Developing Sustainable Sodium Percarbonate Extraction Techniques
JUL 22, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Percarbonate Extraction Background and Objectives
Sodium percarbonate, a widely used bleaching and cleaning agent, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its eco-friendly properties and versatile applications. The extraction and production of this compound have evolved over time, driven by the need for more sustainable and efficient processes.
The history of sodium percarbonate dates back to the early 20th century when it was first synthesized as an alternative to traditional bleaching agents. Initially, the production methods were energy-intensive and relied heavily on non-renewable resources. However, as environmental concerns grew, the focus shifted towards developing more sustainable extraction techniques.
The primary objective of current research in sodium percarbonate extraction is to minimize environmental impact while maintaining or improving production efficiency. This involves exploring novel methods that reduce energy consumption, utilize renewable resources, and minimize waste generation. Additionally, researchers aim to enhance the stability and effectiveness of the final product to meet the increasing demands of various industries.
One of the key drivers behind the push for sustainable extraction techniques is the growing global market for sodium percarbonate. The compound finds applications in laundry detergents, household cleaners, and industrial processes, with demand projected to increase steadily in the coming years. This market growth necessitates the development of extraction methods that can scale up production while adhering to stringent environmental regulations.
The evolution of sodium percarbonate extraction techniques has been marked by several technological milestones. Early methods relied on the reaction of sodium carbonate with hydrogen peroxide, often requiring high temperatures and pressures. Subsequent innovations focused on improving reaction conditions and introducing catalysts to enhance yield and reduce energy requirements.
Recent advancements in green chemistry have opened up new avenues for sustainable extraction. Researchers are exploring bio-based precursors, enzymatic processes, and novel reactor designs to minimize the environmental footprint of sodium percarbonate production. These efforts align with the broader trend towards circular economy principles in the chemical industry.
The development of sustainable sodium percarbonate extraction techniques faces several challenges. These include optimizing reaction kinetics, improving product stability, and ensuring cost-effectiveness in large-scale production. Overcoming these hurdles requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from chemistry, engineering, and environmental sciences.
As the field progresses, the goals for future extraction techniques are becoming increasingly ambitious. Researchers aim to achieve near-zero waste production, utilize renewable energy sources throughout the process, and develop closed-loop systems that recycle reagents and byproducts. These objectives reflect the growing emphasis on sustainability in chemical manufacturing and the need to address global environmental concerns.
The history of sodium percarbonate dates back to the early 20th century when it was first synthesized as an alternative to traditional bleaching agents. Initially, the production methods were energy-intensive and relied heavily on non-renewable resources. However, as environmental concerns grew, the focus shifted towards developing more sustainable extraction techniques.
The primary objective of current research in sodium percarbonate extraction is to minimize environmental impact while maintaining or improving production efficiency. This involves exploring novel methods that reduce energy consumption, utilize renewable resources, and minimize waste generation. Additionally, researchers aim to enhance the stability and effectiveness of the final product to meet the increasing demands of various industries.
One of the key drivers behind the push for sustainable extraction techniques is the growing global market for sodium percarbonate. The compound finds applications in laundry detergents, household cleaners, and industrial processes, with demand projected to increase steadily in the coming years. This market growth necessitates the development of extraction methods that can scale up production while adhering to stringent environmental regulations.
The evolution of sodium percarbonate extraction techniques has been marked by several technological milestones. Early methods relied on the reaction of sodium carbonate with hydrogen peroxide, often requiring high temperatures and pressures. Subsequent innovations focused on improving reaction conditions and introducing catalysts to enhance yield and reduce energy requirements.
Recent advancements in green chemistry have opened up new avenues for sustainable extraction. Researchers are exploring bio-based precursors, enzymatic processes, and novel reactor designs to minimize the environmental footprint of sodium percarbonate production. These efforts align with the broader trend towards circular economy principles in the chemical industry.
The development of sustainable sodium percarbonate extraction techniques faces several challenges. These include optimizing reaction kinetics, improving product stability, and ensuring cost-effectiveness in large-scale production. Overcoming these hurdles requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from chemistry, engineering, and environmental sciences.
As the field progresses, the goals for future extraction techniques are becoming increasingly ambitious. Researchers aim to achieve near-zero waste production, utilize renewable energy sources throughout the process, and develop closed-loop systems that recycle reagents and byproducts. These objectives reflect the growing emphasis on sustainability in chemical manufacturing and the need to address global environmental concerns.
