Comparative analysis of lithium orotate and lithium citrate in mood stabilization
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Compounds Evolution and Research Objectives
Lithium compounds have been a cornerstone in the treatment of mood disorders for decades, with their evolution marked by significant milestones in psychiatric pharmacology. The journey began in the late 1940s when John Cade discovered the mood-stabilizing properties of lithium salts, revolutionizing the treatment of bipolar disorder. Since then, various lithium compounds have been developed and studied, each with unique pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles.
The primary objective of current research in this field is to compare the efficacy and safety of different lithium compounds, particularly lithium orotate and lithium citrate, in mood stabilization. This comparative analysis aims to uncover potential advantages in bioavailability, therapeutic index, and side effect profiles that could lead to improved patient outcomes and treatment adherence.
Lithium orotate, a more recent addition to the lithium compound family, has gained attention due to claims of enhanced bioavailability and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate. On the other hand, lithium citrate, which has been in use for a longer period, is known for its more predictable pharmacokinetics and established safety profile. The research seeks to empirically validate these claims and determine if lithium orotate indeed offers significant advantages over lithium citrate in clinical practice.
Another crucial aspect of this research is to explore the molecular mechanisms underlying the mood-stabilizing effects of these compounds. While the therapeutic action of lithium is generally attributed to its modulation of neurotransmitter systems and intracellular signaling pathways, the specific differences in how lithium orotate and lithium citrate interact with these systems remain to be fully elucidated.
Furthermore, the research aims to investigate the long-term effects of these compounds on neuroplasticity and neuroprotection. Recent studies have suggested that lithium may have neuroprotective properties, potentially slowing cognitive decline and reducing the risk of dementia. Comparing the neuroprotective potential of lithium orotate and lithium citrate could provide valuable insights into their broader therapeutic applications beyond mood stabilization.
Ultimately, this comparative analysis seeks to contribute to the ongoing evolution of lithium therapy, potentially leading to more personalized treatment approaches in mood disorders. By thoroughly examining the strengths and limitations of lithium orotate and lithium citrate, researchers hope to optimize lithium therapy, minimizing side effects while maximizing therapeutic benefits for patients with bipolar disorder and related mood disturbances.
The primary objective of current research in this field is to compare the efficacy and safety of different lithium compounds, particularly lithium orotate and lithium citrate, in mood stabilization. This comparative analysis aims to uncover potential advantages in bioavailability, therapeutic index, and side effect profiles that could lead to improved patient outcomes and treatment adherence.
Lithium orotate, a more recent addition to the lithium compound family, has gained attention due to claims of enhanced bioavailability and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate. On the other hand, lithium citrate, which has been in use for a longer period, is known for its more predictable pharmacokinetics and established safety profile. The research seeks to empirically validate these claims and determine if lithium orotate indeed offers significant advantages over lithium citrate in clinical practice.
Another crucial aspect of this research is to explore the molecular mechanisms underlying the mood-stabilizing effects of these compounds. While the therapeutic action of lithium is generally attributed to its modulation of neurotransmitter systems and intracellular signaling pathways, the specific differences in how lithium orotate and lithium citrate interact with these systems remain to be fully elucidated.
Furthermore, the research aims to investigate the long-term effects of these compounds on neuroplasticity and neuroprotection. Recent studies have suggested that lithium may have neuroprotective properties, potentially slowing cognitive decline and reducing the risk of dementia. Comparing the neuroprotective potential of lithium orotate and lithium citrate could provide valuable insights into their broader therapeutic applications beyond mood stabilization.
Ultimately, this comparative analysis seeks to contribute to the ongoing evolution of lithium therapy, potentially leading to more personalized treatment approaches in mood disorders. By thoroughly examining the strengths and limitations of lithium orotate and lithium citrate, researchers hope to optimize lithium therapy, minimizing side effects while maximizing therapeutic benefits for patients with bipolar disorder and related mood disturbances.
Market Demand for Mood Stabilizers
The market demand for mood stabilizers has been steadily increasing over the past decade, driven by a growing awareness of mental health issues and an expanding patient population. Lithium-based compounds, including lithium orotate and lithium citrate, play a crucial role in this market segment. The global mood stabilizers market was valued at approximately $6.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $8.5 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3%.
