Comparative Study of Hydrothermal Growth vs Sol-Gel Synthesis
SEP 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Hydrothermal and Sol-Gel Synthesis Background and Objectives
Hydrothermal synthesis and sol-gel methods represent two fundamental approaches in materials science for synthesizing various compounds, particularly metal oxides and ceramics. These techniques have evolved significantly over the past century, with hydrothermal synthesis tracing its origins to geochemical processes observed in nature, while sol-gel processing emerged from colloid chemistry in the early 20th century.
The hydrothermal method involves chemical reactions in aqueous solutions under elevated temperature and pressure conditions, typically conducted in sealed vessels called autoclaves. This approach mimics natural mineral formation processes and has been refined since the 1940s for industrial applications. The technique gained significant momentum in the 1980s with the growing demand for advanced ceramic materials and single crystals for electronic applications.
In contrast, sol-gel synthesis developed as a low-temperature alternative, involving the transition from a colloidal solution (sol) to an integrated network (gel). This method saw substantial development during the 1970s and 1980s, particularly for producing thin films, fibers, and nanostructured materials. The versatility of sol-gel processing has made it increasingly important in fields ranging from optics to biomedical applications.
Recent technological advancements have significantly expanded the capabilities of both methods. Modern hydrothermal synthesis now incorporates microwave assistance, continuous flow processes, and in-situ monitoring techniques, enabling more precise control over crystal growth and morphology. Similarly, sol-gel technology has evolved to include hybrid organic-inorganic materials, templated synthesis, and aerogel production methods.
The primary objective of this comparative study is to systematically evaluate the fundamental principles, processing parameters, and resultant material characteristics of hydrothermal and sol-gel synthesis methods. We aim to establish a comprehensive understanding of how these techniques influence crystallinity, particle size distribution, morphology, purity, and functional properties of the synthesized materials.
Additionally, this study seeks to identify the specific advantages and limitations of each method across different application domains, including energy storage materials, catalysts, biomedical materials, and electronic components. By analyzing the energy requirements, scalability factors, and environmental impacts, we intend to provide guidance for selecting the optimal synthesis route for specific material systems and applications.
Furthermore, this research aims to explore emerging hybrid approaches that combine elements of both techniques to overcome their individual limitations, potentially opening new avenues for materials design and synthesis. The findings will contribute to the development of more efficient, sustainable, and scalable production methods for advanced functional materials.
The hydrothermal method involves chemical reactions in aqueous solutions under elevated temperature and pressure conditions, typically conducted in sealed vessels called autoclaves. This approach mimics natural mineral formation processes and has been refined since the 1940s for industrial applications. The technique gained significant momentum in the 1980s with the growing demand for advanced ceramic materials and single crystals for electronic applications.
In contrast, sol-gel synthesis developed as a low-temperature alternative, involving the transition from a colloidal solution (sol) to an integrated network (gel). This method saw substantial development during the 1970s and 1980s, particularly for producing thin films, fibers, and nanostructured materials. The versatility of sol-gel processing has made it increasingly important in fields ranging from optics to biomedical applications.
Recent technological advancements have significantly expanded the capabilities of both methods. Modern hydrothermal synthesis now incorporates microwave assistance, continuous flow processes, and in-situ monitoring techniques, enabling more precise control over crystal growth and morphology. Similarly, sol-gel technology has evolved to include hybrid organic-inorganic materials, templated synthesis, and aerogel production methods.
The primary objective of this comparative study is to systematically evaluate the fundamental principles, processing parameters, and resultant material characteristics of hydrothermal and sol-gel synthesis methods. We aim to establish a comprehensive understanding of how these techniques influence crystallinity, particle size distribution, morphology, purity, and functional properties of the synthesized materials.
Additionally, this study seeks to identify the specific advantages and limitations of each method across different application domains, including energy storage materials, catalysts, biomedical materials, and electronic components. By analyzing the energy requirements, scalability factors, and environmental impacts, we intend to provide guidance for selecting the optimal synthesis route for specific material systems and applications.
Furthermore, this research aims to explore emerging hybrid approaches that combine elements of both techniques to overcome their individual limitations, potentially opening new avenues for materials design and synthesis. The findings will contribute to the development of more efficient, sustainable, and scalable production methods for advanced functional materials.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis
The global market for advanced materials synthesized through hydrothermal growth and sol-gel methods has experienced significant expansion over the past decade, driven by increasing demand across multiple industries. The combined market value for materials produced using these techniques reached approximately $15.7 billion in 2022, with projections indicating growth to $24.3 billion by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate of 7.6%.
