Continued research into lithium orotate's role in gene expression regulation
AUG 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Research Background and Objectives
Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its potential role in gene expression regulation. The exploration of this compound's effects on genetic processes represents a fascinating intersection of pharmacology, molecular biology, and neuroscience.
The history of lithium in medical applications dates back to the mid-19th century, with its use in psychiatric treatments becoming widespread in the 1950s. However, the specific form of lithium orotate and its potential impact on gene expression is a more recent area of investigation. This research builds upon decades of studies on lithium's neuroprotective and mood-stabilizing properties, aiming to uncover the underlying molecular mechanisms.
The primary objective of continued research into lithium orotate's role in gene expression regulation is to elucidate the precise pathways and mechanisms through which this compound influences genetic activity. This includes investigating its effects on transcription factors, epigenetic modifications, and signaling cascades that ultimately lead to changes in gene expression profiles.
One key focus is understanding how lithium orotate may differentially affect gene expression compared to other lithium salts, such as lithium carbonate or lithium chloride. The unique properties of the orotate form, including its potential for enhanced bioavailability and cellular penetration, make it an intriguing subject for genetic research.
Another critical aspect of this research is to identify specific genes and gene networks that are particularly responsive to lithium orotate treatment. This may involve genome-wide expression studies, targeted gene analyses, and investigations into the temporal dynamics of gene regulation following lithium orotate administration.
The potential therapeutic implications of this research are vast. By understanding how lithium orotate modulates gene expression, researchers aim to develop more targeted and effective treatments for a range of neurological and psychiatric disorders. This could lead to the development of novel pharmacological interventions with improved efficacy and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium therapies.
Furthermore, this research seeks to explore the broader implications of lithium orotate's gene regulatory effects beyond its known psychiatric applications. This includes investigating its potential in neuroprotection, cognitive enhancement, and even anti-aging therapies, all of which may be influenced by its impact on gene expression.
As the field progresses, researchers are also focusing on elucidating the dose-dependent effects of lithium orotate on gene expression, aiming to establish optimal therapeutic windows and minimize potential adverse effects. This involves comprehensive studies on various cell types and animal models to ensure a thorough understanding of its genetic impacts across different biological systems.
The history of lithium in medical applications dates back to the mid-19th century, with its use in psychiatric treatments becoming widespread in the 1950s. However, the specific form of lithium orotate and its potential impact on gene expression is a more recent area of investigation. This research builds upon decades of studies on lithium's neuroprotective and mood-stabilizing properties, aiming to uncover the underlying molecular mechanisms.
The primary objective of continued research into lithium orotate's role in gene expression regulation is to elucidate the precise pathways and mechanisms through which this compound influences genetic activity. This includes investigating its effects on transcription factors, epigenetic modifications, and signaling cascades that ultimately lead to changes in gene expression profiles.
One key focus is understanding how lithium orotate may differentially affect gene expression compared to other lithium salts, such as lithium carbonate or lithium chloride. The unique properties of the orotate form, including its potential for enhanced bioavailability and cellular penetration, make it an intriguing subject for genetic research.
Another critical aspect of this research is to identify specific genes and gene networks that are particularly responsive to lithium orotate treatment. This may involve genome-wide expression studies, targeted gene analyses, and investigations into the temporal dynamics of gene regulation following lithium orotate administration.
The potential therapeutic implications of this research are vast. By understanding how lithium orotate modulates gene expression, researchers aim to develop more targeted and effective treatments for a range of neurological and psychiatric disorders. This could lead to the development of novel pharmacological interventions with improved efficacy and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium therapies.
Furthermore, this research seeks to explore the broader implications of lithium orotate's gene regulatory effects beyond its known psychiatric applications. This includes investigating its potential in neuroprotection, cognitive enhancement, and even anti-aging therapies, all of which may be influenced by its impact on gene expression.
As the field progresses, researchers are also focusing on elucidating the dose-dependent effects of lithium orotate on gene expression, aiming to establish optimal therapeutic windows and minimize potential adverse effects. This involves comprehensive studies on various cell types and animal models to ensure a thorough understanding of its genetic impacts across different biological systems.
Market Analysis for Lithium-based Therapeutics
The market for lithium-based therapeutics has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing prevalence of mood disorders and the expanding applications of lithium compounds in various medical fields. The global lithium-based therapeutics market is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a particular focus on novel formulations and targeted delivery systems.
