Application of Solenoid Valves in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Systems
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Solenoid Valve IIoT Integration Background
The integration of solenoid valves into Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems represents a significant advancement in industrial automation and control. This convergence of traditional mechanical components with cutting-edge digital technologies has been driven by the increasing demand for smart, connected, and efficient industrial processes.
Solenoid valves, which have been a staple in fluid control systems for decades, are now being reimagined as intelligent nodes within the broader IIoT ecosystem. This transformation is rooted in the broader Industry 4.0 movement, which aims to create smart factories and interconnected industrial environments.
The journey towards IIoT-enabled solenoid valves began with the recognition that these components, while reliable and effective, lacked the ability to provide real-time data and remote control capabilities. As industries sought to optimize their operations and reduce downtime, the need for more intelligent valve systems became apparent.
Early attempts to integrate solenoid valves into networked systems involved retrofitting existing valves with sensors and basic communication modules. However, these solutions were often piecemeal and lacked the seamless integration required for true IIoT functionality.
The advent of miniaturized electronics, low-power communication protocols, and advanced sensor technologies has paved the way for the development of purpose-built IIoT solenoid valves. These modern valves incorporate embedded sensors, microcontrollers, and wireless communication capabilities, enabling them to become active participants in the industrial data ecosystem.
The evolution of cloud computing and edge processing technologies has further accelerated the adoption of IIoT-enabled solenoid valves. These advancements have made it possible to collect, analyze, and act upon vast amounts of valve-related data in real-time, leading to predictive maintenance strategies and optimized process control.
As the IIoT landscape continues to mature, solenoid valve manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing products that seamlessly integrate with existing industrial control systems and emerging IIoT platforms. This integration aims to provide a holistic view of industrial processes, where solenoid valves are no longer isolated components but integral parts of a connected, data-driven ecosystem.
The ongoing development of IIoT-enabled solenoid valves is driven by several key objectives, including improved operational efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, enhanced safety, and increased flexibility in industrial processes. These goals align with the broader industrial trends of digitalization, automation, and sustainability.
Solenoid valves, which have been a staple in fluid control systems for decades, are now being reimagined as intelligent nodes within the broader IIoT ecosystem. This transformation is rooted in the broader Industry 4.0 movement, which aims to create smart factories and interconnected industrial environments.
The journey towards IIoT-enabled solenoid valves began with the recognition that these components, while reliable and effective, lacked the ability to provide real-time data and remote control capabilities. As industries sought to optimize their operations and reduce downtime, the need for more intelligent valve systems became apparent.
Early attempts to integrate solenoid valves into networked systems involved retrofitting existing valves with sensors and basic communication modules. However, these solutions were often piecemeal and lacked the seamless integration required for true IIoT functionality.
The advent of miniaturized electronics, low-power communication protocols, and advanced sensor technologies has paved the way for the development of purpose-built IIoT solenoid valves. These modern valves incorporate embedded sensors, microcontrollers, and wireless communication capabilities, enabling them to become active participants in the industrial data ecosystem.
The evolution of cloud computing and edge processing technologies has further accelerated the adoption of IIoT-enabled solenoid valves. These advancements have made it possible to collect, analyze, and act upon vast amounts of valve-related data in real-time, leading to predictive maintenance strategies and optimized process control.
As the IIoT landscape continues to mature, solenoid valve manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing products that seamlessly integrate with existing industrial control systems and emerging IIoT platforms. This integration aims to provide a holistic view of industrial processes, where solenoid valves are no longer isolated components but integral parts of a connected, data-driven ecosystem.
The ongoing development of IIoT-enabled solenoid valves is driven by several key objectives, including improved operational efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, enhanced safety, and increased flexibility in industrial processes. These goals align with the broader industrial trends of digitalization, automation, and sustainability.
IIoT Market Demand Analysis
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) market has shown significant growth and demand for advanced technologies, including solenoid valves. This demand is driven by the increasing need for automation, efficiency, and real-time monitoring in industrial processes. Solenoid valves, as crucial components in fluid control systems, are experiencing a surge in demand due to their compatibility with IIoT systems.
The global IIoT market is expanding rapidly, with manufacturing, energy, and utilities sectors leading the adoption. This growth is fueled by the desire for improved operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced productivity. Solenoid valves integrated with IIoT capabilities offer precise control, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance features, making them highly sought after in various industrial applications.