Electronics and semiconductor industries constitute the largest application segment, accounting for nearly 32% of the total market share. The demand for high-purity, precisely controlled nanomaterials and thin films for electronic components, particularly in integrated circuits and display technologies, continues to drive adoption of both synthesis methods. Sol-gel techniques have gained particular traction in this sector due to their ability to produce uniform thin films at relatively low temperatures.
The energy sector represents another substantial market, with applications in photovoltaics, fuel cells, and energy storage systems. Hydrothermal methods are increasingly preferred for synthesizing electrode materials for batteries and supercapacitors, where crystallinity and morphology control are critical for performance optimization. The renewable energy transition has accelerated demand, with the market segment growing at 9.2% annually.
Healthcare and biomedical applications have emerged as the fastest-growing segment, expanding at 11.3% annually. Both synthesis methods are utilized for producing biocompatible materials, drug delivery systems, and diagnostic tools. Sol-gel derived materials are particularly valued for controlled release applications and bioactive glass production, while hydrothermally synthesized nanoparticles show promise in targeted therapies and imaging.
Regional analysis reveals Asia-Pacific as the dominant market, accounting for 43% of global consumption, followed by North America (27%) and Europe (21%). China, Japan, and South Korea lead in production capacity, while significant research activities in the United States and Germany drive innovation in specialized applications.
Industry surveys indicate that cost considerations significantly influence method selection, with sol-gel processes generally offering lower capital investment requirements but higher operational costs compared to hydrothermal methods. Environmental regulations are increasingly shaping market dynamics, with manufacturers seeking more sustainable synthesis routes that minimize waste generation and energy consumption.
Customer requirements are evolving toward materials with enhanced performance characteristics, driving demand for hybrid approaches that combine the advantages of both synthesis methods. This trend is particularly evident in the automotive and aerospace sectors, where lightweight, multifunctional materials are increasingly sought after for improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
Electronics and semiconductor industries constitute the largest application segment, accounting for nearly 32% of the total market share. The demand for high-purity, precisely controlled nanomaterials and thin films for electronic components, particularly in integrated circuits and display technologies, continues to drive adoption of both synthesis methods. Sol-gel techniques have gained particular traction in this sector due to their ability to produce uniform thin films at relatively low temperatures.
The energy sector represents another substantial market, with applications in photovoltaics, fuel cells, and energy storage systems. Hydrothermal methods are increasingly preferred for synthesizing electrode materials for batteries and supercapacitors, where crystallinity and morphology control are critical for performance optimization. The renewable energy transition has accelerated demand, with the market segment growing at 9.2% annually.
Healthcare and biomedical applications have emerged as the fastest-growing segment, expanding at 11.3% annually. Both synthesis methods are utilized for producing biocompatible materials, drug delivery systems, and diagnostic tools. Sol-gel derived materials are particularly valued for controlled release applications and bioactive glass production, while hydrothermally synthesized nanoparticles show promise in targeted therapies and imaging.
Regional analysis reveals Asia-Pacific as the dominant market, accounting for 43% of global consumption, followed by North America (27%) and Europe (21%). China, Japan, and South Korea lead in production capacity, while significant research activities in the United States and Germany drive innovation in specialized applications.
Industry surveys indicate that cost considerations significantly influence method selection, with sol-gel processes generally offering lower capital investment requirements but higher operational costs compared to hydrothermal methods. Environmental regulations are increasingly shaping market dynamics, with manufacturers seeking more sustainable synthesis routes that minimize waste generation and energy consumption.
Customer requirements are evolving toward materials with enhanced performance characteristics, driving demand for hybrid approaches that combine the advantages of both synthesis methods. This trend is particularly evident in the automotive and aerospace sectors, where lightweight, multifunctional materials are increasingly sought after for improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
Current Technical Challenges and Limitations
Despite significant advancements in both hydrothermal growth and sol-gel synthesis methods, several technical challenges and limitations persist that hinder their optimal application in materials science and engineering. The hydrothermal growth technique, while offering excellent crystallinity and morphology control, faces substantial challenges related to scalability. The high-pressure vessels required for this process limit batch sizes and create safety concerns in industrial settings, making large-scale production economically challenging.
