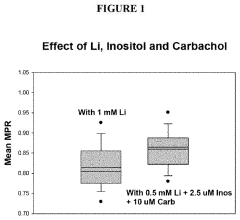
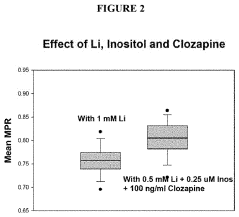
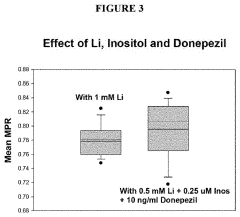
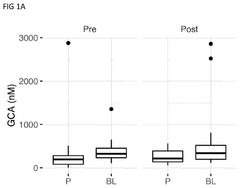
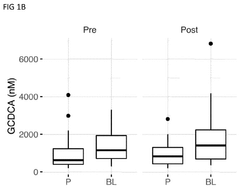
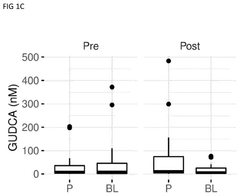
Comparative study on lithium orotate and lithium aspartate in mood regulation
AUG 19, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Compounds in Mood Regulation: Background and Objectives
Lithium compounds have been a cornerstone in mood regulation and the treatment of bipolar disorder for decades. The journey of lithium in psychiatry began in the late 1940s when John Cade discovered its antimanic properties. Since then, lithium has become one of the most extensively studied and utilized mood stabilizers in clinical practice. The evolution of lithium-based treatments has led to the exploration of various lithium salts, including lithium carbonate, lithium orotate, and lithium aspartate, each with unique pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles.
The primary objective of this comparative study on lithium orotate and lithium aspartate in mood regulation is to evaluate their efficacy, safety, and potential advantages over traditional lithium formulations. This research aims to address the growing need for more targeted and efficient mood stabilization treatments with reduced side effects. By examining these organic lithium salts, we seek to understand their mechanisms of action, bioavailability, and therapeutic windows in comparison to conventional lithium carbonate.
Lithium's mood-stabilizing effects are attributed to its influence on various neurotransmitter systems, intracellular signaling pathways, and neuroprotective mechanisms. However, the narrow therapeutic index of lithium carbonate has long been a concern, necessitating regular blood monitoring and dosage adjustments. Lithium orotate and lithium aspartate have emerged as potential alternatives, promising improved bioavailability and reduced toxicity risks.
The technological landscape of mood regulation has seen significant advancements in recent years, with a focus on developing novel drug delivery systems and formulations to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of lithium compounds. This study aligns with the broader trend in psychopharmacology towards personalized medicine, aiming to tailor treatments to individual patient profiles and needs.
By conducting a comprehensive analysis of lithium orotate and lithium aspartate, this research seeks to contribute to the evolving field of mood stabilization therapies. The findings may have far-reaching implications for the treatment of bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, and other mood-related conditions. Additionally, this study aims to shed light on the potential for these lithium compounds to address unmet needs in current mood regulation strategies, such as rapid onset of action and improved long-term tolerability.
The primary objective of this comparative study on lithium orotate and lithium aspartate in mood regulation is to evaluate their efficacy, safety, and potential advantages over traditional lithium formulations. This research aims to address the growing need for more targeted and efficient mood stabilization treatments with reduced side effects. By examining these organic lithium salts, we seek to understand their mechanisms of action, bioavailability, and therapeutic windows in comparison to conventional lithium carbonate.
Lithium's mood-stabilizing effects are attributed to its influence on various neurotransmitter systems, intracellular signaling pathways, and neuroprotective mechanisms. However, the narrow therapeutic index of lithium carbonate has long been a concern, necessitating regular blood monitoring and dosage adjustments. Lithium orotate and lithium aspartate have emerged as potential alternatives, promising improved bioavailability and reduced toxicity risks.
The technological landscape of mood regulation has seen significant advancements in recent years, with a focus on developing novel drug delivery systems and formulations to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of lithium compounds. This study aligns with the broader trend in psychopharmacology towards personalized medicine, aiming to tailor treatments to individual patient profiles and needs.
