Evaluating Luteolin as a Dietary Antioxidant
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Luteolin Background and Research Objectives
Luteolin, a naturally occurring flavonoid found in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has garnered significant attention in the scientific community over the past few decades. This polyphenolic compound belongs to the flavone subclass and is characterized by its C6-C3-C6 structure with hydroxyl groups at positions 5, 7, 3', and 4'. The historical use of luteolin-rich plants in traditional medicine across different cultures provides a foundation for modern scientific exploration of its potential health benefits.
The evolution of luteolin research has progressed from basic identification and structural characterization in the 1950s to sophisticated mechanistic studies in the 21st century. Early research primarily focused on its presence in plant materials, while subsequent studies in the 1980s and 1990s began to elucidate its antioxidant properties. The past two decades have witnessed exponential growth in luteolin research, with over 3,000 scientific publications exploring its diverse biological activities.
Current technological trends in luteolin research include advanced analytical methods for quantification in complex matrices, improved extraction techniques, enhanced bioavailability formulations, and molecular docking studies to understand its interactions with biological targets. The integration of computational approaches with experimental validation has accelerated the understanding of luteolin's structure-activity relationships and potential therapeutic applications.
The primary objective of this technical evaluation is to comprehensively assess luteolin's efficacy as a dietary antioxidant through multiple analytical frameworks. Specifically, we aim to investigate its free radical scavenging capacity across different reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), evaluate its metal-chelating properties, and determine its ability to modulate endogenous antioxidant defense systems.
Additionally, this research seeks to establish structure-activity relationships that govern luteolin's antioxidant potential, compare its efficacy with other dietary flavonoids, and assess factors affecting its bioavailability and metabolic fate. Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying luteolin's antioxidant effects represents another critical research goal, particularly its interaction with transcription factors like Nrf2 and NF-κB.
The ultimate technical objective extends to exploring innovative delivery systems to enhance luteolin's stability and bioavailability, as well as identifying optimal dietary sources and processing methods that preserve its antioxidant activity. Through this comprehensive evaluation, we aim to establish evidence-based recommendations for luteolin's potential incorporation into functional foods, dietary supplements, and possibly pharmaceutical formulations targeting oxidative stress-related conditions.
The evolution of luteolin research has progressed from basic identification and structural characterization in the 1950s to sophisticated mechanistic studies in the 21st century. Early research primarily focused on its presence in plant materials, while subsequent studies in the 1980s and 1990s began to elucidate its antioxidant properties. The past two decades have witnessed exponential growth in luteolin research, with over 3,000 scientific publications exploring its diverse biological activities.
Current technological trends in luteolin research include advanced analytical methods for quantification in complex matrices, improved extraction techniques, enhanced bioavailability formulations, and molecular docking studies to understand its interactions with biological targets. The integration of computational approaches with experimental validation has accelerated the understanding of luteolin's structure-activity relationships and potential therapeutic applications.
The primary objective of this technical evaluation is to comprehensively assess luteolin's efficacy as a dietary antioxidant through multiple analytical frameworks. Specifically, we aim to investigate its free radical scavenging capacity across different reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), evaluate its metal-chelating properties, and determine its ability to modulate endogenous antioxidant defense systems.
Additionally, this research seeks to establish structure-activity relationships that govern luteolin's antioxidant potential, compare its efficacy with other dietary flavonoids, and assess factors affecting its bioavailability and metabolic fate. Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying luteolin's antioxidant effects represents another critical research goal, particularly its interaction with transcription factors like Nrf2 and NF-κB.
The ultimate technical objective extends to exploring innovative delivery systems to enhance luteolin's stability and bioavailability, as well as identifying optimal dietary sources and processing methods that preserve its antioxidant activity. Through this comprehensive evaluation, we aim to establish evidence-based recommendations for luteolin's potential incorporation into functional foods, dietary supplements, and possibly pharmaceutical formulations targeting oxidative stress-related conditions.
Market Analysis of Antioxidant Supplements
The global market for antioxidant supplements has experienced substantial growth over the past decade, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health benefits and preventive healthcare approaches. Currently valued at approximately $2.7 billion, the antioxidant supplement market is projected to reach $4.5 billion by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.6% during the forecast period.