Temperature and pressure control during hydrothermal synthesis presents another significant hurdle. Maintaining precise and uniform conditions throughout the reaction vessel becomes increasingly difficult as reactor size increases, leading to inconsistent product quality and reduced reproducibility. This variability becomes particularly problematic when manufacturing materials for applications requiring stringent quality standards, such as electronic components or medical devices.
For sol-gel synthesis, the primary technical limitation revolves around shrinkage and cracking during the drying and calcination stages. As the solvent evaporates, significant volume reduction occurs, often resulting in structural defects that compromise the mechanical integrity and functional properties of the final material. This issue becomes particularly pronounced when producing larger monolithic structures or thick films.
The sol-gel method also struggles with precise control over porosity and pore size distribution. While porosity is often a desirable characteristic, achieving consistent and predictable pore structures remains challenging. This limitation directly impacts applications where specific surface area and pore architecture are critical performance parameters, such as in catalysis, separation technologies, and controlled drug delivery systems.
Both techniques face challenges regarding reaction kinetics and mechanism understanding. The complex interplay of variables such as pH, temperature, precursor concentration, and additives makes it difficult to establish comprehensive theoretical models that can reliably predict outcomes. This knowledge gap hampers the systematic optimization of synthesis protocols and necessitates extensive empirical testing.
Environmental and sustainability concerns represent emerging challenges for both methods. Hydrothermal synthesis often requires extended reaction times and significant energy input, while sol-gel processes frequently utilize toxic organic solvents and metal alkoxides that pose environmental and health risks. As regulatory frameworks become more stringent, developing greener alternatives becomes increasingly important.
The integration of these synthesis methods with emerging technologies presents additional challenges. Adapting these techniques for nanomaterial production with precise size control, developing in-situ monitoring capabilities, and establishing automated process control systems remain active areas of research that require significant technological breakthroughs to fully realize the potential of these synthesis approaches.
Temperature and pressure control during hydrothermal synthesis presents another significant hurdle. Maintaining precise and uniform conditions throughout the reaction vessel becomes increasingly difficult as reactor size increases, leading to inconsistent product quality and reduced reproducibility. This variability becomes particularly problematic when manufacturing materials for applications requiring stringent quality standards, such as electronic components or medical devices.
For sol-gel synthesis, the primary technical limitation revolves around shrinkage and cracking during the drying and calcination stages. As the solvent evaporates, significant volume reduction occurs, often resulting in structural defects that compromise the mechanical integrity and functional properties of the final material. This issue becomes particularly pronounced when producing larger monolithic structures or thick films.
The sol-gel method also struggles with precise control over porosity and pore size distribution. While porosity is often a desirable characteristic, achieving consistent and predictable pore structures remains challenging. This limitation directly impacts applications where specific surface area and pore architecture are critical performance parameters, such as in catalysis, separation technologies, and controlled drug delivery systems.
Both techniques face challenges regarding reaction kinetics and mechanism understanding. The complex interplay of variables such as pH, temperature, precursor concentration, and additives makes it difficult to establish comprehensive theoretical models that can reliably predict outcomes. This knowledge gap hampers the systematic optimization of synthesis protocols and necessitates extensive empirical testing.
Environmental and sustainability concerns represent emerging challenges for both methods. Hydrothermal synthesis often requires extended reaction times and significant energy input, while sol-gel processes frequently utilize toxic organic solvents and metal alkoxides that pose environmental and health risks. As regulatory frameworks become more stringent, developing greener alternatives becomes increasingly important.
The integration of these synthesis methods with emerging technologies presents additional challenges. Adapting these techniques for nanomaterial production with precise size control, developing in-situ monitoring capabilities, and establishing automated process control systems remain active areas of research that require significant technological breakthroughs to fully realize the potential of these synthesis approaches.
