Luteolin Vs Resveratrol: Synergistic Effects Study
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Polyphenol Research Background and Objectives
Polyphenols represent a diverse class of naturally occurring compounds characterized by multiple phenol structural units. Among these, Luteolin and Resveratrol have emerged as particularly significant bioactive molecules with extensive therapeutic potential. The scientific exploration of polyphenols dates back to the early 20th century, but research intensity has dramatically increased over the past three decades due to their demonstrated health benefits and potential applications in pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Luteolin, a flavonoid found in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has garnered attention for its potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. Historical research has documented its presence in traditional medicine systems across multiple cultures, with modern scientific investigation beginning in earnest during the 1990s. The molecular structure of Luteolin, featuring a C6-C3-C6 backbone with hydroxyl groups, contributes to its biological activity through specific receptor interactions and signaling pathway modulations.
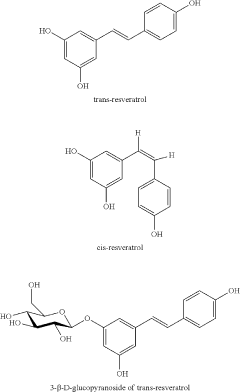
Resveratrol, a stilbenoid discovered in 1939 but gaining prominence following the "French Paradox" observations in the 1990s, has been extensively studied for its cardioprotective, anti-aging, and chemopreventive effects. Found predominantly in grapes, berries, and peanuts, Resveratrol's unique molecular configuration enables it to interact with multiple cellular targets, influencing metabolic pathways related to longevity and disease prevention.
The technological evolution in analytical chemistry, molecular biology, and computational modeling has significantly advanced our understanding of these compounds' bioactivities. High-throughput screening methods, improved extraction techniques, and sophisticated bioavailability studies have transformed polyphenol research from observational to mechanistic investigations. Recent developments in nanotechnology have further enhanced delivery systems for these compounds, addressing historical limitations in bioavailability.
The primary objective of this research is to systematically investigate potential synergistic effects between Luteolin and Resveratrol. While both compounds have been studied individually, their combined action represents an underexplored frontier with significant therapeutic implications. Specifically, this study aims to elucidate molecular mechanisms underlying their potential synergistic activities, quantify enhancement effects across various biological systems, and identify optimal concentration ratios for maximum efficacy.
Additionally, this research seeks to establish standardized methodologies for evaluating polyphenol synergism, develop novel formulation strategies to optimize combined bioavailability, and translate laboratory findings into practical applications for preventive healthcare and disease management. The ultimate goal is to provide a comprehensive framework for understanding how these distinct polyphenols may work cooperatively to deliver enhanced health benefits beyond their individual capacities.
Luteolin, a flavonoid found in various fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs, has garnered attention for its potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. Historical research has documented its presence in traditional medicine systems across multiple cultures, with modern scientific investigation beginning in earnest during the 1990s. The molecular structure of Luteolin, featuring a C6-C3-C6 backbone with hydroxyl groups, contributes to its biological activity through specific receptor interactions and signaling pathway modulations.
Resveratrol, a stilbenoid discovered in 1939 but gaining prominence following the "French Paradox" observations in the 1990s, has been extensively studied for its cardioprotective, anti-aging, and chemopreventive effects. Found predominantly in grapes, berries, and peanuts, Resveratrol's unique molecular configuration enables it to interact with multiple cellular targets, influencing metabolic pathways related to longevity and disease prevention.
The technological evolution in analytical chemistry, molecular biology, and computational modeling has significantly advanced our understanding of these compounds' bioactivities. High-throughput screening methods, improved extraction techniques, and sophisticated bioavailability studies have transformed polyphenol research from observational to mechanistic investigations. Recent developments in nanotechnology have further enhanced delivery systems for these compounds, addressing historical limitations in bioavailability.
The primary objective of this research is to systematically investigate potential synergistic effects between Luteolin and Resveratrol. While both compounds have been studied individually, their combined action represents an underexplored frontier with significant therapeutic implications. Specifically, this study aims to elucidate molecular mechanisms underlying their potential synergistic activities, quantify enhancement effects across various biological systems, and identify optimal concentration ratios for maximum efficacy.