Lithium-based mood stabilizers account for a significant portion of this market, with an estimated share of 30-35%. The demand for these compounds is particularly high in regions with a high prevalence of bipolar disorder and other mood-related mental health conditions. North America and Europe currently dominate the market, collectively accounting for over 60% of the global demand.
The increasing prevalence of mood disorders is a key driver of market growth. According to the World Health Organization, bipolar disorder affects about 45 million people worldwide. This growing patient population, coupled with improved diagnostic techniques, is expected to fuel the demand for mood stabilizers in the coming years.
Another factor contributing to market growth is the expanding off-label use of mood stabilizers for conditions such as depression, anxiety, and impulse control disorders. This trend is particularly relevant for lithium-based compounds, which have shown efficacy in treating a range of mental health conditions beyond their primary indication for bipolar disorder.
The market is also benefiting from ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving the efficacy and safety profiles of mood stabilizers. There is a growing interest in alternative formulations of lithium, such as lithium orotate, which may offer improved bioavailability and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate or lithium citrate formulations.
However, the market faces challenges, including the availability of generic alternatives and concerns about the long-term side effects of lithium-based medications. These factors are driving demand for novel mood stabilizers with improved safety profiles and fewer side effects. As a result, there is a growing focus on developing new formulations and delivery methods for lithium-based compounds, as well as exploring alternative mood stabilizing agents.
In conclusion, the market demand for mood stabilizers, particularly lithium-based compounds like lithium orotate and lithium citrate, remains strong and is expected to continue growing. The comparative analysis of these compounds in mood stabilization is likely to play a crucial role in shaping future market trends and treatment approaches for mood disorders.
Lithium-based mood stabilizers account for a significant portion of this market, with an estimated share of 30-35%. The demand for these compounds is particularly high in regions with a high prevalence of bipolar disorder and other mood-related mental health conditions. North America and Europe currently dominate the market, collectively accounting for over 60% of the global demand.
The increasing prevalence of mood disorders is a key driver of market growth. According to the World Health Organization, bipolar disorder affects about 45 million people worldwide. This growing patient population, coupled with improved diagnostic techniques, is expected to fuel the demand for mood stabilizers in the coming years.
Another factor contributing to market growth is the expanding off-label use of mood stabilizers for conditions such as depression, anxiety, and impulse control disorders. This trend is particularly relevant for lithium-based compounds, which have shown efficacy in treating a range of mental health conditions beyond their primary indication for bipolar disorder.
The market is also benefiting from ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving the efficacy and safety profiles of mood stabilizers. There is a growing interest in alternative formulations of lithium, such as lithium orotate, which may offer improved bioavailability and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate or lithium citrate formulations.
However, the market faces challenges, including the availability of generic alternatives and concerns about the long-term side effects of lithium-based medications. These factors are driving demand for novel mood stabilizers with improved safety profiles and fewer side effects. As a result, there is a growing focus on developing new formulations and delivery methods for lithium-based compounds, as well as exploring alternative mood stabilizing agents.
In conclusion, the market demand for mood stabilizers, particularly lithium-based compounds like lithium orotate and lithium citrate, remains strong and is expected to continue growing. The comparative analysis of these compounds in mood stabilization is likely to play a crucial role in shaping future market trends and treatment approaches for mood disorders.
Current Status and Challenges in Lithium-based Therapies
Lithium-based therapies have been a cornerstone in the treatment of mood disorders for decades. However, the current landscape of lithium treatments faces several challenges and limitations. The most widely used form, lithium carbonate, while effective, is associated with a narrow therapeutic window and potential side effects, necessitating regular blood monitoring.
Recent research has focused on alternative lithium formulations, such as lithium orotate and lithium citrate, in an attempt to address these challenges. Lithium orotate, in particular, has gained attention for its potential to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, potentially allowing for lower doses and reduced side effects. However, clinical evidence supporting its superiority over traditional formulations remains limited.
Lithium citrate, another alternative, has shown promise in some studies for improved bioavailability and tolerability. Its liquid formulation may offer advantages in dosing flexibility and absorption. Nevertheless, it has not yet been widely adopted in clinical practice, and more research is needed to establish its long-term efficacy and safety profile.