In the manufacturing sector, there is a growing demand for smart factories that utilize IIoT-enabled solenoid valves for process automation and quality control. These valves allow for real-time adjustments in production lines, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing waste. The energy sector is also embracing IIoT-integrated solenoid valves for improved control in oil and gas operations, power generation, and distribution systems.
The utilities sector, particularly water and wastewater management, is another key driver of demand for IIoT-enabled solenoid valves. These valves play a crucial role in smart water management systems, helping to reduce water loss, improve distribution efficiency, and ensure water quality through precise control and monitoring.
Market trends indicate a growing preference for miniaturized and energy-efficient solenoid valves that can be easily integrated into existing IIoT infrastructures. There is also an increasing demand for valves with enhanced durability and reliability to withstand harsh industrial environments while maintaining connectivity and performance.
The adoption of IIoT-enabled solenoid valves is not limited to large enterprises. Small and medium-sized businesses are also recognizing the benefits of these technologies in improving their operational efficiency and competitiveness. This trend is expected to further drive market growth and innovation in the coming years.
As industries continue to prioritize digital transformation, the demand for solenoid valves with advanced IIoT capabilities is projected to rise. Manufacturers are focusing on developing valves with improved sensors, data analytics capabilities, and seamless integration with industrial control systems to meet this growing market need.
The global IIoT market is expanding rapidly, with manufacturing, energy, and utilities sectors leading the adoption. This growth is fueled by the desire for improved operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced productivity. Solenoid valves integrated with IIoT capabilities offer precise control, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance features, making them highly sought after in various industrial applications.
In the manufacturing sector, there is a growing demand for smart factories that utilize IIoT-enabled solenoid valves for process automation and quality control. These valves allow for real-time adjustments in production lines, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing waste. The energy sector is also embracing IIoT-integrated solenoid valves for improved control in oil and gas operations, power generation, and distribution systems.
The utilities sector, particularly water and wastewater management, is another key driver of demand for IIoT-enabled solenoid valves. These valves play a crucial role in smart water management systems, helping to reduce water loss, improve distribution efficiency, and ensure water quality through precise control and monitoring.
Market trends indicate a growing preference for miniaturized and energy-efficient solenoid valves that can be easily integrated into existing IIoT infrastructures. There is also an increasing demand for valves with enhanced durability and reliability to withstand harsh industrial environments while maintaining connectivity and performance.
The adoption of IIoT-enabled solenoid valves is not limited to large enterprises. Small and medium-sized businesses are also recognizing the benefits of these technologies in improving their operational efficiency and competitiveness. This trend is expected to further drive market growth and innovation in the coming years.
As industries continue to prioritize digital transformation, the demand for solenoid valves with advanced IIoT capabilities is projected to rise. Manufacturers are focusing on developing valves with improved sensors, data analytics capabilities, and seamless integration with industrial control systems to meet this growing market need.
Solenoid Valve Technology Status
Solenoid valves have become an integral component in modern Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems, playing a crucial role in fluid control and automation processes. The current technology status of solenoid valves in IIoT applications reflects a dynamic landscape of innovation and integration.
In recent years, there has been a significant shift towards smart solenoid valves equipped with advanced sensing and communication capabilities. These valves can now provide real-time data on their operational status, flow rates, and other critical parameters. This enhanced functionality allows for more precise control and monitoring within IIoT ecosystems, enabling predictive maintenance and optimized system performance.
The integration of solenoid valves with IIoT platforms has led to the development of more sophisticated control algorithms. Machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques are being employed to analyze valve performance data, predict potential failures, and automatically adjust valve operations for optimal efficiency. This level of intelligent automation is particularly valuable in complex industrial processes where even minor improvements can lead to substantial cost savings and productivity gains.
Miniaturization and energy efficiency have been key focus areas in solenoid valve technology. Manufacturers are developing compact, low-power valves that can be easily integrated into space-constrained IIoT applications. These advancements have expanded the potential use cases for solenoid valves in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food processing, and smart building management systems.
Wireless connectivity has emerged as a game-changer in solenoid valve technology for IIoT. The adoption of protocols such as LoRaWAN, Bluetooth Low Energy, and NB-IoT has enabled seamless integration of valves into wireless sensor networks. This wireless capability facilitates easier installation, reduces wiring costs, and allows for more flexible system configurations in industrial environments.
