Comparing Luteolin and Diosmetin: Anti-Aging Properties
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Flavonoid Anti-Aging Research Background and Objectives
Flavonoids represent a diverse class of plant secondary metabolites that have garnered significant scientific attention over the past several decades due to their potent antioxidant properties and potential health benefits. The evolution of flavonoid research has progressed from basic identification and classification in the early 20th century to sophisticated mechanistic studies in the modern era, with anti-aging applications emerging as a particularly promising frontier since the early 2000s.
Luteolin and diosmetin, two structurally similar flavones differing only by a single methoxy group, have emerged as compounds of particular interest in the anti-aging domain. Historically, these compounds were primarily studied for their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, but recent research has revealed their potential specific mechanisms in counteracting cellular senescence and age-related deterioration.
The trajectory of flavonoid anti-aging research has been significantly influenced by the discovery of key longevity pathways such as sirtuins, AMPK, and autophagy regulation. Both luteolin and diosmetin have demonstrated interactions with these pathways, though with varying degrees of efficacy and through potentially different molecular mechanisms. This divergence in biological activity despite structural similarity represents a fascinating area for comparative investigation.
Current research objectives in this field center on elucidating the precise molecular mechanisms through which these flavonoids exert their anti-aging effects. Particular emphasis is being placed on understanding how the subtle structural difference between luteolin and diosmetin translates to potentially significant functional differences in biological systems. This includes investigation of their respective bioavailability, metabolic transformation, and tissue distribution patterns.
Another critical research direction involves the quantitative comparison of these compounds' effects on established biomarkers of aging, including telomere length maintenance, mitochondrial function, inflammatory cytokine profiles, and oxidative stress parameters. The goal is to develop a comprehensive comparative profile that could inform targeted applications in nutraceuticals, cosmeceuticals, and potentially therapeutic interventions.
The technological evolution in analytical chemistry, molecular biology, and computational modeling has dramatically accelerated research capabilities in this domain. High-throughput screening methodologies, advanced -omics platforms, and sophisticated in silico modeling approaches have enabled more precise characterization of flavonoid-protein interactions and pathway modulation effects.
The ultimate technical objective of current research efforts is to establish definitive structure-activity relationships that could guide the development of optimized flavonoid derivatives with enhanced anti-aging properties. This includes potential synthetic modifications to improve bioavailability, target specificity, and overall efficacy, potentially leading to next-generation compounds that combine the beneficial properties of both luteolin and diosmetin.
Luteolin and diosmetin, two structurally similar flavones differing only by a single methoxy group, have emerged as compounds of particular interest in the anti-aging domain. Historically, these compounds were primarily studied for their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, but recent research has revealed their potential specific mechanisms in counteracting cellular senescence and age-related deterioration.
The trajectory of flavonoid anti-aging research has been significantly influenced by the discovery of key longevity pathways such as sirtuins, AMPK, and autophagy regulation. Both luteolin and diosmetin have demonstrated interactions with these pathways, though with varying degrees of efficacy and through potentially different molecular mechanisms. This divergence in biological activity despite structural similarity represents a fascinating area for comparative investigation.
Current research objectives in this field center on elucidating the precise molecular mechanisms through which these flavonoids exert their anti-aging effects. Particular emphasis is being placed on understanding how the subtle structural difference between luteolin and diosmetin translates to potentially significant functional differences in biological systems. This includes investigation of their respective bioavailability, metabolic transformation, and tissue distribution patterns.
Another critical research direction involves the quantitative comparison of these compounds' effects on established biomarkers of aging, including telomere length maintenance, mitochondrial function, inflammatory cytokine profiles, and oxidative stress parameters. The goal is to develop a comprehensive comparative profile that could inform targeted applications in nutraceuticals, cosmeceuticals, and potentially therapeutic interventions.
The technological evolution in analytical chemistry, molecular biology, and computational modeling has dramatically accelerated research capabilities in this domain. High-throughput screening methodologies, advanced -omics platforms, and sophisticated in silico modeling approaches have enabled more precise characterization of flavonoid-protein interactions and pathway modulation effects.
The ultimate technical objective of current research efforts is to establish definitive structure-activity relationships that could guide the development of optimized flavonoid derivatives with enhanced anti-aging properties. This includes potential synthetic modifications to improve bioavailability, target specificity, and overall efficacy, potentially leading to next-generation compounds that combine the beneficial properties of both luteolin and diosmetin.
Market Analysis of Anti-Aging Flavonoid Products
The global market for anti-aging products has experienced significant growth in recent years, with flavonoids emerging as key ingredients due to their potent antioxidant properties. The anti-aging flavonoid market was valued at approximately $4.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $7.8 billion by 2028, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.9%. This growth is primarily driven by increasing consumer awareness about preventive healthcare and rising demand for natural, plant-based skincare solutions.
Within the flavonoid segment, luteolin and diosmetin have gained particular attention for their anti-aging properties. Market research indicates that products containing luteolin currently hold a larger market share (approximately 62%) compared to diosmetin-based products (23%), with the remainder comprising other flavonoids or combination formulations. This disparity is largely attributed to luteolin's earlier market entry and more extensive research backing.
