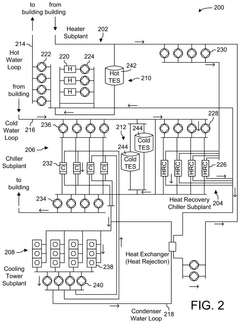
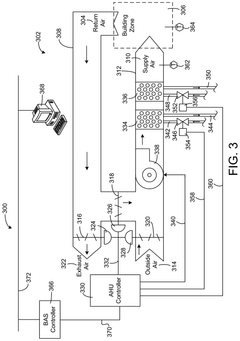
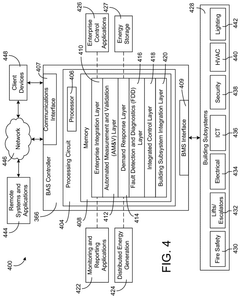
How Smart Solenoid Valves Integrate with Blockchain for Process Security
JUL 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Smart Valve Blockchain Integration: Background and Objectives
The integration of smart solenoid valves with blockchain technology represents a significant advancement in process security and industrial automation. This convergence of two cutting-edge technologies aims to enhance the reliability, transparency, and security of industrial processes across various sectors.
Smart solenoid valves, which are electronically controlled valves used to regulate fluid flow in industrial systems, have been evolving rapidly in recent years. These valves are equipped with sensors and microprocessors, allowing for precise control and real-time monitoring of fluid dynamics. The integration of these smart valves with blockchain technology seeks to address several critical challenges in industrial processes, including data integrity, traceability, and cybersecurity.
Blockchain, a decentralized and immutable digital ledger technology, has gained prominence beyond its initial application in cryptocurrencies. Its potential to provide secure, transparent, and tamper-proof record-keeping has attracted attention from various industries, including manufacturing, supply chain management, and process control.
The primary objective of integrating smart solenoid valves with blockchain is to create a secure, transparent, and efficient system for managing industrial processes. This integration aims to achieve several key goals:
1. Enhanced Security: By leveraging blockchain's cryptographic features, the system can protect against unauthorized access and tampering of valve control data, thereby reducing the risk of cyber-attacks on critical industrial infrastructure.
2. Improved Traceability: Blockchain's immutable ledger can provide a comprehensive audit trail of valve operations, enabling better tracking of process parameters, maintenance activities, and potential issues.
3. Real-time Monitoring and Control: The integration allows for real-time monitoring of valve status and performance metrics, with secure and verifiable data storage on the blockchain.
4. Increased Efficiency: Automating valve control processes through smart contracts on the blockchain can lead to more efficient operations and reduced human error.
5. Regulatory Compliance: The transparent and tamper-proof nature of blockchain can assist in meeting regulatory requirements by providing verifiable records of process controls and safety measures.
As industries continue to embrace digital transformation, the integration of smart solenoid valves with blockchain technology represents a significant step towards creating more secure, efficient, and transparent industrial processes. This technological convergence has the potential to revolutionize process control and security across various sectors, including oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, water treatment, and pharmaceutical production.
Smart solenoid valves, which are electronically controlled valves used to regulate fluid flow in industrial systems, have been evolving rapidly in recent years. These valves are equipped with sensors and microprocessors, allowing for precise control and real-time monitoring of fluid dynamics. The integration of these smart valves with blockchain technology seeks to address several critical challenges in industrial processes, including data integrity, traceability, and cybersecurity.
Blockchain, a decentralized and immutable digital ledger technology, has gained prominence beyond its initial application in cryptocurrencies. Its potential to provide secure, transparent, and tamper-proof record-keeping has attracted attention from various industries, including manufacturing, supply chain management, and process control.
The primary objective of integrating smart solenoid valves with blockchain is to create a secure, transparent, and efficient system for managing industrial processes. This integration aims to achieve several key goals:
1. Enhanced Security: By leveraging blockchain's cryptographic features, the system can protect against unauthorized access and tampering of valve control data, thereby reducing the risk of cyber-attacks on critical industrial infrastructure.
2. Improved Traceability: Blockchain's immutable ledger can provide a comprehensive audit trail of valve operations, enabling better tracking of process parameters, maintenance activities, and potential issues.
3. Real-time Monitoring and Control: The integration allows for real-time monitoring of valve status and performance metrics, with secure and verifiable data storage on the blockchain.
4. Increased Efficiency: Automating valve control processes through smart contracts on the blockchain can lead to more efficient operations and reduced human error.
