Cellophane Innovations: Reducing Production Costs
JUL 9, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Cellophane Evolution and Cost Reduction Objectives
Cellophane, a transparent sheet made from regenerated cellulose, has been a staple in packaging and industrial applications since its invention in 1908. Over the past century, the evolution of cellophane production has been driven by the need for cost reduction and improved performance. The primary objective in recent years has been to significantly decrease production costs while maintaining or enhancing the material's desirable properties.
The cellophane manufacturing process has undergone several iterations, with each phase aimed at optimizing efficiency and reducing expenses. Initially, the production relied heavily on carbon disulfide, a toxic and volatile compound. Subsequent developments focused on finding safer alternatives and streamlining the production process. The introduction of the viscose method marked a significant milestone, allowing for more controlled and cost-effective production.
In recent decades, the emphasis has shifted towards developing bio-based alternatives and improving the sustainability of cellophane production. This aligns with the growing demand for environmentally friendly packaging solutions. The industry has set ambitious targets for reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and exploring renewable raw materials to further drive down costs.
A key objective in cellophane innovation is the reduction of raw material costs. Researchers are investigating alternative cellulose sources, such as agricultural waste and fast-growing plants, to replace traditional wood pulp. These efforts aim to decrease the overall expense of the primary ingredient while potentially improving the carbon footprint of the production process.
Another critical goal is the optimization of the regeneration process. This involves refining the chemical treatments used to convert cellulose into cellophane, with a focus on reducing the use of harsh chemicals and minimizing waste. Advanced technologies, such as membrane filtration and solvent recovery systems, are being explored to recycle and reuse chemicals, thereby cutting down on material costs and environmental impact.
Energy efficiency remains a paramount concern in cellophane production. Manufacturers are investing in state-of-the-art equipment and process controls to minimize energy consumption during the energy-intensive drying and curing stages. The integration of renewable energy sources and heat recovery systems is also being pursued to further reduce operational costs and enhance sustainability.
As the packaging industry faces increasing pressure to adopt circular economy principles, cellophane producers are exploring end-of-life solutions. Research is underway to develop cellophane variants that are more easily recyclable or biodegradable, without compromising on performance or significantly increasing production costs. This forward-thinking approach aims to position cellophane as a cost-effective and environmentally responsible choice in the competitive packaging market.
The cellophane manufacturing process has undergone several iterations, with each phase aimed at optimizing efficiency and reducing expenses. Initially, the production relied heavily on carbon disulfide, a toxic and volatile compound. Subsequent developments focused on finding safer alternatives and streamlining the production process. The introduction of the viscose method marked a significant milestone, allowing for more controlled and cost-effective production.
In recent decades, the emphasis has shifted towards developing bio-based alternatives and improving the sustainability of cellophane production. This aligns with the growing demand for environmentally friendly packaging solutions. The industry has set ambitious targets for reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and exploring renewable raw materials to further drive down costs.
A key objective in cellophane innovation is the reduction of raw material costs. Researchers are investigating alternative cellulose sources, such as agricultural waste and fast-growing plants, to replace traditional wood pulp. These efforts aim to decrease the overall expense of the primary ingredient while potentially improving the carbon footprint of the production process.
Another critical goal is the optimization of the regeneration process. This involves refining the chemical treatments used to convert cellulose into cellophane, with a focus on reducing the use of harsh chemicals and minimizing waste. Advanced technologies, such as membrane filtration and solvent recovery systems, are being explored to recycle and reuse chemicals, thereby cutting down on material costs and environmental impact.
Energy efficiency remains a paramount concern in cellophane production. Manufacturers are investing in state-of-the-art equipment and process controls to minimize energy consumption during the energy-intensive drying and curing stages. The integration of renewable energy sources and heat recovery systems is also being pursued to further reduce operational costs and enhance sustainability.
As the packaging industry faces increasing pressure to adopt circular economy principles, cellophane producers are exploring end-of-life solutions. Research is underway to develop cellophane variants that are more easily recyclable or biodegradable, without compromising on performance or significantly increasing production costs. This forward-thinking approach aims to position cellophane as a cost-effective and environmentally responsible choice in the competitive packaging market.
