Analysis of Temperature and Pressure Effects on Hydrothermal Growth
SEP 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Hydrothermal Growth Technology Background and Objectives
Hydrothermal growth technology represents one of the most significant methods for crystal synthesis, with roots dating back to the mid-19th century when geologists first attempted to replicate natural mineral formation processes. This technique has evolved substantially over the decades, transitioning from geological curiosity to a sophisticated industrial process critical for manufacturing various technological materials, particularly single crystals with specific properties.
The fundamental principle of hydrothermal growth involves dissolving materials in superheated water under high pressure conditions, creating an environment where crystallization can occur at temperatures significantly lower than traditional melt-based methods. This approach mimics natural geothermal processes but in controlled laboratory or industrial settings.
Historical development of hydrothermal technology shows clear evolutionary trends toward more precise control systems, enhanced pressure vessel designs, and improved understanding of solution chemistry. Early systems from the 1950s and 1960s operated with limited temperature and pressure ranges, while modern systems can maintain stable conditions at temperatures exceeding 700°C and pressures above 200 MPa, enabling the synthesis of previously unattainable crystal structures.
The primary technical objective in hydrothermal growth research centers on understanding and optimizing the complex relationship between temperature, pressure, and crystal formation dynamics. Temperature gradients within growth chambers directly influence supersaturation rates and crystal quality, while pressure affects solubility relationships and growth kinetics. These parameters are not independent but interact in complex ways that remain incompletely understood.
Current research aims to develop predictive models that accurately capture these temperature-pressure relationships across different material systems. Such models would enable more efficient process design, reduced experimental iterations, and ultimately lower production costs for industrial applications. Additionally, there is significant interest in expanding the range of materials that can be synthesized using hydrothermal methods.
The technology has particular relevance for electronic materials, including piezoelectric crystals, semiconductor substrates, and optical materials. The growing demand for high-performance materials in telecommunications, quantum computing, and renewable energy sectors has intensified interest in advanced hydrothermal synthesis techniques that can deliver crystals with precisely controlled properties.
Looking forward, the field is moving toward more sophisticated in-situ monitoring capabilities, allowing real-time observation of crystal growth processes under extreme conditions. This represents a significant technical challenge but offers tremendous potential for advancing fundamental understanding and practical applications of hydrothermal growth technology.
The fundamental principle of hydrothermal growth involves dissolving materials in superheated water under high pressure conditions, creating an environment where crystallization can occur at temperatures significantly lower than traditional melt-based methods. This approach mimics natural geothermal processes but in controlled laboratory or industrial settings.
Historical development of hydrothermal technology shows clear evolutionary trends toward more precise control systems, enhanced pressure vessel designs, and improved understanding of solution chemistry. Early systems from the 1950s and 1960s operated with limited temperature and pressure ranges, while modern systems can maintain stable conditions at temperatures exceeding 700°C and pressures above 200 MPa, enabling the synthesis of previously unattainable crystal structures.
The primary technical objective in hydrothermal growth research centers on understanding and optimizing the complex relationship between temperature, pressure, and crystal formation dynamics. Temperature gradients within growth chambers directly influence supersaturation rates and crystal quality, while pressure affects solubility relationships and growth kinetics. These parameters are not independent but interact in complex ways that remain incompletely understood.
Current research aims to develop predictive models that accurately capture these temperature-pressure relationships across different material systems. Such models would enable more efficient process design, reduced experimental iterations, and ultimately lower production costs for industrial applications. Additionally, there is significant interest in expanding the range of materials that can be synthesized using hydrothermal methods.
The technology has particular relevance for electronic materials, including piezoelectric crystals, semiconductor substrates, and optical materials. The growing demand for high-performance materials in telecommunications, quantum computing, and renewable energy sectors has intensified interest in advanced hydrothermal synthesis techniques that can deliver crystals with precisely controlled properties.
Looking forward, the field is moving toward more sophisticated in-situ monitoring capabilities, allowing real-time observation of crystal growth processes under extreme conditions. This represents a significant technical challenge but offers tremendous potential for advancing fundamental understanding and practical applications of hydrothermal growth technology.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis for Hydrothermal Crystals
The global market for hydrothermally grown crystals has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by increasing demand in electronics, optoelectronics, and renewable energy sectors. The unique properties of hydrothermally synthesized materials—including high purity, excellent crystallinity, and customizable dimensions—make them invaluable across multiple industries where precision and performance are paramount.