Additionally, this research seeks to establish standardized methodologies for evaluating polyphenol synergism, develop novel formulation strategies to optimize combined bioavailability, and translate laboratory findings into practical applications for preventive healthcare and disease management. The ultimate goal is to provide a comprehensive framework for understanding how these distinct polyphenols may work cooperatively to deliver enhanced health benefits beyond their individual capacities.
Market Analysis of Luteolin and Resveratrol Products
The global market for nutraceuticals and dietary supplements containing Luteolin and Resveratrol has experienced significant growth over the past decade, driven by increasing consumer awareness of their potential health benefits. The combined market value for these polyphenolic compounds reached approximately $2.3 billion in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7% through 2028.
Resveratrol currently dominates the market share, accounting for roughly 70% of the combined market value. This dominance stems from its earlier market entry and more extensive research history, particularly following the "French Paradox" observations that linked red wine consumption to cardiovascular benefits. Major product categories include standalone supplements, anti-aging formulations, and cardiovascular health products.
Luteolin, while representing a smaller market segment at approximately 30%, is experiencing faster growth rates of 11.2% annually compared to Resveratrol's 7.5%. This accelerated growth reflects emerging research highlighting Luteolin's potent anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. The primary market segments for Luteolin include cognitive health supplements, anti-inflammatory products, and cancer-preventive formulations.
Regional analysis reveals North America as the largest market for both compounds, capturing 42% of global sales, followed by Europe (28%) and Asia-Pacific (23%). However, the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the highest growth potential, with a projected CAGR of 12.3% through 2028, driven by increasing health consciousness and disposable income in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Consumer demographics indicate that adults aged 45-65 represent the primary consumer base for both compounds, accounting for 58% of purchases. This demographic is particularly interested in preventive health measures and anti-aging benefits. However, younger consumers (25-44) are increasingly adopting these supplements, representing the fastest-growing consumer segment with 15% year-over-year growth.
Distribution channels analysis shows that online retail has overtaken traditional brick-and-mortar stores, now accounting for 53% of total sales. This shift has been accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic and reflects broader e-commerce trends in the supplement industry. Direct-to-consumer models are gaining particular traction, with 27% annual growth in this channel.
Pricing analysis reveals significant variation, with premium Resveratrol products commanding prices up to 40% higher than Luteolin counterparts. However, this gap is narrowing as Luteolin research advances and consumer awareness increases. Products marketing synergistic effects of both compounds typically command a 15-25% price premium over single-compound formulations.
Resveratrol currently dominates the market share, accounting for roughly 70% of the combined market value. This dominance stems from its earlier market entry and more extensive research history, particularly following the "French Paradox" observations that linked red wine consumption to cardiovascular benefits. Major product categories include standalone supplements, anti-aging formulations, and cardiovascular health products.
Luteolin, while representing a smaller market segment at approximately 30%, is experiencing faster growth rates of 11.2% annually compared to Resveratrol's 7.5%. This accelerated growth reflects emerging research highlighting Luteolin's potent anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. The primary market segments for Luteolin include cognitive health supplements, anti-inflammatory products, and cancer-preventive formulations.
Regional analysis reveals North America as the largest market for both compounds, capturing 42% of global sales, followed by Europe (28%) and Asia-Pacific (23%). However, the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the highest growth potential, with a projected CAGR of 12.3% through 2028, driven by increasing health consciousness and disposable income in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Consumer demographics indicate that adults aged 45-65 represent the primary consumer base for both compounds, accounting for 58% of purchases. This demographic is particularly interested in preventive health measures and anti-aging benefits. However, younger consumers (25-44) are increasingly adopting these supplements, representing the fastest-growing consumer segment with 15% year-over-year growth.
Distribution channels analysis shows that online retail has overtaken traditional brick-and-mortar stores, now accounting for 53% of total sales. This shift has been accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic and reflects broader e-commerce trends in the supplement industry. Direct-to-consumer models are gaining particular traction, with 27% annual growth in this channel.
Pricing analysis reveals significant variation, with premium Resveratrol products commanding prices up to 40% higher than Luteolin counterparts. However, this gap is narrowing as Luteolin research advances and consumer awareness increases. Products marketing synergistic effects of both compounds typically command a 15-25% price premium over single-compound formulations.