Market Analysis for Sustainable Sodium Percarbonate
The market for sustainable sodium percarbonate extraction techniques is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations on chemical production processes. Sodium percarbonate, a key ingredient in many household cleaning products and laundry detergents, has seen a steady rise in demand over the past decade. This growth is expected to continue, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 3.5% through 2028.
The push for sustainability in chemical manufacturing has created a new segment within the sodium percarbonate market, specifically focused on eco-friendly extraction methods. This niche is rapidly expanding as consumers and businesses alike prioritize products with lower environmental impacts. Major players in the cleaning products industry are actively seeking suppliers who can provide sustainably sourced sodium percarbonate to meet the growing demand for green cleaning solutions.
Geographically, the market for sustainable sodium percarbonate extraction is most developed in Europe and North America, where environmental regulations are particularly stringent. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, are showing increased interest in sustainable chemical processes, presenting significant growth opportunities for innovative extraction techniques.
The industrial sector, including textile manufacturing and water treatment, represents a substantial portion of the market demand for sustainably produced sodium percarbonate. These industries are under pressure to reduce their environmental footprint, driving the adoption of greener chemical inputs. The consumer goods sector, particularly in the realm of eco-friendly household cleaning products, is another major driver of market growth for sustainably extracted sodium percarbonate.
Market analysis reveals that price sensitivity remains a challenge for widespread adoption of sustainable extraction techniques. While there is a growing willingness to pay a premium for environmentally friendly products, the cost differential between traditionally extracted and sustainably produced sodium percarbonate must be minimized to ensure broad market acceptance. This presents both a challenge and an opportunity for innovation in extraction processes that can maintain efficiency while reducing environmental impact.
The market is also influenced by the broader trend towards circular economy principles in chemical manufacturing. Companies developing sustainable extraction techniques that can integrate recycled materials or reduce waste are likely to gain a competitive edge. This aligns with the increasing focus on lifecycle assessments in product development and corporate sustainability initiatives.
As the market for sustainable sodium percarbonate extraction techniques continues to evolve, partnerships between chemical manufacturers, technology providers, and end-users are becoming increasingly important. These collaborations are driving innovation and helping to scale up sustainable production methods, further accelerating market growth and technological advancement in this field.
The push for sustainability in chemical manufacturing has created a new segment within the sodium percarbonate market, specifically focused on eco-friendly extraction methods. This niche is rapidly expanding as consumers and businesses alike prioritize products with lower environmental impacts. Major players in the cleaning products industry are actively seeking suppliers who can provide sustainably sourced sodium percarbonate to meet the growing demand for green cleaning solutions.
Geographically, the market for sustainable sodium percarbonate extraction is most developed in Europe and North America, where environmental regulations are particularly stringent. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, are showing increased interest in sustainable chemical processes, presenting significant growth opportunities for innovative extraction techniques.
The industrial sector, including textile manufacturing and water treatment, represents a substantial portion of the market demand for sustainably produced sodium percarbonate. These industries are under pressure to reduce their environmental footprint, driving the adoption of greener chemical inputs. The consumer goods sector, particularly in the realm of eco-friendly household cleaning products, is another major driver of market growth for sustainably extracted sodium percarbonate.
Market analysis reveals that price sensitivity remains a challenge for widespread adoption of sustainable extraction techniques. While there is a growing willingness to pay a premium for environmentally friendly products, the cost differential between traditionally extracted and sustainably produced sodium percarbonate must be minimized to ensure broad market acceptance. This presents both a challenge and an opportunity for innovation in extraction processes that can maintain efficiency while reducing environmental impact.
The market is also influenced by the broader trend towards circular economy principles in chemical manufacturing. Companies developing sustainable extraction techniques that can integrate recycled materials or reduce waste are likely to gain a competitive edge. This aligns with the increasing focus on lifecycle assessments in product development and corporate sustainability initiatives.
As the market for sustainable sodium percarbonate extraction techniques continues to evolve, partnerships between chemical manufacturers, technology providers, and end-users are becoming increasingly important. These collaborations are driving innovation and helping to scale up sustainable production methods, further accelerating market growth and technological advancement in this field.