In the electronics industry, hydrothermally grown quartz crystals remain essential components in frequency control devices, with the global market for these components projected to reach $3.5 billion by 2025. The telecommunications sector's expansion, particularly with 5G infrastructure deployment, has created substantial demand for high-quality piezoelectric crystals that can operate at higher frequencies with minimal interference.
The optoelectronics market represents another significant demand driver, with hydrothermally grown crystals such as lithium niobate (LiNbO₃) and potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) being crucial for laser systems, optical modulators, and nonlinear optical applications. This segment is growing at approximately 7.2% annually, fueled by advancements in fiber optic communications and photonic integrated circuits.
Renewable energy applications constitute a rapidly expanding market for hydrothermal crystals. Particularly notable is the use of hydrothermally grown zinc oxide (ZnO) and titanium dioxide (TiO₂) in next-generation solar cells, where precise control of crystal morphology directly impacts energy conversion efficiency. The market value for these specialized materials in solar applications alone exceeded $420 million in 2022.
The medical technology sector has emerged as a promising growth area, with hydrothermally synthesized biocompatible crystals finding applications in medical imaging equipment, biosensors, and therapeutic devices. This segment is expected to grow at 9.3% annually through 2028, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and technological advancements in medical diagnostics.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates both production and consumption of hydrothermal crystals, accounting for approximately 45% of the global market. This regional concentration is attributed to the robust electronics manufacturing ecosystem in countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan. North America and Europe follow with significant market shares, particularly in high-value applications requiring advanced crystal specifications.
Industry analysts highlight that the market increasingly demands crystals grown under precisely controlled temperature and pressure conditions, as these parameters directly influence crystal quality, defect density, and ultimately, device performance. This trend underscores the commercial relevance of advanced research into temperature and pressure effects on hydrothermal growth processes.
In the electronics industry, hydrothermally grown quartz crystals remain essential components in frequency control devices, with the global market for these components projected to reach $3.5 billion by 2025. The telecommunications sector's expansion, particularly with 5G infrastructure deployment, has created substantial demand for high-quality piezoelectric crystals that can operate at higher frequencies with minimal interference.
The optoelectronics market represents another significant demand driver, with hydrothermally grown crystals such as lithium niobate (LiNbO₃) and potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) being crucial for laser systems, optical modulators, and nonlinear optical applications. This segment is growing at approximately 7.2% annually, fueled by advancements in fiber optic communications and photonic integrated circuits.
Renewable energy applications constitute a rapidly expanding market for hydrothermal crystals. Particularly notable is the use of hydrothermally grown zinc oxide (ZnO) and titanium dioxide (TiO₂) in next-generation solar cells, where precise control of crystal morphology directly impacts energy conversion efficiency. The market value for these specialized materials in solar applications alone exceeded $420 million in 2022.
The medical technology sector has emerged as a promising growth area, with hydrothermally synthesized biocompatible crystals finding applications in medical imaging equipment, biosensors, and therapeutic devices. This segment is expected to grow at 9.3% annually through 2028, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and technological advancements in medical diagnostics.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates both production and consumption of hydrothermal crystals, accounting for approximately 45% of the global market. This regional concentration is attributed to the robust electronics manufacturing ecosystem in countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan. North America and Europe follow with significant market shares, particularly in high-value applications requiring advanced crystal specifications.
Industry analysts highlight that the market increasingly demands crystals grown under precisely controlled temperature and pressure conditions, as these parameters directly influence crystal quality, defect density, and ultimately, device performance. This trend underscores the commercial relevance of advanced research into temperature and pressure effects on hydrothermal growth processes.
Current Challenges in Temperature-Pressure Control Systems
Despite significant advancements in hydrothermal growth technology, temperature and pressure control systems continue to face substantial challenges that limit process efficiency and crystal quality. Current autoclave systems struggle with maintaining precise temperature gradients across growth chambers, often experiencing fluctuations that can reach ±5°C in industrial-scale operations. These variations significantly impact crystallization kinetics and can introduce defects in grown materials, particularly for temperature-sensitive compounds like quartz and various semiconductor materials.