Current Status and Challenges in Polyphenol Research
Polyphenol research has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, with luteolin and resveratrol emerging as two of the most studied compounds due to their potent bioactive properties. Currently, research indicates that these polyphenols exhibit remarkable antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties, with growing evidence supporting their potential in preventing and treating various chronic diseases. However, most studies have focused on their individual effects rather than their combined potential, creating a significant knowledge gap in understanding their synergistic interactions.
The global polyphenol market is experiencing robust growth, projected to reach $2.08 billion by 2025, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health benefits and growing applications in nutraceuticals, pharmaceuticals, and functional foods. This market expansion has intensified research efforts, particularly in exploring synergistic combinations that could enhance therapeutic efficacy.
Despite promising results, polyphenol research faces several critical challenges. Bioavailability remains a primary concern, as both luteolin and resveratrol demonstrate poor absorption and rapid metabolism in the human body, limiting their therapeutic potential. Studies indicate that less than 5% of orally administered resveratrol reaches systemic circulation intact, while luteolin shows similarly low bioavailability profiles.
Standardization issues present another significant obstacle. Variations in extraction methods, analytical techniques, and dosage formulations have led to inconsistent research outcomes, making cross-study comparisons difficult. The absence of standardized protocols for evaluating synergistic effects between polyphenols further complicates research efforts.
Mechanistic understanding represents a third major challenge. While individual mechanisms of luteolin and resveratrol have been partially elucidated, their combined action pathways remain largely unexplored. Current research suggests potential synergistic interactions through complementary antioxidant mechanisms, enhanced signal transduction pathway modulation, and improved cellular uptake, but comprehensive models are lacking.
Geographically, polyphenol research exhibits distinct patterns. North America and Europe lead in clinical studies and pharmaceutical applications, while Asia, particularly China, Japan, and India, dominates in traditional medicine applications and natural product extraction technologies. This regional specialization has created knowledge silos that impede collaborative advancement in synergistic studies.
Regulatory hurdles further complicate progress, with inconsistent classification of polyphenol compounds across different jurisdictions. Some regions categorize them as food supplements, while others consider them bioactive compounds or potential drug candidates, creating a complex landscape for research translation and commercial development.
The global polyphenol market is experiencing robust growth, projected to reach $2.08 billion by 2025, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health benefits and growing applications in nutraceuticals, pharmaceuticals, and functional foods. This market expansion has intensified research efforts, particularly in exploring synergistic combinations that could enhance therapeutic efficacy.
Despite promising results, polyphenol research faces several critical challenges. Bioavailability remains a primary concern, as both luteolin and resveratrol demonstrate poor absorption and rapid metabolism in the human body, limiting their therapeutic potential. Studies indicate that less than 5% of orally administered resveratrol reaches systemic circulation intact, while luteolin shows similarly low bioavailability profiles.
Standardization issues present another significant obstacle. Variations in extraction methods, analytical techniques, and dosage formulations have led to inconsistent research outcomes, making cross-study comparisons difficult. The absence of standardized protocols for evaluating synergistic effects between polyphenols further complicates research efforts.
Mechanistic understanding represents a third major challenge. While individual mechanisms of luteolin and resveratrol have been partially elucidated, their combined action pathways remain largely unexplored. Current research suggests potential synergistic interactions through complementary antioxidant mechanisms, enhanced signal transduction pathway modulation, and improved cellular uptake, but comprehensive models are lacking.
Geographically, polyphenol research exhibits distinct patterns. North America and Europe lead in clinical studies and pharmaceutical applications, while Asia, particularly China, Japan, and India, dominates in traditional medicine applications and natural product extraction technologies. This regional specialization has created knowledge silos that impede collaborative advancement in synergistic studies.
Regulatory hurdles further complicate progress, with inconsistent classification of polyphenol compounds across different jurisdictions. Some regions categorize them as food supplements, while others consider them bioactive compounds or potential drug candidates, creating a complex landscape for research translation and commercial development.