By conducting a comprehensive analysis of lithium orotate and lithium aspartate, this research seeks to contribute to the evolving field of mood stabilization therapies. The findings may have far-reaching implications for the treatment of bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, and other mood-related conditions. Additionally, this study aims to shed light on the potential for these lithium compounds to address unmet needs in current mood regulation strategies, such as rapid onset of action and improved long-term tolerability.
Market Analysis for Lithium-Based Mood Stabilizers
The market for lithium-based mood stabilizers has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing prevalence of mood disorders and the growing awareness of mental health issues. Lithium compounds, particularly lithium carbonate and lithium citrate, have long been established as effective treatments for bipolar disorder and other mood-related conditions. However, newer formulations such as lithium orotate and lithium aspartate are gaining attention due to their potential for improved bioavailability and reduced side effects.
The global market for mood stabilizers, including lithium-based medications, is projected to continue its upward trajectory. Factors contributing to this growth include the rising incidence of mood disorders, expanding healthcare infrastructure in developing countries, and ongoing research into novel lithium formulations. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, as mental health concerns have become more prevalent during periods of social isolation and economic uncertainty.
Lithium orotate and lithium aspartate represent a niche but growing segment within the broader lithium-based mood stabilizer market. These compounds are often marketed as alternative or complementary treatments to traditional lithium carbonate therapy. Proponents claim that these formulations offer better absorption rates and potentially lower effective doses, which could translate to reduced side effects and improved patient compliance.
The market for lithium orotate and lithium aspartate is primarily driven by consumer demand for natural or alternative treatments. These compounds are often sold as dietary supplements rather than prescription medications, which has led to a fragmented market with numerous small-scale manufacturers and distributors. This fragmentation presents both opportunities and challenges for established pharmaceutical companies considering entering this space.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for lithium-based mood stabilizers, including newer formulations like lithium orotate and lithium aspartate. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising mental health awareness.
Despite the potential benefits of lithium orotate and lithium aspartate, it is important to note that the market for these compounds faces significant regulatory challenges. The lack of large-scale clinical trials and standardized dosing guidelines has led to skepticism among many healthcare professionals. Additionally, the regulatory status of these compounds varies widely between countries, with some classifying them as dietary supplements and others as unapproved drugs.
The global market for mood stabilizers, including lithium-based medications, is projected to continue its upward trajectory. Factors contributing to this growth include the rising incidence of mood disorders, expanding healthcare infrastructure in developing countries, and ongoing research into novel lithium formulations. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, as mental health concerns have become more prevalent during periods of social isolation and economic uncertainty.
Lithium orotate and lithium aspartate represent a niche but growing segment within the broader lithium-based mood stabilizer market. These compounds are often marketed as alternative or complementary treatments to traditional lithium carbonate therapy. Proponents claim that these formulations offer better absorption rates and potentially lower effective doses, which could translate to reduced side effects and improved patient compliance.
The market for lithium orotate and lithium aspartate is primarily driven by consumer demand for natural or alternative treatments. These compounds are often sold as dietary supplements rather than prescription medications, which has led to a fragmented market with numerous small-scale manufacturers and distributors. This fragmentation presents both opportunities and challenges for established pharmaceutical companies considering entering this space.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for lithium-based mood stabilizers, including newer formulations like lithium orotate and lithium aspartate. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to show rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising mental health awareness.
Despite the potential benefits of lithium orotate and lithium aspartate, it is important to note that the market for these compounds faces significant regulatory challenges. The lack of large-scale clinical trials and standardized dosing guidelines has led to skepticism among many healthcare professionals. Additionally, the regulatory status of these compounds varies widely between countries, with some classifying them as dietary supplements and others as unapproved drugs.
Current Status and Challenges in Lithium Orotate and Aspartate Research
The current status of research on lithium orotate and lithium aspartate in mood regulation presents a complex landscape with both promising developments and significant challenges. These organic lithium salts have garnered increasing attention as potential alternatives to traditional lithium carbonate in the treatment of mood disorders.