Security and reliability remain critical concerns in the current state of solenoid valve technology for IIoT. As these valves become more connected and software-dependent, efforts are being made to enhance cybersecurity measures to protect against potential vulnerabilities. Redundancy features and fail-safe mechanisms are being incorporated to ensure system integrity and safety in case of communication failures or cyber attacks.
The ongoing development of edge computing capabilities is further enhancing the role of solenoid valves in IIoT systems. By processing data closer to the source, edge-enabled valves can make faster decisions, reduce latency, and minimize the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to central servers. This approach not only improves system responsiveness but also addresses concerns related to data privacy and bandwidth limitations.
In recent years, there has been a significant shift towards smart solenoid valves equipped with advanced sensing and communication capabilities. These valves can now provide real-time data on their operational status, flow rates, and other critical parameters. This enhanced functionality allows for more precise control and monitoring within IIoT ecosystems, enabling predictive maintenance and optimized system performance.
The integration of solenoid valves with IIoT platforms has led to the development of more sophisticated control algorithms. Machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques are being employed to analyze valve performance data, predict potential failures, and automatically adjust valve operations for optimal efficiency. This level of intelligent automation is particularly valuable in complex industrial processes where even minor improvements can lead to substantial cost savings and productivity gains.
Miniaturization and energy efficiency have been key focus areas in solenoid valve technology. Manufacturers are developing compact, low-power valves that can be easily integrated into space-constrained IIoT applications. These advancements have expanded the potential use cases for solenoid valves in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food processing, and smart building management systems.
Wireless connectivity has emerged as a game-changer in solenoid valve technology for IIoT. The adoption of protocols such as LoRaWAN, Bluetooth Low Energy, and NB-IoT has enabled seamless integration of valves into wireless sensor networks. This wireless capability facilitates easier installation, reduces wiring costs, and allows for more flexible system configurations in industrial environments.
Security and reliability remain critical concerns in the current state of solenoid valve technology for IIoT. As these valves become more connected and software-dependent, efforts are being made to enhance cybersecurity measures to protect against potential vulnerabilities. Redundancy features and fail-safe mechanisms are being incorporated to ensure system integrity and safety in case of communication failures or cyber attacks.
The ongoing development of edge computing capabilities is further enhancing the role of solenoid valves in IIoT systems. By processing data closer to the source, edge-enabled valves can make faster decisions, reduce latency, and minimize the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to central servers. This approach not only improves system responsiveness but also addresses concerns related to data privacy and bandwidth limitations.
Current IIoT Solenoid Solutions
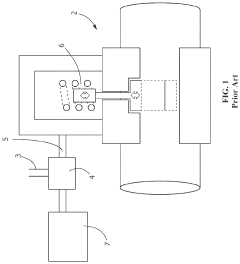
01 Solenoid valve design and structure
Solenoid valves are electromechanical devices that control the flow of fluids. They consist of a solenoid coil, plunger, and valve body. When energized, the coil creates a magnetic field that moves the plunger, opening or closing the valve. Various designs exist to optimize performance, efficiency, and reliability for different applications.- Solenoid valve design and structure: Solenoid valves are electromechanical devices that control the flow of fluids. They consist of a solenoid coil, plunger, and valve body. When energized, the coil creates a magnetic field that moves the plunger, opening or closing the valve. Various designs exist to optimize performance, efficiency, and reliability for different applications.
- Solenoid valve control systems: Advanced control systems for solenoid valves incorporate electronic components and software to enhance precision and functionality. These systems may include microcontrollers, sensors, and communication interfaces to enable remote operation, diagnostics, and integration with larger automation systems. Pulse-width modulation and other techniques can be used to improve valve response and energy efficiency.
- Solenoid valve applications in automotive systems: Solenoid valves play crucial roles in various automotive systems, including fuel injection, transmission control, and exhaust gas recirculation. They are designed to withstand harsh environments, high temperatures, and rapid cycling. Specialized solenoid valves are developed to meet specific requirements of different vehicle subsystems, focusing on reliability, response time, and fuel efficiency.
- Miniaturization and integration of solenoid valves: Advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques have led to the development of compact and integrated solenoid valve solutions. These miniaturized valves can be incorporated into complex assemblies or manifolds, reducing space requirements and simplifying installation. Micro-solenoid valves find applications in medical devices, analytical instruments, and portable equipment.