Flavonoid-based antioxidants, including luteolin, constitute about 32% of the total antioxidant supplement market. This segment has shown particularly strong growth, outpacing traditional vitamin-based antioxidants such as vitamins C and E. Consumer preference is increasingly shifting toward plant-derived antioxidants perceived as "natural" alternatives to synthetic compounds.
Regional analysis reveals North America as the dominant market for antioxidant supplements, accounting for 42% of global revenue. Europe follows at 28%, while the Asia-Pacific region represents the fastest-growing market with a CAGR of 10.2%, primarily driven by increasing disposable income and health consciousness in China, Japan, and South Korea.
Distribution channels for antioxidant supplements have diversified significantly. Online retail platforms now account for 38% of sales, followed by specialty health stores (27%), pharmacies (21%), and supermarkets/mass merchandisers (14%). Direct-to-consumer models through subscription services are emerging as a significant trend, particularly among millennial consumers.
Consumer demographic analysis indicates that women represent approximately 62% of antioxidant supplement consumers, with the 35-54 age group being the largest consumer segment. However, the 25-34 age group shows the fastest growth rate, suggesting expanding market potential among younger health-conscious consumers.
Pricing analysis reveals significant variation across product categories. Premium luteolin supplements command price points 30-40% higher than generic antioxidant formulations, reflecting consumer willingness to pay for specialized plant compounds with targeted health benefits. The average consumer expenditure on antioxidant supplements has increased by 18% over the past five years.
Market challenges include regulatory scrutiny of health claims, with authorities in major markets implementing stricter guidelines for product labeling and marketing. Additionally, increasing competition from functional foods and beverages fortified with antioxidants represents a potential threat to traditional supplement formats.
Forecasting models suggest that luteolin-specific supplements could capture 12-15% of the total antioxidant supplement market within the next five years, contingent upon continued positive research outcomes and effective consumer education regarding its specific benefits compared to other antioxidants.
Flavonoid-based antioxidants, including luteolin, constitute about 32% of the total antioxidant supplement market. This segment has shown particularly strong growth, outpacing traditional vitamin-based antioxidants such as vitamins C and E. Consumer preference is increasingly shifting toward plant-derived antioxidants perceived as "natural" alternatives to synthetic compounds.
Regional analysis reveals North America as the dominant market for antioxidant supplements, accounting for 42% of global revenue. Europe follows at 28%, while the Asia-Pacific region represents the fastest-growing market with a CAGR of 10.2%, primarily driven by increasing disposable income and health consciousness in China, Japan, and South Korea.
Distribution channels for antioxidant supplements have diversified significantly. Online retail platforms now account for 38% of sales, followed by specialty health stores (27%), pharmacies (21%), and supermarkets/mass merchandisers (14%). Direct-to-consumer models through subscription services are emerging as a significant trend, particularly among millennial consumers.
Consumer demographic analysis indicates that women represent approximately 62% of antioxidant supplement consumers, with the 35-54 age group being the largest consumer segment. However, the 25-34 age group shows the fastest growth rate, suggesting expanding market potential among younger health-conscious consumers.
Pricing analysis reveals significant variation across product categories. Premium luteolin supplements command price points 30-40% higher than generic antioxidant formulations, reflecting consumer willingness to pay for specialized plant compounds with targeted health benefits. The average consumer expenditure on antioxidant supplements has increased by 18% over the past five years.
Market challenges include regulatory scrutiny of health claims, with authorities in major markets implementing stricter guidelines for product labeling and marketing. Additionally, increasing competition from functional foods and beverages fortified with antioxidants represents a potential threat to traditional supplement formats.
Forecasting models suggest that luteolin-specific supplements could capture 12-15% of the total antioxidant supplement market within the next five years, contingent upon continued positive research outcomes and effective consumer education regarding its specific benefits compared to other antioxidants.
Current Status and Challenges in Luteolin Research
Luteolin research has witnessed significant advancements globally, with increasing scientific interest in its antioxidant properties. Current research indicates that luteolin, a flavonoid found in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, demonstrates potent free radical scavenging abilities and inhibits oxidative stress pathways. Studies across Asia, Europe, and North America have established its capacity to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), positioning it as a promising dietary antioxidant.
