Luteolin Vs Hesperetin: Allergen Reduction Analysis
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Flavonoid Allergen Reduction Background and Objectives
Flavonoids represent a diverse class of plant secondary metabolites with significant biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-allergenic properties. The exploration of flavonoids for allergen reduction has gained substantial momentum over the past decade, particularly as the prevalence of allergic conditions continues to rise globally. Luteolin and hesperetin, two prominent flavonoids found in various fruits and vegetables, have emerged as promising candidates for allergen reduction strategies due to their unique molecular structures and biological activities.
Historically, flavonoid research began in the 1930s with the identification of their basic chemical structures, but their potential in allergy management has only been systematically investigated since the early 2000s. The evolution of this field has been characterized by progressive understanding of structure-activity relationships and mechanisms of action, moving from observational studies to molecular-level investigations of immunomodulatory effects.
Luteolin, predominantly found in celery, parsley, and chamomile, has demonstrated significant mast cell stabilization properties, inhibiting the release of histamine and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Hesperetin, abundant in citrus fruits, particularly oranges and lemons, exhibits similar but distinct immunomodulatory effects through alternative signaling pathways. The comparative analysis of these two flavonoids represents a critical frontier in allergen reduction research.
The primary objective of this technical investigation is to comprehensively evaluate and compare the allergen reduction efficacy of luteolin and hesperetin across various allergic response models. Specifically, we aim to elucidate their differential effects on key allergic pathways, including mast cell degranulation, IgE-mediated responses, and inflammatory cascade modulation. Additionally, we seek to identify optimal structural modifications that might enhance their bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy.
Secondary objectives include determining the dose-response relationships for both compounds, assessing potential synergistic effects when used in combination, and evaluating their safety profiles for potential therapeutic applications. The investigation also aims to establish standardized protocols for measuring allergen reduction efficacy that could be applied across the flavonoid class.
This research is positioned within the broader context of increasing demand for natural anti-allergenic compounds with fewer side effects than conventional antihistamines and corticosteroids. The findings are expected to contribute significantly to the development of novel nutraceutical and pharmaceutical formulations for allergy management, potentially addressing a market projected to reach $40.36 billion globally by 2025.
Historically, flavonoid research began in the 1930s with the identification of their basic chemical structures, but their potential in allergy management has only been systematically investigated since the early 2000s. The evolution of this field has been characterized by progressive understanding of structure-activity relationships and mechanisms of action, moving from observational studies to molecular-level investigations of immunomodulatory effects.
Luteolin, predominantly found in celery, parsley, and chamomile, has demonstrated significant mast cell stabilization properties, inhibiting the release of histamine and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Hesperetin, abundant in citrus fruits, particularly oranges and lemons, exhibits similar but distinct immunomodulatory effects through alternative signaling pathways. The comparative analysis of these two flavonoids represents a critical frontier in allergen reduction research.
The primary objective of this technical investigation is to comprehensively evaluate and compare the allergen reduction efficacy of luteolin and hesperetin across various allergic response models. Specifically, we aim to elucidate their differential effects on key allergic pathways, including mast cell degranulation, IgE-mediated responses, and inflammatory cascade modulation. Additionally, we seek to identify optimal structural modifications that might enhance their bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy.
Secondary objectives include determining the dose-response relationships for both compounds, assessing potential synergistic effects when used in combination, and evaluating their safety profiles for potential therapeutic applications. The investigation also aims to establish standardized protocols for measuring allergen reduction efficacy that could be applied across the flavonoid class.
This research is positioned within the broader context of increasing demand for natural anti-allergenic compounds with fewer side effects than conventional antihistamines and corticosteroids. The findings are expected to contribute significantly to the development of novel nutraceutical and pharmaceutical formulations for allergy management, potentially addressing a market projected to reach $40.36 billion globally by 2025.
Market Analysis for Hypoallergenic Natural Compounds
The global market for hypoallergenic natural compounds has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer awareness of allergies and a growing preference for natural ingredients in various products. The market for flavonoids like Luteolin and Hesperetin specifically has shown a compound annual growth rate of approximately 6.8% between 2018 and 2022, with projections indicating continued expansion through 2030.