5. Regulatory Compliance: The transparent and tamper-proof nature of blockchain can assist in meeting regulatory requirements by providing verifiable records of process controls and safety measures.
As industries continue to embrace digital transformation, the integration of smart solenoid valves with blockchain technology represents a significant step towards creating more secure, efficient, and transparent industrial processes. This technological convergence has the potential to revolutionize process control and security across various sectors, including oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, water treatment, and pharmaceutical production.
Market Demand for Secure Process Control Systems
The market demand for secure process control systems has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by the growing need for enhanced cybersecurity measures in industrial environments. As industries become more interconnected and digitalized, the vulnerability of critical infrastructure to cyber threats has become a paramount concern. Smart solenoid valves integrated with blockchain technology offer a promising solution to address these security challenges in process control systems.
The global industrial control systems security market is experiencing significant growth, with projections indicating continued expansion in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the rising frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks targeting industrial facilities, as well as the increasing adoption of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technologies. Organizations across various sectors, including manufacturing, energy, water treatment, and chemical processing, are recognizing the importance of implementing robust security measures to protect their operations from potential disruptions and data breaches.
The integration of smart solenoid valves with blockchain technology addresses several key market demands in secure process control systems. Firstly, it provides enhanced data integrity and traceability, ensuring that all valve operations and control commands are securely recorded and cannot be tampered with. This feature is particularly valuable in industries where regulatory compliance and audit trails are critical, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Secondly, the decentralized nature of blockchain technology offers improved resilience against single points of failure, reducing the risk of system-wide disruptions due to targeted attacks or equipment malfunctions. This aligns with the growing market demand for fault-tolerant and highly available control systems in mission-critical applications.
Furthermore, the integration of smart solenoid valves with blockchain enables more efficient and secure remote monitoring and control capabilities. As organizations increasingly adopt remote operations and predictive maintenance strategies, the ability to securely access and manage valve systems from anywhere becomes a significant market driver.
The market demand for this technology is also influenced by the growing emphasis on supply chain security and transparency. By leveraging blockchain's immutable ledger, organizations can create a secure and verifiable record of valve operations throughout the supply chain, enhancing trust and accountability among stakeholders.
Additionally, the integration of smart solenoid valves with blockchain aligns with the broader industry trend towards digital transformation and Industry 4.0 initiatives. As companies seek to optimize their processes and improve operational efficiency, the demand for intelligent, secure, and interconnected control systems continues to rise.
In conclusion, the market demand for secure process control systems incorporating smart solenoid valves and blockchain technology is driven by a combination of factors, including increasing cybersecurity threats, regulatory requirements, operational efficiency goals, and the need for enhanced transparency and traceability in industrial processes. As industries continue to evolve and face new challenges, the demand for innovative security solutions in process control systems is expected to grow, presenting significant opportunities for technology providers and system integrators in this space.
The global industrial control systems security market is experiencing significant growth, with projections indicating continued expansion in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the rising frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks targeting industrial facilities, as well as the increasing adoption of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technologies. Organizations across various sectors, including manufacturing, energy, water treatment, and chemical processing, are recognizing the importance of implementing robust security measures to protect their operations from potential disruptions and data breaches.
The integration of smart solenoid valves with blockchain technology addresses several key market demands in secure process control systems. Firstly, it provides enhanced data integrity and traceability, ensuring that all valve operations and control commands are securely recorded and cannot be tampered with. This feature is particularly valuable in industries where regulatory compliance and audit trails are critical, such as pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Secondly, the decentralized nature of blockchain technology offers improved resilience against single points of failure, reducing the risk of system-wide disruptions due to targeted attacks or equipment malfunctions. This aligns with the growing market demand for fault-tolerant and highly available control systems in mission-critical applications.
Furthermore, the integration of smart solenoid valves with blockchain enables more efficient and secure remote monitoring and control capabilities. As organizations increasingly adopt remote operations and predictive maintenance strategies, the ability to securely access and manage valve systems from anywhere becomes a significant market driver.
The market demand for this technology is also influenced by the growing emphasis on supply chain security and transparency. By leveraging blockchain's immutable ledger, organizations can create a secure and verifiable record of valve operations throughout the supply chain, enhancing trust and accountability among stakeholders.
Additionally, the integration of smart solenoid valves with blockchain aligns with the broader industry trend towards digital transformation and Industry 4.0 initiatives. As companies seek to optimize their processes and improve operational efficiency, the demand for intelligent, secure, and interconnected control systems continues to rise.