Pressure regulation systems exhibit similar limitations, with most commercial setups unable to respond rapidly to sudden pressure changes during critical growth phases. The lag time between pressure detection and adjustment can range from several seconds to minutes, creating conditions where metastable phases may form or where desired crystal structures become compromised. This is particularly problematic for materials requiring precise supercritical conditions, where even minor pressure deviations can dramatically alter solubility relationships.
Sensor technology represents another significant challenge area. Current in-situ monitoring capabilities remain limited by the harsh conditions inside hydrothermal chambers. Most temperature sensors cannot withstand the corrosive environments typical of mineralizer solutions, while pressure transducers often suffer from drift under prolonged exposure to extreme conditions. This forces many operations to rely on external measurements that provide only approximations of actual growth conditions.
The integration of control systems presents additional complications. Most existing setups employ separate control mechanisms for temperature and pressure, failing to account for the complex interdependencies between these parameters. This siloed approach to parameter management results in suboptimal response to process variations and can lead to cascading instabilities during growth cycles. Advanced algorithms capable of predictive control remain largely absent from commercial systems.
Material limitations further constrain control system performance. Autoclave liners and components must simultaneously withstand extreme temperatures, high pressures, and corrosive chemical environments. Current materials often represent compromises that limit either maximum operating conditions or service lifetime. Specialized alloys and composites that could potentially overcome these limitations remain prohibitively expensive for widespread implementation.
Energy efficiency concerns also impact control system design. Maintaining precise temperature profiles requires significant power input, with most systems operating at thermal efficiencies below 40%. This not only increases operational costs but also introduces thermal management challenges that can affect temperature stability. Next-generation systems will need to address these efficiency gaps while simultaneously improving control precision.
Pressure regulation systems exhibit similar limitations, with most commercial setups unable to respond rapidly to sudden pressure changes during critical growth phases. The lag time between pressure detection and adjustment can range from several seconds to minutes, creating conditions where metastable phases may form or where desired crystal structures become compromised. This is particularly problematic for materials requiring precise supercritical conditions, where even minor pressure deviations can dramatically alter solubility relationships.
Sensor technology represents another significant challenge area. Current in-situ monitoring capabilities remain limited by the harsh conditions inside hydrothermal chambers. Most temperature sensors cannot withstand the corrosive environments typical of mineralizer solutions, while pressure transducers often suffer from drift under prolonged exposure to extreme conditions. This forces many operations to rely on external measurements that provide only approximations of actual growth conditions.
The integration of control systems presents additional complications. Most existing setups employ separate control mechanisms for temperature and pressure, failing to account for the complex interdependencies between these parameters. This siloed approach to parameter management results in suboptimal response to process variations and can lead to cascading instabilities during growth cycles. Advanced algorithms capable of predictive control remain largely absent from commercial systems.
Material limitations further constrain control system performance. Autoclave liners and components must simultaneously withstand extreme temperatures, high pressures, and corrosive chemical environments. Current materials often represent compromises that limit either maximum operating conditions or service lifetime. Specialized alloys and composites that could potentially overcome these limitations remain prohibitively expensive for widespread implementation.
Energy efficiency concerns also impact control system design. Maintaining precise temperature profiles requires significant power input, with most systems operating at thermal efficiencies below 40%. This not only increases operational costs but also introduces thermal management challenges that can affect temperature stability. Next-generation systems will need to address these efficiency gaps while simultaneously improving control precision.
Current Temperature-Pressure Parameter Optimization Methods
01 Temperature effects on crystal growth and quality
Temperature plays a crucial role in hydrothermal crystal growth processes, directly affecting growth rates, crystal morphology, and defect formation. Higher temperatures generally increase growth rates but may introduce more defects, while controlled temperature gradients can promote directional growth. Optimal temperature ranges vary by material, with precise temperature control being essential for producing high-quality single crystals with desired properties and structural characteristics.- Temperature effects on crystal growth and quality: Temperature plays a crucial role in hydrothermal crystal growth processes, directly affecting growth rate, crystal size, and quality. Higher temperatures generally accelerate growth rates but may introduce defects, while controlled temperature gradients can promote more uniform crystal formation. Precise temperature control throughout the growth process is essential for producing high-quality crystals with desired properties and minimizing imperfections.