- Energy-efficient solenoid valve designs: Innovative solenoid valve designs focus on reducing power consumption and heat generation. This includes the use of low-power coils, latching mechanisms, and optimized magnetic circuits. Some designs incorporate energy recovery systems or utilize alternative actuation methods to minimize energy use while maintaining performance. These energy-efficient valves are particularly valuable in battery-powered or energy-sensitive applications.
02 Solenoid valve control systems
Control systems for solenoid valves include electronic circuits and microcontrollers that regulate valve operation. These systems can incorporate sensors, feedback mechanisms, and advanced algorithms to ensure precise timing, pressure control, and flow regulation. They may also feature diagnostic capabilities and remote monitoring options.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of solenoid valves
Solenoid valves find widespread use in various industries and applications. They are commonly employed in automotive systems, industrial automation, HVAC systems, irrigation, and fluid dispensing equipment. Specific applications include fuel injection systems, pneumatic controls, and water management systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Energy efficiency and power management
Improving energy efficiency in solenoid valves is a key focus area. This includes developing low-power solenoids, implementing pulse-width modulation techniques, and utilizing energy-saving control strategies. Some designs incorporate energy recovery circuits or use permanent magnets to reduce power consumption during steady-state operation.Expand Specific Solutions05 Miniaturization and integration
There is a trend towards miniaturization and integration of solenoid valves. This involves developing compact valve designs, integrating multiple valves into a single assembly, and combining valves with other components such as sensors or actuators. These advancements enable space-saving solutions and improved performance in confined spaces.Expand Specific Solutions
Key IIoT Solenoid Valve Players
The application of solenoid valves in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The competitive landscape is diverse, featuring established industrial players like Eaton Corp., BorgWarner, and Danfoss A/S, alongside specialized valve manufacturers such as RPE Srl and Norgren Kloehn, Inc. Tech giants like IBM are also entering the space, integrating IIoT solutions. The technology's maturity is progressing rapidly, with companies like Chengdu Qinchuan IoT Technology Co., Ltd. and Guangzhou Xinwa Technology Co., Ltd. driving innovation in smart utility management. This convergence of traditional valve expertise and IoT capabilities is shaping a dynamic market with significant growth potential.
Eaton Corp.
Technical Solution: Eaton's approach to integrating solenoid valves in IIoT systems focuses on smart, connected solutions. Their technology incorporates advanced sensors and actuators into solenoid valves, enabling real-time monitoring and control. The company's SmartWire-DT system allows for seamless integration of solenoid valves into industrial networks, facilitating data collection and analysis[1]. Eaton's solenoid valves feature predictive maintenance capabilities, using machine learning algorithms to analyze valve performance data and predict potential failures before they occur[2]. This proactive approach significantly reduces downtime and maintenance costs in industrial processes.
Strengths: Comprehensive IIoT integration, advanced predictive maintenance, and robust industrial networking. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial costs and complexity in implementation for smaller operations.
International Business Machines Corp.
Technical Solution: IBM's approach to integrating solenoid valves in IIoT systems leverages their expertise in artificial intelligence and cloud computing. Their solution utilizes the IBM Watson IoT platform to collect and analyze data from solenoid valves across industrial processes. The system employs advanced machine learning algorithms to optimize valve performance, predict maintenance needs, and identify potential process improvements. IBM's technology enables real-time monitoring of valve health and performance, with the ability to detect anomalies and trigger automated responses[5]. The company's blockchain-based solution ensures secure and transparent data sharing across the supply chain, enhancing traceability and compliance in industries such as pharmaceuticals and food processing[6].
Strengths: Advanced AI and machine learning capabilities, robust data analytics, and secure blockchain integration. Weaknesses: May require significant expertise to implement and maintain, potentially limiting accessibility for smaller companies.
Core IIoT Solenoid Innovations
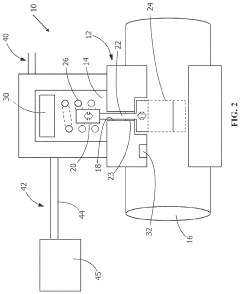
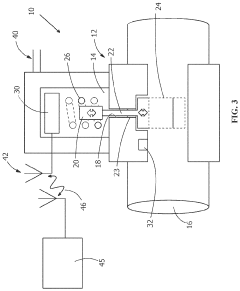
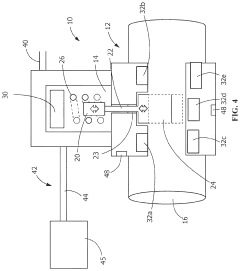
Smart Solenoid Valve
PatentPendingUS20230392709A1
Innovation
- Integration of electronic functionality within the solenoid valve, including control circuitry and sensors, allowing for bidirectional communication with a control module via a low voltage communications connection or wireless link, enabling continuous power supply and monitoring without the need for external relays, and allowing data collection for remote analysis.