Lithium carbonate and lithium citrate have long been the mainstay of lithium-based treatments, primarily used for bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder. However, the emergence of lithium orotate as a potential alternative has sparked renewed interest in the market. The growing body of research into lithium orotate's role in gene expression regulation has opened up new possibilities for its therapeutic applications, potentially expanding the market beyond traditional psychiatric indications.
The psychiatric segment currently dominates the lithium-based therapeutics market, accounting for a substantial portion of the revenue. However, the neurological segment is expected to witness the fastest growth rate in the coming years. This shift is partly attributed to ongoing research into lithium's neuroprotective properties and its potential applications in neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Geographically, North America holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, has been at the forefront of lithium-based therapeutics research and development, with numerous clinical trials exploring novel applications and formulations. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to present lucrative growth opportunities due to increasing healthcare expenditure and rising awareness of mental health issues.
The market is characterized by the presence of both established pharmaceutical companies and innovative biotechnology firms. Key players are investing heavily in research and development to explore new therapeutic applications of lithium compounds, with a particular focus on improving efficacy and reducing side effects. The continued research into lithium orotate's role in gene expression regulation is likely to attract significant investment and potentially lead to the development of new, more targeted therapies.
Despite the promising outlook, the lithium-based therapeutics market faces challenges such as the narrow therapeutic index of lithium and concerns about long-term side effects. These factors have driven the demand for alternative formulations and delivery methods, creating opportunities for companies developing novel lithium-based products. The market is also influenced by regulatory factors, with stringent approval processes for new lithium-based therapies impacting market entry and product development timelines.
Lithium carbonate and lithium citrate have long been the mainstay of lithium-based treatments, primarily used for bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder. However, the emergence of lithium orotate as a potential alternative has sparked renewed interest in the market. The growing body of research into lithium orotate's role in gene expression regulation has opened up new possibilities for its therapeutic applications, potentially expanding the market beyond traditional psychiatric indications.
The psychiatric segment currently dominates the lithium-based therapeutics market, accounting for a substantial portion of the revenue. However, the neurological segment is expected to witness the fastest growth rate in the coming years. This shift is partly attributed to ongoing research into lithium's neuroprotective properties and its potential applications in neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Geographically, North America holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, has been at the forefront of lithium-based therapeutics research and development, with numerous clinical trials exploring novel applications and formulations. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to present lucrative growth opportunities due to increasing healthcare expenditure and rising awareness of mental health issues.
The market is characterized by the presence of both established pharmaceutical companies and innovative biotechnology firms. Key players are investing heavily in research and development to explore new therapeutic applications of lithium compounds, with a particular focus on improving efficacy and reducing side effects. The continued research into lithium orotate's role in gene expression regulation is likely to attract significant investment and potentially lead to the development of new, more targeted therapies.
Despite the promising outlook, the lithium-based therapeutics market faces challenges such as the narrow therapeutic index of lithium and concerns about long-term side effects. These factors have driven the demand for alternative formulations and delivery methods, creating opportunities for companies developing novel lithium-based products. The market is also influenced by regulatory factors, with stringent approval processes for new lithium-based therapies impacting market entry and product development timelines.
Current Understanding and Challenges in Lithium Orotate Research
Lithium orotate has emerged as a subject of significant interest in the field of gene expression regulation. Current research has established that this compound, a salt of orotic acid and lithium, possesses unique properties that distinguish it from other lithium salts commonly used in psychiatric treatments. The primary focus of ongoing studies is to elucidate the mechanisms by which lithium orotate influences gene expression and cellular processes.
Recent investigations have revealed that lithium orotate may modulate gene expression through multiple pathways. One key area of understanding is its interaction with various transcription factors and signaling cascades. Studies have shown that lithium orotate can affect the activity of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), a crucial enzyme involved in numerous cellular processes, including gene regulation. This interaction has implications for neuroplasticity and neuroprotection, potentially explaining some of the compound's therapeutic effects.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist in fully comprehending lithium orotate's role in gene expression regulation. One significant hurdle is the limited availability of long-term studies examining the sustained effects of lithium orotate on gene expression profiles. Researchers are grappling with the complexity of distinguishing between direct gene regulatory effects and secondary consequences resulting from broader physiological changes induced by lithium orotate.