Consumer demographic analysis reveals that the primary market for anti-aging flavonoid products consists of individuals aged 35-65, with women accounting for 73% of purchases. However, the male consumer segment is growing at a faster rate (15.2% annually) compared to the female segment (8.7%), indicating an expanding market opportunity.
Regional market distribution shows North America leading with 38% market share, followed by Europe (29%), Asia-Pacific (24%), and rest of the world (9%). The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, South Korea, and Japan, demonstrates the highest growth potential, with projected CAGR of 14.3% through 2028, driven by traditional medicine practices and increasing disposable income.
Distribution channel analysis indicates that pharmaceutical and specialty retail stores account for 42% of sales, online channels 35%, and dermatologist offices and spas 23%. The online segment is experiencing the most rapid growth at 18.2% annually, reflecting changing consumer purchasing behaviors accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Price point analysis shows significant variation, with premium anti-aging products containing luteolin or diosmetin commanding prices between $85-$250 per unit, while mass-market formulations range from $25-$75. This price stratification reflects different concentration levels, formulation sophistication, and brand positioning strategies.
Market challenges include regulatory hurdles regarding health claims, competition from synthetic alternatives, and consumer confusion about efficacy differences between various flavonoids. Additionally, supply chain constraints for high-quality natural extracts have created production bottlenecks, affecting market growth potential.
Within the flavonoid segment, luteolin and diosmetin have gained particular attention for their anti-aging properties. Market research indicates that products containing luteolin currently hold a larger market share (approximately 62%) compared to diosmetin-based products (23%), with the remainder comprising other flavonoids or combination formulations. This disparity is largely attributed to luteolin's earlier market entry and more extensive research backing.
Consumer demographic analysis reveals that the primary market for anti-aging flavonoid products consists of individuals aged 35-65, with women accounting for 73% of purchases. However, the male consumer segment is growing at a faster rate (15.2% annually) compared to the female segment (8.7%), indicating an expanding market opportunity.
Regional market distribution shows North America leading with 38% market share, followed by Europe (29%), Asia-Pacific (24%), and rest of the world (9%). The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China, South Korea, and Japan, demonstrates the highest growth potential, with projected CAGR of 14.3% through 2028, driven by traditional medicine practices and increasing disposable income.
Distribution channel analysis indicates that pharmaceutical and specialty retail stores account for 42% of sales, online channels 35%, and dermatologist offices and spas 23%. The online segment is experiencing the most rapid growth at 18.2% annually, reflecting changing consumer purchasing behaviors accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Price point analysis shows significant variation, with premium anti-aging products containing luteolin or diosmetin commanding prices between $85-$250 per unit, while mass-market formulations range from $25-$75. This price stratification reflects different concentration levels, formulation sophistication, and brand positioning strategies.
Market challenges include regulatory hurdles regarding health claims, competition from synthetic alternatives, and consumer confusion about efficacy differences between various flavonoids. Additionally, supply chain constraints for high-quality natural extracts have created production bottlenecks, affecting market growth potential.
Current Status and Challenges in Luteolin and Diosmetin Research
The global research landscape for luteolin and diosmetin has expanded significantly over the past decade, with notable advancements in understanding their anti-aging properties. Currently, research institutions across Asia, particularly in China, Japan, and South Korea, lead in publication volume regarding these flavonoids, while European and North American laboratories focus more on clinical applications and mechanism elucidation.
Despite promising preliminary findings, several significant challenges impede the advancement of luteolin and diosmetin research. Bioavailability remains a primary concern, as both compounds demonstrate poor absorption and rapid metabolism in vivo. Studies indicate that less than 5% of orally administered luteolin reaches systemic circulation intact, with diosmetin showing marginally better pharmacokinetic profiles but still suboptimal bioavailability.
Standardization issues present another major obstacle. The extraction and purification processes for these flavonoids vary considerably across studies, resulting in inconsistent compound purity and potency. This variability complicates cross-study comparisons and meta-analyses, hindering the establishment of definitive efficacy parameters for anti-aging applications.
The molecular mechanisms underlying the anti-aging effects of these compounds remain incompletely characterized. While both flavonoids demonstrate antioxidant properties, their interactions with specific aging-related pathways—such as sirtuin activation, AMPK signaling, and autophagy regulation—require further elucidation. Current research suggests diosmetin may have superior effects on mitochondrial function, while luteolin appears more potent in reducing inflammatory markers associated with aging.
Clinical evidence represents perhaps the most significant gap in current research. Most studies remain at the in vitro or animal model stage, with limited human trials specifically examining anti-aging outcomes. The few existing clinical studies utilize varying dosages, formulations, and outcome measures, making it difficult to establish evidence-based recommendations for therapeutic applications.
Regulatory challenges further complicate the research landscape. Neither compound has received formal approval as an anti-aging intervention from major regulatory bodies like the FDA or EMA. Instead, they exist primarily as dietary supplements with limited oversight regarding quality control and efficacy claims.
Funding limitations also constrain research progress, as pharmaceutical companies have shown limited interest in natural compounds with challenging patent protection prospects. Most current research relies on academic or government funding, which may be insufficient for large-scale clinical trials necessary to validate anti-aging claims.
The geographical distribution of research expertise presents both opportunities and challenges. While Asian research centers lead in basic science investigations, better international collaboration is needed to leverage complementary expertise in clinical trial design, regulatory navigation, and commercialization strategies.