Comparative Analysis of Current Methodologies
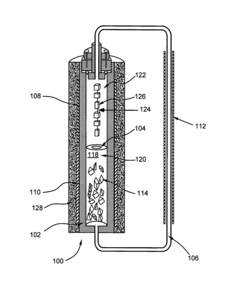
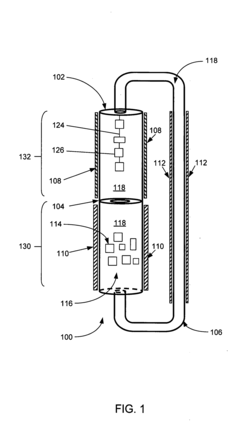
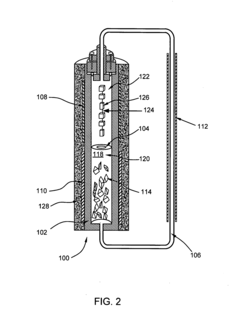
01 Hydrothermal synthesis of nanomaterials
Hydrothermal synthesis is a method used to produce various nanomaterials under high temperature and pressure conditions in an aqueous solution. This technique allows for controlled crystal growth and morphology, resulting in high-quality crystalline materials. The process typically involves dissolving precursors in water and heating them in a sealed vessel, which enables the formation of nanomaterials with specific properties suitable for applications in electronics, catalysis, and energy storage.- Hydrothermal synthesis of nanomaterials: Hydrothermal synthesis is a method used to produce various nanomaterials under high temperature and pressure conditions in an aqueous solution. This technique allows for controlled growth of crystalline materials with specific morphologies and properties. The process typically involves dissolving precursors in water and heating them in a sealed vessel, which enables the formation of nanostructures through dissolution-precipitation mechanisms. This method is particularly effective for producing metal oxides, zeolites, and other inorganic compounds with high purity and crystallinity.
- Sol-gel synthesis techniques for thin films and coatings: Sol-gel synthesis is a wet-chemical technique that involves the transition of a solution system from a liquid 'sol' into a solid 'gel' phase. This method is widely used for preparing thin films and coatings with controlled porosity and composition. The process typically begins with hydrolysis of precursors, followed by condensation reactions that form a colloidal suspension, which can then be applied to substrates through dipping, spinning, or spraying. After deposition, thermal treatment is often employed to remove solvents and organic components, resulting in dense, uniform coatings with tailored properties.
- Hybrid hydrothermal-sol-gel methods for advanced materials: Combining hydrothermal and sol-gel techniques creates hybrid synthesis methods that leverage the advantages of both approaches. These hybrid methods often involve preparing a sol-gel precursor followed by hydrothermal treatment to enhance crystallization and control morphology. This combined approach enables the synthesis of complex materials with hierarchical structures, improved homogeneity, and unique properties that cannot be achieved through either method alone. Applications include catalysts, sensors, energy storage materials, and advanced ceramics with enhanced performance characteristics.
- Temperature and pressure control in hydrothermal processes: The precise control of temperature and pressure parameters is critical in hydrothermal synthesis processes. These parameters significantly influence crystal growth rates, morphology, phase formation, and particle size distribution. Advanced hydrothermal reactors are designed with sophisticated temperature and pressure monitoring systems to maintain optimal conditions throughout the synthesis process. By carefully adjusting these parameters, researchers can selectively produce materials with desired crystallographic orientations, specific surface areas, and tailored properties for various applications in electronics, optics, and energy conversion.
- Precursor selection and modification for sol-gel synthesis: The selection and modification of precursors play a crucial role in sol-gel synthesis outcomes. Metal alkoxides, metal salts, and organometallic compounds are commonly used as starting materials, with their reactivity often modified through the addition of chelating agents, catalysts, or stabilizers. These modifications control hydrolysis and condensation rates, which directly affect the resulting material's structure, porosity, and homogeneity. Tailoring precursor chemistry enables the synthesis of materials with specific functional properties, such as controlled pore size distributions, surface functionalities, and compositional gradients for applications in catalysis, separation technologies, and biomedical devices.