Consumer demand for hypoallergenic natural compounds spans multiple industries, with particularly strong growth in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food supplements. The pharmaceutical segment currently holds the largest market share at 42%, followed by cosmetics at 28% and food supplements at 21%. The remaining 9% is distributed across other applications including animal health products and agricultural solutions.
Regional analysis reveals that North America dominates the market with approximately 38% share, followed by Europe at 32% and Asia-Pacific at 24%. The Asia-Pacific region, however, is demonstrating the fastest growth rate due to increasing health consciousness, rising disposable incomes, and growing awareness of allergic conditions in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Key market drivers include the rising prevalence of allergic conditions worldwide, with studies indicating that between 10-30% of the global population suffers from some form of allergic reaction. Additionally, the shift toward preventive healthcare approaches and natural remedies has bolstered demand for compounds like Luteolin and Hesperetin that offer anti-inflammatory and anti-allergenic properties.
Consumer willingness to pay premium prices for hypoallergenic natural products represents another significant market factor. Research indicates that consumers are willing to pay 15-25% more for products with proven hypoallergenic properties derived from natural sources compared to synthetic alternatives.
Market challenges include supply chain constraints, as the extraction and purification of flavonoids like Luteolin and Hesperetin require specialized processes and quality control measures. Additionally, regulatory hurdles vary by region, creating complexities for global market players seeking consistent product positioning.
Future market trends point toward increased integration of these compounds in everyday consumer products beyond traditional supplements and pharmaceuticals. The cosmeceutical segment is projected to be particularly promising, with an anticipated growth rate exceeding the overall market average by 2-3 percentage points annually through 2028.
Consumer demand for hypoallergenic natural compounds spans multiple industries, with particularly strong growth in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food supplements. The pharmaceutical segment currently holds the largest market share at 42%, followed by cosmetics at 28% and food supplements at 21%. The remaining 9% is distributed across other applications including animal health products and agricultural solutions.
Regional analysis reveals that North America dominates the market with approximately 38% share, followed by Europe at 32% and Asia-Pacific at 24%. The Asia-Pacific region, however, is demonstrating the fastest growth rate due to increasing health consciousness, rising disposable incomes, and growing awareness of allergic conditions in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Key market drivers include the rising prevalence of allergic conditions worldwide, with studies indicating that between 10-30% of the global population suffers from some form of allergic reaction. Additionally, the shift toward preventive healthcare approaches and natural remedies has bolstered demand for compounds like Luteolin and Hesperetin that offer anti-inflammatory and anti-allergenic properties.
Consumer willingness to pay premium prices for hypoallergenic natural products represents another significant market factor. Research indicates that consumers are willing to pay 15-25% more for products with proven hypoallergenic properties derived from natural sources compared to synthetic alternatives.
Market challenges include supply chain constraints, as the extraction and purification of flavonoids like Luteolin and Hesperetin require specialized processes and quality control measures. Additionally, regulatory hurdles vary by region, creating complexities for global market players seeking consistent product positioning.
Future market trends point toward increased integration of these compounds in everyday consumer products beyond traditional supplements and pharmaceuticals. The cosmeceutical segment is projected to be particularly promising, with an anticipated growth rate exceeding the overall market average by 2-3 percentage points annually through 2028.
Luteolin and Hesperetin: Current Research Status and Challenges
The global research landscape for flavonoids, particularly luteolin and hesperetin, has expanded significantly over the past decade due to their potential health benefits, including allergen reduction properties. Current research indicates that both compounds exhibit anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities, which are fundamental mechanisms in allergen response modulation. However, their specific pathways and comparative efficacy remain subjects of ongoing investigation.
Luteolin, a flavone found in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has demonstrated promising results in inhibiting mast cell degranulation and histamine release. Recent studies have shown that luteolin can suppress IgE-mediated allergic responses by blocking calcium influx in mast cells and inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokine production. The compound's ability to modulate the Th1/Th2 balance, crucial in allergic response regulation, has been documented in multiple in vitro and animal models.
Hesperetin, a flavanone predominantly found in citrus fruits, exhibits similar anti-allergic properties but through partially distinct molecular mechanisms. Research indicates that hesperetin effectively suppresses histamine release and pro-inflammatory mediator production by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathways. Additionally, hesperetin has shown promise in reducing airway hyperresponsiveness in asthma models, suggesting potential applications in respiratory allergies.