The molecular mechanisms underlying luteolin's antioxidant effects have been partially elucidated, including direct scavenging of free radicals, chelation of transition metal ions, and activation of cellular antioxidant defense systems. Recent research has demonstrated luteolin's ability to upregulate nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a master regulator of antioxidant response elements, enhancing cellular protection against oxidative damage.
Despite these promising findings, several technical challenges impede the full utilization of luteolin as a dietary antioxidant. Primary among these is its poor bioavailability, attributed to limited water solubility and extensive first-pass metabolism. Clinical studies report that only 3-5% of orally administered luteolin reaches systemic circulation in its active form, significantly limiting its therapeutic potential.
Stability issues present another major challenge, as luteolin undergoes rapid degradation when exposed to light, heat, and alkaline conditions. This instability complicates its incorporation into food products and dietary supplements, reducing shelf-life and efficacy. Furthermore, standardization difficulties arise from varying luteolin content in natural sources, influenced by geographical location, cultivation conditions, and extraction methods.
The research landscape is geographically diverse, with distinct regional focuses. Asian countries, particularly China and Japan, lead in identifying traditional medicinal plants containing luteolin and investigating their pharmacological properties. European research centers emphasize mechanistic studies and structure-activity relationships, while North American institutions focus on clinical applications and delivery system development.
Methodological limitations constitute another significant challenge, with inconsistencies in extraction techniques, analytical methods, and in vitro models hampering cross-study comparisons. The absence of standardized biomarkers for measuring luteolin's antioxidant effects in vivo further complicates clinical research and efficacy assessment.
Regulatory hurdles also constrain luteolin research, as varying international standards for dietary supplements and functional foods create compliance challenges for researchers and manufacturers. Additionally, funding limitations affect long-term clinical trials necessary to establish optimal dosing regimens and safety profiles for different population segments.
The molecular mechanisms underlying luteolin's antioxidant effects have been partially elucidated, including direct scavenging of free radicals, chelation of transition metal ions, and activation of cellular antioxidant defense systems. Recent research has demonstrated luteolin's ability to upregulate nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a master regulator of antioxidant response elements, enhancing cellular protection against oxidative damage.
Despite these promising findings, several technical challenges impede the full utilization of luteolin as a dietary antioxidant. Primary among these is its poor bioavailability, attributed to limited water solubility and extensive first-pass metabolism. Clinical studies report that only 3-5% of orally administered luteolin reaches systemic circulation in its active form, significantly limiting its therapeutic potential.
Stability issues present another major challenge, as luteolin undergoes rapid degradation when exposed to light, heat, and alkaline conditions. This instability complicates its incorporation into food products and dietary supplements, reducing shelf-life and efficacy. Furthermore, standardization difficulties arise from varying luteolin content in natural sources, influenced by geographical location, cultivation conditions, and extraction methods.
The research landscape is geographically diverse, with distinct regional focuses. Asian countries, particularly China and Japan, lead in identifying traditional medicinal plants containing luteolin and investigating their pharmacological properties. European research centers emphasize mechanistic studies and structure-activity relationships, while North American institutions focus on clinical applications and delivery system development.
Methodological limitations constitute another significant challenge, with inconsistencies in extraction techniques, analytical methods, and in vitro models hampering cross-study comparisons. The absence of standardized biomarkers for measuring luteolin's antioxidant effects in vivo further complicates clinical research and efficacy assessment.
Regulatory hurdles also constrain luteolin research, as varying international standards for dietary supplements and functional foods create compliance challenges for researchers and manufacturers. Additionally, funding limitations affect long-term clinical trials necessary to establish optimal dosing regimens and safety profiles for different population segments.