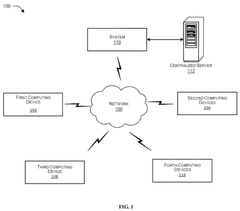
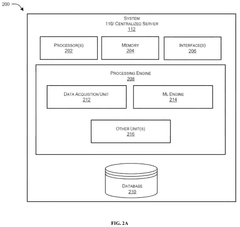
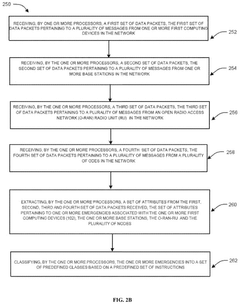
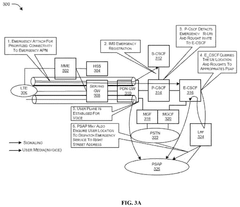
System and method for detecting and handling machine emergencies in a network
PatentPendingUS20240356812A1
Innovation
- A system and method utilizing a machine learning engine to identify and classify machine emergencies within a 3GPP network, enrich emergency messages with data like location and machine ID, and redirect them to appropriate servers, enabling SIM-less emergency attach and handling of various emergency types through predefined classes and quality of service profiles.
IIoT Solenoid Valve Standards
The development of standards for solenoid valves in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems is crucial for ensuring interoperability, reliability, and security across diverse industrial applications. These standards encompass various aspects, including communication protocols, data formats, and performance metrics.
One of the primary standards governing IIoT solenoid valves is the IEC 61508, which focuses on functional safety for electrical, electronic, and programmable electronic safety-related systems. This standard provides guidelines for the entire lifecycle of safety-critical systems, including solenoid valves used in IIoT environments.
The ISA/IEC 62443 series of standards addresses cybersecurity in industrial automation and control systems. These standards are particularly relevant for IIoT solenoid valves, as they provide a framework for securing networked devices against cyber threats and ensuring the integrity of data transmission.
In terms of communication protocols, the OPC UA (Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture) standard has gained significant traction in IIoT applications. It provides a secure and reliable method for data exchange between devices, including solenoid valves, and higher-level systems.
The NAMUR NE 107 recommendation, while not specifically designed for IIoT, has been widely adopted for standardizing diagnostic information from field devices. This standard is particularly useful for solenoid valves in IIoT systems, as it provides a consistent way to communicate device status and potential issues.
For wireless communication, standards such as WirelessHART and ISA100.11a are commonly used in industrial settings. These standards ensure reliable and secure wireless communication for IIoT devices, including solenoid valves, in challenging industrial environments.
The development of edge computing standards, such as the EdgeX Foundry framework, is also relevant for IIoT solenoid valves. These standards facilitate the integration of edge devices and enable local processing of data, reducing latency and improving system responsiveness.
As IIoT systems continue to evolve, new standards are emerging to address specific challenges. For instance, the development of time-sensitive networking (TSN) standards aims to provide deterministic, low-latency communication for critical industrial applications, which can benefit the precise control of solenoid valves in IIoT systems.
One of the primary standards governing IIoT solenoid valves is the IEC 61508, which focuses on functional safety for electrical, electronic, and programmable electronic safety-related systems. This standard provides guidelines for the entire lifecycle of safety-critical systems, including solenoid valves used in IIoT environments.
The ISA/IEC 62443 series of standards addresses cybersecurity in industrial automation and control systems. These standards are particularly relevant for IIoT solenoid valves, as they provide a framework for securing networked devices against cyber threats and ensuring the integrity of data transmission.
In terms of communication protocols, the OPC UA (Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture) standard has gained significant traction in IIoT applications. It provides a secure and reliable method for data exchange between devices, including solenoid valves, and higher-level systems.
The NAMUR NE 107 recommendation, while not specifically designed for IIoT, has been widely adopted for standardizing diagnostic information from field devices. This standard is particularly useful for solenoid valves in IIoT systems, as it provides a consistent way to communicate device status and potential issues.