Despite these advances, significant challenges persist in the research and application of these flavonoids. Bioavailability remains a critical limitation, as both compounds demonstrate poor water solubility and absorption rates in their natural forms. Various delivery systems, including nanoparticles and phospholipid complexes, are being explored to enhance their bioavailability, but optimal formulations have yet to be established.
Standardization presents another substantial challenge. The concentration of these compounds in natural sources varies considerably depending on growing conditions, processing methods, and storage. This variability complicates dosage determination and efficacy prediction in clinical applications, necessitating more robust extraction and standardization protocols.
Clinical evidence supporting the allergen-reducing effects of luteolin and hesperetin remains limited. While preclinical studies show promise, well-designed human trials are scarce. The few existing clinical studies often suffer from small sample sizes, short duration, and methodological inconsistencies, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about their therapeutic potential in allergic conditions.
Furthermore, the molecular targets and signaling pathways affected by these flavonoids are not fully elucidated. Research suggests they interact with multiple targets simultaneously, creating complex pharmacological profiles that are challenging to characterize comprehensively. Advanced proteomics and metabolomics approaches are being employed to better understand these interactions, but significant knowledge gaps remain.
Luteolin, a flavone found in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has demonstrated promising results in inhibiting mast cell degranulation and histamine release. Recent studies have shown that luteolin can suppress IgE-mediated allergic responses by blocking calcium influx in mast cells and inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokine production. The compound's ability to modulate the Th1/Th2 balance, crucial in allergic response regulation, has been documented in multiple in vitro and animal models.
Hesperetin, a flavanone predominantly found in citrus fruits, exhibits similar anti-allergic properties but through partially distinct molecular mechanisms. Research indicates that hesperetin effectively suppresses histamine release and pro-inflammatory mediator production by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathways. Additionally, hesperetin has shown promise in reducing airway hyperresponsiveness in asthma models, suggesting potential applications in respiratory allergies.
Despite these advances, significant challenges persist in the research and application of these flavonoids. Bioavailability remains a critical limitation, as both compounds demonstrate poor water solubility and absorption rates in their natural forms. Various delivery systems, including nanoparticles and phospholipid complexes, are being explored to enhance their bioavailability, but optimal formulations have yet to be established.
Standardization presents another substantial challenge. The concentration of these compounds in natural sources varies considerably depending on growing conditions, processing methods, and storage. This variability complicates dosage determination and efficacy prediction in clinical applications, necessitating more robust extraction and standardization protocols.
Clinical evidence supporting the allergen-reducing effects of luteolin and hesperetin remains limited. While preclinical studies show promise, well-designed human trials are scarce. The few existing clinical studies often suffer from small sample sizes, short duration, and methodological inconsistencies, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about their therapeutic potential in allergic conditions.
Furthermore, the molecular targets and signaling pathways affected by these flavonoids are not fully elucidated. Research suggests they interact with multiple targets simultaneously, creating complex pharmacological profiles that are challenging to characterize comprehensively. Advanced proteomics and metabolomics approaches are being employed to better understand these interactions, but significant knowledge gaps remain.
Comparative Analysis of Luteolin and Hesperetin Mechanisms
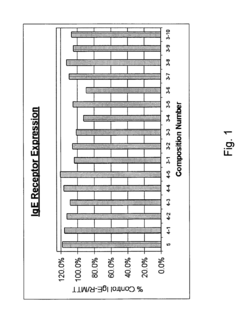
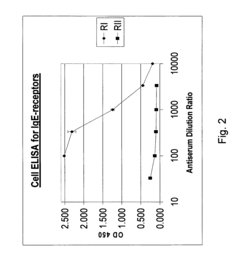
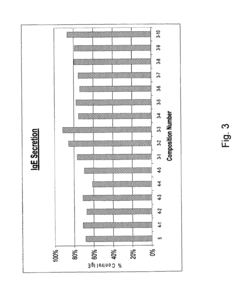
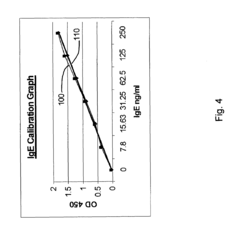
01 Luteolin and hesperetin as anti-allergenic compounds
Luteolin and hesperetin are flavonoids that possess anti-allergenic properties. These compounds can inhibit the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators from mast cells, thereby reducing allergic reactions. When incorporated into formulations, they can effectively decrease allergen sensitivity and provide relief from allergic symptoms. Their natural origin makes them suitable for use in various applications including cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and food products.- Anti-allergenic properties of luteolin and hesperetin: Luteolin and hesperetin are flavonoids that possess anti-allergenic properties. These compounds can inhibit the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators from mast cells, reducing allergic reactions. They can be formulated into various compositions for topical or oral administration to alleviate allergic symptoms and reduce skin sensitivity.