In conclusion, the market demand for secure process control systems incorporating smart solenoid valves and blockchain technology is driven by a combination of factors, including increasing cybersecurity threats, regulatory requirements, operational efficiency goals, and the need for enhanced transparency and traceability in industrial processes. As industries continue to evolve and face new challenges, the demand for innovative security solutions in process control systems is expected to grow, presenting significant opportunities for technology providers and system integrators in this space.
Current Challenges in Smart Valve and Blockchain Integration
The integration of smart solenoid valves with blockchain technology for process security presents several significant challenges that need to be addressed. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent complexity of combining two distinct technological domains: industrial control systems and distributed ledger technology. This integration requires a deep understanding of both fields, which is often lacking in traditional engineering teams.
Security concerns pose another major challenge. While blockchain offers enhanced security through its decentralized and immutable nature, the interface between smart valves and the blockchain network introduces new potential vulnerabilities. Ensuring end-to-end security from the physical valve to the digital ledger requires robust encryption, secure communication protocols, and tamper-proof hardware implementations.
Scalability issues also present a significant hurdle. Industrial processes often involve numerous valves operating in real-time, generating vast amounts of data. The current blockchain architectures may struggle to handle the high-frequency transactions and data storage requirements of large-scale valve networks. This limitation could lead to latency issues and impact the real-time responsiveness crucial for many industrial applications.
Interoperability between different blockchain platforms and existing industrial control systems is another challenge. Many industries have legacy systems that are not easily compatible with blockchain technology. Developing standardized interfaces and protocols to ensure seamless integration across diverse systems and blockchain networks is a complex task that requires industry-wide collaboration.
The energy consumption of blockchain networks, particularly those using proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, is a concern when considering large-scale industrial applications. Smart valve systems integrated with such networks could significantly increase the overall energy footprint of industrial processes, potentially offsetting any efficiency gains.
Regulatory compliance and legal frameworks present additional challenges. The use of blockchain in critical industrial processes may face scrutiny from regulatory bodies, especially in sectors with strict safety and quality control requirements. Ensuring that blockchain-based valve control systems meet all necessary regulatory standards and can provide auditable records is a complex undertaking.
Lastly, the cost of implementation and the need for specialized expertise pose significant barriers to adoption. Upgrading existing valve systems to integrate with blockchain technology requires substantial investment in hardware, software, and personnel training. Many organizations may struggle to justify these costs without clear demonstrations of long-term benefits and return on investment.
Security concerns pose another major challenge. While blockchain offers enhanced security through its decentralized and immutable nature, the interface between smart valves and the blockchain network introduces new potential vulnerabilities. Ensuring end-to-end security from the physical valve to the digital ledger requires robust encryption, secure communication protocols, and tamper-proof hardware implementations.
Scalability issues also present a significant hurdle. Industrial processes often involve numerous valves operating in real-time, generating vast amounts of data. The current blockchain architectures may struggle to handle the high-frequency transactions and data storage requirements of large-scale valve networks. This limitation could lead to latency issues and impact the real-time responsiveness crucial for many industrial applications.
Interoperability between different blockchain platforms and existing industrial control systems is another challenge. Many industries have legacy systems that are not easily compatible with blockchain technology. Developing standardized interfaces and protocols to ensure seamless integration across diverse systems and blockchain networks is a complex task that requires industry-wide collaboration.
The energy consumption of blockchain networks, particularly those using proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, is a concern when considering large-scale industrial applications. Smart valve systems integrated with such networks could significantly increase the overall energy footprint of industrial processes, potentially offsetting any efficiency gains.
Regulatory compliance and legal frameworks present additional challenges. The use of blockchain in critical industrial processes may face scrutiny from regulatory bodies, especially in sectors with strict safety and quality control requirements. Ensuring that blockchain-based valve control systems meet all necessary regulatory standards and can provide auditable records is a complex undertaking.
Lastly, the cost of implementation and the need for specialized expertise pose significant barriers to adoption. Upgrading existing valve systems to integrate with blockchain technology requires substantial investment in hardware, software, and personnel training. Many organizations may struggle to justify these costs without clear demonstrations of long-term benefits and return on investment.
