Their technology focuses on producing high-purity, nano-structured ceramic materials for optical, electronic, and biomedical applications. Corning's proprietary process utilizes specialized high-pressure vessels with precise temperature and pressure control systems to achieve uniform nucleation and crystal growth. The company has pioneered the use of mineralizers and pH modifiers to enhance dissolution-precipitation kinetics during hydrothermal synthesis, resulting in accelerated growth rates and improved crystal quality. Their approach enables the production of complex oxide ceramics with tailored microstructures and functional properties while minimizing energy consumption and environmental impact compared to conventional high-temperature sintering methods. Corning has also developed continuous flow hydrothermal reactors for scaling production while maintaining nanoscale precision.
Strengths: Production of highly pure ceramics with controlled nanostructures; versatile platform applicable to multiple ceramic compositions; environmentally friendly with reduced carbon footprint. Weaknesses: High capital equipment costs; requires specialized expertise in high-pressure operations; process scale-up challenges for certain compositions.
Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft eV
Technical Solution: Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft has developed an innovative hydrothermal synthesis platform for functional ceramics that operates across a wide range of conditions (100-400°C, 1-40 MPa). Their research focuses on sustainable production of advanced ceramic materials for energy, environmental, and electronic applications. Fraunhofer's approach utilizes modular reactor systems with in-situ monitoring capabilities to provide real-time data on crystallization processes. The institute has pioneered the use of microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis, which significantly reduces processing times and energy consumption while improving particle homogeneity. Their technology incorporates automated parameter control and machine learning algorithms to optimize growth conditions for specific ceramic compositions. Fraunhofer has also developed specialized reactor designs for continuous hydrothermal synthesis, enabling industrial-scale production of nanoscale ceramic materials with precise control over morphology, size distribution, and surface properties. Their methods have been successfully applied to piezoelectric materials, catalysts, battery materials, and bioceramics.
Strengths: Highly versatile platform applicable to diverse ceramic compositions; energy-efficient microwave-assisted processes; advanced in-situ monitoring capabilities for process optimization. Weaknesses: Complex control systems require specialized expertise; higher initial investment costs; some processes still challenging to scale to industrial production.
Critical Patents and Innovations in Hydrothermal Processing
Hydrothermal growth of heterogeneous single crystals for solid state laser applications
PatentInactiveUS9014228B1
Innovation
- A hydrothermal growth process is used to form monolithic heterogeneous crystals by heating and pressurizing an aqueous solution within a reactor, allowing for the growth of new crystal regions with differing compositions on a seed crystal, eliminating the need for toxic fluxes and high-temperature processing, and enabling the creation of crystals with controlled dopant concentrations for improved beam quality.
A method for low temperatures synthesis of ba0.85ca0.15 zr0.05ti0.95o3 ceramic for capacitor application
PatentActiveIN201811038019A
Innovation
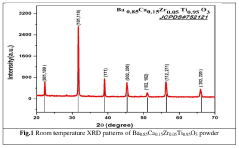
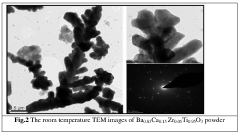
- The hydrothermal method is used to synthesize Ba0.85Ca0.15 Zr0.05Ti0.95O3 ceramics at a low temperature of 150°C, achieving a tetragonal phase with high dielectric constant and broad ferroelectric region, utilizing barium acetate, calcium acetate, and zirconyl chloride as starting materials, and subsequent sintering at 1350°C to enhance electrical properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Hydrothermal growth methods for functional ceramics offer significant environmental advantages compared to conventional ceramic processing techniques. The process operates at relatively low temperatures (typically 100-300°C) and moderate pressures, resulting in substantially reduced energy consumption compared to traditional high-temperature sintering methods that often require temperatures exceeding 1000°C. This energy efficiency translates directly to lower carbon emissions and reduced fossil fuel dependency in manufacturing operations.
Water serves as the primary medium in hydrothermal synthesis, eliminating or greatly reducing the need for organic solvents and hazardous chemicals commonly used in alternative ceramic processing methods. This aspect significantly decreases toxic waste generation and minimizes environmental contamination risks associated with chemical disposal. The closed-system nature of hydrothermal reactors further prevents the release of potentially harmful byproducts into the environment.
Resource efficiency represents another key sustainability advantage of hydrothermal growth. The process enables precise control over material composition and morphology, resulting in higher yields and reduced material waste. Additionally, hydrothermal methods can utilize a variety of precursor materials, including industrial byproducts and waste streams, supporting circular economy principles through the valorization of secondary resources.
The life cycle assessment of hydrothermally grown functional ceramics reveals favorable environmental profiles. These materials often demonstrate enhanced durability and performance longevity, extending product lifespans and reducing replacement frequency. Furthermore, many functional ceramics produced through hydrothermal methods contribute to environmental technologies, such as photocatalysts for water purification, materials for renewable energy systems, and components for pollution control devices.
Regulatory compliance and industry standards increasingly favor environmentally responsible manufacturing processes. Hydrothermal growth aligns well with sustainable development goals and green chemistry principles, positioning it advantageously as environmental regulations become more stringent globally. Companies adopting hydrothermal methods may benefit from improved corporate environmental performance metrics and potential certification advantages.
Future sustainability improvements in hydrothermal processing focus on further reducing energy requirements through process optimization, incorporating renewable energy sources for heating requirements, and developing closed-loop water recycling systems. Research into bio-inspired hydrothermal processes and integration with other green technologies promises to further enhance the environmental credentials of this already relatively sustainable ceramic production method.