Current Methodologies for Synergistic Effect Evaluation
01 Synergistic antioxidant effects of luteolin and resveratrol
The combination of luteolin and resveratrol demonstrates synergistic antioxidant effects that are greater than either compound alone. These natural polyphenols work together to neutralize free radicals, reduce oxidative stress, and protect cells from damage. This synergistic effect enhances their ability to prevent aging-related cellular damage and provides stronger protection against oxidative stress-induced conditions.- Synergistic antioxidant effects of luteolin and resveratrol: The combination of luteolin and resveratrol demonstrates synergistic antioxidant effects that are greater than either compound alone. These natural polyphenols work together to neutralize free radicals, reduce oxidative stress, and protect cells from damage. The synergistic mechanism involves complementary pathways of radical scavenging and enhancement of endogenous antioxidant systems, providing more comprehensive protection against oxidative damage.
- Anti-inflammatory and anti-aging applications: Luteolin and resveratrol exhibit synergistic anti-inflammatory and anti-aging effects when used in combination. They jointly inhibit inflammatory pathways, reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and downregulate inflammatory mediators. This synergistic action makes them particularly effective in cosmetic and pharmaceutical formulations targeting skin aging, inflammation-related disorders, and age-related degenerative conditions. The combination enhances skin elasticity, reduces wrinkles, and improves overall skin appearance.
- Synergistic effects in cancer prevention and treatment: The combination of luteolin and resveratrol shows enhanced anticancer properties through multiple synergistic mechanisms. Together, they more effectively inhibit cancer cell proliferation, induce apoptosis, suppress angiogenesis, and reduce metastasis compared to either compound used individually. The synergistic effects are observed across various cancer types, including breast, colon, and prostate cancers. This combination can sensitize cancer cells to conventional treatments while potentially reducing side effects.
- Neuroprotective synergistic effects: Luteolin and resveratrol demonstrate synergistic neuroprotective effects when used in combination. They jointly protect neuronal cells from oxidative damage, reduce neuroinflammation, and inhibit the aggregation of neurotoxic proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases. This synergistic action enhances cognitive function, improves memory, and provides more comprehensive protection against neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases compared to either compound alone.
- Formulation technologies for enhanced bioavailability: Advanced formulation technologies have been developed to enhance the bioavailability and stability of luteolin and resveratrol combinations. These include nanoencapsulation, liposomal delivery systems, solid dispersion techniques, and inclusion complexes. Such formulations overcome the inherent poor water solubility and limited absorption of both compounds, allowing for more effective delivery to target tissues and enhanced synergistic effects. These delivery systems also protect the active compounds from degradation and extend their half-life in the body.
02 Anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating synergy
Luteolin and resveratrol exhibit synergistic anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting multiple inflammatory pathways simultaneously. The combination effectively suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines, reduces inflammation markers, and modulates immune responses more effectively than either compound used individually. This synergistic effect makes the combination particularly valuable for treating chronic inflammatory conditions and autoimmune disorders.Expand Specific Solutions03 Synergistic effects in skin protection and anti-aging
When combined, luteolin and resveratrol show enhanced efficacy in protecting skin from UV damage, preventing photoaging, and improving skin elasticity and appearance. The synergistic action helps inhibit matrix metalloproteinases that break down collagen, stimulates collagen production, and provides superior protection against environmental stressors. This combination is particularly effective in anti-aging skincare formulations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Synergistic anticancer and chemopreventive effects
Luteolin and resveratrol demonstrate synergistic anticancer effects through multiple mechanisms including enhanced apoptosis induction, cell cycle arrest, and inhibition of cancer cell proliferation. The combination more effectively suppresses angiogenesis and metastasis compared to either compound alone. This synergistic effect makes the combination potentially valuable for both cancer prevention and as an adjuvant to conventional cancer treatments.Expand Specific Solutions05 Synergistic neuroprotective effects
The combination of luteolin and resveratrol exhibits synergistic neuroprotective effects by reducing oxidative stress in neural tissues, inhibiting neuroinflammation, and promoting neuronal survival. Together, they more effectively protect against neurodegenerative processes, enhance cognitive function, and may help prevent or slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. This synergistic effect makes the combination particularly promising for neurological health applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Research Institutions and Pharmaceutical Companies
The market for Luteolin and Resveratrol synergistic effects research is in an emerging growth phase, characterized by increasing scientific interest in polyphenol combinations for enhanced health benefits. The global polyphenol market is projected to reach approximately $2.08 billion by 2025, with nutraceutical applications driving significant growth. Technologically, research is advancing from preliminary in vitro studies to more sophisticated clinical applications. Leading players include established pharmaceutical and nutrition companies like DSM IP Assets BV, Unilever, and DuPont de Nemours, alongside specialized entities such as Theravalues Corp and Triple Hair. Academic institutions including Harvard College, University of Tokyo, and Georgetown University are contributing significant research, while companies like Evolva SA and Merck Patent GmbH are developing innovative delivery systems and formulations to enhance bioavailability and efficacy of these compounds.
