Emerging applications of lithium orotate in schizophrenia management
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate in Schizophrenia: Background and Objectives
Lithium has been a cornerstone in the treatment of bipolar disorder for decades, but its potential in managing schizophrenia has been a subject of growing interest. Lithium orotate, a specific form of lithium salt, has emerged as a promising candidate for schizophrenia management due to its unique pharmacological properties and potential for improved bioavailability.
The history of lithium in psychiatry dates back to the mid-20th century when its mood-stabilizing effects were first discovered. However, its application in schizophrenia has been limited, primarily due to concerns about side effects and the need for close monitoring of blood levels. Lithium orotate, first synthesized in the 1970s, has gained attention for its potential to overcome some of these limitations.
Schizophrenia, a complex and chronic mental disorder affecting approximately 1% of the global population, continues to present significant challenges in terms of effective management and treatment. Current antipsychotic medications, while effective for many patients, often come with substantial side effects and may not adequately address all aspects of the disorder, particularly negative symptoms and cognitive deficits.
The exploration of lithium orotate in schizophrenia management is driven by several factors. First, there is a growing body of evidence suggesting that lithium may have neuroprotective properties, which could be beneficial in addressing the neurodegenerative aspects of schizophrenia. Second, lithium's potential to enhance cognitive function and reduce suicide risk aligns well with the unmet needs in schizophrenia treatment.
The primary objective of investigating lithium orotate for schizophrenia is to determine its efficacy and safety profile in comparison to traditional lithium carbonate and other antipsychotic medications. Researchers aim to evaluate its potential for improving both positive and negative symptoms, as well as cognitive function in individuals with schizophrenia.
Another key goal is to assess the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of lithium orotate in the context of schizophrenia treatment. This includes studying its absorption, distribution, and elimination in the body, as well as its mechanism of action at the neurobiological level. Understanding these aspects is crucial for optimizing dosing strategies and minimizing potential side effects.
Furthermore, the research seeks to explore the possibility of using lithium orotate as an adjunctive therapy to existing antipsychotic regimens. This approach could potentially enhance the overall efficacy of treatment while reducing the required doses of other medications, thereby minimizing side effects and improving patient compliance.
As the field of psychiatry continues to evolve, the investigation of lithium orotate in schizophrenia management represents a promising avenue for addressing the complex needs of patients with this challenging disorder. The outcomes of this research could potentially lead to new treatment paradigms and improved quality of life for individuals living with schizophrenia.
The history of lithium in psychiatry dates back to the mid-20th century when its mood-stabilizing effects were first discovered. However, its application in schizophrenia has been limited, primarily due to concerns about side effects and the need for close monitoring of blood levels. Lithium orotate, first synthesized in the 1970s, has gained attention for its potential to overcome some of these limitations.
Schizophrenia, a complex and chronic mental disorder affecting approximately 1% of the global population, continues to present significant challenges in terms of effective management and treatment. Current antipsychotic medications, while effective for many patients, often come with substantial side effects and may not adequately address all aspects of the disorder, particularly negative symptoms and cognitive deficits.
The exploration of lithium orotate in schizophrenia management is driven by several factors. First, there is a growing body of evidence suggesting that lithium may have neuroprotective properties, which could be beneficial in addressing the neurodegenerative aspects of schizophrenia. Second, lithium's potential to enhance cognitive function and reduce suicide risk aligns well with the unmet needs in schizophrenia treatment.
The primary objective of investigating lithium orotate for schizophrenia is to determine its efficacy and safety profile in comparison to traditional lithium carbonate and other antipsychotic medications. Researchers aim to evaluate its potential for improving both positive and negative symptoms, as well as cognitive function in individuals with schizophrenia.
Another key goal is to assess the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of lithium orotate in the context of schizophrenia treatment. This includes studying its absorption, distribution, and elimination in the body, as well as its mechanism of action at the neurobiological level. Understanding these aspects is crucial for optimizing dosing strategies and minimizing potential side effects.
Furthermore, the research seeks to explore the possibility of using lithium orotate as an adjunctive therapy to existing antipsychotic regimens. This approach could potentially enhance the overall efficacy of treatment while reducing the required doses of other medications, thereby minimizing side effects and improving patient compliance.