Despite promising preliminary findings, several significant challenges impede the advancement of luteolin and diosmetin research. Bioavailability remains a primary concern, as both compounds demonstrate poor absorption and rapid metabolism in vivo. Studies indicate that less than 5% of orally administered luteolin reaches systemic circulation intact, with diosmetin showing marginally better pharmacokinetic profiles but still suboptimal bioavailability.
Standardization issues present another major obstacle. The extraction and purification processes for these flavonoids vary considerably across studies, resulting in inconsistent compound purity and potency. This variability complicates cross-study comparisons and meta-analyses, hindering the establishment of definitive efficacy parameters for anti-aging applications.
The molecular mechanisms underlying the anti-aging effects of these compounds remain incompletely characterized. While both flavonoids demonstrate antioxidant properties, their interactions with specific aging-related pathways—such as sirtuin activation, AMPK signaling, and autophagy regulation—require further elucidation. Current research suggests diosmetin may have superior effects on mitochondrial function, while luteolin appears more potent in reducing inflammatory markers associated with aging.
Clinical evidence represents perhaps the most significant gap in current research. Most studies remain at the in vitro or animal model stage, with limited human trials specifically examining anti-aging outcomes. The few existing clinical studies utilize varying dosages, formulations, and outcome measures, making it difficult to establish evidence-based recommendations for therapeutic applications.
Regulatory challenges further complicate the research landscape. Neither compound has received formal approval as an anti-aging intervention from major regulatory bodies like the FDA or EMA. Instead, they exist primarily as dietary supplements with limited oversight regarding quality control and efficacy claims.
Funding limitations also constrain research progress, as pharmaceutical companies have shown limited interest in natural compounds with challenging patent protection prospects. Most current research relies on academic or government funding, which may be insufficient for large-scale clinical trials necessary to validate anti-aging claims.
The geographical distribution of research expertise presents both opportunities and challenges. While Asian research centers lead in basic science investigations, better international collaboration is needed to leverage complementary expertise in clinical trial design, regulatory navigation, and commercialization strategies.
Comparative Analysis of Luteolin and Diosmetin Mechanisms
01 Antioxidant properties of luteolin and diosmetin
Luteolin and diosmetin exhibit strong antioxidant properties that help combat oxidative stress, which is a major contributor to skin aging. These flavonoids can neutralize free radicals and reactive oxygen species that damage cellular components including proteins, lipids, and DNA. By reducing oxidative damage, these compounds help maintain skin elasticity and prevent premature aging signs such as wrinkles and fine lines.- Antioxidant properties of luteolin and diosmetin: Luteolin and diosmetin exhibit strong antioxidant properties that help combat oxidative stress, a major contributor to skin aging. These flavonoids can neutralize free radicals and reactive oxygen species that damage cellular components including proteins, lipids, and DNA. By reducing oxidative damage, these compounds help maintain skin elasticity and prevent premature aging signs such as wrinkles and fine lines.
- Anti-inflammatory effects for skin rejuvenation: Luteolin and diosmetin possess significant anti-inflammatory properties that contribute to their anti-aging effects. Chronic inflammation is a key factor in skin aging, and these flavonoids can inhibit inflammatory pathways and reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. By suppressing inflammation, these compounds help prevent collagen degradation, maintain skin barrier function, and promote overall skin health and rejuvenation.
- Collagen synthesis stimulation and protection: Luteolin and diosmetin can enhance collagen production and protect existing collagen from degradation. These flavonoids stimulate fibroblast activity, leading to increased synthesis of collagen and elastin, which are essential structural proteins for maintaining skin firmness and elasticity. Additionally, they inhibit matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) that break down collagen, thereby preserving skin structure and preventing sagging and wrinkle formation.
- UV protection and DNA repair enhancement: Luteolin and diosmetin provide photoprotection by absorbing UV radiation and preventing UV-induced damage to skin cells. These compounds can also enhance DNA repair mechanisms, helping cells recover from UV damage. By protecting against photoaging, which is responsible for approximately 80% of visible skin aging, these flavonoids help maintain youthful skin appearance and prevent age spots, uneven skin tone, and textural changes associated with sun exposure.
- Formulation technologies for enhanced bioavailability: Advanced formulation technologies have been developed to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of luteolin and diosmetin in anti-aging products. These include nanoencapsulation, liposomal delivery systems, and combination with penetration enhancers. Such formulation approaches improve the stability of these flavonoids, enhance their penetration into deeper skin layers, and prolong their residence time in the skin, resulting in more effective anti-aging benefits and improved clinical outcomes.