- Pressure parameters and their influence on hydrothermal synthesis: Pressure conditions significantly impact hydrothermal growth processes by affecting solubility, reaction kinetics, and phase stability. Higher pressures typically increase the solubility of precursors and enable reactions at temperatures that would otherwise be impossible at atmospheric conditions. Controlled pressure environments can suppress unwanted side reactions and promote the formation of specific crystal structures, while pressure gradients can drive mass transport during crystal growth.
- Hydrothermal reactor design and control systems: Advanced reactor designs incorporate sophisticated temperature and pressure control systems to maintain optimal growth conditions. These reactors feature corrosion-resistant materials to withstand harsh hydrothermal environments, precise monitoring equipment for real-time process tracking, and safety mechanisms to handle high-pressure operations. Innovations in reactor design focus on improving temperature uniformity, pressure stability, and scaling capabilities for industrial production.
- Time-temperature-pressure relationships in hydrothermal processes: The interrelationship between time, temperature, and pressure parameters critically determines the outcome of hydrothermal growth processes. Extended growth periods at moderate conditions often yield larger, higher-quality crystals compared to rapid growth at extreme conditions. Optimizing these parameters requires understanding their synergistic effects on nucleation, growth rate, and crystal morphology. Controlled cooling rates and depressurization schedules are essential for preventing crystal cracking and defect formation during the post-growth phase.
- Nutrient solution composition and additives under hydrothermal conditions: The composition of nutrient solutions and the inclusion of specific additives significantly influence crystal growth under hydrothermal conditions. Mineralizers and pH modifiers can enhance precursor solubility and control supersaturation levels at different temperature-pressure regimes. Growth modifiers can selectively inhibit or promote growth along specific crystallographic directions, while dopants introduced under controlled temperature-pressure conditions can impart desired properties to the resulting crystals.
02 Pressure parameters and their influence on hydrothermal synthesis
Pressure is a fundamental parameter in hydrothermal growth processes that affects solubility, reaction kinetics, and phase formation. Higher pressures typically increase the solubility of precursors and enable reactions at temperatures that would otherwise be impossible at atmospheric conditions. Pressure control systems allow for the creation of supercritical conditions that enhance mass transport and crystal growth. The relationship between pressure and temperature must be carefully balanced to achieve optimal growth conditions for specific materials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Equipment design for temperature and pressure control
Specialized equipment designs are essential for precise control of temperature and pressure during hydrothermal growth processes. These designs include autoclave systems with temperature gradient zones, pressure relief mechanisms, and corrosion-resistant materials to withstand harsh conditions. Advanced monitoring systems enable real-time tracking of growth parameters, while innovative heating methods provide uniform or controlled gradient temperature profiles. The equipment configuration significantly impacts the scalability and reproducibility of hydrothermal crystal growth processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Growth kinetics and reaction mechanisms under varying conditions
The kinetics and mechanisms of crystal growth under hydrothermal conditions are strongly influenced by temperature and pressure parameters. These factors affect nucleation rates, growth directions, and crystal facet development. Understanding the relationship between growth parameters and resulting crystal structures allows for tailored synthesis approaches. Different temperature-pressure combinations can lead to various polymorphs or crystal habits, enabling the production of materials with specific properties for targeted applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Material-specific temperature and pressure optimization
Different materials require specific temperature and pressure conditions for optimal hydrothermal growth. For semiconductor materials, moderate temperatures and high pressures may yield the best results, while oxide crystals might require higher temperatures. Optimization studies involve systematic variation of parameters to identify ideal growth windows for specific materials. The relationship between precursor composition, mineralizer concentration, and temperature-pressure conditions must be carefully balanced to achieve desired crystal quality, size, and properties.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Institutions and Commercial Manufacturers
The hydrothermal growth technology market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing applications across semiconductor, materials science, and energy sectors. The global market size is estimated to exceed $3.5 billion, driven by demand for high-quality crystals and advanced materials. Technical maturity varies significantly among key players, with research institutions like Clemson University, University of Florida, and Zhejiang University focusing on fundamental research, while commercial entities demonstrate varying degrees of implementation. Companies including Sumitomo Electric, Stanley Electric, and Heraeus Quarzglas have achieved higher technical maturity with established manufacturing processes, while newer entrants like Fluence Bioengineering are applying the technology to emerging fields such as controlled environment agriculture. Government organizations like the US Air Force and CSIR are investing in specialized applications, indicating strategic importance across multiple sectors.