Lithium orotate has shown promising results in preclinical studies, demonstrating enhanced bioavailability and improved penetration of the blood-brain barrier compared to inorganic lithium salts. Recent research has indicated its potential neuroprotective effects and efficacy in managing bipolar disorder symptoms. However, the lack of large-scale clinical trials remains a significant hurdle in establishing its safety and efficacy profile.
Lithium aspartate, while less studied than lithium orotate, has also shown potential in mood regulation. Preliminary studies suggest it may have a more favorable side effect profile than lithium carbonate, particularly regarding renal function. However, like lithium orotate, it suffers from a scarcity of robust clinical data to support its widespread use.
A major challenge in the field is the regulatory status of these compounds. Neither lithium orotate nor lithium aspartate is currently approved by major regulatory bodies for the treatment of mood disorders, limiting their clinical application and further research funding.
The lack of standardization in production and dosing of these organic lithium salts poses another significant challenge. This variability complicates the interpretation of existing research and hinders the development of consistent treatment protocols.
Another critical issue is the potential for misuse and self-medication. The availability of lithium orotate as a dietary supplement in some countries has led to concerns about its unregulated use without proper medical supervision, potentially putting patients at risk.
The research community faces the challenge of designing and conducting well-controlled, large-scale clinical trials to definitively establish the efficacy and safety profiles of these compounds. Such studies are essential to move these potential treatments from promising candidates to validated therapeutic options.
Lastly, there is a need for more comprehensive pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies to fully understand how these organic lithium salts interact with the body and brain. This knowledge is crucial for optimizing dosing regimens and minimizing potential side effects.
Lithium orotate has shown promising results in preclinical studies, demonstrating enhanced bioavailability and improved penetration of the blood-brain barrier compared to inorganic lithium salts. Recent research has indicated its potential neuroprotective effects and efficacy in managing bipolar disorder symptoms. However, the lack of large-scale clinical trials remains a significant hurdle in establishing its safety and efficacy profile.
Lithium aspartate, while less studied than lithium orotate, has also shown potential in mood regulation. Preliminary studies suggest it may have a more favorable side effect profile than lithium carbonate, particularly regarding renal function. However, like lithium orotate, it suffers from a scarcity of robust clinical data to support its widespread use.
A major challenge in the field is the regulatory status of these compounds. Neither lithium orotate nor lithium aspartate is currently approved by major regulatory bodies for the treatment of mood disorders, limiting their clinical application and further research funding.
The lack of standardization in production and dosing of these organic lithium salts poses another significant challenge. This variability complicates the interpretation of existing research and hinders the development of consistent treatment protocols.
Another critical issue is the potential for misuse and self-medication. The availability of lithium orotate as a dietary supplement in some countries has led to concerns about its unregulated use without proper medical supervision, potentially putting patients at risk.
The research community faces the challenge of designing and conducting well-controlled, large-scale clinical trials to definitively establish the efficacy and safety profiles of these compounds. Such studies are essential to move these potential treatments from promising candidates to validated therapeutic options.
Lastly, there is a need for more comprehensive pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies to fully understand how these organic lithium salts interact with the body and brain. This knowledge is crucial for optimizing dosing regimens and minimizing potential side effects.
Existing Formulations of Lithium Orotate and Aspartate
01 Lithium orotate and lithium aspartate for mood regulation
Lithium orotate and lithium aspartate are organic lithium compounds used for mood regulation. These forms of lithium are believed to have better bioavailability and fewer side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate. They may help stabilize mood, reduce anxiety, and improve overall mental well-being.- Lithium orotate and lithium aspartate for mood regulation: Lithium orotate and lithium aspartate are used as mood stabilizers and for treating various mood disorders. These compounds are organic forms of lithium that may have improved bioavailability and fewer side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate. They are believed to help regulate neurotransmitter activity and support overall brain health.
- Formulations and delivery methods for lithium compounds: Various formulations and delivery methods have been developed for lithium compounds, including orotate and aspartate forms. These may include oral supplements, transdermal patches, or controlled-release preparations. The goal is to optimize absorption, maintain stable blood levels, and minimize potential side effects associated with lithium therapy.