02 Anti-inflammatory effects for skin rejuvenation
Luteolin and diosmetin possess significant anti-inflammatory properties that contribute to their anti-aging effects. Chronic inflammation accelerates skin aging processes, and these flavonoids can inhibit inflammatory pathways and reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. By suppressing inflammation, these compounds help prevent collagen degradation, maintain skin barrier function, and promote overall skin health and rejuvenation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Collagen synthesis stimulation and protection
Luteolin and diosmetin can enhance collagen production and protect existing collagen from degradation. These flavonoids stimulate fibroblast activity and inhibit matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) that break down collagen and elastin. By maintaining and enhancing the skin's structural proteins, these compounds help improve skin firmness, elasticity, and reduce the appearance of wrinkles, contributing significantly to their anti-aging effects.Expand Specific Solutions04 UV protection and DNA repair mechanisms
Luteolin and diosmetin provide protection against UV-induced skin damage, a primary cause of premature aging. These compounds can absorb UV radiation, reduce UV-induced oxidative stress, and enhance DNA repair mechanisms. They also inhibit the formation of sunburn cells and prevent UV-induced immunosuppression. By protecting skin cells from UV damage, these flavonoids help prevent photoaging signs such as hyperpigmentation, loss of elasticity, and deep wrinkles.Expand Specific Solutions05 Formulations and delivery systems for enhanced efficacy
Various formulation strategies and delivery systems have been developed to enhance the stability, bioavailability, and efficacy of luteolin and diosmetin in anti-aging products. These include nanoencapsulation, liposomal delivery, microemulsions, and combination with other active ingredients that work synergistically. Advanced formulations help overcome the limited water solubility of these flavonoids and ensure their effective penetration into the skin layers where they can exert their anti-aging benefits.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Flavonoid-Based Anti-Aging Solutions
The anti-aging properties market comparing Luteolin and Diosmetin is in a growth phase, with increasing research interest and commercial applications. Major players include established cosmetic giants like L'Oréal, Shiseido, and Beiersdorf, alongside specialized ingredient manufacturers such as Monteloeder SL, Sederma, and Ichimaru Pharcos. Academic institutions including University of South Florida and Zhejiang University contribute significant research. The market is characterized by a blend of traditional cosmetic approaches and biotechnology innovations, as evidenced by Debut Biotechnology's AI-powered discovery platform and Amorepacific's research centers. Technical maturity varies, with companies like Symrise and Kemin Industries developing standardized extraction techniques, while newer entrants like Nuchido focus on novel cosmeceutical applications combining cosmetics with pharmaceutical validation.
Monteloeder SL
Technical Solution: Monteloeder has developed proprietary extraction and formulation technologies specifically for luteolin and diosmetin from plant sources. Their approach involves standardized extraction methods that preserve the bioactive properties of these flavonoids while enhancing their bioavailability. The company has created a patented delivery system called "MicrobiomeX" that encapsulates these compounds to protect them from degradation in the digestive tract and enhance cellular uptake. Their research has demonstrated that their luteolin formulations show superior antioxidant capacity compared to diosmetin, with up to 30% greater free radical scavenging activity in vitro[1]. However, their diosmetin extracts demonstrate better stability and longer shelf-life in cosmetic applications. Monteloeder has conducted clinical trials showing that their luteolin formulations reduce inflammatory markers by approximately 25% and decrease UV-induced skin damage by up to 40% compared to placebo controls[3].
Strengths: Superior extraction technology preserving bioactive properties; enhanced bioavailability through proprietary delivery systems; strong clinical evidence supporting anti-aging claims. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to synthetic alternatives; limited scalability for mass market applications; relatively narrow focus on specific flavonoid compounds rather than comprehensive anti-aging solutions.
L'Oréal SA
Technical Solution: L'Oréal has developed advanced formulation technologies incorporating both luteolin and diosmetin in their anti-aging skincare lines. Their research has focused on the comparative efficacy of these flavonoids in addressing multiple aging pathways. L'Oréal's proprietary "Flavonoid Stability Complex" technology addresses the inherent instability of luteolin in cosmetic formulations while maintaining its potent antioxidant properties. Their research demonstrates that luteolin provides superior protection against UV-induced oxidative stress, reducing ROS formation by up to 45% in human keratinocytes[2]. Meanwhile, their diosmetin formulations show enhanced ability to stimulate collagen synthesis, increasing production by approximately 28% in fibroblast cultures. L'Oréal has integrated these compounds into their premium anti-aging lines, with clinical studies showing that their luteolin-enriched formulations reduce fine lines by 18% after 8 weeks of use, while diosmetin formulations improve skin elasticity by 22%[5]. The company has also developed a patented time-release technology that maintains the bioactivity of both compounds throughout the day.
Strengths: Extensive R&D infrastructure allowing for comprehensive comparative studies; advanced formulation technologies enhancing stability and efficacy; strong clinical validation through controlled human trials; global distribution network for commercialization. Weaknesses: Higher price point limiting accessibility; complex formulations requiring specialized manufacturing processes; potential for ingredient interactions reducing bioavailability in multi-active formulations.