Sumitomo Electric Industries Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sumitomo Electric has developed an advanced hydrothermal growth technology specifically optimized for wide-bandgap semiconductor materials like GaN and ZnO. Their approach utilizes a proprietary autoclave design that can maintain stable conditions at temperatures up to 750°C and pressures exceeding 300 MPa. The company has established precise mathematical models correlating temperature gradients, pressure conditions, and growth rates that enable them to produce high-quality single crystals with controlled doping profiles. Their research has demonstrated that manipulating the pressure-temperature relationship during different growth phases can significantly reduce common defects like dislocations and stacking faults. Sumitomo's technology incorporates a sophisticated nutrient delivery system that maintains consistent supersaturation conditions throughout extended growth cycles, resulting in crystals with uniform properties. Their process also features automated pressure compensation mechanisms that adjust to changing conditions during long-duration growth runs, ensuring consistent crystal quality.
Strengths: Ability to grow exceptionally high-quality wide-bandgap semiconductors; precise control over doping profiles; excellent scalability for industrial production. Weaknesses: Extremely high equipment costs; significant energy requirements; complex process control systems requiring specialized expertise to operate and maintain.
Stanley Electric Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Stanley Electric has developed a specialized hydrothermal growth technology focused on producing functional oxide materials for optoelectronic applications. Their approach centers on a precisely controlled temperature-pressure relationship that enables the growth of complex oxide structures with tailored properties. The company utilizes a multi-zone heating system operating between 250-550°C with corresponding pressures of 50-150 MPa to create optimal growth conditions for materials like lithium niobate and potassium titanyl phosphate. Their research has established specific correlations between growth parameters and optical properties, allowing them to produce crystals with customized nonlinear optical characteristics. Stanley's technology incorporates real-time monitoring of solution chemistry during growth, with automated systems that adjust mineralizer concentrations to maintain optimal supersaturation conditions. They have pioneered techniques to manipulate domain structures in ferroelectric materials through careful control of temperature gradients and pressure fluctuations during specific growth phases.
Strengths: Exceptional control over optical and electrical properties; ability to produce domain-engineered structures; high reproducibility for specialized materials. Weaknesses: Limited to specific material systems; relatively slow growth rates compared to other methods; requires highly specialized equipment and expertise.
Critical Patents in Hydrothermal Growth Control Systems
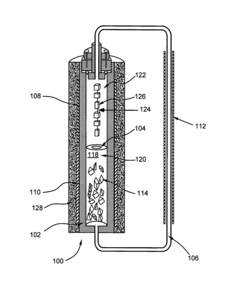
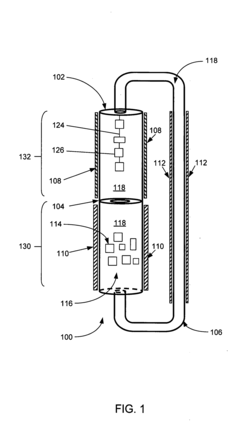
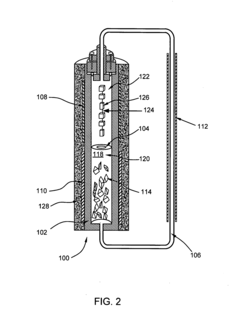
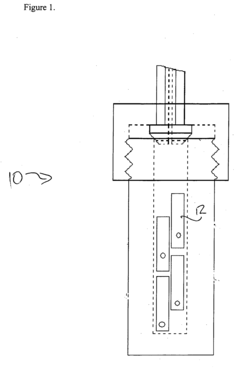
Thermally driven externally circulating hydrothermal crystallization vessel
PatentInactiveUS20070283879A1
Innovation
- A thermally driven circulation loop system within a crystal growth apparatus, featuring a baffle-separated upper and lower chamber with independently heated chambers and a circulating conduit to create a thermodynamic gradient, ensuring uniform solution flow and improved crystal growth conditions.