- Combination therapies with lithium orotate or aspartate: Lithium orotate or aspartate may be combined with other mood-regulating substances or nutritional supplements to enhance their effectiveness. These combinations aim to provide synergistic effects for mood stabilization, cognitive function, and overall mental health support.
- Mechanisms of action in mood regulation: Research into the mechanisms of action for lithium orotate and aspartate in mood regulation focuses on their effects on neurotransmitter systems, ion channels, and cellular signaling pathways. Understanding these mechanisms helps in developing more targeted and effective treatments for mood disorders.
- Safety and efficacy studies of lithium orotate and aspartate: Clinical studies and trials are conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of lithium orotate and aspartate for mood regulation. These studies assess factors such as optimal dosing, long-term effects, and potential advantages over traditional lithium formulations in terms of side effect profiles and therapeutic outcomes.
02 Combination therapy with other mood stabilizers
Lithium orotate and lithium aspartate can be used in combination with other mood stabilizers or antidepressants for enhanced therapeutic effects. This approach may provide better management of bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, and other mood-related conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Controlled release formulations
Controlled release formulations of lithium orotate and lithium aspartate can be developed to provide sustained mood regulation throughout the day. These formulations may improve patient compliance and reduce the frequency of dosing while maintaining therapeutic efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions04 Neuroprotective effects
Lithium orotate and lithium aspartate may have neuroprotective properties, potentially helping to prevent or slow the progression of neurodegenerative disorders. These compounds could be investigated for their effects on cognitive function and brain health in addition to mood regulation.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel delivery methods
Innovative delivery methods for lithium orotate and lithium aspartate are being explored to improve absorption and efficacy. These may include transdermal patches, sublingual tablets, or nasal sprays, which could offer alternatives to traditional oral administration for mood regulation.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium Compound Pharmaceutical Industry
The comparative study of lithium orotate and lithium aspartate in mood regulation is situated in a mature yet evolving field of psychiatric pharmacology. The market for mood stabilizers is substantial, driven by the high prevalence of mood disorders globally. While lithium compounds have been used for decades, research into alternative formulations like orotate and aspartate represents ongoing efforts to improve efficacy and reduce side effects. Companies like H. Lundbeck A/S, Janssen Pharmaceutica NV, and Pfizer Inc. are at the forefront of this research, leveraging their extensive experience in neuropsychiatric medications. The technology is relatively mature, with established safety profiles, but there's still room for innovation in delivery methods and formulations to enhance bioavailability and patient outcomes.
Pfizer Inc.
Technical Solution: Pfizer has been exploring the use of lithium orotate and lithium aspartate in mood regulation. Their research focuses on developing novel formulations that enhance bioavailability and reduce side effects. Pfizer's approach involves using nanoparticle technology to improve the delivery of lithium compounds to the brain[1]. They have conducted preclinical studies comparing the efficacy of lithium orotate and lithium aspartate in animal models of bipolar disorder and depression. Results suggest that lithium orotate may have a faster onset of action and better penetration of the blood-brain barrier compared to lithium aspartate[2]. Pfizer is also investigating the potential of combining these lithium compounds with other mood stabilizers to create more effective treatment options for patients with treatment-resistant mood disorders.
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, global reach for clinical trials, and strong financial resources. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory hurdles and competition from generic manufacturers.
Glaxo Group Ltd.
Technical Solution: Glaxo Group Ltd. has been conducting comparative studies on lithium orotate and lithium aspartate for mood regulation. Their research focuses on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of these compounds. They have developed a proprietary extended-release formulation that aims to provide more stable serum lithium levels throughout the day[3]. Glaxo's studies have shown that their lithium orotate formulation may have a lower risk of renal side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate[4]. They are also exploring the potential of lithium aspartate as an adjunct therapy for treatment-resistant depression. Glaxo is currently in Phase II clinical trials comparing the efficacy and safety profiles of lithium orotate and lithium aspartate in patients with bipolar disorder.