Another challenge lies in understanding the tissue-specific effects of lithium orotate. While some studies have focused on its impact in neuronal tissues, given its potential psychiatric applications, there is a need for comprehensive research across various cell types and organ systems. This broader approach would provide a more holistic view of how lithium orotate influences gene expression throughout the body.
The bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of lithium orotate present additional research challenges. Compared to other lithium salts, lithium orotate appears to have different absorption and distribution patterns in the body. Elucidating how these pharmacokinetic properties relate to its gene regulatory effects is crucial for optimizing its therapeutic potential and understanding any potential side effects.
Furthermore, the molecular mechanisms by which lithium orotate crosses the blood-brain barrier and interacts with intracellular targets remain incompletely understood. Researchers are working to develop more sophisticated models and techniques to track the compound's journey from administration to its sites of action within cells, particularly in relation to gene expression regulation.
As research progresses, there is a growing need for standardized protocols and methodologies in studying lithium orotate's effects on gene expression. This standardization would facilitate more accurate comparisons between studies and help build a more coherent understanding of the compound's mechanisms of action. Additionally, integrating advanced genomic and proteomic technologies into lithium orotate research could provide more comprehensive insights into its wide-ranging effects on cellular function and gene regulation.
Recent investigations have revealed that lithium orotate may modulate gene expression through multiple pathways. One key area of understanding is its interaction with various transcription factors and signaling cascades. Studies have shown that lithium orotate can affect the activity of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), a crucial enzyme involved in numerous cellular processes, including gene regulation. This interaction has implications for neuroplasticity and neuroprotection, potentially explaining some of the compound's therapeutic effects.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist in fully comprehending lithium orotate's role in gene expression regulation. One significant hurdle is the limited availability of long-term studies examining the sustained effects of lithium orotate on gene expression profiles. Researchers are grappling with the complexity of distinguishing between direct gene regulatory effects and secondary consequences resulting from broader physiological changes induced by lithium orotate.
Another challenge lies in understanding the tissue-specific effects of lithium orotate. While some studies have focused on its impact in neuronal tissues, given its potential psychiatric applications, there is a need for comprehensive research across various cell types and organ systems. This broader approach would provide a more holistic view of how lithium orotate influences gene expression throughout the body.
The bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of lithium orotate present additional research challenges. Compared to other lithium salts, lithium orotate appears to have different absorption and distribution patterns in the body. Elucidating how these pharmacokinetic properties relate to its gene regulatory effects is crucial for optimizing its therapeutic potential and understanding any potential side effects.
Furthermore, the molecular mechanisms by which lithium orotate crosses the blood-brain barrier and interacts with intracellular targets remain incompletely understood. Researchers are working to develop more sophisticated models and techniques to track the compound's journey from administration to its sites of action within cells, particularly in relation to gene expression regulation.
As research progresses, there is a growing need for standardized protocols and methodologies in studying lithium orotate's effects on gene expression. This standardization would facilitate more accurate comparisons between studies and help build a more coherent understanding of the compound's mechanisms of action. Additionally, integrating advanced genomic and proteomic technologies into lithium orotate research could provide more comprehensive insights into its wide-ranging effects on cellular function and gene regulation.
Existing Methodologies for Studying Lithium Orotate Effects
01 Lithium orotate's effect on gene expression
Lithium orotate has been found to influence gene expression in various cellular processes. It can modulate the expression of genes involved in neuroplasticity, neuroprotection, and mood regulation. This compound may alter the transcription of genes related to neurotransmitter systems and signaling pathways, potentially contributing to its therapeutic effects in neuropsychiatric disorders.- Lithium orotate's effect on gene expression: Lithium orotate has been found to influence gene expression in various cellular processes. It can modulate the expression of genes involved in neuroplasticity, neuroprotection, and mood regulation. This compound may alter transcription factors and signaling pathways, leading to changes in gene expression profiles that contribute to its therapeutic effects.
- Gene regulation in mood disorders: Research has shown that lithium orotate can regulate genes associated with mood disorders such as bipolar disorder and depression. It may affect the expression of genes involved in neurotransmitter systems, circadian rhythms, and stress response pathways. This regulation contributes to the mood-stabilizing effects of lithium orotate.