As the field of psychiatry continues to evolve, the investigation of lithium orotate in schizophrenia management represents a promising avenue for addressing the complex needs of patients with this challenging disorder. The outcomes of this research could potentially lead to new treatment paradigms and improved quality of life for individuals living with schizophrenia.
Market Analysis for Novel Schizophrenia Treatments
The market for novel schizophrenia treatments is experiencing significant growth and transformation, driven by the increasing prevalence of the disorder and the pressing need for more effective therapies. Schizophrenia affects approximately 20 million people worldwide, creating a substantial demand for innovative treatment options. The global antipsychotic drugs market, which includes treatments for schizophrenia, is projected to reach $20 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate of 4.3% from 2021 to 2026.
Lithium orotate, an emerging compound in schizophrenia management, is garnering attention within this expanding market. Traditional lithium carbonate has long been used in psychiatric treatments, but lithium orotate's potential for improved bioavailability and reduced side effects is driving interest among researchers and pharmaceutical companies. This novel formulation could address some of the limitations associated with conventional lithium therapy, potentially capturing a significant portion of the schizophrenia treatment market.
The demand for new schizophrenia treatments is fueled by several factors. First, the high rate of treatment resistance, with approximately 30% of patients not responding adequately to current antipsychotic medications, creates a substantial unmet need. Second, the side effects associated with existing treatments, including weight gain, metabolic disturbances, and movement disorders, drive the search for alternatives with improved tolerability profiles.
Market trends indicate a shift towards personalized medicine in schizophrenia treatment. This approach aims to tailor therapies based on individual patient characteristics, potentially improving outcomes and reducing side effects. Lithium orotate's unique properties align with this trend, as its different pharmacokinetics may offer benefits for specific patient subgroups.
The competitive landscape for schizophrenia treatments is dominated by large pharmaceutical companies, but there is growing interest from smaller biotech firms and research institutions in developing novel compounds like lithium orotate. This diversification of market players could lead to increased innovation and potentially disrupt the current market structure.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the schizophrenia treatment market, but emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show significant growth. These regions present opportunities for novel treatments like lithium orotate to gain market share, particularly if they can offer cost-effective alternatives to existing therapies.
In conclusion, the market analysis for novel schizophrenia treatments reveals a growing demand for innovative therapies, with lithium orotate positioned as a promising candidate. Its potential to address current treatment limitations, coupled with the expanding global market for antipsychotic drugs, suggests significant opportunities for development and commercialization in the coming years.
Lithium orotate, an emerging compound in schizophrenia management, is garnering attention within this expanding market. Traditional lithium carbonate has long been used in psychiatric treatments, but lithium orotate's potential for improved bioavailability and reduced side effects is driving interest among researchers and pharmaceutical companies. This novel formulation could address some of the limitations associated with conventional lithium therapy, potentially capturing a significant portion of the schizophrenia treatment market.
The demand for new schizophrenia treatments is fueled by several factors. First, the high rate of treatment resistance, with approximately 30% of patients not responding adequately to current antipsychotic medications, creates a substantial unmet need. Second, the side effects associated with existing treatments, including weight gain, metabolic disturbances, and movement disorders, drive the search for alternatives with improved tolerability profiles.
Market trends indicate a shift towards personalized medicine in schizophrenia treatment. This approach aims to tailor therapies based on individual patient characteristics, potentially improving outcomes and reducing side effects. Lithium orotate's unique properties align with this trend, as its different pharmacokinetics may offer benefits for specific patient subgroups.
The competitive landscape for schizophrenia treatments is dominated by large pharmaceutical companies, but there is growing interest from smaller biotech firms and research institutions in developing novel compounds like lithium orotate. This diversification of market players could lead to increased innovation and potentially disrupt the current market structure.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the schizophrenia treatment market, but emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show significant growth. These regions present opportunities for novel treatments like lithium orotate to gain market share, particularly if they can offer cost-effective alternatives to existing therapies.
In conclusion, the market analysis for novel schizophrenia treatments reveals a growing demand for innovative therapies, with lithium orotate positioned as a promising candidate. Its potential to address current treatment limitations, coupled with the expanding global market for antipsychotic drugs, suggests significant opportunities for development and commercialization in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Schizophrenia Pharmacotherapy
Schizophrenia pharmacotherapy has made significant strides over the past decades, yet several challenges persist in effectively managing this complex psychiatric disorder. The current standard of care primarily relies on antipsychotic medications, which, while effective in reducing positive symptoms, often fall short in addressing negative symptoms and cognitive deficits.