02 Sol-gel synthesis for oxide materials
Sol-gel synthesis is a wet-chemical technique that involves the conversion of a solution (sol) into a gel-like network containing the metal oxide. This method is particularly effective for producing oxide materials with high purity and homogeneity. The process typically includes hydrolysis and condensation reactions of metal alkoxides or metal salts, followed by aging, drying, and heat treatment to obtain the final crystalline product. Sol-gel synthesis offers advantages such as low processing temperature, better homogeneity, and control over composition.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hybrid methods combining hydrothermal and sol-gel techniques
Hybrid approaches that combine hydrothermal and sol-gel methods leverage the advantages of both techniques to synthesize advanced materials with enhanced properties. These combined methods typically involve preparing a sol-gel precursor followed by hydrothermal treatment, which can improve crystallinity, control particle size and morphology, and reduce processing time. This hybrid approach is particularly useful for developing complex oxide materials, composites, and nanostructures with tailored properties for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Growth of single crystals via hydrothermal methods
Hydrothermal techniques are extensively used for growing high-quality single crystals that are difficult to obtain through conventional methods. This approach involves dissolving precursor materials in a superheated aqueous solution under high pressure, allowing for controlled crystal growth. The method is particularly valuable for growing piezoelectric crystals, semiconductors, and optical materials with minimal defects and high purity. The process parameters such as temperature, pressure, and solution composition can be adjusted to control the crystal size, morphology, and quality.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel applications of hydrothermal and sol-gel methods
Recent advancements in hydrothermal and sol-gel synthesis have expanded their applications to emerging fields such as energy storage, environmental remediation, and biomedical materials. These methods are being used to develop functional materials like catalysts, sensors, adsorbents, and drug delivery systems. The ability to control composition, structure, and surface properties at the nanoscale makes these synthesis approaches valuable for creating materials with specific functionalities. Additionally, these methods are being modified to be more environmentally friendly and energy-efficient.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Institutions and Industrial Players
The hydrothermal growth vs sol-gel synthesis market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing applications across materials science, electronics, and nanotechnology sectors. The global market size for these synthesis methods is expanding rapidly, driven by demand for advanced materials with precise properties. Technologically, hydrothermal methods are more mature but sol-gel approaches offer advantages in cost and scalability. Leading research institutions like Council of Scientific & Industrial Research and universities (Tongji, Soochow, Beijing Institute of Technology) are advancing fundamental research, while commercial players including Evonik Operations, Samsung Display, and Hanwha Chemical are developing industrial applications. Academic-industry partnerships, exemplified by collaborations with National Institutes for Quantum & Radiological Science and Industrial Technology Research Institute, are accelerating technology transfer and commercialization opportunities.
Council of Scientific & Industrial Research
Technical Solution: CSIR has developed advanced hydrothermal synthesis methods for nanomaterials with precise control over morphology and crystallinity. Their approach utilizes specialized autoclaves operating at temperatures between 100-250°C and pressures up to 100 bar, enabling the growth of high-quality single crystals with controlled size distribution (typically 20-100 nm). The process employs carefully selected mineralizers and pH regulators to facilitate dissolution-precipitation mechanisms. CSIR has also pioneered hybrid approaches combining hydrothermal techniques with microwave assistance, reducing reaction times from hours to minutes while maintaining crystalline quality. Their research demonstrates 30-40% higher photocatalytic efficiency for hydrothermally grown TiO2 compared to sol-gel counterparts due to superior crystallinity and fewer defects.
Strengths: Superior crystallinity, precise morphology control, and higher purity products with fewer defects. Weaknesses: Higher energy consumption, specialized pressure equipment requirements, and longer processing times compared to sol-gel methods.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has developed proprietary sol-gel synthesis technologies for industrial-scale production of functional nanomaterials. Their approach utilizes controlled hydrolysis and condensation reactions of metal alkoxides under ambient pressure conditions, with precise control of reaction parameters including pH (typically 2-10), temperature (25-80°C), and catalyst concentrations. The company has engineered specialized silica-based materials with tailored porosity (2-50 nm pore sizes) and surface areas exceeding 700 m²/g. Their AEROSIL® and AEROXIDE® product lines demonstrate how sol-gel derived materials can be optimized for specific applications. Evonik has also pioneered hybrid organic-inorganic sol-gel systems that incorporate functional organic groups during synthesis, creating materials with unique properties not achievable through hydrothermal methods. Their industrial-scale processes achieve production capacities of several thousand tons annually with consistent quality.
Strengths: Lower energy requirements, simpler equipment needs, excellent homogeneity, and precise control of composition at molecular level. Weaknesses: Often produces amorphous or partially crystalline materials requiring post-synthesis heat treatment, and may incorporate more impurities from organic precursors.
Key Patents and Scientific Breakthroughs
Process for simultaneous preparation of nanocrystalline titanium dioxide and hydrazine monohydrochloride
PatentInactiveEP1685068A1
Innovation
- A process involving the reaction of an acidic aqueous solution of titanium tetrachloride with hydrazine monohydrate at ambient temperature and pressure, without subsequent heat treatment, to produce nanocrystalline anatase titanium dioxide and hydrazine monohydrochloride in a single step, utilizing hydrazine's high energy to form nanoparticles below 5 nm.