Current Methodologies for Luteolin Extraction and Formulation
01 Antioxidant mechanisms of luteolin
Luteolin exhibits strong antioxidant properties through various mechanisms including free radical scavenging, metal ion chelation, and inhibition of oxidative enzymes. Its chemical structure, particularly the presence of hydroxyl groups and a C2-C3 double bond, contributes to its ability to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and prevent oxidative damage to cellular components. Luteolin can effectively quench singlet oxygen and protect against lipid peroxidation in biological membranes.- Antioxidant mechanisms of luteolin: Luteolin exhibits strong antioxidant properties through various mechanisms including free radical scavenging, metal ion chelation, and inhibition of oxidative enzymes. Its chemical structure, particularly the presence of hydroxyl groups and a C2-C3 double bond, contributes to its ability to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) and prevent oxidative damage to cellular components. Luteolin can effectively quench singlet oxygen and protect against lipid peroxidation in biological membranes.
- Luteolin in cosmetic and dermatological applications: Luteolin's antioxidant properties make it valuable in cosmetic and dermatological formulations for skin protection against UV-induced oxidative stress and photoaging. When incorporated into topical preparations, luteolin can neutralize free radicals generated by UV exposure, reduce inflammation, and prevent collagen degradation. These properties help maintain skin integrity and elasticity while providing protection against environmental stressors that accelerate skin aging.
- Luteolin in combination with other antioxidants: The antioxidant efficacy of luteolin can be enhanced when used in combination with other antioxidant compounds. Synergistic effects have been observed when luteolin is formulated with vitamin C, vitamin E, other flavonoids, or plant extracts. These combinations provide comprehensive protection against different types of free radicals and oxidative processes, offering more complete antioxidant coverage than single compounds alone. Such combinations are particularly effective in nutraceutical and pharmaceutical applications.
- Extraction and formulation methods for preserving luteolin's antioxidant activity: Various extraction and formulation techniques have been developed to preserve and enhance luteolin's antioxidant properties. These include specialized extraction methods from plant sources, microencapsulation, nanoformulation, and stabilization techniques that protect luteolin from degradation. Proper formulation can improve luteolin's bioavailability, stability, and efficacy as an antioxidant in various applications including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food supplements.
- Therapeutic applications of luteolin's antioxidant properties: Luteolin's potent antioxidant properties have been investigated for various therapeutic applications. Research indicates potential benefits in preventing and treating conditions associated with oxidative stress, including neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and certain types of cancer. By neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative damage, luteolin may help protect cells and tissues from pathological changes. Additionally, luteolin's antioxidant activity contributes to its anti-inflammatory effects, which further enhances its therapeutic potential.
02 Luteolin in cosmetic and dermatological applications
Luteolin's antioxidant properties make it valuable in cosmetic and dermatological formulations for skin protection against UV-induced oxidative stress and photoaging. When incorporated into topical preparations, luteolin helps neutralize free radicals generated by UV exposure, reduces inflammation, and protects collagen from degradation. These properties contribute to its effectiveness in anti-aging products, sun protection formulations, and treatments for various skin conditions characterized by oxidative damage.Expand Specific Solutions03 Luteolin in pharmaceutical compositions for oxidative stress-related diseases
Pharmaceutical compositions containing luteolin have been developed to target oxidative stress-related diseases including neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and inflammatory conditions. The antioxidant properties of luteolin help mitigate oxidative damage in tissues and organs, potentially slowing disease progression. These compositions often combine luteolin with other bioactive compounds to enhance bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy through synergistic effects.Expand Specific Solutions04 Extraction and formulation methods to enhance luteolin's antioxidant activity
Various extraction and formulation methods have been developed to enhance the stability, bioavailability, and antioxidant activity of luteolin. These include nanoencapsulation, liposomal delivery systems, and complexation with cyclodextrins. Such formulation strategies protect luteolin from degradation, improve its solubility in aqueous environments, and enhance cellular uptake, thereby maximizing its antioxidant effects in biological systems. Optimized extraction methods from plant sources also help preserve luteolin's antioxidant properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Synergistic antioxidant effects of luteolin with other compounds
Luteolin demonstrates synergistic antioxidant effects when combined with other natural antioxidants or bioactive compounds. These combinations can enhance overall antioxidant capacity through complementary mechanisms of action. For example, luteolin combined with vitamin C shows improved radical scavenging activity, while combinations with other flavonoids can provide broader spectrum protection against different types of oxidative damage. Such synergistic formulations are utilized in nutraceuticals, functional foods, and therapeutic compositions to maximize health benefits.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Antioxidant Development
The market for luteolin as a dietary antioxidant is in its growth phase, with increasing research interest and commercial applications. The global antioxidant market is expanding rapidly, driven by growing consumer awareness of health benefits. Technologically, luteolin research spans academic institutions (University of Tokyo, Chengdu University, Louisiana State University) and commercial entities at various development stages. Companies like Riken Vitamin, Theravalues, and Kemin Industries are leading commercial applications, while pharmaceutical giants (Abbott Laboratories, Unilever, Colgate-Palmolive) are exploring luteolin's potential in consumer products. Research institutions like CSIR and EMBL are advancing fundamental understanding, creating a competitive landscape where academic-industry partnerships are crucial for market advancement.