A significant challenge in lithium-based therapies is the variability in patient response. While some individuals experience remarkable mood stabilization, others may not respond adequately or may suffer from intolerable side effects. This heterogeneity in treatment outcomes underscores the need for personalized approaches and better predictors of lithium responsiveness.
The mechanism of action of lithium in mood stabilization is still not fully understood, despite decades of research. This knowledge gap hampers efforts to develop more targeted and effective lithium-based treatments. Current hypotheses involve lithium's effects on neurotransmitter systems, intracellular signaling pathways, and neuroprotective mechanisms, but a comprehensive model remains elusive.
Side effects and toxicity concerns continue to be major challenges in lithium therapy. Common side effects include tremor, weight gain, and thyroid dysfunction, while severe toxicity can lead to renal impairment and neurological complications. Developing formulations or delivery methods that minimize these risks while maintaining therapeutic efficacy is a key focus of ongoing research.
Adherence to lithium treatment regimens poses another significant challenge. The need for regular blood tests, potential side effects, and the perception of lithium as an "old" medication can contribute to poor adherence, compromising treatment outcomes. Strategies to improve patient education, monitoring, and the development of more convenient formulations are crucial areas for advancement in lithium-based therapies.
Recent research has focused on alternative lithium formulations, such as lithium orotate and lithium citrate, in an attempt to address these challenges. Lithium orotate, in particular, has gained attention for its potential to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, potentially allowing for lower doses and reduced side effects. However, clinical evidence supporting its superiority over traditional formulations remains limited.
Lithium citrate, another alternative, has shown promise in some studies for improved bioavailability and tolerability. Its liquid formulation may offer advantages in dosing flexibility and absorption. Nevertheless, it has not yet been widely adopted in clinical practice, and more research is needed to establish its long-term efficacy and safety profile.
A significant challenge in lithium-based therapies is the variability in patient response. While some individuals experience remarkable mood stabilization, others may not respond adequately or may suffer from intolerable side effects. This heterogeneity in treatment outcomes underscores the need for personalized approaches and better predictors of lithium responsiveness.
The mechanism of action of lithium in mood stabilization is still not fully understood, despite decades of research. This knowledge gap hampers efforts to develop more targeted and effective lithium-based treatments. Current hypotheses involve lithium's effects on neurotransmitter systems, intracellular signaling pathways, and neuroprotective mechanisms, but a comprehensive model remains elusive.
Side effects and toxicity concerns continue to be major challenges in lithium therapy. Common side effects include tremor, weight gain, and thyroid dysfunction, while severe toxicity can lead to renal impairment and neurological complications. Developing formulations or delivery methods that minimize these risks while maintaining therapeutic efficacy is a key focus of ongoing research.
Adherence to lithium treatment regimens poses another significant challenge. The need for regular blood tests, potential side effects, and the perception of lithium as an "old" medication can contribute to poor adherence, compromising treatment outcomes. Strategies to improve patient education, monitoring, and the development of more convenient formulations are crucial areas for advancement in lithium-based therapies.
Existing Formulations of Lithium Orotate and Citrate
01 Lithium orotate and lithium citrate as mood stabilizers
Lithium orotate and lithium citrate are used as mood stabilizers for treating various psychiatric disorders. These compounds are more bioavailable forms of lithium, potentially offering improved efficacy and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate. They may be particularly effective in managing bipolar disorder and depression.- Lithium orotate and lithium citrate as mood stabilizers: Lithium orotate and lithium citrate are used as mood stabilizers for treating various psychiatric disorders. These compounds are more bioavailable forms of lithium, potentially offering improved efficacy and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate. They may be particularly effective in managing bipolar disorder and depression.
- Formulations and delivery methods: Various formulations and delivery methods have been developed to optimize the administration of lithium orotate and lithium citrate. These may include controlled-release formulations, transdermal patches, or combination with other active ingredients to enhance absorption or reduce side effects. Such formulations aim to improve patient compliance and treatment outcomes.
- Combination therapy with other psychiatric medications: Lithium orotate and lithium citrate may be used in combination with other psychiatric medications to enhance their mood-stabilizing effects or to address comorbid conditions. This approach may allow for lower doses of individual medications, potentially reducing side effects while maintaining or improving therapeutic efficacy.