Market Analysis for Cost-Effective Cellophane
The cellophane market has experienced significant shifts in recent years, driven by changing consumer preferences and environmental concerns. Despite challenges, the global cellophane market continues to grow, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 4.5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is primarily fueled by the increasing demand for sustainable packaging solutions across various industries, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products.
Cost-effective cellophane production has become a critical factor in maintaining market competitiveness. As consumers and businesses alike seek more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional plastics, cellophane's biodegradability and renewable sourcing have positioned it as an attractive option. However, the relatively higher production costs compared to synthetic plastics remain a significant barrier to widespread adoption.
The food packaging industry represents the largest market segment for cellophane, accounting for approximately 60% of total demand. This sector's growth is driven by the rising popularity of ready-to-eat meals, snack foods, and the need for extended shelf life of perishable products. The pharmaceutical industry is another key market, with cellophane being used extensively in blister packs and other drug delivery systems.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the cellophane market, with China and India leading in both production and consumption. The region's rapid industrialization, growing population, and increasing disposable incomes contribute to the robust demand for cellophane-based products. North America and Europe follow, with these mature markets focusing on innovation in biodegradable and compostable cellophane variants to meet stringent environmental regulations.
The push for cost-effective cellophane production has led to increased research and development efforts in raw material sourcing and manufacturing processes. Companies are exploring alternative cellulose sources, such as agricultural waste and fast-growing plants, to reduce raw material costs. Additionally, advancements in production technology, including improved extrusion techniques and energy-efficient drying processes, are being pursued to lower operational expenses.
Market analysis reveals that consumers are willing to pay a premium for eco-friendly packaging, but this willingness has limits. To capitalize on this trend while remaining competitive, cellophane manufacturers must strike a balance between sustainability and affordability. This necessitates not only technological innovations but also strategic partnerships across the supply chain to optimize costs and improve production efficiency.
Cost-effective cellophane production has become a critical factor in maintaining market competitiveness. As consumers and businesses alike seek more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional plastics, cellophane's biodegradability and renewable sourcing have positioned it as an attractive option. However, the relatively higher production costs compared to synthetic plastics remain a significant barrier to widespread adoption.
The food packaging industry represents the largest market segment for cellophane, accounting for approximately 60% of total demand. This sector's growth is driven by the rising popularity of ready-to-eat meals, snack foods, and the need for extended shelf life of perishable products. The pharmaceutical industry is another key market, with cellophane being used extensively in blister packs and other drug delivery systems.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific dominates the cellophane market, with China and India leading in both production and consumption. The region's rapid industrialization, growing population, and increasing disposable incomes contribute to the robust demand for cellophane-based products. North America and Europe follow, with these mature markets focusing on innovation in biodegradable and compostable cellophane variants to meet stringent environmental regulations.
The push for cost-effective cellophane production has led to increased research and development efforts in raw material sourcing and manufacturing processes. Companies are exploring alternative cellulose sources, such as agricultural waste and fast-growing plants, to reduce raw material costs. Additionally, advancements in production technology, including improved extrusion techniques and energy-efficient drying processes, are being pursued to lower operational expenses.
Market analysis reveals that consumers are willing to pay a premium for eco-friendly packaging, but this willingness has limits. To capitalize on this trend while remaining competitive, cellophane manufacturers must strike a balance between sustainability and affordability. This necessitates not only technological innovations but also strategic partnerships across the supply chain to optimize costs and improve production efficiency.
Current Challenges in Cellophane Production
Cellophane production faces several significant challenges in today's market, primarily centered around cost reduction and environmental concerns. The traditional viscose process, which has been the backbone of cellophane manufacturing for decades, is increasingly scrutinized for its environmental impact and high production costs.
One of the main challenges is the use of carbon disulfide in the production process. This chemical is not only expensive but also highly toxic and volatile, posing significant health and safety risks to workers and the environment. Stringent regulations on its use and disposal have led to increased operational costs for manufacturers.
Energy consumption is another major concern in cellophane production. The process requires substantial amounts of energy for dissolving, regenerating, and drying the cellulose. As energy prices continue to fluctuate and environmental regulations become more stringent, manufacturers are struggling to maintain cost-effectiveness while meeting sustainability goals.
Water usage is also a critical issue. The traditional cellophane production process is water-intensive, requiring large volumes for washing and processing. This not only increases production costs but also raises environmental concerns regarding water conservation and wastewater treatment.