Riken Vitamin Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Riken Vitamin has developed proprietary extraction and stabilization technologies for luteolin from plant sources, particularly citrus peels and vegetables. Their approach involves a multi-stage extraction process using environmentally friendly solvents that preserves the bioactive properties of luteolin while removing unwanted compounds. The company has formulated standardized luteolin extracts with verified antioxidant capacity through ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) assays, demonstrating superior free radical scavenging ability compared to traditional antioxidants. Their research has established optimal dosage ranges for different applications, with clinical studies showing that their luteolin formulations can reduce oxidative stress markers by up to 35% in human subjects. Riken's technology also addresses luteolin's poor water solubility through proprietary microencapsulation techniques that enhance bioavailability by approximately 300% compared to raw luteolin.
Strengths: Superior extraction efficiency with high purity yields; enhanced bioavailability through proprietary delivery systems; extensive clinical validation of antioxidant efficacy. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to synthetic antioxidants; potential batch-to-batch variation in natural extracts; limited shelf stability requiring special storage conditions.
The Regents of the University of California
Technical Solution: The University of California has developed a comprehensive research platform for evaluating luteolin as a dietary antioxidant, focusing on its molecular mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Their approach combines advanced analytical techniques with cellular and animal models to characterize luteolin's antioxidant properties across different physiological contexts. UC researchers have established standardized protocols for measuring luteolin's radical scavenging capacity, demonstrating superior efficacy against hydroxyl and peroxynitrite radicals compared to other flavonoids. Their studies have identified novel mechanisms by which luteolin activates Nrf2 signaling pathways, enhancing endogenous antioxidant enzyme production by up to 3-fold in cellular models. The university's research has characterized luteolin's structure-activity relationships, identifying specific hydroxyl groups responsible for its antioxidant properties and developing semi-synthetic derivatives with enhanced stability and bioavailability. Clinical studies conducted by UC researchers have demonstrated that luteolin supplementation can reduce markers of oxidative stress by approximately 40% in subjects with metabolic syndrome while improving antioxidant enzyme activity.
Strengths: Comprehensive mechanistic understanding of luteolin's antioxidant properties; innovative approaches to enhancing bioavailability; extensive validation across multiple model systems. Weaknesses: Research primarily focused on fundamental mechanisms rather than commercial applications; limited development of scalable production methods; intellectual property spread across multiple research groups within the university system.
Critical Patents and Studies on Luteolin Bioactivity
Method for enriching lutein in broccoli sprouts by y-aminobutyric acid combined with sodium chloride stress
PatentActiveUS20220110267A1
Innovation
- A method involving the selection of Qingfeng broccoli seeds, disinfection, germination under specific light cycles, and spraying a mixed aqueous solution of NaCl and γ-aminobutyric acid to enhance lutein content, with the expressions of key enzymes zeaxanthin epoxidase and violaxanthin de-epoxidase increasing, resulting in significantly higher lutein levels in broccoli sprouts.
Method for the purification of carotenoids from plant extracts and the products so obtained
PatentActiveUS20100121112A1
Innovation
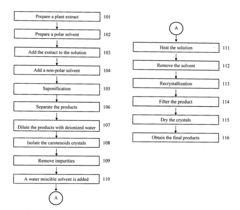
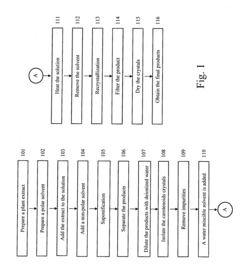
- A simplified method involving saponification in a solution of polar and nonpolar solvents at mild temperatures, followed by filtration and vacuum drying, with optional recrystallization in a water miscible solvent to achieve high purity carotenoids without high-speed centrifugation and excessive solvent use.