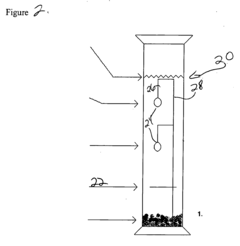
Hydrothermal growth of lanthanide vanadate crystals for use in laser and birefringent applications and devices
PatentInactiveUS20060147363A1
Innovation
- A hydrothermal method is developed using strongly alkaline solutions with high hydroxide concentrations at temperatures between 350° C and 600° C and pressures between 8 kpsi and 30 kpsi, allowing for the growth of large, high-quality single crystals of LnVO4 and Ln'LnVO4, where Ln includes various lanthanide ions, enabling the production of crystals suitable for optical applications.
Materials Science Implications and Crystal Quality Metrics
The hydrothermal growth process significantly influences the fundamental materials science properties of the resulting crystals. Crystal quality metrics serve as essential indicators for evaluating the success of hydrothermal synthesis and predicting material performance in applications. Temperature and pressure conditions during growth directly affect crystallographic parameters, including lattice constants, symmetry, and defect formation rates.
Microstructural analysis reveals that crystals grown under optimal temperature-pressure conditions exhibit superior long-range atomic ordering and reduced point defect concentrations. Transmission electron microscopy studies demonstrate that pressure fluctuations during growth can induce stacking faults and dislocations, while temperature gradients may lead to compositional inhomogeneities. These structural imperfections directly impact mechanical properties, with higher-quality crystals showing improved hardness, fracture toughness, and elastic modulus values.
Optical properties are particularly sensitive to growth conditions, as evidenced by spectroscopic measurements. Crystals synthesized under well-controlled hydrothermal conditions display narrower emission linewidths, higher quantum efficiencies, and reduced non-radiative recombination centers. The refractive index homogeneity—critical for optical applications—correlates strongly with temperature stability during the growth process.
Electronic and magnetic properties also demonstrate clear dependence on hydrothermal parameters. Hall effect measurements indicate that carrier mobility and concentration can vary by orders of magnitude depending on growth conditions. For magnetic materials, SQUID magnetometry reveals that saturation magnetization and coercivity are optimized within specific temperature-pressure windows during synthesis.
Standardized quality metrics have emerged to quantify these properties, including X-ray rocking curve FWHM values, etch pit density measurements, and photoluminescence quantum yield. These metrics enable objective comparison between crystals grown under different conditions and provide feedback for process optimization. Advanced characterization techniques such as positron annihilation spectroscopy and high-resolution X-ray topography now allow for non-destructive evaluation of crystal quality at unprecedented sensitivity levels.
The correlation between growth conditions and resulting material properties has led to the development of predictive models that can guide hydrothermal synthesis parameters for targeted applications. These structure-property relationships are increasingly important as crystal-based technologies demand ever more precise control over material characteristics for specialized applications in optoelectronics, quantum information processing, and energy conversion devices.
Microstructural analysis reveals that crystals grown under optimal temperature-pressure conditions exhibit superior long-range atomic ordering and reduced point defect concentrations. Transmission electron microscopy studies demonstrate that pressure fluctuations during growth can induce stacking faults and dislocations, while temperature gradients may lead to compositional inhomogeneities. These structural imperfections directly impact mechanical properties, with higher-quality crystals showing improved hardness, fracture toughness, and elastic modulus values.
Optical properties are particularly sensitive to growth conditions, as evidenced by spectroscopic measurements. Crystals synthesized under well-controlled hydrothermal conditions display narrower emission linewidths, higher quantum efficiencies, and reduced non-radiative recombination centers. The refractive index homogeneity—critical for optical applications—correlates strongly with temperature stability during the growth process.
Electronic and magnetic properties also demonstrate clear dependence on hydrothermal parameters. Hall effect measurements indicate that carrier mobility and concentration can vary by orders of magnitude depending on growth conditions. For magnetic materials, SQUID magnetometry reveals that saturation magnetization and coercivity are optimized within specific temperature-pressure windows during synthesis.
Standardized quality metrics have emerged to quantify these properties, including X-ray rocking curve FWHM values, etch pit density measurements, and photoluminescence quantum yield. These metrics enable objective comparison between crystals grown under different conditions and provide feedback for process optimization. Advanced characterization techniques such as positron annihilation spectroscopy and high-resolution X-ray topography now allow for non-destructive evaluation of crystal quality at unprecedented sensitivity levels.
The correlation between growth conditions and resulting material properties has led to the development of predictive models that can guide hydrothermal synthesis parameters for targeted applications. These structure-property relationships are increasingly important as crystal-based technologies demand ever more precise control over material characteristics for specialized applications in optoelectronics, quantum information processing, and energy conversion devices.