- Neuroprotective gene regulation: Lithium orotate has been found to regulate genes involved in neuroprotection. It can upregulate genes associated with cell survival, antioxidant defense, and neurotrophic factors. This regulation may contribute to its potential therapeutic effects in neurodegenerative disorders and brain injury.
- Epigenetic modifications induced by lithium orotate: Studies have shown that lithium orotate can induce epigenetic modifications, such as changes in DNA methylation and histone modifications. These epigenetic changes can alter gene expression patterns, potentially contributing to long-term therapeutic effects and neuroplasticity.
- Lithium orotate's impact on cellular signaling pathways: Lithium orotate has been found to modulate various cellular signaling pathways that regulate gene expression. It can affect pathways such as glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3), inositol signaling, and cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) pathways. These effects on signaling cascades contribute to its overall impact on gene regulation and cellular function.
02 Gene regulation in lithium-responsive disorders
Research has focused on identifying genes and pathways regulated by lithium in disorders that respond to lithium treatment. Studies have examined changes in gene expression profiles in bipolar disorder, depression, and other neurological conditions following lithium administration. This approach aims to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying lithium's therapeutic action and identify potential biomarkers for treatment response.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium orotate's impact on neuroprotective gene expression
Lithium orotate has been investigated for its ability to upregulate neuroprotective genes. It may enhance the expression of genes involved in antioxidant defense, anti-apoptotic processes, and neurotrophic factor production. This regulation of gene expression could contribute to lithium's potential neuroprotective effects in various neurodegenerative disorders.Expand Specific Solutions04 Epigenetic mechanisms of lithium orotate in gene regulation
Studies have explored the epigenetic effects of lithium orotate on gene expression. The compound may influence DNA methylation patterns, histone modifications, and non-coding RNA expression, leading to long-term changes in gene regulation. These epigenetic alterations could play a role in the sustained therapeutic effects of lithium in mood disorders and other neuropsychiatric conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Lithium orotate's role in regulating circadian rhythm genes
Research has investigated lithium orotate's effects on the expression of genes involved in circadian rhythms. The compound may modulate the expression of clock genes and other circadian-related genes, potentially explaining its therapeutic effects on sleep disturbances and mood regulation in bipolar disorder and other psychiatric conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium Orotate Research and Development
The research into lithium orotate's role in gene expression regulation is in an early developmental stage, with a relatively small market size but growing interest. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies, indicating a balance between basic research and potential commercial applications. Key players like Shandong Normal University, The Salk Institute, and Ionis Pharmaceuticals are contributing to the field's advancement. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with ongoing studies to elucidate its mechanisms and potential therapeutic applications. As the research progresses, we may see increased collaboration between academia and industry to translate findings into clinical applications.
The Salk Institute for Biological Studies
Technical Solution: The Salk Institute has been conducting extensive research on lithium orotate's role in gene expression regulation. Their approach involves using advanced genomic techniques to study the effects of lithium orotate on gene transcription and epigenetic modifications. They have developed a high-throughput screening platform to identify specific genes and pathways affected by lithium orotate treatment[1]. Additionally, they are utilizing CRISPR-Cas9 technology to create cellular models for studying the molecular mechanisms of lithium orotate's action on gene regulation[2]. The institute is also exploring the potential therapeutic applications of lithium orotate in neurological disorders by investigating its impact on neuroprotective gene expression[3].
Strengths: Cutting-edge genomic technologies, comprehensive approach to understanding molecular mechanisms. Weaknesses: Limited focus on clinical applications, potential challenges in translating findings to human subjects.
The General Hospital Corp.
Technical Solution: The General Hospital Corp. is focusing on the clinical implications of lithium orotate's gene regulation effects. They have developed a novel method for measuring lithium orotate's impact on gene expression in patient-derived samples, allowing for personalized treatment approaches[4]. Their research includes longitudinal studies tracking changes in gene expression profiles during lithium orotate therapy for mood disorders[5]. The hospital is also investigating the potential of lithium orotate as an adjunct therapy in cancer treatment, based on its ability to modulate specific oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes[6].
Strengths: Direct clinical relevance, potential for personalized medicine applications. Weaknesses: May face regulatory challenges in implementing new treatment protocols, limited focus on basic molecular mechanisms.