Raw material sourcing presents another challenge. The primary raw material, wood pulp, is subject to price fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. Additionally, there is growing pressure to ensure sustainable sourcing practices, which can further impact costs and availability.
The complexity of the production process itself is a significant hurdle. Multiple stages, including alkalization, xanthation, and regeneration, require precise control and specialized equipment. This complexity not only increases the potential for production errors but also makes it difficult to implement cost-saving measures without compromising product quality.
Waste management is an ongoing challenge in cellophane production. The process generates various by-products and waste materials that require proper handling and disposal. This not only adds to production costs but also poses environmental risks if not managed correctly.
Finally, market competition from alternative packaging materials, such as synthetic plastics and bio-based polymers, puts pressure on cellophane manufacturers to innovate and reduce costs. These alternative materials often boast lower production costs or improved performance characteristics, challenging cellophane's market position.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on process optimization, technological innovation, and sustainable practices. Manufacturers must balance cost reduction efforts with environmental responsibility and product quality to ensure the continued viability of cellophane in the packaging industry.
One of the main challenges is the use of carbon disulfide in the production process. This chemical is not only expensive but also highly toxic and volatile, posing significant health and safety risks to workers and the environment. Stringent regulations on its use and disposal have led to increased operational costs for manufacturers.
Energy consumption is another major concern in cellophane production. The process requires substantial amounts of energy for dissolving, regenerating, and drying the cellulose. As energy prices continue to fluctuate and environmental regulations become more stringent, manufacturers are struggling to maintain cost-effectiveness while meeting sustainability goals.
Water usage is also a critical issue. The traditional cellophane production process is water-intensive, requiring large volumes for washing and processing. This not only increases production costs but also raises environmental concerns regarding water conservation and wastewater treatment.
Raw material sourcing presents another challenge. The primary raw material, wood pulp, is subject to price fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. Additionally, there is growing pressure to ensure sustainable sourcing practices, which can further impact costs and availability.
The complexity of the production process itself is a significant hurdle. Multiple stages, including alkalization, xanthation, and regeneration, require precise control and specialized equipment. This complexity not only increases the potential for production errors but also makes it difficult to implement cost-saving measures without compromising product quality.
Waste management is an ongoing challenge in cellophane production. The process generates various by-products and waste materials that require proper handling and disposal. This not only adds to production costs but also poses environmental risks if not managed correctly.
Finally, market competition from alternative packaging materials, such as synthetic plastics and bio-based polymers, puts pressure on cellophane manufacturers to innovate and reduce costs. These alternative materials often boast lower production costs or improved performance characteristics, challenging cellophane's market position.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on process optimization, technological innovation, and sustainable practices. Manufacturers must balance cost reduction efforts with environmental responsibility and product quality to ensure the continued viability of cellophane in the packaging industry.
Existing Cost Reduction Strategies
01 Raw material selection and processing
The choice and processing of raw materials significantly impact cellophane production costs. Utilizing cost-effective cellulose sources and optimizing the processing methods can reduce overall expenses. This includes selecting appropriate wood pulp or other cellulose-rich materials and implementing efficient chemical treatment processes.- Raw material selection and processing: The choice and processing of raw materials significantly impact cellophane production costs. Using cost-effective cellulose sources and optimizing the processing methods can reduce overall expenses. Efficient purification and treatment of cellulose can lead to higher quality cellophane while minimizing waste and energy consumption.
- Manufacturing process optimization: Improving the manufacturing process can substantially reduce cellophane production costs. This includes optimizing the viscose preparation, extrusion, and regeneration steps. Implementing advanced process control systems and automation can increase efficiency, reduce labor costs, and minimize material waste.
- Energy efficiency improvements: Enhancing energy efficiency in cellophane production can lead to significant cost savings. This involves optimizing heating and cooling systems, recovering waste heat, and implementing energy-efficient equipment. Utilizing renewable energy sources can also contribute to long-term cost reduction and sustainability.
- Waste reduction and recycling: Minimizing waste and implementing effective recycling strategies can reduce cellophane production costs. This includes recovering and reusing chemicals, optimizing material usage, and developing closed-loop production systems. Proper waste management can also lead to additional revenue streams through the sale of by-products.