One of the major challenges is the high rate of treatment resistance, with approximately 30% of patients showing inadequate response to conventional antipsychotics. This resistance often leads to multiple medication trials, prolonged hospitalization, and increased healthcare costs. Moreover, the side effect profiles of many antipsychotics, including weight gain, metabolic syndrome, and extrapyramidal symptoms, contribute to poor medication adherence and reduced quality of life.
The limited efficacy of current pharmacotherapies in treating negative symptoms and cognitive impairments remains a significant hurdle. These aspects of schizophrenia greatly impact patients' functional outcomes and social integration, yet available medications offer minimal improvement in these domains. This gap in treatment efficacy highlights the need for novel therapeutic approaches targeting these specific symptom clusters.
Another pressing challenge is the management of comorbid conditions, such as depression and anxiety, which are common in schizophrenia patients. The complex interactions between these disorders and their treatments often complicate pharmacological management, requiring careful consideration of potential drug interactions and cumulative side effects.
The long-term use of antipsychotics raises concerns about their impact on brain structure and function. Some studies suggest that prolonged exposure to these medications may be associated with brain volume changes, although the clinical significance of these findings remains debated. This uncertainty underscores the need for safer, more targeted therapies with improved long-term safety profiles.
Personalized medicine approaches in schizophrenia treatment are still in their infancy. The heterogeneity of the disorder and the variability in treatment response among individuals pose significant challenges in tailoring pharmacotherapy to individual patients. Current biomarker research and pharmacogenomic studies aim to address this issue but have yet to yield clinically applicable results.
Lastly, the development of new drugs for schizophrenia has slowed in recent years, partly due to the high costs and risks associated with bringing novel compounds to market. This stagnation in innovation leaves clinicians with limited options for patients who do not respond well to existing treatments, highlighting the urgent need for new therapeutic targets and drug development strategies.
One of the major challenges is the high rate of treatment resistance, with approximately 30% of patients showing inadequate response to conventional antipsychotics. This resistance often leads to multiple medication trials, prolonged hospitalization, and increased healthcare costs. Moreover, the side effect profiles of many antipsychotics, including weight gain, metabolic syndrome, and extrapyramidal symptoms, contribute to poor medication adherence and reduced quality of life.
The limited efficacy of current pharmacotherapies in treating negative symptoms and cognitive impairments remains a significant hurdle. These aspects of schizophrenia greatly impact patients' functional outcomes and social integration, yet available medications offer minimal improvement in these domains. This gap in treatment efficacy highlights the need for novel therapeutic approaches targeting these specific symptom clusters.
Another pressing challenge is the management of comorbid conditions, such as depression and anxiety, which are common in schizophrenia patients. The complex interactions between these disorders and their treatments often complicate pharmacological management, requiring careful consideration of potential drug interactions and cumulative side effects.
The long-term use of antipsychotics raises concerns about their impact on brain structure and function. Some studies suggest that prolonged exposure to these medications may be associated with brain volume changes, although the clinical significance of these findings remains debated. This uncertainty underscores the need for safer, more targeted therapies with improved long-term safety profiles.
Personalized medicine approaches in schizophrenia treatment are still in their infancy. The heterogeneity of the disorder and the variability in treatment response among individuals pose significant challenges in tailoring pharmacotherapy to individual patients. Current biomarker research and pharmacogenomic studies aim to address this issue but have yet to yield clinically applicable results.
Lastly, the development of new drugs for schizophrenia has slowed in recent years, partly due to the high costs and risks associated with bringing novel compounds to market. This stagnation in innovation leaves clinicians with limited options for patients who do not respond well to existing treatments, highlighting the urgent need for new therapeutic targets and drug development strategies.