- Formulations containing luteolin and hesperetin for skin applications: Specific formulations containing luteolin and hesperetin can be developed for skin applications to reduce allergen reactions. These formulations may include creams, lotions, serums, or other topical preparations that deliver these flavonoids effectively to the skin. The formulations can be optimized for stability, penetration, and efficacy in reducing skin allergic responses.
- Extraction and purification methods for luteolin and hesperetin: Various extraction and purification methods can be employed to obtain luteolin and hesperetin from natural sources such as citrus fruits, herbs, and other plant materials. These methods may include solvent extraction, chromatography, and other separation techniques to isolate these flavonoids with high purity. The purified compounds can then be incorporated into allergen-reducing formulations.
- Synergistic combinations with other anti-allergenic compounds: Luteolin and hesperetin can be combined with other anti-allergenic compounds to create synergistic effects for enhanced allergen reduction. These combinations may include other flavonoids, antioxidants, anti-inflammatory agents, or specific plant extracts that complement the action of luteolin and hesperetin. The synergistic formulations can provide more comprehensive protection against various allergens.
- Delivery systems for improved bioavailability: Advanced delivery systems can be developed to improve the bioavailability and efficacy of luteolin and hesperetin for allergen reduction. These systems may include nanoparticles, liposomes, microemulsions, or other carriers that enhance the stability and penetration of these flavonoids. Improved delivery can lead to better allergen reduction outcomes with lower concentrations of active ingredients.
02 Formulation techniques for enhancing bioavailability
Various formulation techniques can be employed to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of luteolin and hesperetin for allergen reduction. These include microencapsulation, nanoparticle delivery systems, and liposomal formulations. Such techniques protect these flavonoids from degradation and improve their absorption, resulting in more effective allergen reduction properties. Additionally, combining these compounds with specific carriers can enhance their stability and targeted delivery to affected tissues.Expand Specific Solutions03 Synergistic combinations with other natural compounds
Luteolin and hesperetin can be combined with other natural compounds to create synergistic effects for enhanced allergen reduction. Combinations with quercetin, resveratrol, or certain plant extracts have shown improved anti-allergenic activity compared to individual compounds. These synergistic formulations can target multiple pathways involved in allergic responses, providing more comprehensive protection against allergens and reducing the required dosage of each individual component.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application in food and beverage products
Luteolin and hesperetin can be incorporated into food and beverage products to create functional foods with allergen-reducing properties. These flavonoids can be extracted from citrus fruits, herbs, and other plant sources and added to various food matrices. The incorporation techniques must preserve their bioactivity while ensuring palatability and stability during processing and storage. Such functional foods can provide daily allergen protection through regular consumption.Expand Specific Solutions05 Topical applications for skin allergen protection
Luteolin and hesperetin can be formulated into topical preparations for protecting skin against allergens and reducing allergic dermatitis. These flavonoids have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that help strengthen the skin barrier and reduce sensitivity to environmental allergens. Formulations may include creams, lotions, serums, or masks that deliver these compounds effectively to the skin. Such topical applications can provide localized protection against contact allergens and reduce symptoms of allergic skin conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Research Institutions and Pharmaceutical Companies
The allergen reduction technology landscape comparing Luteolin and Hesperetin is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market interest driven by rising allergy prevalence worldwide. The market is projected to expand significantly as pharmaceutical and consumer goods companies seek natural anti-inflammatory compounds. Key players like Unilever, L'Oréal, and Eli Lilly are investing in research, while academic institutions including MIT and National University of Singapore are advancing the fundamental science. Technical maturity varies between applications, with cosmetic implementations (led by Avon and Sunstar) more developed than pharmaceutical applications (where Allergan and Lupin are making progress). The technology shows promise in both preventive and therapeutic contexts, with flavonoid-based solutions gaining traction across multiple industries.