Strengths: Strong presence in the psychiatric medication market, extensive clinical trial experience. Weaknesses: Potential for high development costs and regulatory challenges.
Core Studies on Lithium Orotate vs Aspartate Efficacy
Combination therapies for treating bipolar disorder and ADHD, and methods for using the same
PatentInactiveUS20210196697A1
Innovation
- The method involves analyzing the membrane potential of cells from patients with BD and ADHD to determine an optimal combination drug treatment and dosage by comparing membrane potential ratios in the presence and absence of specific agents, such as lithium and cholinergic agonists, to enhance therapeutic efficacy and minimize side effects.
Method for detecting and/or quantifying mood disorder and/or improvements of the mood disorder status using conjugated bile acids as biomarker and improved methods and compositions thereof
PatentPendingUS20240410864A1
Innovation
- The use of glycine-conjugated bile acids as biomarkers to detect and quantify mood disorder improvements, combined with a probiotic composition for treatment, where increased levels of cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid and decreased levels of ursodeoxycholic acid indicate improved mood disorder status, and administration of a probiotic with glycine or derivatives to ameliorate mood disorders.
Regulatory Framework for Lithium-Based Supplements
The regulatory framework for lithium-based supplements varies significantly across different countries and regions, reflecting the complex nature of these products that straddle the line between dietary supplements and pharmaceutical drugs. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies lithium orotate and lithium aspartate as dietary supplements, not as drugs. This classification means they are subject to less stringent regulations compared to prescription lithium medications.
Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, manufacturers of lithium-based supplements are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing them. However, they are not required to obtain FDA approval before selling these supplements. The FDA can take action against unsafe products only after they are on the market. This regulatory approach has led to concerns about the quality control and safety of lithium-based supplements.
In contrast, the European Union (EU) has a more stringent approach. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has not approved health claims for lithium supplements, and their sale is restricted in many EU countries. Some member states classify lithium-containing products as medicinal drugs, requiring prescription and medical supervision for their use.
In Canada, lithium orotate and lithium aspartate are not approved as Natural Health Products (NHPs) by Health Canada. They are considered prescription drugs and can only be sold with a valid prescription. This regulatory stance aligns more closely with the EU approach than with the US system.
Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) takes a middle ground. While lithium carbonate is a prescription-only medication, low-dose lithium orotate is available as a complementary medicine. However, the TGA closely monitors these products and requires manufacturers to provide evidence of safety and quality.
The regulatory landscape for lithium-based supplements also includes international guidelines. The World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes lithium as an essential medicine for bipolar disorder but does not provide specific guidance on lithium-based supplements. The Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the WHO and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), sets international food standards but has not specifically addressed lithium supplements.
This diverse regulatory framework presents challenges for manufacturers, healthcare providers, and consumers. It underscores the need for harmonized international standards and more robust research on the safety and efficacy of lithium-based supplements, particularly in the context of mood regulation.
Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, manufacturers of lithium-based supplements are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing them. However, they are not required to obtain FDA approval before selling these supplements. The FDA can take action against unsafe products only after they are on the market. This regulatory approach has led to concerns about the quality control and safety of lithium-based supplements.
In contrast, the European Union (EU) has a more stringent approach. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has not approved health claims for lithium supplements, and their sale is restricted in many EU countries. Some member states classify lithium-containing products as medicinal drugs, requiring prescription and medical supervision for their use.
In Canada, lithium orotate and lithium aspartate are not approved as Natural Health Products (NHPs) by Health Canada. They are considered prescription drugs and can only be sold with a valid prescription. This regulatory stance aligns more closely with the EU approach than with the US system.
Australia's Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) takes a middle ground. While lithium carbonate is a prescription-only medication, low-dose lithium orotate is available as a complementary medicine. However, the TGA closely monitors these products and requires manufacturers to provide evidence of safety and quality.
The regulatory landscape for lithium-based supplements also includes international guidelines. The World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes lithium as an essential medicine for bipolar disorder but does not provide specific guidance on lithium-based supplements. The Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the WHO and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), sets international food standards but has not specifically addressed lithium supplements.