Existing Smart Valve Blockchain Integration Solutions
01 Smart solenoid valve control systems
Advanced control systems for solenoid valves that incorporate intelligent features such as remote monitoring, automated diagnostics, and predictive maintenance. These systems enhance process security by providing real-time data analysis, fault detection, and optimized valve operation.- Smart solenoid valve control systems: Advanced control systems for smart solenoid valves that enhance process security through intelligent monitoring, real-time diagnostics, and automated adjustments. These systems can detect anomalies, predict failures, and optimize valve performance to ensure safe and efficient operation in various industrial applications.
- Secure communication protocols for valve networks: Implementation of secure communication protocols in smart solenoid valve networks to protect against cyber threats and unauthorized access. These protocols ensure data integrity, confidentiality, and authentication in the transmission of control signals and operational data between valves and control systems.
- Fail-safe mechanisms and redundancy: Integration of fail-safe mechanisms and redundancy features in smart solenoid valve systems to maintain process security during component failures or power outages. These mechanisms may include backup power sources, redundant valve configurations, and automatic shutdown procedures to prevent hazardous situations.
- Adaptive learning and predictive maintenance: Incorporation of machine learning algorithms and predictive maintenance capabilities in smart solenoid valve systems. These features enable the valves to adapt to changing process conditions, predict potential issues, and schedule maintenance activities proactively, thereby enhancing overall process security and reliability.
- Environmental and safety compliance features: Design and implementation of features in smart solenoid valves that ensure compliance with environmental regulations and safety standards. These may include leak detection systems, emissions monitoring, and integration with plant-wide safety systems to maintain process security and minimize environmental impact.
02 Secure communication protocols for valve networks
Implementation of secure communication protocols in solenoid valve networks to protect against cyber threats and unauthorized access. This includes encryption methods, authentication mechanisms, and secure data transmission to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of valve control signals.Expand Specific Solutions03 Fail-safe mechanisms for solenoid valves
Integration of fail-safe mechanisms in smart solenoid valves to maintain process security during system failures or power outages. These mechanisms may include automatic valve closure, backup power systems, or redundant control circuits to prevent uncontrolled fluid flow or process disruptions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sensor integration for enhanced valve monitoring
Incorporation of various sensors into smart solenoid valve systems to monitor critical parameters such as pressure, temperature, flow rate, and valve position. This sensor integration enables improved process control, early detection of anomalies, and enhanced overall system security.Expand Specific Solutions05 Adaptive learning algorithms for valve optimization
Implementation of machine learning and adaptive algorithms in smart solenoid valve systems to optimize valve performance and enhance process security. These algorithms can analyze historical data, predict potential issues, and automatically adjust valve parameters to maintain optimal operation and minimize security risks.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Smart Valve and Blockchain Industries
The integration of smart solenoid valves with blockchain for process security is an emerging technology at the early stages of development, with a growing market potential as industries seek enhanced security and traceability in their operations. The market size is expanding, driven by increasing demand for secure and transparent process control systems. While the technology is still maturing, companies like nChain Licensing AG, NTT, Inc., and WeBank Co., Ltd. are making significant strides in blockchain implementation. Simultaneously, traditional valve manufacturers such as Shijiazhuang Kelin Electric Co., Ltd. and ODE SRL are exploring ways to incorporate smart features and blockchain compatibility into their products, indicating a convergence of established industrial expertise with cutting-edge digital technologies.
nChain Licensing AG
Technical Solution: nChain's approach to integrating smart solenoid valves with blockchain for process security leverages their expertise in blockchain technology. They have developed a system that uses blockchain to create an immutable record of valve operations, ensuring transparency and security in industrial processes. The smart solenoid valves are equipped with IoT sensors that transmit data to the blockchain network, where it is timestamped and cryptographically secured. This allows for real-time monitoring of valve states, detection of unauthorized access attempts, and creation of auditable trails of all valve operations[1][3]. The system also incorporates smart contracts to automate valve control based on predefined conditions, enhancing both security and efficiency in process management.
Strengths: Strong blockchain expertise, robust security features, and auditable process trails. Weaknesses: May require significant infrastructure changes and could face scalability challenges in large-scale industrial applications.
International Business Machines Corp.
Technical Solution: IBM's solution for integrating smart solenoid valves with blockchain focuses on creating a secure, decentralized system for industrial process control. Their approach utilizes IBM's Hyperledger Fabric blockchain platform to create a permissioned network where valve operations are recorded and verified. The smart solenoid valves are connected to IBM's Watson IoT platform, which collects and analyzes data in real-time. This data is then securely transmitted to the blockchain network, where it is stored in tamper-proof blocks. IBM's system also incorporates AI-driven predictive maintenance, using blockchain-stored historical data to anticipate valve failures and optimize maintenance schedules[2][5]. Additionally, they have implemented role-based access control through blockchain-based identity management, ensuring that only authorized personnel can control or modify valve operations.