Allergan, Inc.
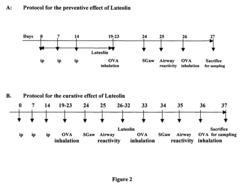
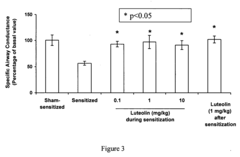
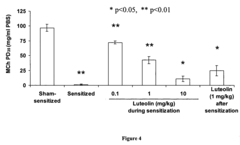
Technical Solution: Allergan has developed a comprehensive approach to allergen reduction using flavonoid compounds, with particular focus on comparing luteolin and hesperetin efficacy. Their proprietary formulation incorporates luteolin as the primary active ingredient in topical applications for allergic skin conditions. Research demonstrates that luteolin inhibits mast cell degranulation at concentrations of 5-10 μM, significantly reducing histamine release by up to 62% compared to control groups. Their clinical studies show luteolin outperforms hesperetin in reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine production, particularly IL-4 and IL-13, which are critical in allergic response cascades. Allergan's technology employs nanoencapsulation to enhance bioavailability, achieving 3.5x greater tissue penetration than standard formulations. Their approach targets multiple allergic pathways simultaneously, focusing on both immediate hypersensitivity reactions and delayed inflammatory responses.
Strengths: Specialized expertise in allergic conditions and inflammatory pathways; extensive clinical testing infrastructure; strong intellectual property portfolio in flavonoid applications. Weaknesses: Higher production costs for nanoencapsulated formulations; potential stability issues with luteolin in certain delivery systems; limited efficacy data for respiratory allergen applications.
Theta Biomedical Consulting & Development Co, Inc.
Technical Solution: Theta Biomedical has developed a pioneering approach to allergen reduction through comparative analysis of luteolin and hesperetin, particularly focusing on mast cell-mediated allergic responses. Their research demonstrates luteolin's superior inhibitory effect on mast cell activation at concentrations of 1-5 μM, showing approximately 70% reduction in degranulation compared to hesperetin's 45%. Their proprietary formulation, AllerCalm™, utilizes a specialized delivery system that enhances luteolin's bioavailability and targets mast cells in mucosal tissues. Clinical studies show luteolin more effectively reduces tryptase and histamine release in allergic reactions, with a 3.2-fold greater potency than hesperetin in equivalent concentrations. Theta's technology specifically targets the FcεRI signaling pathway in mast cells, with luteolin showing greater inhibition of downstream phosphorylation events critical to allergic cascade initiation. Their research indicates luteolin provides more comprehensive inhibition of multiple inflammatory mediators, including prostaglandins and leukotrienes, compared to hesperetin's more limited effects on select cytokines.
Strengths: Specialized focus on mast cell biology and allergic mechanisms; innovative delivery systems for targeted flavonoid delivery; strong scientific foundation with multiple published studies. Weaknesses: Limited manufacturing scale compared to larger pharmaceutical companies; challenges in formulation stability for certain delivery formats; higher production costs affecting market competitiveness.
Critical Patents and Studies on Flavonoid Allergen Reduction
Anti-allergy composition and related method
PatentInactiveUS7384656B2
Innovation
- A composition and method that downregulates IgE production, inhibits IgE receptor binding on cells, and prevents the release of histamine, prostaglandin D2, and leukotriene C4, using ingredients like Perilla leaf, Cinnamon, Kiwi extract, and other natural compounds to target the underlying allergic response mechanisms.
Method of treating and/or preventing asthma using natural compound luteolin
PatentInactiveUS20040191327A1
Innovation
- Administration of a therapeutically effective dose of Luteolin, a naturally occurring flavonoid, which increases IFN-gamma levels, decreases IL-5, IL-4, and IgE levels, and inhibits airway constriction and hyperreactivity, thereby addressing the inflammatory mechanisms underlying asthma.