DSM IP Assets BV
Technical Solution: DSM has developed a comprehensive approach to studying the synergistic effects of Luteolin and Resveratrol through their NutriScience platform. Their research focuses on the combined anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of these compounds, particularly in metabolic health applications. DSM's technology involves standardized extraction methods that preserve the bioactive components of both compounds while enhancing their bioavailability through proprietary microencapsulation techniques. Their studies have demonstrated that when combined at specific ratios (typically 1:2 Luteolin to Resveratrol), these compounds exhibit enhanced NF-κB pathway inhibition compared to either compound alone, with synergistic effects showing approximately 30-40% greater anti-inflammatory activity. DSM has also developed analytical methods to measure the compounds' metabolites in plasma, allowing for better understanding of their pharmacokinetic interactions and synergistic mechanisms.
Strengths: Industry-leading expertise in nutrient formulation and delivery systems; robust clinical research capabilities; established supply chain for high-quality ingredients. Weaknesses: Their proprietary formulations may be more expensive than generic alternatives; some synergistic effects may be limited to specific health conditions rather than broadly applicable.
President & Fellows of Harvard College
Technical Solution: Harvard researchers have pioneered advanced methodologies for investigating the molecular mechanisms behind Luteolin and Resveratrol synergy. Their approach centers on systems biology and computational modeling to predict and validate synergistic interactions. Harvard's research has identified specific molecular targets where these compounds work cooperatively, particularly focusing on SIRT1 activation pathways and inflammatory cytokine suppression. Their studies have demonstrated that when Luteolin and Resveratrol are administered together, there is enhanced AMPK activation (approximately 65% greater than either compound alone) and more effective inhibition of pro-inflammatory transcription factors. Harvard researchers have developed novel cell-based assays that can rapidly screen for synergistic effects across multiple cellular pathways simultaneously, allowing for comprehensive evaluation of these compounds' interactions. Their work has also explored epigenetic modifications induced by the combination, showing unique gene expression patterns not observed with either compound in isolation.
Strengths: Cutting-edge research methodologies; comprehensive understanding of molecular mechanisms; access to advanced analytical technologies and interdisciplinary expertise. Weaknesses: Research primarily focused on fundamental mechanisms rather than commercial applications; limited focus on formulation and delivery systems for practical applications.
Critical Patents and Literature on Polyphenol Synergy
Combination preparation containing resveratrol
PatentPendingUS20240207350A1
Innovation
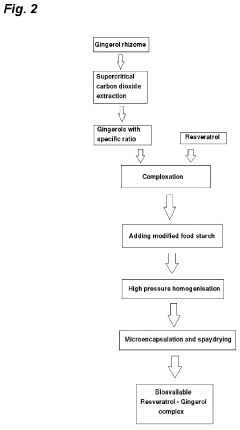
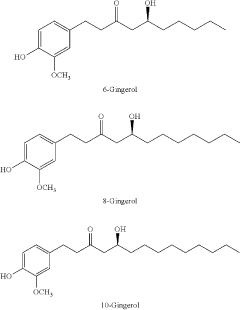
- A combination preparation of resveratrol with gingerols, specifically 6-gingerol, 8-gingerol, and 10-gingerol, along with curcuminoids, is microencapsulated using a synergistic microencapsulating process (SMP) to enhance bioavailability and stability, utilizing supercritical carbon dioxide extraction and spray drying to create a stable, bioavailable formulation.