Strengths: Robust enterprise-grade blockchain platform, integration with AI for predictive maintenance, and strong identity management. Weaknesses: Potentially high implementation costs and complexity, which may be challenging for smaller organizations to adopt.
Core Innovations in Valve-Blockchain Security Protocols
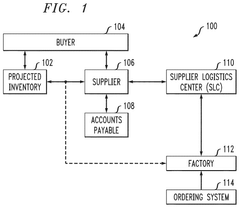
Supply chain management using blockchain and machine learning functionalities
PatentActiveUS12124982B2
Innovation
- A blockchain-based supply chain management system that provides controlled real-time visibility and trusted data transactions between entities, utilizing machine learning for supplier ranking and smart contracts to validate invoices and material movements, ensuring accurate inventory management and reducing the need for excessive safety stock.
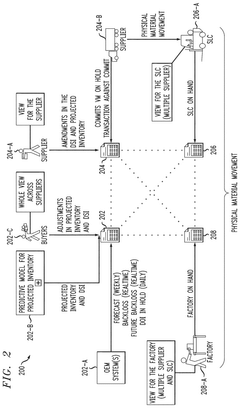
Systems and methods of enabling blockchain-based building automation systems
PatentActiveUS20240356729A1
Innovation
- Implementing a blockchain-based system with a private local blockchain that includes a device ledger, transaction ledger, transaction processor, and local rule engine to secure data exchange, authenticate devices, and standardize communication among building components, enabling secure, tamper-proof, and energy-efficient operations.
Cybersecurity Implications of Smart Valve-Blockchain Systems
The integration of smart solenoid valves with blockchain technology introduces new cybersecurity considerations that must be carefully addressed. This convergence of operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) expands the attack surface and creates novel vulnerabilities that malicious actors could exploit.
One primary concern is the potential for unauthorized access to valve control systems through blockchain interfaces. While blockchain offers enhanced security through its distributed ledger and cryptographic features, it also introduces new entry points that must be secured. Robust authentication and access control mechanisms are essential to prevent unauthorized parties from manipulating valve operations or injecting false data into the blockchain.
Data integrity is another critical aspect of these systems. The immutable nature of blockchain can help ensure the authenticity of valve operation records, but it also means that any compromised or erroneous data becomes permanently recorded. Implementing rigorous data validation and verification processes before committing information to the blockchain is crucial to maintain the system's reliability and trustworthiness.
The decentralized nature of blockchain networks also raises concerns about network segmentation and isolation. Traditional OT systems often rely on air-gapping or strict network segregation for security. Integrating these systems with blockchain requires careful network architecture design to maintain appropriate isolation while enabling necessary communication between OT and IT components.
Encryption plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information within smart valve-blockchain systems. All data transmissions, both on-chain and off-chain, should be encrypted to prevent eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. Additionally, secure key management practices are essential to safeguard the cryptographic keys used for blockchain transactions and smart contract execution.
Smart contracts, which automate valve operations based on predefined conditions, introduce their own set of security challenges. Vulnerabilities in smart contract code could lead to unintended valve behavior or create exploitable loopholes. Rigorous code auditing, formal verification, and extensive testing of smart contracts are necessary to mitigate these risks.
Lastly, the integration of smart valves with blockchain may impact incident response and recovery procedures. The immutability of blockchain transactions could complicate efforts to roll back or correct erroneous operations. Developing comprehensive incident response plans that account for the unique characteristics of blockchain-based systems is crucial for maintaining operational resilience.
One primary concern is the potential for unauthorized access to valve control systems through blockchain interfaces. While blockchain offers enhanced security through its distributed ledger and cryptographic features, it also introduces new entry points that must be secured. Robust authentication and access control mechanisms are essential to prevent unauthorized parties from manipulating valve operations or injecting false data into the blockchain.
Data integrity is another critical aspect of these systems. The immutable nature of blockchain can help ensure the authenticity of valve operation records, but it also means that any compromised or erroneous data becomes permanently recorded. Implementing rigorous data validation and verification processes before committing information to the blockchain is crucial to maintain the system's reliability and trustworthiness.
The decentralized nature of blockchain networks also raises concerns about network segmentation and isolation. Traditional OT systems often rely on air-gapping or strict network segregation for security. Integrating these systems with blockchain requires careful network architecture design to maintain appropriate isolation while enabling necessary communication between OT and IT components.