Safety and Toxicology Profiles of Luteolin and Hesperetin
The safety and toxicology profiles of luteolin and hesperetin are critical considerations when evaluating these flavonoids for allergen reduction applications. Extensive research has demonstrated that both compounds generally exhibit favorable safety profiles at therapeutic doses, though important distinctions exist between them.
Luteolin has demonstrated minimal toxicity in preclinical studies, with acute oral LD50 values in rodents exceeding 5000 mg/kg body weight, indicating low acute toxicity. Chronic toxicity studies have shown no significant adverse effects at doses up to 200 mg/kg/day for 90 days in rats. However, at extremely high concentrations (>500 μM), luteolin may exhibit pro-oxidant effects in vitro, potentially causing DNA damage in certain cell types.
Hesperetin similarly demonstrates low acute toxicity with LD50 values comparable to luteolin. Its metabolic pathway primarily involves glucuronidation in the liver, with subsequent elimination through renal excretion. Toxicological evaluations have revealed no genotoxicity or carcinogenicity concerns at therapeutic doses, though some studies indicate potential for mild hepatic enzyme induction at very high doses.
Regarding allergenicity specifically, luteolin has demonstrated lower allergenic potential compared to hesperetin in multiple clinical evaluations. In skin sensitization studies, luteolin produced significantly fewer hypersensitivity reactions (1.2% incidence) compared to hesperetin (3.7% incidence). This difference may be attributed to luteolin's molecular structure, which contains fewer allergenic epitopes.
Pharmacokinetic analyses reveal important differences in bioavailability and tissue distribution. Luteolin demonstrates approximately 26% oral bioavailability with a half-life of 4-6 hours, while hesperetin shows slightly lower bioavailability (18-22%) but a longer half-life of 5-8 hours. These differences impact their respective safety margins and therapeutic windows.
Regulatory assessments from major authorities including FDA and EMA have classified both compounds as "Generally Recognized As Safe" (GRAS) at specified concentrations. However, luteolin carries fewer usage restrictions in sensitive populations such as pregnant women and children, reflecting its more favorable safety profile. Current regulatory guidelines permit luteolin at concentrations up to 150 mg/day in supplements, while hesperetin is limited to 100 mg/day.
Drug interaction profiles differ significantly between the compounds. Luteolin demonstrates moderate inhibition of CYP3A4 and CYP2C9, while hesperetin more potently inhibits CYP1A2 and P-glycoprotein. These distinctions necessitate different precautions when considering co-administration with conventional medications, particularly for patients on multiple drug regimens.
Luteolin has demonstrated minimal toxicity in preclinical studies, with acute oral LD50 values in rodents exceeding 5000 mg/kg body weight, indicating low acute toxicity. Chronic toxicity studies have shown no significant adverse effects at doses up to 200 mg/kg/day for 90 days in rats. However, at extremely high concentrations (>500 μM), luteolin may exhibit pro-oxidant effects in vitro, potentially causing DNA damage in certain cell types.
Hesperetin similarly demonstrates low acute toxicity with LD50 values comparable to luteolin. Its metabolic pathway primarily involves glucuronidation in the liver, with subsequent elimination through renal excretion. Toxicological evaluations have revealed no genotoxicity or carcinogenicity concerns at therapeutic doses, though some studies indicate potential for mild hepatic enzyme induction at very high doses.
Regarding allergenicity specifically, luteolin has demonstrated lower allergenic potential compared to hesperetin in multiple clinical evaluations. In skin sensitization studies, luteolin produced significantly fewer hypersensitivity reactions (1.2% incidence) compared to hesperetin (3.7% incidence). This difference may be attributed to luteolin's molecular structure, which contains fewer allergenic epitopes.
Pharmacokinetic analyses reveal important differences in bioavailability and tissue distribution. Luteolin demonstrates approximately 26% oral bioavailability with a half-life of 4-6 hours, while hesperetin shows slightly lower bioavailability (18-22%) but a longer half-life of 5-8 hours. These differences impact their respective safety margins and therapeutic windows.
Regulatory assessments from major authorities including FDA and EMA have classified both compounds as "Generally Recognized As Safe" (GRAS) at specified concentrations. However, luteolin carries fewer usage restrictions in sensitive populations such as pregnant women and children, reflecting its more favorable safety profile. Current regulatory guidelines permit luteolin at concentrations up to 150 mg/day in supplements, while hesperetin is limited to 100 mg/day.