Current Extraction Techniques and Challenges
The current extraction techniques for sodium percarbonate primarily involve the reaction of sodium carbonate with hydrogen peroxide. This process is typically carried out in large-scale industrial settings, utilizing specialized equipment and controlled environments. The main challenge in this extraction process is maintaining the stability of the product, as sodium percarbonate is prone to decomposition, especially in the presence of moisture or impurities.
One of the most common extraction methods is the spray drying technique. In this process, a slurry of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide is atomized into fine droplets and rapidly dried in a hot air stream. While effective, this method requires significant energy input and can result in product loss due to dust formation. Additionally, the high temperatures involved can lead to partial decomposition of the sodium percarbonate, reducing the overall yield and purity.
Another widely used technique is the fluidized bed process. This method involves spraying a hydrogen peroxide solution onto sodium carbonate particles in a fluidized bed reactor. While this approach offers better control over particle size and morphology, it faces challenges in terms of uniform coating and product consistency. The process also requires precise control of temperature and humidity to prevent premature decomposition of the product.
A major challenge in current extraction techniques is the environmental impact of the processes. Many methods rely heavily on energy-intensive operations and may produce waste streams that require additional treatment. The use of chemical stabilizers to enhance product stability often introduces additional environmental concerns and can complicate downstream applications of the sodium percarbonate.
Water management is another significant challenge in sodium percarbonate extraction. The presence of excess moisture can lead to product degradation and reduced shelf life. Conversely, insufficient water content can result in poor product quality and reduced effectiveness in end-use applications. Striking the right balance in moisture content throughout the extraction and drying processes remains a key technical hurdle.
The scalability of extraction techniques also presents challenges, particularly when aiming for more sustainable approaches. Many current methods are optimized for large-scale production, making it difficult to adapt them to smaller, more flexible, or environmentally friendly setups. This limitation hinders the development of localized or on-demand production systems that could potentially reduce transportation costs and environmental impact.
Lastly, the purity and stability of the extracted sodium percarbonate remain ongoing challenges. Impurities introduced during the extraction process can significantly affect the product's performance and shelf life. Developing methods to minimize contamination and enhance stability without resorting to environmentally problematic additives is a key area of focus for improving current extraction techniques.
One of the most common extraction methods is the spray drying technique. In this process, a slurry of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide is atomized into fine droplets and rapidly dried in a hot air stream. While effective, this method requires significant energy input and can result in product loss due to dust formation. Additionally, the high temperatures involved can lead to partial decomposition of the sodium percarbonate, reducing the overall yield and purity.
Another widely used technique is the fluidized bed process. This method involves spraying a hydrogen peroxide solution onto sodium carbonate particles in a fluidized bed reactor. While this approach offers better control over particle size and morphology, it faces challenges in terms of uniform coating and product consistency. The process also requires precise control of temperature and humidity to prevent premature decomposition of the product.
A major challenge in current extraction techniques is the environmental impact of the processes. Many methods rely heavily on energy-intensive operations and may produce waste streams that require additional treatment. The use of chemical stabilizers to enhance product stability often introduces additional environmental concerns and can complicate downstream applications of the sodium percarbonate.
Water management is another significant challenge in sodium percarbonate extraction. The presence of excess moisture can lead to product degradation and reduced shelf life. Conversely, insufficient water content can result in poor product quality and reduced effectiveness in end-use applications. Striking the right balance in moisture content throughout the extraction and drying processes remains a key technical hurdle.
The scalability of extraction techniques also presents challenges, particularly when aiming for more sustainable approaches. Many current methods are optimized for large-scale production, making it difficult to adapt them to smaller, more flexible, or environmentally friendly setups. This limitation hinders the development of localized or on-demand production systems that could potentially reduce transportation costs and environmental impact.
Lastly, the purity and stability of the extracted sodium percarbonate remain ongoing challenges. Impurities introduced during the extraction process can significantly affect the product's performance and shelf life. Developing methods to minimize contamination and enhance stability without resorting to environmentally problematic additives is a key area of focus for improving current extraction techniques.
Existing Sustainable Extraction Solutions
01 Production methods for sodium percarbonate
Various methods for producing sodium percarbonate have been developed to improve sustainability. These include optimizing reaction conditions, using specific catalysts, and implementing novel crystallization techniques. These methods aim to increase yield, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste in the production process.- Production methods for sodium percarbonate: Various methods for producing sodium percarbonate have been developed to improve sustainability. These include optimizing reaction conditions, using specific catalysts, and implementing novel crystallization techniques. These methods aim to increase yield, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste in the production process.