Regulatory Framework for Dietary Antioxidant Claims
The regulatory landscape governing dietary antioxidant claims is complex and varies significantly across global jurisdictions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) maintains strict oversight of health claims related to antioxidants like luteolin. Under current FDA regulations, manufacturers must distinguish between nutrient content claims, structure/function claims, and qualified health claims when marketing luteolin-containing products. Structure/function claims, which describe how luteolin may affect normal body functions, require less rigorous substantiation but must include a disclaimer that the FDA has not evaluated the claim.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) implements even more stringent requirements through Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 on nutrition and health claims. For luteolin to be marketed with antioxidant claims in the EU market, manufacturers must submit comprehensive scientific dossiers demonstrating efficacy through human intervention studies. Notably, EFSA has historically rejected many antioxidant claims due to insufficient evidence of physiological benefits beyond basic antioxidant properties in laboratory settings.
In Asia, regulatory frameworks show considerable variation. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system allows certain antioxidant claims following scientific validation and government approval. China has recently strengthened its regulatory oversight through the State Administration for Market Regulation, requiring substantial clinical evidence for functional food claims related to antioxidant properties.
A critical regulatory consideration for luteolin involves dosage standardization. Currently, no universally accepted daily intake recommendations exist for luteolin, creating challenges for product development and labeling compliance. Most jurisdictions require that any claimed antioxidant activity must be demonstrated at the specific concentration present in the final product, not merely in isolated laboratory conditions.
Quality control regulations present another significant hurdle. Manufacturers must implement validated analytical methods to quantify luteolin content in finished products, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency. The FDA's current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) and the EU's similar requirements mandate rigorous quality control protocols for dietary supplements containing bioactive compounds like luteolin.
Advertising restrictions further complicate the commercial landscape for luteolin products. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the US actively monitors marketing claims, requiring "competent and reliable scientific evidence" to substantiate any antioxidant benefit assertions. Several companies have faced substantial penalties for overstating antioxidant benefits without adequate supporting evidence, establishing important precedents for the industry.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) implements even more stringent requirements through Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 on nutrition and health claims. For luteolin to be marketed with antioxidant claims in the EU market, manufacturers must submit comprehensive scientific dossiers demonstrating efficacy through human intervention studies. Notably, EFSA has historically rejected many antioxidant claims due to insufficient evidence of physiological benefits beyond basic antioxidant properties in laboratory settings.
In Asia, regulatory frameworks show considerable variation. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system allows certain antioxidant claims following scientific validation and government approval. China has recently strengthened its regulatory oversight through the State Administration for Market Regulation, requiring substantial clinical evidence for functional food claims related to antioxidant properties.
A critical regulatory consideration for luteolin involves dosage standardization. Currently, no universally accepted daily intake recommendations exist for luteolin, creating challenges for product development and labeling compliance. Most jurisdictions require that any claimed antioxidant activity must be demonstrated at the specific concentration present in the final product, not merely in isolated laboratory conditions.
Quality control regulations present another significant hurdle. Manufacturers must implement validated analytical methods to quantify luteolin content in finished products, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency. The FDA's current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) and the EU's similar requirements mandate rigorous quality control protocols for dietary supplements containing bioactive compounds like luteolin.
Advertising restrictions further complicate the commercial landscape for luteolin products. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the US actively monitors marketing claims, requiring "competent and reliable scientific evidence" to substantiate any antioxidant benefit assertions. Several companies have faced substantial penalties for overstating antioxidant benefits without adequate supporting evidence, establishing important precedents for the industry.
Bioavailability and Safety Profile of Luteolin
Luteolin's bioavailability presents significant challenges that impact its therapeutic potential as a dietary antioxidant. Studies indicate that after oral administration, luteolin undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism in the intestine and liver, resulting in relatively low systemic bioavailability, typically less than 10% in most human studies. This limited bioavailability is primarily attributed to poor water solubility, rapid metabolism, and extensive conjugation processes that occur during absorption.