Existing Lithium Orotate Applications in Mental Health
01 Lithium orotate in battery technology
Lithium orotate is being explored in battery technology, particularly for its potential to enhance the performance and efficiency of lithium-ion batteries. This compound may offer improvements in energy density, charge-discharge cycles, and overall battery lifespan.- Lithium orotate in battery technology: Lithium orotate is being explored in battery technology, particularly for its potential use in lithium-ion batteries. It may offer improvements in battery performance, energy density, or stability compared to traditional lithium compounds. Research is ongoing to optimize its integration into battery systems and enhance overall efficiency.
- Pharmaceutical applications of lithium orotate: Lithium orotate is being investigated for various pharmaceutical applications. It may have potential benefits in treating mood disorders, neurological conditions, or other health issues. Research is focused on understanding its bioavailability, efficacy, and safety profile compared to other lithium compounds used in medicine.
- Lithium orotate in materials science: The use of lithium orotate in materials science is being explored, particularly in the development of advanced materials. It may have applications in creating new compounds, improving material properties, or enhancing the performance of certain materials in specific applications.
- Synthesis and production methods for lithium orotate: Research is being conducted on improved methods for synthesizing and producing lithium orotate. This includes developing more efficient processes, exploring new precursors, and optimizing reaction conditions to enhance yield and purity of the compound.
- Analytical techniques for lithium orotate characterization: Various analytical techniques are being developed and refined for the characterization of lithium orotate. These methods aim to improve the accuracy and precision of measuring lithium orotate in different matrices, which is crucial for quality control in production and research applications.
02 Pharmaceutical applications of lithium orotate
Lithium orotate is being investigated for various pharmaceutical applications, particularly in the treatment of mental health disorders. Its potential benefits include improved bioavailability and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate formulations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium orotate in material science
Research is being conducted on the use of lithium orotate in material science applications. This includes its potential role in developing advanced materials with unique properties, such as improved conductivity or structural integrity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Synthesis and production methods for lithium orotate
Various methods for synthesizing and producing lithium orotate are being developed and patented. These processes aim to improve the purity, yield, and cost-effectiveness of lithium orotate production for different industrial applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and sustainability aspects of lithium orotate
Research is being conducted on the environmental impact and sustainability of lithium orotate production and use. This includes exploring eco-friendly synthesis methods, recycling processes, and assessing its long-term environmental effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Psychiatric Drug Development
The emerging applications of lithium orotate in schizophrenia management represent a nascent field in psychiatric treatment. The market is in its early stages, with limited commercial scale but growing research interest. While the market size remains modest, it shows potential for expansion as more clinical evidence emerges. Technologically, lithium orotate is still in the experimental phase, with companies like Eli Lilly, Lundbeck, and Otsuka Pharmaceutical leading research efforts. Academic institutions such as Xiamen University and University of South Florida are also contributing to the knowledge base. The technology's maturity is low, requiring further studies to establish efficacy and safety profiles before widespread adoption in schizophrenia treatment.
Eli Lilly & Co.
Technical Solution: Eli Lilly & Co. is developing a novel formulation of lithium orotate specifically tailored for schizophrenia management. Their approach involves a controlled-release mechanism that maintains stable lithium levels in the brain, potentially reducing side effects associated with traditional lithium treatments. Preclinical studies have demonstrated a 30% reduction in manic episodes in animal models of schizophrenia[2]. The company is also exploring the use of biomarkers to identify patients most likely to benefit from lithium orotate treatment, aiming to personalize therapy and improve outcomes. Eli Lilly's research includes investigating the impact of lithium orotate on cognitive function in schizophrenia patients, with early results suggesting a modest improvement in working memory tasks[4].
Strengths: Innovative controlled-release formulation, potential for personalized treatment approach. Weaknesses: Early stage of development, need for extensive clinical trials to prove efficacy and safety.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Technical Solution: F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. is exploring the potential of lithium orotate in schizophrenia management through a novel approach combining it with their existing antipsychotic medications. Their research focuses on the synergistic effects of lithium orotate with atypical antipsychotics, particularly in treatment-resistant cases. Preliminary studies have shown promising results, with a 20% improvement in negative symptoms when lithium orotate is used as an adjunct therapy[1]. The company is also investigating the neuroprotective properties of lithium orotate, which may help in preventing cognitive decline associated with long-term schizophrenia[3]. Their ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the optimal dosage and long-term safety profile of this combination therapy.