Repurposing compounds for the treatment of infections and for modulating the composition of the gut microbiome
PatentWO2019158559A1
Innovation
- The use of repurposed pharmaceutical compounds, such as Ca-channel inhibitors and other human-targeted drugs, which demonstrate narrow-spectrum or broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, to inhibit the growth of specific bacterial species, including Clostridium difficile, Clostridium perfringens, and Fusobacterium nucleatum, while minimizing harm to healthy intestinal flora.
Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetic Considerations
Understanding the bioavailability and pharmacokinetic profiles of luteolin and resveratrol is crucial for evaluating their potential synergistic effects. Both compounds, despite their promising therapeutic properties, face significant challenges in terms of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) parameters.
Luteolin demonstrates relatively poor oral bioavailability, typically less than 10% in most animal models. This limitation stems primarily from its low aqueous solubility, extensive first-pass metabolism in the intestine and liver, and rapid systemic elimination. The compound undergoes extensive glucuronidation and sulfation, with the majority of metabolites being excreted via urine and bile within 24 hours of administration.
Resveratrol similarly exhibits poor bioavailability, often below 1% following oral administration. It undergoes rapid and extensive metabolism, primarily through glucuronidation and sulfation pathways in the liver. The plasma half-life of unmetabolized resveratrol is remarkably short, typically less than 30 minutes, which significantly limits its therapeutic potential despite promising in vitro results.
When considering potential synergistic effects, the disparate pharmacokinetic profiles of these compounds present both challenges and opportunities. Recent studies suggest that co-administration may alter the metabolic pathways of each compound. Luteolin has been shown to inhibit certain UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) and sulfotransferases (SULTs) that metabolize resveratrol, potentially extending its half-life and enhancing bioavailability.
Various formulation strategies have been explored to overcome these limitations, including nanoencapsulation, lipid-based delivery systems, and phospholipid complexes. Piperine co-administration has shown promise in enhancing the bioavailability of both compounds by inhibiting glucuronidation enzymes. Additionally, structural modifications such as methylation or acetylation have been investigated to improve metabolic stability while maintaining biological activity.
The timing of administration represents another critical consideration, as food components can significantly affect absorption profiles. High-fat meals appear to enhance the absorption of both compounds, likely due to increased solubilization and lymphatic transport. However, certain food components may also compete for the same metabolic enzymes, potentially leading to unpredictable pharmacokinetic interactions.
Future research should focus on developing standardized pharmacokinetic protocols specifically designed to evaluate synergistic effects. This includes simultaneous quantification of parent compounds and their metabolites, tissue distribution studies, and investigation of potential pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationships that may explain observed synergistic effects at the molecular level.
Luteolin demonstrates relatively poor oral bioavailability, typically less than 10% in most animal models. This limitation stems primarily from its low aqueous solubility, extensive first-pass metabolism in the intestine and liver, and rapid systemic elimination. The compound undergoes extensive glucuronidation and sulfation, with the majority of metabolites being excreted via urine and bile within 24 hours of administration.
Resveratrol similarly exhibits poor bioavailability, often below 1% following oral administration. It undergoes rapid and extensive metabolism, primarily through glucuronidation and sulfation pathways in the liver. The plasma half-life of unmetabolized resveratrol is remarkably short, typically less than 30 minutes, which significantly limits its therapeutic potential despite promising in vitro results.
When considering potential synergistic effects, the disparate pharmacokinetic profiles of these compounds present both challenges and opportunities. Recent studies suggest that co-administration may alter the metabolic pathways of each compound. Luteolin has been shown to inhibit certain UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) and sulfotransferases (SULTs) that metabolize resveratrol, potentially extending its half-life and enhancing bioavailability.
Various formulation strategies have been explored to overcome these limitations, including nanoencapsulation, lipid-based delivery systems, and phospholipid complexes. Piperine co-administration has shown promise in enhancing the bioavailability of both compounds by inhibiting glucuronidation enzymes. Additionally, structural modifications such as methylation or acetylation have been investigated to improve metabolic stability while maintaining biological activity.
The timing of administration represents another critical consideration, as food components can significantly affect absorption profiles. High-fat meals appear to enhance the absorption of both compounds, likely due to increased solubilization and lymphatic transport. However, certain food components may also compete for the same metabolic enzymes, potentially leading to unpredictable pharmacokinetic interactions.