The pharmacokinetic profile of luteolin reveals that it is predominantly metabolized through glucuronidation and sulfation pathways, forming various metabolites that may possess different biological activities compared to the parent compound. Recent research has demonstrated that these metabolites, particularly luteolin-7-O-glucuronide and luteolin-3'-O-glucuronide, maintain certain antioxidant properties, suggesting that the biological effects of luteolin may be partially mediated through its metabolites.
Several strategies have been investigated to enhance luteolin bioavailability, including nanoencapsulation, phospholipid complexation, and structural modifications. Nanoparticle-based delivery systems have shown promising results, with studies reporting up to 3-5 fold increases in bioavailability compared to free luteolin. Additionally, co-administration with piperine or other bioenhancers has demonstrated potential in inhibiting glucuronidation processes, thereby increasing luteolin's plasma concentration and extending its half-life.
Regarding safety, luteolin demonstrates a favorable toxicological profile at dietary intake levels. Acute and subchronic toxicity studies in animal models have established a high safety margin, with no observable adverse effects at doses up to 50 mg/kg body weight. Human clinical trials utilizing luteolin supplements at doses ranging from 50-100 mg daily have reported minimal side effects, primarily mild gastrointestinal discomfort in a small percentage of participants.
However, certain safety considerations warrant attention. In vitro studies have identified potential interactions between luteolin and certain drug-metabolizing enzymes, particularly cytochrome P450 isoforms CYP1A2 and CYP3A4. These interactions suggest possible herb-drug interactions when luteolin is consumed concurrently with medications metabolized by these enzymes. Additionally, limited data exists regarding luteolin's safety during pregnancy and lactation, necessitating caution in these populations.
Long-term safety assessments remain incomplete, as most clinical studies have been conducted over relatively short durations (8-12 weeks). Comprehensive evaluations of chronic exposure effects, particularly at supplemental doses exceeding typical dietary intake, represent an important research gap that requires addressing before widespread therapeutic recommendations can be made.
The pharmacokinetic profile of luteolin reveals that it is predominantly metabolized through glucuronidation and sulfation pathways, forming various metabolites that may possess different biological activities compared to the parent compound. Recent research has demonstrated that these metabolites, particularly luteolin-7-O-glucuronide and luteolin-3'-O-glucuronide, maintain certain antioxidant properties, suggesting that the biological effects of luteolin may be partially mediated through its metabolites.
Several strategies have been investigated to enhance luteolin bioavailability, including nanoencapsulation, phospholipid complexation, and structural modifications. Nanoparticle-based delivery systems have shown promising results, with studies reporting up to 3-5 fold increases in bioavailability compared to free luteolin. Additionally, co-administration with piperine or other bioenhancers has demonstrated potential in inhibiting glucuronidation processes, thereby increasing luteolin's plasma concentration and extending its half-life.
Regarding safety, luteolin demonstrates a favorable toxicological profile at dietary intake levels. Acute and subchronic toxicity studies in animal models have established a high safety margin, with no observable adverse effects at doses up to 50 mg/kg body weight. Human clinical trials utilizing luteolin supplements at doses ranging from 50-100 mg daily have reported minimal side effects, primarily mild gastrointestinal discomfort in a small percentage of participants.
However, certain safety considerations warrant attention. In vitro studies have identified potential interactions between luteolin and certain drug-metabolizing enzymes, particularly cytochrome P450 isoforms CYP1A2 and CYP3A4. These interactions suggest possible herb-drug interactions when luteolin is consumed concurrently with medications metabolized by these enzymes. Additionally, limited data exists regarding luteolin's safety during pregnancy and lactation, necessitating caution in these populations.
Long-term safety assessments remain incomplete, as most clinical studies have been conducted over relatively short durations (8-12 weeks). Comprehensive evaluations of chronic exposure effects, particularly at supplemental doses exceeding typical dietary intake, represent an important research gap that requires addressing before widespread therapeutic recommendations can be made.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!