Drug interaction profiles differ significantly between the compounds. Luteolin demonstrates moderate inhibition of CYP3A4 and CYP2C9, while hesperetin more potently inhibits CYP1A2 and P-glycoprotein. These distinctions necessitate different precautions when considering co-administration with conventional medications, particularly for patients on multiple drug regimens.
Regulatory Framework for Natural Anti-Allergen Compounds
The regulatory landscape governing natural anti-allergen compounds such as Luteolin and Hesperetin is complex and multifaceted, spanning across different jurisdictions and regulatory bodies. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates these compounds primarily through the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) when marketed as dietary supplements, or as food additives if incorporated into food products.
The European Union employs a more stringent approach through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which requires substantial scientific evidence for health claims related to allergen reduction. Novel Food Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 is particularly relevant for innovative applications of these flavonoids, requiring comprehensive safety assessments before market authorization.
In Asia, regulatory frameworks vary significantly. Japan's Foods for Specified Health Uses (FOSHU) system provides a pathway for anti-allergen compounds with demonstrated efficacy, while China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has established specific guidelines for traditional herbal preparations containing these flavonoids.
International harmonization efforts are being led by the Codex Alimentarius Commission, which is developing standards for bioactive compounds including flavonoids. These standards aim to facilitate global trade while ensuring consumer safety across different regulatory environments.
Specific to allergen reduction claims, regulatory bodies typically require clinical evidence demonstrating mechanism of action, efficacy, and safety. For Luteolin and Hesperetin, this includes documentation of their anti-inflammatory pathways, mast cell stabilization properties, and histamine inhibition capabilities. The required evidence threshold varies by jurisdiction but generally includes in vitro studies, animal models, and human clinical trials.
Recent regulatory developments include the FDA's 2022 guidance on substantiating structure-function claims for anti-allergenic compounds and the EFSA's updated scientific opinion on flavonoid safety assessments. These developments reflect growing regulatory recognition of natural compounds' potential in allergen management.
Compliance challenges for manufacturers include standardization of active compounds, quality control measures, and appropriate labeling requirements. The natural variability in flavonoid content across plant sources necessitates robust analytical methods to ensure consistent dosing and efficacy in final products.
Future regulatory trends point toward increased scrutiny of safety profiles, particularly regarding potential drug interactions, while simultaneously developing accelerated approval pathways for natural compounds with substantial supporting evidence.
The European Union employs a more stringent approach through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which requires substantial scientific evidence for health claims related to allergen reduction. Novel Food Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 is particularly relevant for innovative applications of these flavonoids, requiring comprehensive safety assessments before market authorization.
In Asia, regulatory frameworks vary significantly. Japan's Foods for Specified Health Uses (FOSHU) system provides a pathway for anti-allergen compounds with demonstrated efficacy, while China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has established specific guidelines for traditional herbal preparations containing these flavonoids.
International harmonization efforts are being led by the Codex Alimentarius Commission, which is developing standards for bioactive compounds including flavonoids. These standards aim to facilitate global trade while ensuring consumer safety across different regulatory environments.
Specific to allergen reduction claims, regulatory bodies typically require clinical evidence demonstrating mechanism of action, efficacy, and safety. For Luteolin and Hesperetin, this includes documentation of their anti-inflammatory pathways, mast cell stabilization properties, and histamine inhibition capabilities. The required evidence threshold varies by jurisdiction but generally includes in vitro studies, animal models, and human clinical trials.
Recent regulatory developments include the FDA's 2022 guidance on substantiating structure-function claims for anti-allergenic compounds and the EFSA's updated scientific opinion on flavonoid safety assessments. These developments reflect growing regulatory recognition of natural compounds' potential in allergen management.
Compliance challenges for manufacturers include standardization of active compounds, quality control measures, and appropriate labeling requirements. The natural variability in flavonoid content across plant sources necessitates robust analytical methods to ensure consistent dosing and efficacy in final products.
Future regulatory trends point toward increased scrutiny of safety profiles, particularly regarding potential drug interactions, while simultaneously developing accelerated approval pathways for natural compounds with substantial supporting evidence.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!