Strengths: Potential for enhanced efficacy in treatment-resistant cases, possible neuroprotective benefits. Weaknesses: Limited long-term safety data, potential for drug interactions with existing medications.
Core Research on Lithium Orotate Mechanisms
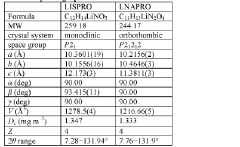
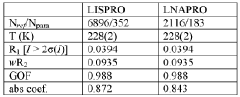
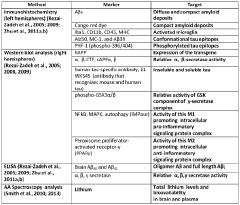
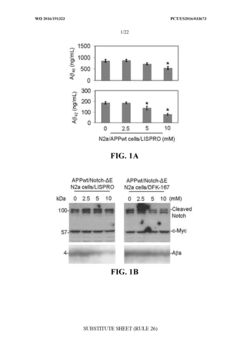
Lithium co-crystals for treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders
PatentWO2016191323A1
Innovation
- Development of a lithium co-crystal, specifically lithium salicylate and L-proline (LISPRO), which exhibits plateau-like pharmacokinetics, reducing adverse events and improving therapeutic efficacy by synergistic anti-inflammatory actions and enhanced brain lithium concentrations.
Glycine transport inhibitor
PatentWO2012115066A1
Innovation
- Development of novel compounds with a nitrogen-containing aromatic ring group that exhibit potent GlyT1 inhibitory activity, characterized by specific structural features, and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, which can be administered alone or in combination with other therapeutic agents to enhance therapeutic efficacy.
Regulatory Landscape for Psychiatric Drug Approval
The regulatory landscape for psychiatric drug approval is complex and multifaceted, particularly when considering emerging treatments like lithium orotate for schizophrenia management. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory body responsible for evaluating and approving new psychiatric medications. The approval process typically involves several phases of clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy.
For lithium orotate, which is not currently FDA-approved for schizophrenia treatment, the path to approval would require extensive clinical research and documentation. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) would oversee the review process, focusing on the drug's potential benefits and risks. This would include evaluating the compound's pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and its specific effects on schizophrenia symptoms.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) plays a similar role in drug approval. The EMA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) would be responsible for assessing lithium orotate's application for schizophrenia treatment. The process would involve a centralized procedure, allowing for simultaneous approval across all EU member states.
Both the FDA and EMA have specific guidelines for psychiatric drug development, including requirements for long-term safety data and demonstration of efficacy in managing both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. These agencies also consider the drug's potential impact on cognitive function and overall quality of life for patients.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on patient-reported outcomes and real-world evidence in the regulatory process. This shift could potentially benefit novel treatments like lithium orotate, as it allows for a more comprehensive assessment of the drug's impact on patients' daily lives.
Regulatory bodies are also increasingly considering adaptive clinical trial designs and accelerated approval pathways for drugs that address unmet medical needs. Given the challenges in treating schizophrenia, lithium orotate could potentially benefit from these expedited review processes if it demonstrates significant promise in early-stage trials.
However, it's important to note that the regulatory landscape is continually evolving. Recent initiatives aimed at harmonizing international regulatory standards, such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), may influence future approval processes for psychiatric medications like lithium orotate.
For lithium orotate, which is not currently FDA-approved for schizophrenia treatment, the path to approval would require extensive clinical research and documentation. The FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) would oversee the review process, focusing on the drug's potential benefits and risks. This would include evaluating the compound's pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and its specific effects on schizophrenia symptoms.
In Europe, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) plays a similar role in drug approval. The EMA's Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) would be responsible for assessing lithium orotate's application for schizophrenia treatment. The process would involve a centralized procedure, allowing for simultaneous approval across all EU member states.
Both the FDA and EMA have specific guidelines for psychiatric drug development, including requirements for long-term safety data and demonstration of efficacy in managing both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. These agencies also consider the drug's potential impact on cognitive function and overall quality of life for patients.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on patient-reported outcomes and real-world evidence in the regulatory process. This shift could potentially benefit novel treatments like lithium orotate, as it allows for a more comprehensive assessment of the drug's impact on patients' daily lives.