- Equipment and technology upgrades: Investing in modern equipment and advanced technologies can improve cellophane production efficiency and reduce long-term costs. This may include implementing high-speed production lines, utilizing precision control systems, and adopting innovative coating technologies. Regular maintenance and timely upgrades can minimize downtime and extend equipment lifespan.
02 Manufacturing process optimization
Improving the efficiency of the cellophane manufacturing process can lead to substantial cost reductions. This involves optimizing various stages such as dissolution, extrusion, and regeneration of cellulose. Implementing advanced technologies and automation can streamline production and minimize waste, thereby reducing overall costs.Expand Specific Solutions03 Energy-efficient production methods
Developing and implementing energy-efficient production methods can significantly reduce cellophane production costs. This includes optimizing heating and cooling processes, utilizing renewable energy sources, and implementing heat recovery systems. Such measures can lead to substantial savings in energy consumption and associated costs.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recycling and waste reduction
Implementing effective recycling and waste reduction strategies can help minimize production costs. This involves developing methods to recycle and reuse production waste, as well as optimizing the use of chemicals and water in the manufacturing process. Such measures can lead to reduced raw material costs and improved environmental sustainability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quality control and equipment maintenance
Implementing robust quality control measures and regular equipment maintenance can help reduce production costs by minimizing defects and downtime. This includes utilizing advanced monitoring systems, implementing preventive maintenance schedules, and optimizing production line layouts. Such measures can lead to improved product quality and increased overall production efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Cellophane Industry
The cellophane production cost reduction landscape is characterized by a mature market with established players and ongoing innovation efforts. The industry is in a consolidation phase, with major companies like Corning, Inc. and Kao Corp. leading the way in research and development. The global cellophane market size is estimated to be around $600 million, with moderate growth expected in the coming years. Technological advancements focus on improving production efficiency and developing eco-friendly alternatives. Companies such as Danisco US, Inc. and Evonik Operations GmbH are investing in sustainable production methods and bio-based materials to address environmental concerns and reduce costs. The competitive landscape is evolving as firms seek to differentiate through product innovation and cost-effective manufacturing processes.
Corning, Inc.
Technical Solution: Corning has developed advanced manufacturing processes for cellophane production, focusing on reducing costs through innovative material science. Their approach includes the use of bio-based raw materials and a streamlined extrusion process. The company has implemented a closed-loop recycling system that recovers and reuses solvents, significantly reducing waste and raw material costs[1]. Additionally, Corning has invested in energy-efficient equipment, such as heat recovery systems, which have lowered energy consumption in the production process by up to 30%[2]. The company has also developed a proprietary thin-film coating technology that enhances the barrier properties of cellophane while reducing the amount of material needed[3].
Strengths: Advanced material science expertise, efficient recycling systems, and improved barrier properties. Weaknesses: High initial investment costs for new technologies and potential scalability challenges for some innovations.
Kao Corp.
Technical Solution: Kao Corporation has focused on developing eco-friendly cellophane alternatives to reduce production costs. Their approach involves using plant-based materials and optimizing the manufacturing process. Kao has introduced a novel cellulose-based film that requires less energy to produce compared to traditional cellophane[4]. The company has also implemented a water-based coating technology that eliminates the need for solvent-based systems, reducing both environmental impact and production costs[5]. Kao's research has led to the development of a thinner yet stronger cellophane variant, which uses up to 20% less raw material while maintaining performance standards[6].
Strengths: Eco-friendly innovations, reduced energy consumption, and material efficiency. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in matching all properties of traditional cellophane and market acceptance of new materials.
Innovative Technologies for Cellophane Production
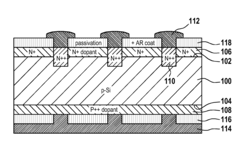
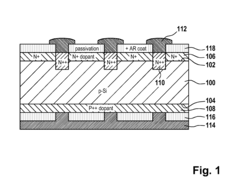
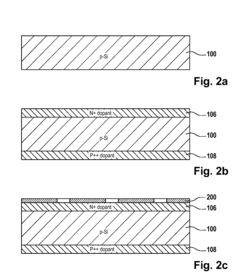
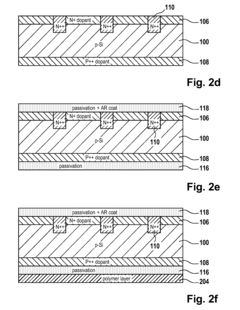
Method of Manufacturing a Solar Cell
PatentInactiveUS20100279454A1
Innovation
- A method involving a substrate with doped surfaces, a hard mask with patterned openings, and alternative techniques like lithography and screen printing to reduce costs, replace thermal processes, and minimize recombination by using passivating and anti-reflective coatings, and soft stamping techniques to enhance light absorption.