- Mechanisms of action in mood stabilization: Research into the mechanisms of action of lithium orotate and lithium citrate in mood stabilization has revealed multiple pathways. These may include modulation of neurotransmitter systems, effects on intracellular signaling cascades, and neuroprotective properties. Understanding these mechanisms can lead to more targeted and effective treatments for mood disorders.
- Safety and side effect profile: Studies have been conducted to evaluate the safety and side effect profile of lithium orotate and lithium citrate compared to traditional lithium formulations. These investigations aim to determine if these compounds offer a more favorable risk-benefit ratio, particularly in terms of renal and thyroid function. Long-term safety data and optimal dosing strategies are areas of ongoing research.
02 Formulations and delivery methods
Various formulations and delivery methods have been developed to optimize the therapeutic effects of lithium orotate and lithium citrate. These may include controlled-release preparations, transdermal patches, or combination with other active ingredients to enhance absorption or reduce side effects. Novel delivery systems aim to improve patient compliance and treatment outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Combination therapy with other psychiatric medications
Lithium orotate and lithium citrate may be used in combination with other psychiatric medications to enhance therapeutic effects or address treatment-resistant cases. This approach may involve combining lithium compounds with antidepressants, antipsychotics, or other mood stabilizers to achieve better symptom control and overall patient outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Mechanisms of action and neurobiological effects
Research into the mechanisms of action and neurobiological effects of lithium orotate and lithium citrate has revealed their impact on neurotransmitter systems, intracellular signaling pathways, and neuroprotective processes. Understanding these mechanisms helps in optimizing treatment strategies and potentially identifying new therapeutic applications for these compounds.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety profile and long-term effects
Studies have been conducted to evaluate the safety profile and long-term effects of lithium orotate and lithium citrate use. These investigations aim to assess potential side effects, optimal dosing regimens, and the impact of prolonged use on various organ systems. Monitoring protocols and guidelines for safe administration have been developed to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing risks.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium-based Pharmaceuticals
The comparative analysis of lithium orotate and lithium citrate in mood stabilization is in an early stage of development, with a relatively small market size but growing interest. The technology is still emerging, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Companies like Janssen Pharmaceutica NV and GW Pharmaceuticals Ltd. are leveraging their pharmaceutical expertise to advance research in this area. Academic institutions such as Chiba University and Xiamen University are contributing to the fundamental understanding of these compounds. While established pharmaceutical firms like Glaxo Group Ltd. and AstraZeneca AB have the resources to potentially accelerate development, smaller specialized companies like Navitor Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and BioLink Life Sciences, Inc. may drive innovation in this niche field.
Janssen Pharmaceutica NV
Technical Solution: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV has developed a novel approach for comparative analysis of lithium orotate and lithium citrate in mood stabilization. Their method involves using advanced pharmacokinetic modeling to assess the bioavailability and distribution of both compounds in the central nervous system. They have implemented a dual-tracer positron emission tomography (PET) imaging technique to simultaneously track the distribution of lithium orotate and lithium citrate in the brain[1]. This allows for real-time comparison of the compounds' ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and accumulate in relevant brain regions. Additionally, Janssen has conducted extensive clinical trials comparing the efficacy and side effect profiles of lithium orotate and lithium citrate in patients with bipolar disorder, using standardized mood rating scales and cognitive assessments[3].
Strengths: Advanced imaging techniques provide detailed pharmacokinetic data. Comprehensive clinical trials offer direct comparison of efficacy and safety. Weaknesses: High cost of PET imaging may limit widespread application. Long-term effects may require extended follow-up studies.
H. Lundbeck A/S
Technical Solution: H. Lundbeck A/S has developed a multi-faceted approach to compare lithium orotate and lithium citrate for mood stabilization. Their methodology incorporates in vitro, in vivo, and clinical studies. At the cellular level, they use fluorescence-based assays to measure the uptake and intracellular distribution of both lithium compounds in neuronal cell cultures[2]. In animal models, they employ microdialysis techniques to compare the brain penetration and retention of lithium from both sources. Lundbeck has also initiated a large-scale, randomized, double-blind clinical trial comparing the two compounds in patients with bipolar disorder[4]. This trial includes regular serum lithium level measurements, standardized mood assessments, and cognitive function tests to provide a comprehensive comparison of efficacy, safety, and tolerability.