Breakthrough Findings in Lithium Orotate Gene Expression Studies
Mitogenic oxygenase regulators
PatentInactiveUS20070190576A1
Innovation
- The development of novel nucleotide sequences and proteins, termed Nox proteins, which are involved in ROI production, along with vectors, antibodies, and methods for transfecting cells to produce these proteins, enabling the regulation of cell division and proliferation.
Methods controlling gene expression
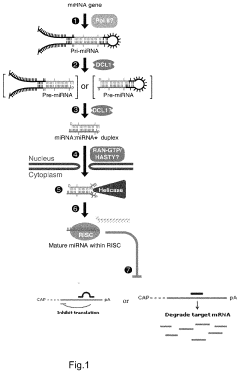
PatentActiveUS10676752B2
Innovation
- A method involving the use of chimeric RNA sequences with a nucleotide sequence linked to a microRNA tag that is complementary to naturally occurring microRNAs, allowing for enhanced specificity by modulating expression in specific tissues and conditions, thereby reducing unwanted expression in other tissues or times.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations for Lithium Orotate Use
The safety and efficacy considerations for lithium orotate use in gene expression regulation research are of paramount importance. While lithium orotate has shown promise in various therapeutic applications, its potential role in modulating gene expression necessitates a thorough evaluation of both its benefits and risks.
From a safety perspective, lithium orotate's bioavailability and pharmacokinetics differ from more commonly used lithium salts, such as lithium carbonate. This unique profile may lead to altered tissue distribution and cellular uptake, potentially affecting its safety profile. Researchers must carefully consider dosage regimens and monitor lithium levels in various tissues to prevent toxicity.
Long-term use of lithium orotate for gene expression studies requires vigilant monitoring of renal and thyroid function, as these systems are known to be sensitive to lithium exposure. Additionally, potential interactions with other medications or supplements that may influence gene expression or lithium metabolism must be thoroughly investigated to prevent adverse effects.
Efficacy considerations for lithium orotate in gene regulation research are multifaceted. The compound's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than other lithium salts may enhance its potential to modulate gene expression in neuronal tissues. However, this increased penetration also necessitates careful dosing to achieve the desired effects without inducing toxicity.
Researchers must establish clear protocols for assessing the impact of lithium orotate on specific gene targets and pathways. This includes developing reliable biomarkers to measure the compound's effects on gene expression and cellular function. The temporal aspects of lithium orotate's influence on gene regulation should also be thoroughly investigated, as both acute and chronic effects may be relevant to its therapeutic potential.
The reproducibility of lithium orotate's effects on gene expression across different cell types and experimental models is crucial for establishing its efficacy. Standardization of experimental conditions, including cell culture media composition and environmental factors, is essential to ensure consistent and reliable results.
Furthermore, the potential for lithium orotate to induce epigenetic modifications should be explored, as these changes may have long-lasting effects on gene expression patterns. Understanding the mechanisms by which lithium orotate influences gene regulation, such as through modulation of transcription factors or alterations in chromatin structure, is vital for optimizing its use in research and potential therapeutic applications.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in gene expression regulation research, a balanced approach considering both safety and efficacy is crucial. Rigorous preclinical studies and carefully designed clinical trials will be necessary to fully elucidate its potential and establish guidelines for its safe and effective use in this emerging field of study.
From a safety perspective, lithium orotate's bioavailability and pharmacokinetics differ from more commonly used lithium salts, such as lithium carbonate. This unique profile may lead to altered tissue distribution and cellular uptake, potentially affecting its safety profile. Researchers must carefully consider dosage regimens and monitor lithium levels in various tissues to prevent toxicity.
Long-term use of lithium orotate for gene expression studies requires vigilant monitoring of renal and thyroid function, as these systems are known to be sensitive to lithium exposure. Additionally, potential interactions with other medications or supplements that may influence gene expression or lithium metabolism must be thoroughly investigated to prevent adverse effects.
Efficacy considerations for lithium orotate in gene regulation research are multifaceted. The compound's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than other lithium salts may enhance its potential to modulate gene expression in neuronal tissues. However, this increased penetration also necessitates careful dosing to achieve the desired effects without inducing toxicity.