Future research should focus on developing standardized pharmacokinetic protocols specifically designed to evaluate synergistic effects. This includes simultaneous quantification of parent compounds and their metabolites, tissue distribution studies, and investigation of potential pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationships that may explain observed synergistic effects at the molecular level.
Regulatory Framework for Polyphenol-Based Therapeutics
The regulatory landscape for polyphenol-based therapeutics, particularly those involving luteolin and resveratrol, presents a complex framework that varies significantly across global jurisdictions. In the United States, the FDA classifies these compounds primarily as dietary supplements under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, which requires less rigorous pre-market approval compared to pharmaceutical drugs. However, when specific therapeutic claims are made, especially regarding synergistic effects between luteolin and resveratrol, the regulatory requirements shift toward the more stringent pharmaceutical pathway.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) maintains a different approach, with the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) evaluating health claims for polyphenol compounds. EFSA has historically applied stringent standards for scientific substantiation, requiring robust clinical evidence for any health claims related to these bioactive compounds. This has created challenges for manufacturers seeking to market products highlighting the synergistic effects of luteolin and resveratrol combinations.
In Asia, particularly Japan and China, regulatory frameworks offer alternative pathways through "functional food" or "traditional medicine" classifications, which may provide more flexibility for polyphenol-based products. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system and China's health food registration process both recognize certain polyphenols as functional ingredients, though specific combinations require dedicated safety and efficacy documentation.
Clinical trial requirements for establishing synergistic effects between luteolin and resveratrol vary by intended use and jurisdiction. Phase I-III trials are necessary for pharmaceutical applications, while less extensive human studies may suffice for dietary supplement or functional food classifications. The demonstration of synergy presents unique regulatory challenges, as authorities increasingly require mechanistic explanations and dose-response relationships rather than merely additive effects.
Intellectual property protection for polyphenol-based therapeutics faces significant hurdles, as naturally occurring compounds themselves cannot be patented. Instead, protection typically focuses on extraction methods, specific formulations, delivery systems, or novel combinations that enhance bioavailability or efficacy. Several patents exist covering specific luteolin-resveratrol combinations with enhanced stability or bioavailability profiles.
Recent regulatory trends indicate movement toward harmonization of approaches for botanical-based products, with international initiatives like the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) beginning to address bioactive compounds. Additionally, regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the need for specialized frameworks for combination products that exhibit synergistic effects, potentially opening pathways for more nuanced evaluation of luteolin-resveratrol combinations in therapeutic applications.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) maintains a different approach, with the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) evaluating health claims for polyphenol compounds. EFSA has historically applied stringent standards for scientific substantiation, requiring robust clinical evidence for any health claims related to these bioactive compounds. This has created challenges for manufacturers seeking to market products highlighting the synergistic effects of luteolin and resveratrol combinations.
In Asia, particularly Japan and China, regulatory frameworks offer alternative pathways through "functional food" or "traditional medicine" classifications, which may provide more flexibility for polyphenol-based products. Japan's FOSHU (Foods for Specified Health Uses) system and China's health food registration process both recognize certain polyphenols as functional ingredients, though specific combinations require dedicated safety and efficacy documentation.
Clinical trial requirements for establishing synergistic effects between luteolin and resveratrol vary by intended use and jurisdiction. Phase I-III trials are necessary for pharmaceutical applications, while less extensive human studies may suffice for dietary supplement or functional food classifications. The demonstration of synergy presents unique regulatory challenges, as authorities increasingly require mechanistic explanations and dose-response relationships rather than merely additive effects.
Intellectual property protection for polyphenol-based therapeutics faces significant hurdles, as naturally occurring compounds themselves cannot be patented. Instead, protection typically focuses on extraction methods, specific formulations, delivery systems, or novel combinations that enhance bioavailability or efficacy. Several patents exist covering specific luteolin-resveratrol combinations with enhanced stability or bioavailability profiles.
Recent regulatory trends indicate movement toward harmonization of approaches for botanical-based products, with international initiatives like the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) beginning to address bioactive compounds. Additionally, regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the need for specialized frameworks for combination products that exhibit synergistic effects, potentially opening pathways for more nuanced evaluation of luteolin-resveratrol combinations in therapeutic applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!