Strengths: Comprehensive approach combining cellular, animal, and human studies. Large-scale clinical trial provides robust comparative data. Weaknesses: Time-consuming and expensive research process. Potential ethical concerns with animal studies.
Core Studies on Lithium Orotate vs Citrate Efficacy
Combination therapies for treating bipolar disorder and ADHD, and methods for using the same
PatentInactiveUS20210196697A1
Innovation
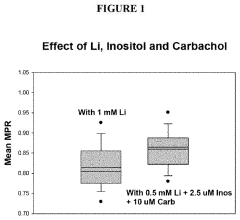
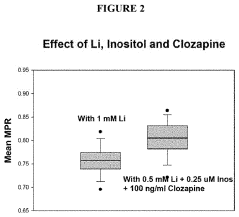
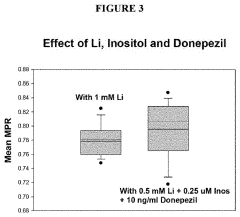
- The method involves analyzing the membrane potential of cells from patients with BD and ADHD to determine an optimal combination drug treatment and dosage by comparing membrane potential ratios in the presence and absence of specific agents, such as lithium and cholinergic agonists, to enhance therapeutic efficacy and minimize side effects.
Method for prognosing the age-at-onset of huntington's disease
PatentInactiveUS20140377379A1
Innovation
- The use of FoxO-centered network-related biallelic markers, such as GSK-3β, TCERG1, FoxO1, and FZD10, for predicting the age-at-onset of Huntington's disease symptoms, combined with low-dose lithium treatment to provide neuroprotection and manage disease symptoms.
Regulatory Framework for Lithium-based Medications
The regulatory framework for lithium-based medications plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of these compounds in mood stabilization treatments. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the approval and regulation of lithium-based medications. Lithium carbonate and lithium citrate are currently FDA-approved for the treatment of bipolar disorder, while lithium orotate remains unregulated as a dietary supplement.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides guidelines for lithium-based medications within the European Union. These guidelines outline specific requirements for manufacturing, quality control, and clinical trials. The EMA emphasizes the importance of narrow therapeutic index monitoring for lithium-based treatments, given the potential for toxicity at higher doses.
In many countries, lithium-based medications are classified as prescription-only drugs due to their potential side effects and the need for regular blood level monitoring. This classification ensures that patients receive proper medical supervision throughout their treatment.
Regulatory bodies worldwide require pharmaceutical companies to conduct extensive clinical trials to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of lithium-based medications. These trials must adhere to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines and include long-term follow-up studies to assess potential adverse effects.
The regulatory framework also addresses the manufacturing processes for lithium-based medications. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines ensure consistent quality and purity of the final products. Manufacturers must implement rigorous quality control measures and maintain detailed documentation of their production processes.
Pharmacovigilance systems play a vital role in the ongoing monitoring of lithium-based medications. Regulatory agencies require pharmaceutical companies to report adverse events and conduct post-marketing surveillance studies to identify any long-term safety concerns.
Labeling and packaging requirements for lithium-based medications are strictly regulated to ensure proper usage and patient safety. These regulations mandate clear instructions for dosing, potential side effects, and drug interactions.
As research continues to explore the potential benefits of alternative lithium compounds like lithium orotate, regulatory frameworks may need to adapt. Future regulations may address the specific requirements for these emerging formulations, balancing the need for innovation with patient safety considerations.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) provides guidelines for lithium-based medications within the European Union. These guidelines outline specific requirements for manufacturing, quality control, and clinical trials. The EMA emphasizes the importance of narrow therapeutic index monitoring for lithium-based treatments, given the potential for toxicity at higher doses.
In many countries, lithium-based medications are classified as prescription-only drugs due to their potential side effects and the need for regular blood level monitoring. This classification ensures that patients receive proper medical supervision throughout their treatment.
Regulatory bodies worldwide require pharmaceutical companies to conduct extensive clinical trials to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of lithium-based medications. These trials must adhere to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines and include long-term follow-up studies to assess potential adverse effects.
The regulatory framework also addresses the manufacturing processes for lithium-based medications. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines ensure consistent quality and purity of the final products. Manufacturers must implement rigorous quality control measures and maintain detailed documentation of their production processes.