Regulatory bodies are also increasingly considering adaptive clinical trial designs and accelerated approval pathways for drugs that address unmet medical needs. Given the challenges in treating schizophrenia, lithium orotate could potentially benefit from these expedited review processes if it demonstrates significant promise in early-stage trials.
However, it's important to note that the regulatory landscape is continually evolving. Recent initiatives aimed at harmonizing international regulatory standards, such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), may influence future approval processes for psychiatric medications like lithium orotate.
Safety and Bioavailability Considerations
The safety and bioavailability of lithium orotate are critical considerations in its emerging applications for schizophrenia management. Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention due to its potential for improved bioavailability compared to traditional lithium carbonate formulations.
Safety profiles of lithium orotate indicate a potentially lower risk of side effects and toxicity compared to conventional lithium treatments. This is attributed to the lower dosage required for therapeutic effects, which may reduce the likelihood of lithium accumulation in the body. However, long-term safety data for lithium orotate in schizophrenia treatment remains limited, necessitating further research and clinical trials.
Bioavailability studies suggest that lithium orotate may have enhanced absorption and distribution properties. The orotic acid component is believed to facilitate lithium transport across cell membranes, potentially leading to more efficient uptake in the brain. This improved bioavailability could result in lower effective doses, potentially mitigating some of the systemic side effects associated with traditional lithium therapy.
Pharmacokinetic investigations have shown that lithium orotate may have a more stable serum concentration profile compared to lithium carbonate. This could translate to more consistent therapeutic effects and potentially reduce the frequency of blood level monitoring required for patients. However, standardized protocols for dosing and monitoring lithium orotate in schizophrenia management are yet to be established.
Despite these promising aspects, concerns remain regarding the lack of comprehensive clinical data on lithium orotate's long-term effects in schizophrenia patients. The absence of large-scale, controlled studies comparing lithium orotate to established treatments limits definitive conclusions about its safety and efficacy profile in this specific patient population.
Regulatory considerations also play a crucial role in the adoption of lithium orotate for schizophrenia management. Currently, lithium orotate is not FDA-approved for psychiatric use, which presents challenges for its integration into standard treatment protocols. This regulatory status underscores the need for rigorous clinical trials to establish its safety and efficacy in schizophrenia care.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in terms of improved safety and bioavailability, further research is essential to fully elucidate its potential in schizophrenia management. Comprehensive studies addressing long-term safety, optimal dosing strategies, and comparative efficacy are necessary to position lithium orotate as a viable alternative or adjunct to current schizophrenia treatments.
Safety profiles of lithium orotate indicate a potentially lower risk of side effects and toxicity compared to conventional lithium treatments. This is attributed to the lower dosage required for therapeutic effects, which may reduce the likelihood of lithium accumulation in the body. However, long-term safety data for lithium orotate in schizophrenia treatment remains limited, necessitating further research and clinical trials.
Bioavailability studies suggest that lithium orotate may have enhanced absorption and distribution properties. The orotic acid component is believed to facilitate lithium transport across cell membranes, potentially leading to more efficient uptake in the brain. This improved bioavailability could result in lower effective doses, potentially mitigating some of the systemic side effects associated with traditional lithium therapy.
Pharmacokinetic investigations have shown that lithium orotate may have a more stable serum concentration profile compared to lithium carbonate. This could translate to more consistent therapeutic effects and potentially reduce the frequency of blood level monitoring required for patients. However, standardized protocols for dosing and monitoring lithium orotate in schizophrenia management are yet to be established.
Despite these promising aspects, concerns remain regarding the lack of comprehensive clinical data on lithium orotate's long-term effects in schizophrenia patients. The absence of large-scale, controlled studies comparing lithium orotate to established treatments limits definitive conclusions about its safety and efficacy profile in this specific patient population.
Regulatory considerations also play a crucial role in the adoption of lithium orotate for schizophrenia management. Currently, lithium orotate is not FDA-approved for psychiatric use, which presents challenges for its integration into standard treatment protocols. This regulatory status underscores the need for rigorous clinical trials to establish its safety and efficacy in schizophrenia care.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in terms of improved safety and bioavailability, further research is essential to fully elucidate its potential in schizophrenia management. Comprehensive studies addressing long-term safety, optimal dosing strategies, and comparative efficacy are necessary to position lithium orotate as a viable alternative or adjunct to current schizophrenia treatments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!