Thermally driven externally circulating hydrothermal crystallization vessel
PatentInactiveUS20070283879A1
Innovation
- A thermally driven circulation loop system within a crystal growth apparatus, featuring a baffle-separated upper and lower chamber with independently heated chambers and a circulating conduit to create a thermodynamic gradient, ensuring uniform solution flow and improved crystal growth conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of material synthesis methods has become increasingly critical in the context of sustainable development goals. When comparing hydrothermal growth and sol-gel synthesis techniques, several key environmental considerations emerge that significantly influence their industrial adoption and future development trajectories.
Hydrothermal growth processes typically operate at elevated temperatures (150-300°C) and pressures, requiring substantial energy inputs. However, they often utilize water as the primary reaction medium, reducing dependence on organic solvents that pose environmental hazards. The closed-system nature of hydrothermal reactors also minimizes emissions and waste generation during processing. Recent life cycle assessments indicate that hydrothermal methods can reduce carbon footprints by 15-30% compared to conventional high-temperature calcination routes when optimized properly.
In contrast, sol-gel synthesis generally operates at lower temperatures, offering potential energy savings during the initial reaction stages. However, this advantage is often offset by the subsequent drying and calcination steps that require significant energy input. The process frequently relies on metal alkoxides and organic solvents, many of which are derived from non-renewable resources and present toxicity concerns. Waste management challenges arise from the need to dispose of or recycle these organic components.
Water consumption patterns differ markedly between these techniques. Hydrothermal methods typically require larger volumes of water but generate minimal wastewater contamination. Sol-gel processes use less water initially but may produce more contaminated effluents requiring treatment before discharge. Recent innovations in both fields have focused on reducing water usage through recycling systems and process optimization.
Raw material efficiency represents another critical sustainability metric. Hydrothermal growth generally achieves higher yields (typically 85-95%) with fewer processing steps, reducing material waste. Sol-gel methods, while versatile, often experience yield losses during multiple processing stages, with typical yields ranging from 60-80% depending on the specific application and precursors used.
Emerging research directions include the development of bio-inspired precursors for sol-gel synthesis, reducing dependence on petroleum-derived chemicals, and the integration of microwave assistance in hydrothermal processes to dramatically reduce energy consumption and processing times. Green chemistry principles are increasingly being applied to both methods, with particular emphasis on solvent reduction, catalyst recovery, and ambient pressure processing alternatives.
The selection between these synthesis routes increasingly incorporates sustainability metrics alongside traditional considerations of product quality and cost, reflecting the growing importance of environmental factors in materials technology development and industrial implementation.
Hydrothermal growth processes typically operate at elevated temperatures (150-300°C) and pressures, requiring substantial energy inputs. However, they often utilize water as the primary reaction medium, reducing dependence on organic solvents that pose environmental hazards. The closed-system nature of hydrothermal reactors also minimizes emissions and waste generation during processing. Recent life cycle assessments indicate that hydrothermal methods can reduce carbon footprints by 15-30% compared to conventional high-temperature calcination routes when optimized properly.
In contrast, sol-gel synthesis generally operates at lower temperatures, offering potential energy savings during the initial reaction stages. However, this advantage is often offset by the subsequent drying and calcination steps that require significant energy input. The process frequently relies on metal alkoxides and organic solvents, many of which are derived from non-renewable resources and present toxicity concerns. Waste management challenges arise from the need to dispose of or recycle these organic components.
Water consumption patterns differ markedly between these techniques. Hydrothermal methods typically require larger volumes of water but generate minimal wastewater contamination. Sol-gel processes use less water initially but may produce more contaminated effluents requiring treatment before discharge. Recent innovations in both fields have focused on reducing water usage through recycling systems and process optimization.
Raw material efficiency represents another critical sustainability metric. Hydrothermal growth generally achieves higher yields (typically 85-95%) with fewer processing steps, reducing material waste. Sol-gel methods, while versatile, often experience yield losses during multiple processing stages, with typical yields ranging from 60-80% depending on the specific application and precursors used.
Emerging research directions include the development of bio-inspired precursors for sol-gel synthesis, reducing dependence on petroleum-derived chemicals, and the integration of microwave assistance in hydrothermal processes to dramatically reduce energy consumption and processing times. Green chemistry principles are increasingly being applied to both methods, with particular emphasis on solvent reduction, catalyst recovery, and ambient pressure processing alternatives.