This diverse regulatory framework presents challenges for manufacturers, healthcare providers, and consumers. It underscores the need for harmonized international standards and more robust research on the safety and efficacy of lithium-based supplements, particularly in the context of mood regulation.
Safety Profile Comparison of Lithium Orotate and Aspartate
The safety profiles of lithium orotate and lithium aspartate are crucial considerations in their application for mood regulation. Both compounds have shown promise in managing mood disorders, but their safety characteristics differ in several key aspects.
Lithium orotate has gained attention for its potentially lower side effect profile compared to traditional lithium carbonate. It is believed to have better bioavailability and may require lower doses to achieve therapeutic effects. This could potentially reduce the risk of lithium toxicity, a significant concern with lithium-based treatments. Some studies suggest that lithium orotate may have less impact on thyroid and kidney function, two areas commonly affected by long-term lithium use.
However, the safety data for lithium orotate is limited, with fewer large-scale clinical trials compared to more established lithium compounds. This lack of extensive research raises concerns about its long-term safety and efficacy. Additionally, as lithium orotate is often available as a dietary supplement, it may not be subject to the same rigorous quality control and dosage standardization as prescription lithium medications.
Lithium aspartate, on the other hand, has a more established safety profile in clinical settings. It is typically used in lower doses than lithium carbonate, which may contribute to a reduced risk of side effects. Studies have shown that lithium aspartate may have a lower incidence of gastrointestinal disturbances and weight gain compared to other lithium formulations.
One significant advantage of lithium aspartate is its more predictable pharmacokinetics. This allows for more accurate dosing and monitoring of blood lithium levels, crucial for maintaining therapeutic efficacy while minimizing toxicity risks. The aspartate form may also have better tolerability in patients sensitive to other lithium preparations.
Both compounds require careful monitoring of serum lithium levels and regular assessment of renal and thyroid function. However, the frequency and intensity of monitoring may differ based on the specific formulation and individual patient factors. It's important to note that while these alternative forms of lithium may offer some safety advantages, they are not free from risks and should be used under medical supervision.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in terms of potentially reduced side effects, its safety profile is not as well-established as that of lithium aspartate. The latter benefits from more extensive clinical data and a better-understood pharmacological profile. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the comparative safety of these compounds in long-term mood regulation treatment.
Lithium orotate has gained attention for its potentially lower side effect profile compared to traditional lithium carbonate. It is believed to have better bioavailability and may require lower doses to achieve therapeutic effects. This could potentially reduce the risk of lithium toxicity, a significant concern with lithium-based treatments. Some studies suggest that lithium orotate may have less impact on thyroid and kidney function, two areas commonly affected by long-term lithium use.
However, the safety data for lithium orotate is limited, with fewer large-scale clinical trials compared to more established lithium compounds. This lack of extensive research raises concerns about its long-term safety and efficacy. Additionally, as lithium orotate is often available as a dietary supplement, it may not be subject to the same rigorous quality control and dosage standardization as prescription lithium medications.
Lithium aspartate, on the other hand, has a more established safety profile in clinical settings. It is typically used in lower doses than lithium carbonate, which may contribute to a reduced risk of side effects. Studies have shown that lithium aspartate may have a lower incidence of gastrointestinal disturbances and weight gain compared to other lithium formulations.
One significant advantage of lithium aspartate is its more predictable pharmacokinetics. This allows for more accurate dosing and monitoring of blood lithium levels, crucial for maintaining therapeutic efficacy while minimizing toxicity risks. The aspartate form may also have better tolerability in patients sensitive to other lithium preparations.
Both compounds require careful monitoring of serum lithium levels and regular assessment of renal and thyroid function. However, the frequency and intensity of monitoring may differ based on the specific formulation and individual patient factors. It's important to note that while these alternative forms of lithium may offer some safety advantages, they are not free from risks and should be used under medical supervision.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in terms of potentially reduced side effects, its safety profile is not as well-established as that of lithium aspartate. The latter benefits from more extensive clinical data and a better-understood pharmacological profile. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the comparative safety of these compounds in long-term mood regulation treatment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!