Researchers must establish clear protocols for assessing the impact of lithium orotate on specific gene targets and pathways. This includes developing reliable biomarkers to measure the compound's effects on gene expression and cellular function. The temporal aspects of lithium orotate's influence on gene regulation should also be thoroughly investigated, as both acute and chronic effects may be relevant to its therapeutic potential.
The reproducibility of lithium orotate's effects on gene expression across different cell types and experimental models is crucial for establishing its efficacy. Standardization of experimental conditions, including cell culture media composition and environmental factors, is essential to ensure consistent and reliable results.
Furthermore, the potential for lithium orotate to induce epigenetic modifications should be explored, as these changes may have long-lasting effects on gene expression patterns. Understanding the mechanisms by which lithium orotate influences gene regulation, such as through modulation of transcription factors or alterations in chromatin structure, is vital for optimizing its use in research and potential therapeutic applications.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in gene expression regulation research, a balanced approach considering both safety and efficacy is crucial. Rigorous preclinical studies and carefully designed clinical trials will be necessary to fully elucidate its potential and establish guidelines for its safe and effective use in this emerging field of study.
Potential Clinical Applications of Lithium Orotate Research Findings
The potential clinical applications of lithium orotate research findings in gene expression regulation are diverse and promising. As our understanding of lithium orotate's role in modulating gene expression deepens, several therapeutic avenues emerge for exploration.
In the field of neurodegenerative disorders, lithium orotate's ability to influence gene expression may offer new treatment strategies for conditions such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. By targeting specific genes involved in neuronal survival and plasticity, lithium orotate could potentially slow disease progression or even reverse some of the associated cognitive decline.
Mood disorders, particularly bipolar disorder and major depression, represent another area where lithium orotate's gene regulatory effects could be harnessed. By modulating the expression of genes involved in neurotransmitter signaling and synaptic plasticity, lithium orotate may offer a more targeted approach to mood stabilization with potentially fewer side effects than traditional lithium carbonate treatments.
In the realm of cancer therapy, lithium orotate's influence on gene expression could be leveraged to develop novel treatment strategies. By selectively targeting genes involved in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and metastasis, lithium orotate-based therapies might enhance the efficacy of existing cancer treatments or serve as a standalone therapeutic option for certain types of cancer.
Inflammatory disorders present another potential application for lithium orotate research. By regulating genes involved in the inflammatory response, lithium orotate could offer new treatment options for conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and psoriasis.
In the field of regenerative medicine, lithium orotate's ability to influence gene expression could be harnessed to promote tissue repair and regeneration. This could have applications in wound healing, organ regeneration, and even stem cell therapies.
Lastly, the potential neuroprotective effects of lithium orotate, mediated through its influence on gene expression, could be explored for the prevention and treatment of traumatic brain injuries and stroke. By modulating genes involved in neuronal survival and plasticity, lithium orotate might help mitigate the long-term consequences of these acute neurological events.
In the field of neurodegenerative disorders, lithium orotate's ability to influence gene expression may offer new treatment strategies for conditions such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. By targeting specific genes involved in neuronal survival and plasticity, lithium orotate could potentially slow disease progression or even reverse some of the associated cognitive decline.
Mood disorders, particularly bipolar disorder and major depression, represent another area where lithium orotate's gene regulatory effects could be harnessed. By modulating the expression of genes involved in neurotransmitter signaling and synaptic plasticity, lithium orotate may offer a more targeted approach to mood stabilization with potentially fewer side effects than traditional lithium carbonate treatments.
In the realm of cancer therapy, lithium orotate's influence on gene expression could be leveraged to develop novel treatment strategies. By selectively targeting genes involved in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and metastasis, lithium orotate-based therapies might enhance the efficacy of existing cancer treatments or serve as a standalone therapeutic option for certain types of cancer.
Inflammatory disorders present another potential application for lithium orotate research. By regulating genes involved in the inflammatory response, lithium orotate could offer new treatment options for conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and psoriasis.
In the field of regenerative medicine, lithium orotate's ability to influence gene expression could be harnessed to promote tissue repair and regeneration. This could have applications in wound healing, organ regeneration, and even stem cell therapies.
Lastly, the potential neuroprotective effects of lithium orotate, mediated through its influence on gene expression, could be explored for the prevention and treatment of traumatic brain injuries and stroke. By modulating genes involved in neuronal survival and plasticity, lithium orotate might help mitigate the long-term consequences of these acute neurological events.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!