The selection between these synthesis routes increasingly incorporates sustainability metrics alongside traditional considerations of product quality and cost, reflecting the growing importance of environmental factors in materials technology development and industrial implementation.
Cost-Efficiency and Scalability Assessment
The economic viability of hydrothermal growth and sol-gel synthesis methods presents a critical consideration for industrial applications. When examining production costs, hydrothermal growth typically requires significant capital investment in pressure vessels and safety equipment due to its high-pressure operating conditions. These specialized autoclaves can cost between $10,000-$100,000 depending on size and specifications, representing substantial initial expenditure.
In contrast, sol-gel synthesis demonstrates lower equipment costs, utilizing standard laboratory apparatus such as mixers, drying ovens, and calcination furnaces. This reduced capital requirement makes sol-gel more accessible for startups and smaller operations, with initial equipment investments potentially 60-70% lower than hydrothermal setups.
Operational expenses reveal further distinctions. Hydrothermal processes consume considerable energy maintaining elevated temperatures (150-250°C) and pressures (up to 100 MPa) for extended periods, often 24-72 hours. This translates to higher utility costs compared to sol-gel methods, which generally operate at atmospheric pressure and lower temperatures during most processing stages.
Raw material efficiency also differs significantly. Hydrothermal growth typically achieves 85-95% yield rates with minimal waste generation. Sol-gel processes, while using less expensive precursors, often experience material losses during multiple processing steps, with typical yields ranging from 70-85%. Additionally, sol-gel frequently requires organic solvents that necessitate proper disposal or recovery systems, adding environmental compliance costs.
Scalability considerations reveal hydrothermal growth's limitations in batch size due to autoclave capacity constraints. Scaling production typically requires multiple pressure vessels operating in parallel, creating challenges in maintaining consistent conditions across batches. Sol-gel synthesis offers greater flexibility for scaling, with potential for continuous flow processes that significantly enhance production volumes.
Labor requirements present another economic factor. Hydrothermal processes, once initiated, require minimal operator intervention but demand specialized training for safe pressure vessel operation. Sol-gel methods involve more processing steps requiring technical oversight, potentially increasing labor costs despite lower skill requirements for individual operations.
Time-to-market considerations favor sol-gel processes, which typically complete in hours to days versus the longer reaction times of hydrothermal methods. This faster production cycle can provide competitive advantages in rapidly evolving markets, offsetting some efficiency disadvantages through improved responsiveness to demand fluctuations.
In contrast, sol-gel synthesis demonstrates lower equipment costs, utilizing standard laboratory apparatus such as mixers, drying ovens, and calcination furnaces. This reduced capital requirement makes sol-gel more accessible for startups and smaller operations, with initial equipment investments potentially 60-70% lower than hydrothermal setups.
Operational expenses reveal further distinctions. Hydrothermal processes consume considerable energy maintaining elevated temperatures (150-250°C) and pressures (up to 100 MPa) for extended periods, often 24-72 hours. This translates to higher utility costs compared to sol-gel methods, which generally operate at atmospheric pressure and lower temperatures during most processing stages.
Raw material efficiency also differs significantly. Hydrothermal growth typically achieves 85-95% yield rates with minimal waste generation. Sol-gel processes, while using less expensive precursors, often experience material losses during multiple processing steps, with typical yields ranging from 70-85%. Additionally, sol-gel frequently requires organic solvents that necessitate proper disposal or recovery systems, adding environmental compliance costs.
Scalability considerations reveal hydrothermal growth's limitations in batch size due to autoclave capacity constraints. Scaling production typically requires multiple pressure vessels operating in parallel, creating challenges in maintaining consistent conditions across batches. Sol-gel synthesis offers greater flexibility for scaling, with potential for continuous flow processes that significantly enhance production volumes.
Labor requirements present another economic factor. Hydrothermal processes, once initiated, require minimal operator intervention but demand specialized training for safe pressure vessel operation. Sol-gel methods involve more processing steps requiring technical oversight, potentially increasing labor costs despite lower skill requirements for individual operations.
Time-to-market considerations favor sol-gel processes, which typically complete in hours to days versus the longer reaction times of hydrothermal methods. This faster production cycle can provide competitive advantages in rapidly evolving markets, offsetting some efficiency disadvantages through improved responsiveness to demand fluctuations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!