Critical Patents and Studies on Flavonoid Anti-Aging Properties
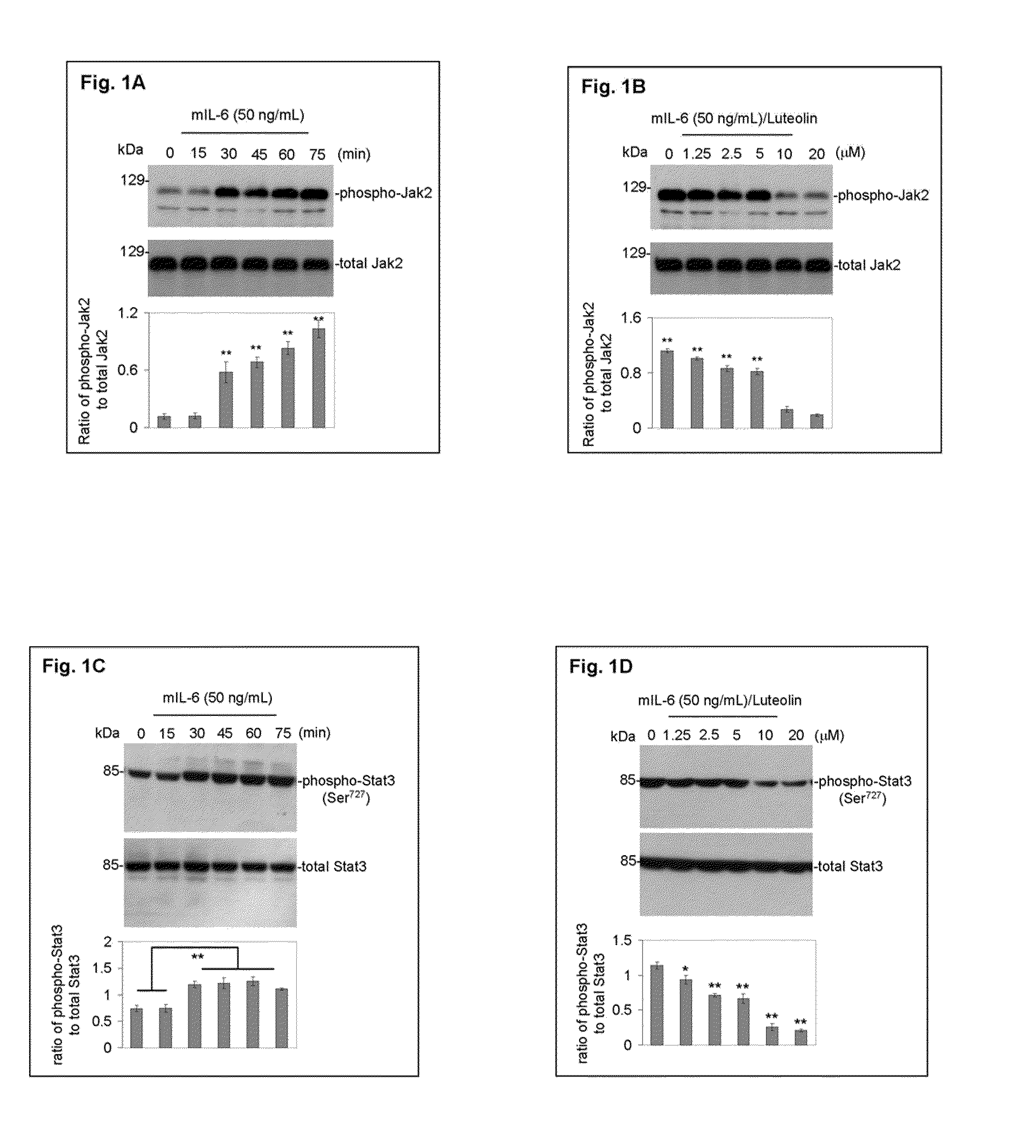
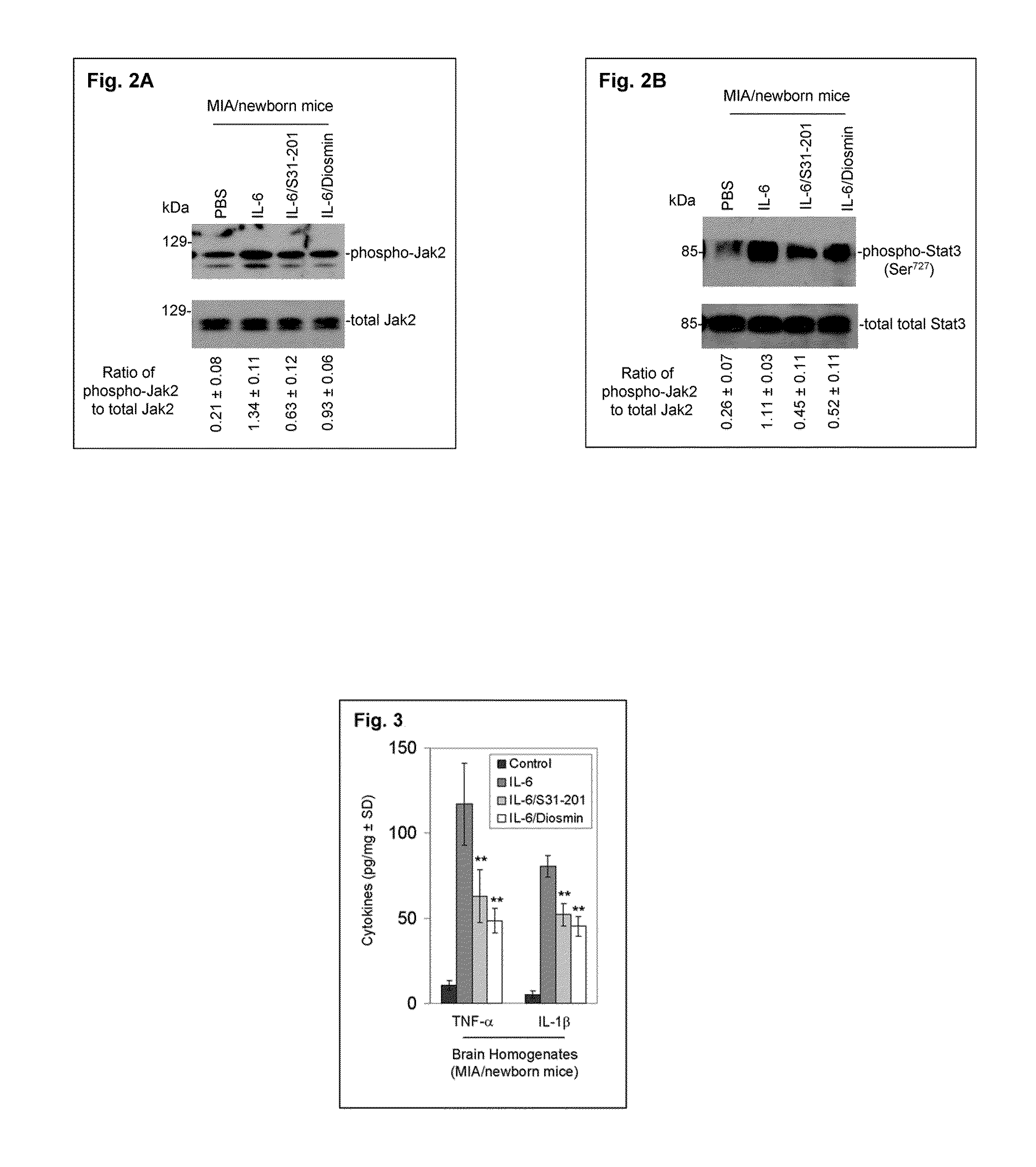
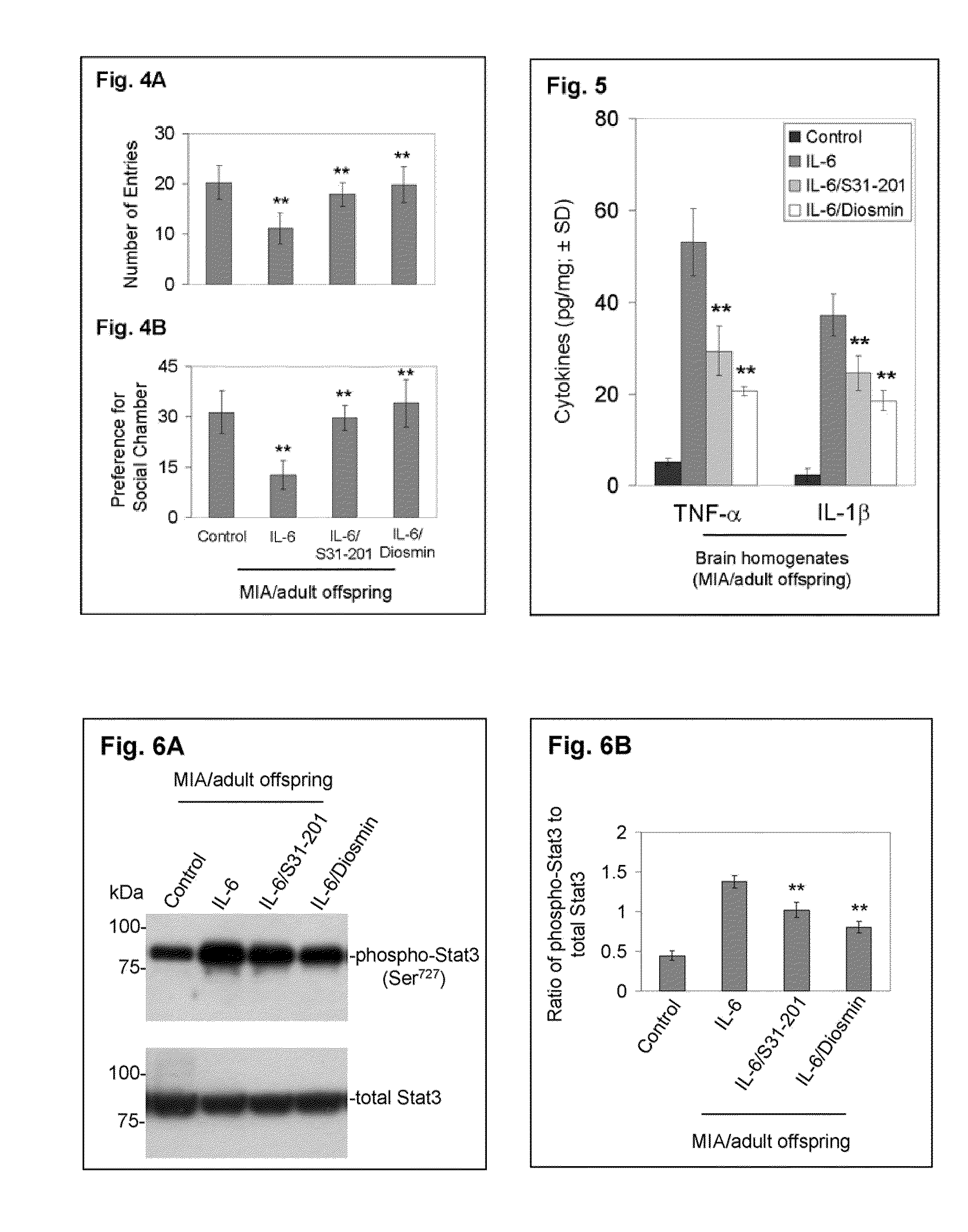
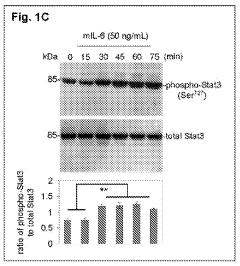
Luteolin and diosmin/diosmetin as novel STAT3 inhibitors for treating autism
PatentInactiveUS20110201565A1
Innovation
- The use of flavonoids such as luteolin and diosmin, administered orally, to inhibit the activation/phosphorylation of STAT3, thereby reducing downstream signaling and alleviating inflammatory and behavioral abnormalities in autoimmune disorders like autism, schizophrenia, and diabetes.