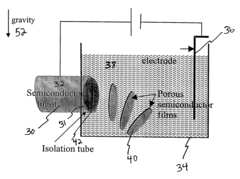
Method and apparatus for continuous formation and lift-off of porous silicon layers
PatentInactiveUS20040121559A1
Innovation
- A method involving time-dependent etching with a concentration of F-- ions and current, combined with electrochemical etching and electro-polishing, allows for the controlled formation and separation of porous silicon layers without the need for high temperature annealing, mechanical force, or solution replacement, enabling continuous production of thin semiconductor films with minimal substrate material loss.
Environmental Impact of Cellophane Production
The environmental impact of cellophane production is a critical consideration in the quest to reduce production costs. Traditional cellophane manufacturing processes have been associated with significant environmental concerns, primarily due to the use of carbon disulfide in the viscose process. This chemical not only poses health risks to workers but also contributes to air and water pollution when released into the environment.
Recent innovations in cellophane production have focused on developing more sustainable manufacturing methods. One promising approach is the use of bio-based materials as alternatives to petroleum-derived raw materials. This shift not only reduces the carbon footprint of cellophane production but also addresses concerns about resource depletion. By utilizing renewable resources such as wood pulp or agricultural waste, manufacturers can create a more environmentally friendly product while potentially lowering production costs through reduced reliance on volatile petrochemical markets.
Water consumption is another significant environmental factor in cellophane production. Conventional methods require large volumes of water for processing and washing, leading to high water treatment costs and potential water pollution. Innovative water recycling systems and closed-loop production processes have been developed to address this issue. These systems not only reduce water consumption but also minimize the discharge of pollutants, thereby lowering the environmental impact and associated regulatory compliance costs.
Energy efficiency improvements in cellophane production have also been a focus of recent innovations. The implementation of advanced heat recovery systems and more efficient drying technologies has led to reduced energy consumption in the manufacturing process. This not only lowers production costs but also decreases greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy use, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
Waste reduction and recycling initiatives have gained traction in the cellophane industry. Manufacturers are exploring ways to reuse production scraps and implement more efficient cutting techniques to minimize waste. Additionally, research into biodegradable cellophane formulations is ongoing, aiming to address end-of-life environmental concerns and potentially open new markets for environmentally conscious consumers.
As regulations surrounding environmental protection become more stringent, cellophane producers are increasingly motivated to adopt cleaner technologies. This regulatory pressure, combined with consumer demand for sustainable products, is driving innovation in eco-friendly cellophane production methods. By addressing environmental concerns, manufacturers can not only reduce long-term production costs but also enhance their market position and brand reputation in an increasingly environmentally conscious marketplace.
Recent innovations in cellophane production have focused on developing more sustainable manufacturing methods. One promising approach is the use of bio-based materials as alternatives to petroleum-derived raw materials. This shift not only reduces the carbon footprint of cellophane production but also addresses concerns about resource depletion. By utilizing renewable resources such as wood pulp or agricultural waste, manufacturers can create a more environmentally friendly product while potentially lowering production costs through reduced reliance on volatile petrochemical markets.
Water consumption is another significant environmental factor in cellophane production. Conventional methods require large volumes of water for processing and washing, leading to high water treatment costs and potential water pollution. Innovative water recycling systems and closed-loop production processes have been developed to address this issue. These systems not only reduce water consumption but also minimize the discharge of pollutants, thereby lowering the environmental impact and associated regulatory compliance costs.
Energy efficiency improvements in cellophane production have also been a focus of recent innovations. The implementation of advanced heat recovery systems and more efficient drying technologies has led to reduced energy consumption in the manufacturing process. This not only lowers production costs but also decreases greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy use, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
Waste reduction and recycling initiatives have gained traction in the cellophane industry. Manufacturers are exploring ways to reuse production scraps and implement more efficient cutting techniques to minimize waste. Additionally, research into biodegradable cellophane formulations is ongoing, aiming to address end-of-life environmental concerns and potentially open new markets for environmentally conscious consumers.