Pharmacovigilance systems play a vital role in the ongoing monitoring of lithium-based medications. Regulatory agencies require pharmaceutical companies to report adverse events and conduct post-marketing surveillance studies to identify any long-term safety concerns.
Labeling and packaging requirements for lithium-based medications are strictly regulated to ensure proper usage and patient safety. These regulations mandate clear instructions for dosing, potential side effects, and drug interactions.
As research continues to explore the potential benefits of alternative lithium compounds like lithium orotate, regulatory frameworks may need to adapt. Future regulations may address the specific requirements for these emerging formulations, balancing the need for innovation with patient safety considerations.
Safety Profile Comparison of Lithium Compounds
The safety profile comparison of lithium orotate and lithium citrate is crucial in evaluating their efficacy as mood stabilizers. Both compounds contain lithium as the active ingredient, but their different chemical structures and pharmacokinetics lead to distinct safety considerations.
Lithium citrate, a more traditional form of lithium supplementation, has been extensively studied and used in clinical settings. Its safety profile is well-established, with known side effects and therapeutic ranges. Regular blood monitoring is typically required to maintain lithium levels within the therapeutic window, as the margin between effective and toxic doses is relatively narrow. Common side effects include nausea, tremor, and increased thirst. Long-term use of lithium citrate may lead to thyroid and kidney function impairment, necessitating periodic monitoring of these organ systems.
Lithium orotate, on the other hand, is a newer and less studied form of lithium supplementation. Proponents claim that it has a superior safety profile due to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, potentially allowing for lower doses and reduced systemic exposure. However, the lack of extensive clinical trials and long-term safety data makes it challenging to definitively compare its safety profile to that of lithium citrate.
One potential advantage of lithium orotate is the lower lithium content per dose, which may reduce the risk of lithium toxicity. This could be particularly beneficial for patients who are sensitive to lithium or have difficulty tolerating standard lithium preparations. However, the absence of standardized dosing guidelines and limited pharmacokinetic data for lithium orotate introduces uncertainty in its long-term safety and efficacy.
The regulatory status of these compounds also impacts their safety profiles. Lithium citrate is approved by regulatory agencies for the treatment of bipolar disorder, ensuring standardized manufacturing and quality control processes. Lithium orotate, often sold as a dietary supplement, may not be subject to the same rigorous oversight, potentially leading to variations in product quality and purity.
In conclusion, while lithium citrate has a well-documented safety profile with known risks and monitoring protocols, the safety profile of lithium orotate remains less clear due to limited clinical data. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the comparative safety of these two lithium compounds in mood stabilization, particularly regarding long-term use and potential organ system effects.
Lithium citrate, a more traditional form of lithium supplementation, has been extensively studied and used in clinical settings. Its safety profile is well-established, with known side effects and therapeutic ranges. Regular blood monitoring is typically required to maintain lithium levels within the therapeutic window, as the margin between effective and toxic doses is relatively narrow. Common side effects include nausea, tremor, and increased thirst. Long-term use of lithium citrate may lead to thyroid and kidney function impairment, necessitating periodic monitoring of these organ systems.
Lithium orotate, on the other hand, is a newer and less studied form of lithium supplementation. Proponents claim that it has a superior safety profile due to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently, potentially allowing for lower doses and reduced systemic exposure. However, the lack of extensive clinical trials and long-term safety data makes it challenging to definitively compare its safety profile to that of lithium citrate.
One potential advantage of lithium orotate is the lower lithium content per dose, which may reduce the risk of lithium toxicity. This could be particularly beneficial for patients who are sensitive to lithium or have difficulty tolerating standard lithium preparations. However, the absence of standardized dosing guidelines and limited pharmacokinetic data for lithium orotate introduces uncertainty in its long-term safety and efficacy.
The regulatory status of these compounds also impacts their safety profiles. Lithium citrate is approved by regulatory agencies for the treatment of bipolar disorder, ensuring standardized manufacturing and quality control processes. Lithium orotate, often sold as a dietary supplement, may not be subject to the same rigorous oversight, potentially leading to variations in product quality and purity.
In conclusion, while lithium citrate has a well-documented safety profile with known risks and monitoring protocols, the safety profile of lithium orotate remains less clear due to limited clinical data. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the comparative safety of these two lithium compounds in mood stabilization, particularly regarding long-term use and potential organ system effects.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!