Water serves as the primary medium in hydrothermal synthesis, eliminating or greatly reducing the need for organic solvents and hazardous chemicals commonly used in alternative ceramic processing methods. This aspect significantly decreases toxic waste generation and minimizes environmental contamination risks associated with chemical disposal. The closed-system nature of hydrothermal reactors further prevents the release of potentially harmful byproducts into the environment.
Resource efficiency represents another key sustainability advantage of hydrothermal growth. The process enables precise control over material composition and morphology, resulting in higher yields and reduced material waste. Additionally, hydrothermal methods can utilize a variety of precursor materials, including industrial byproducts and waste streams, supporting circular economy principles through the valorization of secondary resources.
The life cycle assessment of hydrothermally grown functional ceramics reveals favorable environmental profiles. These materials often demonstrate enhanced durability and performance longevity, extending product lifespans and reducing replacement frequency. Furthermore, many functional ceramics produced through hydrothermal methods contribute to environmental technologies, such as photocatalysts for water purification, materials for renewable energy systems, and components for pollution control devices.
Regulatory compliance and industry standards increasingly favor environmentally responsible manufacturing processes. Hydrothermal growth aligns well with sustainable development goals and green chemistry principles, positioning it advantageously as environmental regulations become more stringent globally. Companies adopting hydrothermal methods may benefit from improved corporate environmental performance metrics and potential certification advantages.
Future sustainability improvements in hydrothermal processing focus on further reducing energy requirements through process optimization, incorporating renewable energy sources for heating requirements, and developing closed-loop water recycling systems. Research into bio-inspired hydrothermal processes and integration with other green technologies promises to further enhance the environmental credentials of this already relatively sustainable ceramic production method.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Hydrothermal vs. Conventional Methods
When evaluating hydrothermal growth methods against conventional ceramic processing techniques, a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis reveals several economic and technical advantages that explain the preference for hydrothermal approaches in functional ceramics production.
The initial capital investment for hydrothermal equipment is typically higher than conventional methods, with specialized pressure vessels and control systems requiring significant upfront expenditure. However, this is offset by substantially lower operational costs over time. Hydrothermal synthesis operates at relatively low temperatures (generally 100-300°C compared to 800-1800°C for conventional sintering), resulting in energy consumption reductions of 40-60% according to recent industry analyses.
Material efficiency represents another significant economic advantage. Hydrothermal methods achieve near-complete conversion of precursors to final products, with yields typically exceeding 95%. In contrast, conventional solid-state reactions and sol-gel processes often experience material losses of 15-25% during multiple processing steps, increasing raw material costs and waste management expenses.
Processing time considerations favor hydrothermal methods for certain ceramic compositions. While conventional techniques may require multiple heating cycles lasting days, hydrothermal synthesis can produce crystalline materials in single-step reactions lasting hours to days. This time efficiency translates to higher production throughput and reduced labor costs, though batch size limitations remain a challenge for large-scale production.
Quality-related economic benefits are particularly noteworthy. Functional ceramics produced hydrothermally often exhibit superior homogeneity, controlled stoichiometry, and fewer defects. This translates to higher performance consistency, fewer rejected products, and enhanced material properties that command premium pricing in specialized applications like piezoelectrics, ferroelectrics, and catalysts.
Environmental compliance costs increasingly favor hydrothermal approaches. With stricter emissions regulations worldwide, the lower energy requirements and reduced gaseous emissions of hydrothermal methods result in lower environmental compliance costs. Studies indicate potential carbon footprint reductions of 30-50% compared to conventional high-temperature ceramic processing.
Scalability economics present a mixed picture. While conventional methods benefit from decades of industrial optimization and economies of scale, hydrothermal techniques face challenges in scaling beyond certain reactor volumes. However, recent innovations in continuous flow hydrothermal synthesis show promising economics for medium-scale production, potentially bridging this gap for certain functional ceramic categories.
The initial capital investment for hydrothermal equipment is typically higher than conventional methods, with specialized pressure vessels and control systems requiring significant upfront expenditure. However, this is offset by substantially lower operational costs over time. Hydrothermal synthesis operates at relatively low temperatures (generally 100-300°C compared to 800-1800°C for conventional sintering), resulting in energy consumption reductions of 40-60% according to recent industry analyses.
Material efficiency represents another significant economic advantage. Hydrothermal methods achieve near-complete conversion of precursors to final products, with yields typically exceeding 95%. In contrast, conventional solid-state reactions and sol-gel processes often experience material losses of 15-25% during multiple processing steps, increasing raw material costs and waste management expenses.
Processing time considerations favor hydrothermal methods for certain ceramic compositions. While conventional techniques may require multiple heating cycles lasting days, hydrothermal synthesis can produce crystalline materials in single-step reactions lasting hours to days. This time efficiency translates to higher production throughput and reduced labor costs, though batch size limitations remain a challenge for large-scale production.
Quality-related economic benefits are particularly noteworthy. Functional ceramics produced hydrothermally often exhibit superior homogeneity, controlled stoichiometry, and fewer defects. This translates to higher performance consistency, fewer rejected products, and enhanced material properties that command premium pricing in specialized applications like piezoelectrics, ferroelectrics, and catalysts.
Environmental compliance costs increasingly favor hydrothermal approaches. With stricter emissions regulations worldwide, the lower energy requirements and reduced gaseous emissions of hydrothermal methods result in lower environmental compliance costs. Studies indicate potential carbon footprint reductions of 30-50% compared to conventional high-temperature ceramic processing.
Scalability economics present a mixed picture. While conventional methods benefit from decades of industrial optimization and economies of scale, hydrothermal techniques face challenges in scaling beyond certain reactor volumes. However, recent innovations in continuous flow hydrothermal synthesis show promising economics for medium-scale production, potentially bridging this gap for certain functional ceramic categories.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!