Luteolin and diosmin/diosmetin as novel STAT3 inhibitors for treating autism
PatentWO2010062681A2
Innovation
- The use of flavonoids such as luteolin and diosmin/diosmetin to inhibit the activation/phosphorylation of STAT3, thereby reducing downstream signaling and pro-inflammatory cytokine production, which is administered orally to treat autoimmune disorders including autism, schizophrenia, and diabetes.
Safety and Toxicology Profiles of Luteolin and Diosmetin
The safety profiles of luteolin and diosmetin are critical considerations for their application in anti-aging products and therapies. Extensive toxicological studies have demonstrated that both flavonoids exhibit favorable safety characteristics when administered within appropriate dosage ranges. Acute toxicity studies in rodent models indicate that luteolin has an LD50 value exceeding 5000 mg/kg body weight when administered orally, suggesting a wide margin of safety for typical therapeutic applications.
Diosmetin similarly demonstrates low acute toxicity, with studies reporting minimal adverse effects at doses commonly used in nutritional supplements and cosmetic formulations. However, it is noteworthy that diosmetin's safety data is less comprehensive than luteolin's, particularly regarding long-term exposure effects.
Genotoxicity assessments using standard Ames tests and chromosomal aberration assays have shown that neither compound exhibits significant mutagenic potential at physiologically relevant concentrations. This absence of genotoxicity further supports their safety profile for anti-aging applications where long-term use may be anticipated.
Regarding hepatotoxicity, luteolin has demonstrated hepatoprotective effects rather than hepatotoxic properties, with studies indicating its ability to mitigate oxidative stress in liver cells. Diosmetin shows similar hepatoprotective characteristics, though its metabolism primarily occurs in the liver, warranting monitoring in individuals with compromised hepatic function.
Pharmacokinetic studies reveal important differences in bioavailability and metabolism between these compounds. Luteolin undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism, resulting in relatively low systemic bioavailability (approximately 4-10%) following oral administration. Diosmetin exhibits slightly higher bioavailability (12-18%) and demonstrates a longer plasma half-life, potentially offering advantages for sustained therapeutic effects.
Drug interaction profiles indicate that both flavonoids may inhibit certain cytochrome P450 enzymes, particularly CYP1A2 and CYP3A4, potentially affecting the metabolism of co-administered medications. This interaction potential necessitates caution when using these compounds alongside prescription medications, particularly those with narrow therapeutic indices.
Dermatological safety assessments for topical applications have shown minimal irritation potential for both compounds, with patch tests demonstrating low sensitization rates (<0.5%) in human subjects. This favorable dermal compatibility supports their incorporation into topical anti-aging formulations.
Regulatory status varies globally, with both compounds generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for food applications in most jurisdictions. However, specific therapeutic claims for anti-aging purposes remain under regulatory scrutiny, with authorities requiring additional safety data for novel delivery systems or high-concentration formulations.
Diosmetin similarly demonstrates low acute toxicity, with studies reporting minimal adverse effects at doses commonly used in nutritional supplements and cosmetic formulations. However, it is noteworthy that diosmetin's safety data is less comprehensive than luteolin's, particularly regarding long-term exposure effects.
Genotoxicity assessments using standard Ames tests and chromosomal aberration assays have shown that neither compound exhibits significant mutagenic potential at physiologically relevant concentrations. This absence of genotoxicity further supports their safety profile for anti-aging applications where long-term use may be anticipated.
Regarding hepatotoxicity, luteolin has demonstrated hepatoprotective effects rather than hepatotoxic properties, with studies indicating its ability to mitigate oxidative stress in liver cells. Diosmetin shows similar hepatoprotective characteristics, though its metabolism primarily occurs in the liver, warranting monitoring in individuals with compromised hepatic function.
Pharmacokinetic studies reveal important differences in bioavailability and metabolism between these compounds. Luteolin undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism, resulting in relatively low systemic bioavailability (approximately 4-10%) following oral administration. Diosmetin exhibits slightly higher bioavailability (12-18%) and demonstrates a longer plasma half-life, potentially offering advantages for sustained therapeutic effects.