Encryption plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information within smart valve-blockchain systems. All data transmissions, both on-chain and off-chain, should be encrypted to prevent eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. Additionally, secure key management practices are essential to safeguard the cryptographic keys used for blockchain transactions and smart contract execution.
Smart contracts, which automate valve operations based on predefined conditions, introduce their own set of security challenges. Vulnerabilities in smart contract code could lead to unintended valve behavior or create exploitable loopholes. Rigorous code auditing, formal verification, and extensive testing of smart contracts are necessary to mitigate these risks.
Lastly, the integration of smart valves with blockchain may impact incident response and recovery procedures. The immutability of blockchain transactions could complicate efforts to roll back or correct erroneous operations. Developing comprehensive incident response plans that account for the unique characteristics of blockchain-based systems is crucial for maintaining operational resilience.
Regulatory Framework for Industrial IoT Security
The regulatory framework for Industrial IoT security in the context of integrating smart solenoid valves with blockchain for process security is a complex and evolving landscape. As the adoption of IoT devices in industrial settings continues to grow, governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the need for comprehensive guidelines to ensure the security and integrity of these systems.
At the international level, organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have developed standards specifically addressing IoT security. The ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27002 standards provide a framework for information security management systems, which can be applied to Industrial IoT environments. Additionally, the ISO/IEC 30141 standard focuses on the Internet of Things Reference Architecture, offering guidance on security considerations for IoT systems.
In the United States, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has published several guidelines relevant to Industrial IoT security. The NIST Special Publication 800-82 provides guidance on industrial control systems security, while the NIST Cybersecurity Framework offers a risk-based approach to managing cybersecurity risk in critical infrastructure sectors.
The European Union has introduced the Cybersecurity Act, which establishes a framework for EU-wide cybersecurity certification schemes for ICT products, services, and processes. This regulation is particularly relevant for Industrial IoT devices and systems, including smart solenoid valves integrated with blockchain technology.
Specific to blockchain technology, regulatory bodies are still grappling with how to effectively govern its use in industrial settings. The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) has published guidelines on blockchain security, which can be applied to the integration of blockchain with smart solenoid valves for process security.
In the context of smart solenoid valves, regulatory frameworks often intersect with industry-specific standards. For instance, in the oil and gas industry, the American Petroleum Institute (API) has developed standards that address the use of smart valves and associated control systems. These standards, while not specifically focused on blockchain integration, provide a foundation for ensuring the security and reliability of valve operations in critical processes.
As the integration of smart solenoid valves with blockchain technology for process security is a relatively new application, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies are collaborating to develop guidelines that address the unique challenges posed by this convergence of technologies. Future regulations may focus on areas such as data integrity, access control, and the auditability of blockchain-based industrial control systems.
At the international level, organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have developed standards specifically addressing IoT security. The ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27002 standards provide a framework for information security management systems, which can be applied to Industrial IoT environments. Additionally, the ISO/IEC 30141 standard focuses on the Internet of Things Reference Architecture, offering guidance on security considerations for IoT systems.
In the United States, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has published several guidelines relevant to Industrial IoT security. The NIST Special Publication 800-82 provides guidance on industrial control systems security, while the NIST Cybersecurity Framework offers a risk-based approach to managing cybersecurity risk in critical infrastructure sectors.
The European Union has introduced the Cybersecurity Act, which establishes a framework for EU-wide cybersecurity certification schemes for ICT products, services, and processes. This regulation is particularly relevant for Industrial IoT devices and systems, including smart solenoid valves integrated with blockchain technology.
Specific to blockchain technology, regulatory bodies are still grappling with how to effectively govern its use in industrial settings. The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) has published guidelines on blockchain security, which can be applied to the integration of blockchain with smart solenoid valves for process security.
In the context of smart solenoid valves, regulatory frameworks often intersect with industry-specific standards. For instance, in the oil and gas industry, the American Petroleum Institute (API) has developed standards that address the use of smart valves and associated control systems. These standards, while not specifically focused on blockchain integration, provide a foundation for ensuring the security and reliability of valve operations in critical processes.
As the integration of smart solenoid valves with blockchain technology for process security is a relatively new application, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies are collaborating to develop guidelines that address the unique challenges posed by this convergence of technologies. Future regulations may focus on areas such as data integrity, access control, and the auditability of blockchain-based industrial control systems.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!