For wireless communication, standards such as WirelessHART and ISA100.11a are commonly used in industrial settings. These standards ensure reliable and secure wireless communication for IIoT devices, including solenoid valves, in challenging industrial environments.
The development of edge computing standards, such as the EdgeX Foundry framework, is also relevant for IIoT solenoid valves. These standards facilitate the integration of edge devices and enable local processing of data, reducing latency and improving system responsiveness.
As IIoT systems continue to evolve, new standards are emerging to address specific challenges. For instance, the development of time-sensitive networking (TSN) standards aims to provide deterministic, low-latency communication for critical industrial applications, which can benefit the precise control of solenoid valves in IIoT systems.
Cybersecurity in IIoT Valves
The integration of solenoid valves into Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems has brought significant advancements in automation and control. However, this interconnectedness also introduces new cybersecurity vulnerabilities that must be addressed to ensure the integrity and reliability of industrial processes.
One of the primary cybersecurity concerns in IIoT valve systems is unauthorized access. Malicious actors may attempt to gain control of valve operations, potentially causing disruptions or safety hazards. To mitigate this risk, robust authentication and access control mechanisms must be implemented. Multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and secure remote access protocols are essential components of a comprehensive security strategy.
Data integrity is another critical aspect of cybersecurity in IIoT valve systems. As valves transmit operational data and receive control commands, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of this information is paramount. Encryption of data in transit and at rest, along with digital signatures and secure communication protocols such as TLS/SSL, can help protect against data tampering and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Network segmentation plays a crucial role in isolating IIoT valve systems from potential threats. By implementing virtual LANs (VLANs) and firewalls, organizations can create secure zones that limit the spread of potential breaches and provide granular control over network traffic. This approach also facilitates the implementation of intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) tailored to the specific needs of IIoT environments.
Regular security assessments and vulnerability scanning are essential practices for maintaining the cybersecurity of IIoT valve systems. These evaluations help identify potential weaknesses in the system architecture, software, and configurations. Timely patching and firmware updates for solenoid valves and associated IIoT devices are crucial in addressing known vulnerabilities and protecting against emerging threats.
Incident response and recovery planning are vital components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy for IIoT valve systems. Organizations must develop and regularly test incident response procedures to ensure rapid detection, containment, and mitigation of security breaches. This includes establishing clear communication channels, defining roles and responsibilities, and implementing backup and recovery mechanisms to minimize downtime and data loss in the event of a successful attack.
As the complexity of IIoT valve systems continues to grow, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. By implementing a multi-layered security approach that addresses authentication, data integrity, network segmentation, and incident response, organizations can significantly enhance the resilience of their IIoT valve infrastructure against cyber threats.
One of the primary cybersecurity concerns in IIoT valve systems is unauthorized access. Malicious actors may attempt to gain control of valve operations, potentially causing disruptions or safety hazards. To mitigate this risk, robust authentication and access control mechanisms must be implemented. Multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and secure remote access protocols are essential components of a comprehensive security strategy.
Data integrity is another critical aspect of cybersecurity in IIoT valve systems. As valves transmit operational data and receive control commands, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of this information is paramount. Encryption of data in transit and at rest, along with digital signatures and secure communication protocols such as TLS/SSL, can help protect against data tampering and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Network segmentation plays a crucial role in isolating IIoT valve systems from potential threats. By implementing virtual LANs (VLANs) and firewalls, organizations can create secure zones that limit the spread of potential breaches and provide granular control over network traffic. This approach also facilitates the implementation of intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) tailored to the specific needs of IIoT environments.
Regular security assessments and vulnerability scanning are essential practices for maintaining the cybersecurity of IIoT valve systems. These evaluations help identify potential weaknesses in the system architecture, software, and configurations. Timely patching and firmware updates for solenoid valves and associated IIoT devices are crucial in addressing known vulnerabilities and protecting against emerging threats.
Incident response and recovery planning are vital components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy for IIoT valve systems. Organizations must develop and regularly test incident response procedures to ensure rapid detection, containment, and mitigation of security breaches. This includes establishing clear communication channels, defining roles and responsibilities, and implementing backup and recovery mechanisms to minimize downtime and data loss in the event of a successful attack.
As the complexity of IIoT valve systems continues to grow, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. By implementing a multi-layered security approach that addresses authentication, data integrity, network segmentation, and incident response, organizations can significantly enhance the resilience of their IIoT valve infrastructure against cyber threats.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!