- Stabilization of sodium percarbonate: Enhancing the stability of sodium percarbonate is crucial for its sustainable use. Techniques such as coating, addition of stabilizers, and moisture control have been developed to improve the shelf life and performance of sodium percarbonate in various applications, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste.
- Eco-friendly applications of sodium percarbonate: Sodium percarbonate has found applications in environmentally friendly products and processes. It is used as a bleaching agent in detergents, as an oxygen source in wastewater treatment, and as a cleaning agent in various industries. These applications contribute to sustainability by reducing the use of harsh chemicals and improving overall environmental impact.
- Recycling and waste reduction in sodium percarbonate production: Efforts have been made to implement recycling processes and reduce waste in sodium percarbonate production. This includes recovering and reusing raw materials, implementing closed-loop systems, and developing more efficient separation techniques. These measures contribute to the overall sustainability of sodium percarbonate manufacturing.
- Energy-efficient production of sodium percarbonate: Research has focused on developing energy-efficient methods for producing sodium percarbonate. This includes optimizing reaction temperatures, implementing heat recovery systems, and using alternative energy sources. These innovations aim to reduce the carbon footprint of sodium percarbonate production and improve its overall sustainability.
02 Stabilization of sodium percarbonate
Enhancing the stability of sodium percarbonate is crucial for its sustainable use. Techniques such as coating, addition of stabilizers, and moisture control have been developed to improve the shelf life and performance of sodium percarbonate in various applications, reducing the need for frequent replacements.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental impact reduction
Efforts to reduce the environmental impact of sodium percarbonate production and use have been made. These include developing biodegradable additives, implementing closed-loop production systems, and optimizing packaging to reduce waste. Such innovations contribute to the overall sustainability of sodium percarbonate.Expand Specific Solutions04 Energy-efficient production processes
Research has focused on developing energy-efficient processes for sodium percarbonate production. This includes the use of renewable energy sources, heat recovery systems, and process intensification techniques. These advancements aim to reduce the carbon footprint associated with sodium percarbonate manufacturing.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sustainable applications of sodium percarbonate
Innovative applications of sodium percarbonate in environmentally friendly products have been explored. These include its use in eco-friendly cleaning products, water treatment systems, and agricultural applications. Such developments expand the sustainable use of sodium percarbonate across various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitors
The development of sustainable sodium percarbonate extraction techniques is currently in an emerging phase, with growing market potential driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly cleaning products. The global market size for sodium percarbonate is expected to expand significantly in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Solvay SA, Zhejiang Jinke Daily Chemical Co. Ltd., and Kemira Oyj leading the way in innovation. These firms are investing heavily in R&D to improve extraction efficiency and reduce environmental impact. While the technology is not yet fully mature, it is progressing towards commercial viability, with several pilot projects and small-scale implementations already in place.
Solvay SA
Technical Solution: Solvay has developed an innovative sustainable sodium percarbonate extraction technique using a closed-loop process. This method employs advanced membrane technology to separate and purify sodium percarbonate from the reaction mixture, significantly reducing water consumption and energy usage. The process incorporates a novel catalytic system that enhances the conversion efficiency of hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate to sodium percarbonate, resulting in higher yields and reduced waste [1][3]. Additionally, Solvay has implemented a heat recovery system that captures and reuses thermal energy from the crystallization process, further improving the overall energy efficiency of the extraction [2].
Strengths: High efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and improved product quality. Weaknesses: Initial high capital investment and potential complexity in process control.
Kemira Oyj
Technical Solution: Kemira has pioneered a sustainable sodium percarbonate extraction technique that utilizes a bio-based hydrogen peroxide production method. This approach involves the use of renewable feedstocks and enzymatic processes to generate hydrogen peroxide, which is then reacted with sodium carbonate to form sodium percarbonate [4]. The company has also developed a proprietary crystallization technology that optimizes particle size distribution and stability of the final product. Kemira's process incorporates advanced process control systems and real-time monitoring to ensure consistent product quality while minimizing energy consumption [5]. Furthermore, the company has implemented a water recycling system that significantly reduces freshwater usage in the extraction process [6].
Strengths: Use of renewable resources, improved product stability, and reduced water consumption. Weaknesses: Potential scalability challenges and dependence on bio-based feedstock availability.