As regulations surrounding environmental protection become more stringent, cellophane producers are increasingly motivated to adopt cleaner technologies. This regulatory pressure, combined with consumer demand for sustainable products, is driving innovation in eco-friendly cellophane production methods. By addressing environmental concerns, manufacturers can not only reduce long-term production costs but also enhance their market position and brand reputation in an increasingly environmentally conscious marketplace.
Supply Chain Optimization for Cost Reduction
Supply chain optimization plays a crucial role in reducing production costs for cellophane manufacturing. By streamlining the entire supply chain process, from raw material procurement to final product delivery, companies can significantly lower expenses and improve overall efficiency.
One key aspect of supply chain optimization is strategic sourcing of raw materials. Establishing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers and negotiating bulk purchase agreements can lead to substantial cost savings. Additionally, implementing a just-in-time inventory system can minimize storage costs and reduce waste associated with excess inventory.
Transportation and logistics optimization is another critical factor in cost reduction. Utilizing advanced route planning software and consolidating shipments can minimize transportation expenses. Implementing cross-docking techniques and optimizing warehouse layouts can further enhance efficiency and reduce handling costs.
Embracing digital technologies and automation throughout the supply chain can yield significant benefits. Implementing an integrated Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system can improve visibility across the entire supply chain, enabling better decision-making and resource allocation. Automated inventory management systems can reduce labor costs and minimize errors in stock control.
Collaboration with suppliers and customers is essential for effective supply chain optimization. Sharing demand forecasts and production schedules with suppliers can help them better plan their operations, potentially leading to cost reductions that can be passed on to the cellophane manufacturer. Similarly, working closely with customers to understand their needs and preferences can help optimize production schedules and reduce waste.
Continuous improvement initiatives, such as Six Sigma or Lean Manufacturing principles, can be applied to the supply chain to identify and eliminate inefficiencies. Regular audits and performance assessments can help identify areas for improvement and drive ongoing cost reduction efforts.
Sustainability considerations in supply chain optimization can also contribute to cost reduction. Implementing energy-efficient technologies and processes, reducing packaging waste, and optimizing transportation routes to minimize fuel consumption can lead to both environmental benefits and cost savings.
By focusing on these key areas of supply chain optimization, cellophane manufacturers can achieve significant reductions in production costs, improving their competitiveness in the market and enhancing overall profitability.
One key aspect of supply chain optimization is strategic sourcing of raw materials. Establishing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers and negotiating bulk purchase agreements can lead to substantial cost savings. Additionally, implementing a just-in-time inventory system can minimize storage costs and reduce waste associated with excess inventory.
Transportation and logistics optimization is another critical factor in cost reduction. Utilizing advanced route planning software and consolidating shipments can minimize transportation expenses. Implementing cross-docking techniques and optimizing warehouse layouts can further enhance efficiency and reduce handling costs.
Embracing digital technologies and automation throughout the supply chain can yield significant benefits. Implementing an integrated Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system can improve visibility across the entire supply chain, enabling better decision-making and resource allocation. Automated inventory management systems can reduce labor costs and minimize errors in stock control.
Collaboration with suppliers and customers is essential for effective supply chain optimization. Sharing demand forecasts and production schedules with suppliers can help them better plan their operations, potentially leading to cost reductions that can be passed on to the cellophane manufacturer. Similarly, working closely with customers to understand their needs and preferences can help optimize production schedules and reduce waste.
Continuous improvement initiatives, such as Six Sigma or Lean Manufacturing principles, can be applied to the supply chain to identify and eliminate inefficiencies. Regular audits and performance assessments can help identify areas for improvement and drive ongoing cost reduction efforts.
Sustainability considerations in supply chain optimization can also contribute to cost reduction. Implementing energy-efficient technologies and processes, reducing packaging waste, and optimizing transportation routes to minimize fuel consumption can lead to both environmental benefits and cost savings.
By focusing on these key areas of supply chain optimization, cellophane manufacturers can achieve significant reductions in production costs, improving their competitiveness in the market and enhancing overall profitability.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!