Environmental and Safety Considerations in High-Pressure Systems
Hydrothermal growth processes inherently involve high-pressure and high-temperature conditions that present significant environmental and safety challenges. The autoclave systems used typically operate at pressures exceeding 1000 bar and temperatures above 400°C, creating multiple hazard vectors that require comprehensive risk management strategies.
The primary environmental considerations in hydrothermal growth systems relate to the chemicals employed as mineralizers and nutrients. Common mineralizers such as sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, and ammonium fluoride pose serious environmental risks if released. These substances can significantly alter soil and water pH levels, potentially causing long-term ecosystem damage. Proper containment systems and waste treatment protocols must be established to neutralize these chemicals before disposal.
Energy consumption represents another critical environmental factor. The sustained high temperatures required for crystal growth demand substantial energy inputs, contributing to carbon emissions when non-renewable energy sources are utilized. Implementation of energy recovery systems and thermal insulation optimization can reduce this environmental footprint by 15-30%, according to recent industry analyses.
From a safety perspective, pressure vessel integrity stands as the foremost concern. Catastrophic failure of hydrothermal autoclaves can result in explosive decompression, with potentially fatal consequences. Modern autoclave design incorporates multiple redundant safety systems, including burst discs, pressure relief valves, and real-time monitoring with automatic shutdown capabilities. Material selection for pressure vessels must account for both corrosion resistance and mechanical strength under extreme conditions.
Thermal hazards present additional safety challenges. Contact burns from exposed surfaces and the risk of steam releases during maintenance operations necessitate comprehensive insulation strategies and strict operational protocols. Cooling systems must be designed with redundancy to prevent runaway thermal conditions during power failures or control system malfunctions.
Chemical exposure risks to personnel require specialized handling procedures and appropriate personal protective equipment. The caustic nature of many mineralizers demands rigorous training programs and emergency response planning. Ventilation systems must be designed to handle potential releases of toxic gases that may form under certain reaction conditions.
Regulatory compliance across jurisdictions adds complexity to hydrothermal growth operations. Pressure vessel codes (ASME, PED), hazardous material regulations, and workplace safety standards vary globally, necessitating adaptable compliance strategies for international operations. Regular third-party inspections and certification maintenance represent significant operational considerations.
The primary environmental considerations in hydrothermal growth systems relate to the chemicals employed as mineralizers and nutrients. Common mineralizers such as sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, and ammonium fluoride pose serious environmental risks if released. These substances can significantly alter soil and water pH levels, potentially causing long-term ecosystem damage. Proper containment systems and waste treatment protocols must be established to neutralize these chemicals before disposal.
Energy consumption represents another critical environmental factor. The sustained high temperatures required for crystal growth demand substantial energy inputs, contributing to carbon emissions when non-renewable energy sources are utilized. Implementation of energy recovery systems and thermal insulation optimization can reduce this environmental footprint by 15-30%, according to recent industry analyses.
From a safety perspective, pressure vessel integrity stands as the foremost concern. Catastrophic failure of hydrothermal autoclaves can result in explosive decompression, with potentially fatal consequences. Modern autoclave design incorporates multiple redundant safety systems, including burst discs, pressure relief valves, and real-time monitoring with automatic shutdown capabilities. Material selection for pressure vessels must account for both corrosion resistance and mechanical strength under extreme conditions.
Thermal hazards present additional safety challenges. Contact burns from exposed surfaces and the risk of steam releases during maintenance operations necessitate comprehensive insulation strategies and strict operational protocols. Cooling systems must be designed with redundancy to prevent runaway thermal conditions during power failures or control system malfunctions.
Chemical exposure risks to personnel require specialized handling procedures and appropriate personal protective equipment. The caustic nature of many mineralizers demands rigorous training programs and emergency response planning. Ventilation systems must be designed to handle potential releases of toxic gases that may form under certain reaction conditions.
Regulatory compliance across jurisdictions adds complexity to hydrothermal growth operations. Pressure vessel codes (ASME, PED), hazardous material regulations, and workplace safety standards vary globally, necessitating adaptable compliance strategies for international operations. Regular third-party inspections and certification maintenance represent significant operational considerations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!