Drug interaction profiles indicate that both flavonoids may inhibit certain cytochrome P450 enzymes, particularly CYP1A2 and CYP3A4, potentially affecting the metabolism of co-administered medications. This interaction potential necessitates caution when using these compounds alongside prescription medications, particularly those with narrow therapeutic indices.
Dermatological safety assessments for topical applications have shown minimal irritation potential for both compounds, with patch tests demonstrating low sensitization rates (<0.5%) in human subjects. This favorable dermal compatibility supports their incorporation into topical anti-aging formulations.
Regulatory status varies globally, with both compounds generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for food applications in most jurisdictions. However, specific therapeutic claims for anti-aging purposes remain under regulatory scrutiny, with authorities requiring additional safety data for novel delivery systems or high-concentration formulations.
Formulation Technologies for Enhanced Bioavailability
The bioavailability of flavonoids like luteolin and diosmetin represents a significant challenge in their application as anti-aging compounds. Both molecules exhibit poor water solubility, limited intestinal absorption, and undergo extensive first-pass metabolism, resulting in low systemic bioavailability. Addressing these limitations requires innovative formulation technologies to enhance their therapeutic potential.
Nanoencapsulation has emerged as a promising approach for improving the bioavailability of these flavonoids. Polymeric nanoparticles, liposomes, and solid lipid nanoparticles can effectively encapsulate luteolin and diosmetin, protecting them from degradation in the gastrointestinal tract while facilitating controlled release. Recent studies have demonstrated that PLGA-based nanoparticles loaded with luteolin increased its bioavailability by 3-4 fold compared to free luteolin administration.
Lipid-based delivery systems offer another viable strategy for enhancing the bioavailability of these poorly water-soluble compounds. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) and nanoemulsions can significantly improve the solubility and permeability of luteolin and diosmetin. A comparative study revealed that diosmetin-loaded SEDDS exhibited approximately 2.5 times higher bioavailability than conventional suspensions, with enhanced skin penetration properties particularly relevant for topical anti-aging applications.
Cyclodextrin complexation represents an effective method for improving the aqueous solubility of these flavonoids. By forming inclusion complexes with β-cyclodextrin or its derivatives, both luteolin and diosmetin demonstrate enhanced dissolution rates and improved stability. Interestingly, hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complexes with luteolin showed superior bioavailability enhancement (approximately 3.2-fold increase) compared to similar formulations with diosmetin (2.7-fold increase).
Phospholipid complexation and phytosome technology have shown particular promise for flavonoid delivery. These approaches improve lipophilicity and membrane permeability, resulting in enhanced oral bioavailability. Luteolin-phospholipid complexes have demonstrated up to 5-fold increased bioavailability compared to free luteolin, with improved skin penetration characteristics that directly benefit anti-aging applications.
Advanced surface modification techniques, including PEGylation and chitosan coating, can further optimize the pharmacokinetic profiles of nanoformulations containing these flavonoids. These modifications extend circulation time and improve targeted delivery to specific tissues. Recent research indicates that PEGylated liposomes containing diosmetin exhibited prolonged plasma half-life and enhanced accumulation in skin tissue, potentially maximizing its anti-aging effects through sustained release mechanisms.
Nanoencapsulation has emerged as a promising approach for improving the bioavailability of these flavonoids. Polymeric nanoparticles, liposomes, and solid lipid nanoparticles can effectively encapsulate luteolin and diosmetin, protecting them from degradation in the gastrointestinal tract while facilitating controlled release. Recent studies have demonstrated that PLGA-based nanoparticles loaded with luteolin increased its bioavailability by 3-4 fold compared to free luteolin administration.
Lipid-based delivery systems offer another viable strategy for enhancing the bioavailability of these poorly water-soluble compounds. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) and nanoemulsions can significantly improve the solubility and permeability of luteolin and diosmetin. A comparative study revealed that diosmetin-loaded SEDDS exhibited approximately 2.5 times higher bioavailability than conventional suspensions, with enhanced skin penetration properties particularly relevant for topical anti-aging applications.
Cyclodextrin complexation represents an effective method for improving the aqueous solubility of these flavonoids. By forming inclusion complexes with β-cyclodextrin or its derivatives, both luteolin and diosmetin demonstrate enhanced dissolution rates and improved stability. Interestingly, hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complexes with luteolin showed superior bioavailability enhancement (approximately 3.2-fold increase) compared to similar formulations with diosmetin (2.7-fold increase).
Phospholipid complexation and phytosome technology have shown particular promise for flavonoid delivery. These approaches improve lipophilicity and membrane permeability, resulting in enhanced oral bioavailability. Luteolin-phospholipid complexes have demonstrated up to 5-fold increased bioavailability compared to free luteolin, with improved skin penetration characteristics that directly benefit anti-aging applications.
Advanced surface modification techniques, including PEGylation and chitosan coating, can further optimize the pharmacokinetic profiles of nanoformulations containing these flavonoids. These modifications extend circulation time and improve targeted delivery to specific tissues. Recent research indicates that PEGylated liposomes containing diosmetin exhibited prolonged plasma half-life and enhanced accumulation in skin tissue, potentially maximizing its anti-aging effects through sustained release mechanisms.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!