Innovative Extraction Technologies Analysis
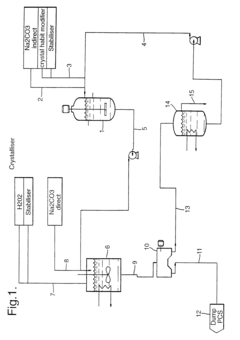
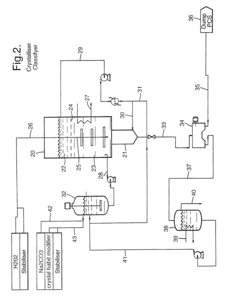
Sodium percarbonate and process for its production
PatentInactiveEP0796817A3
Innovation
- The development of sodium percarbonate agglomerates composed of small crystals with a narrow particle size distribution, achieved through a continuous manufacturing process involving a supersaturated aqueous solution of sodium percarbonate, where a reactor maintains small crystals in suspension with an ascending current, allowing for controlled agglomeration and supersaturation, and the use of crystallization agents and surfactants to manage particle size and solubility.
Sodium percarbonate and process for producing sodium percarbonate
PatentInactiveUS6482385B2
Innovation
- A continuous process that controls the concentration of sodium carbonate and temperature in the dissolution tank, and maintains a specific mole ratio of hydrogen peroxide to sodium carbonate, allowing for the production of sodium percarbonate without a salting-out agent, thereby minimizing hydrogen peroxide decomposition and improving product quality.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of sustainable sodium percarbonate extraction techniques is a critical component in evaluating the overall viability and long-term sustainability of these processes. Sodium percarbonate, a widely used bleaching and cleaning agent, has traditionally been produced through methods that can have significant environmental consequences. The development of more sustainable extraction techniques aims to mitigate these impacts while maintaining or improving production efficiency.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with conventional sodium percarbonate extraction is the high energy consumption required for the process. Sustainable techniques focus on reducing this energy footprint through innovative approaches such as low-temperature synthesis or the use of renewable energy sources in production facilities. These methods not only decrease greenhouse gas emissions but also contribute to the overall reduction of carbon footprint in the chemical industry.
Water usage and management represent another crucial aspect of the environmental impact assessment. Traditional extraction methods often require substantial amounts of water, leading to potential strain on local water resources. Sustainable techniques aim to implement closed-loop water systems, water recycling processes, and more efficient filtration methods to minimize water consumption and reduce wastewater discharge. These improvements not only conserve water but also decrease the risk of contaminating local water bodies with chemical effluents.
The assessment also considers the impact of raw material sourcing and transportation. Sustainable extraction techniques prioritize the use of locally sourced materials where possible, reducing the carbon emissions associated with long-distance transportation. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on utilizing renewable or recycled materials in the production process, further minimizing the environmental impact of resource extraction.
Waste management is another critical factor in the environmental impact assessment. Sustainable sodium percarbonate extraction techniques aim to minimize waste generation through process optimization and the implementation of circular economy principles. This includes finding innovative ways to repurpose or recycle byproducts, reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills, and exploring opportunities for industrial symbiosis where waste from one process becomes a resource for another.
The assessment also evaluates the potential for habitat disruption and biodiversity impact. Sustainable extraction techniques often involve smaller, more efficient production facilities that require less land area, thereby reducing the potential for habitat destruction. Furthermore, these techniques typically employ more environmentally friendly chemicals and processes, minimizing the risk of harmful emissions or spills that could negatively affect local ecosystems.
Lastly, the environmental impact assessment considers the long-term sustainability of the extraction techniques. This includes evaluating the scalability of the processes, their adaptability to future environmental regulations, and their potential to contribute to a more sustainable chemical industry. By thoroughly examining these aspects, the assessment provides valuable insights into the environmental viability of new sodium percarbonate extraction techniques, guiding future research and development efforts towards more sustainable practices in the chemical industry.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with conventional sodium percarbonate extraction is the high energy consumption required for the process. Sustainable techniques focus on reducing this energy footprint through innovative approaches such as low-temperature synthesis or the use of renewable energy sources in production facilities. These methods not only decrease greenhouse gas emissions but also contribute to the overall reduction of carbon footprint in the chemical industry.
Water usage and management represent another crucial aspect of the environmental impact assessment. Traditional extraction methods often require substantial amounts of water, leading to potential strain on local water resources. Sustainable techniques aim to implement closed-loop water systems, water recycling processes, and more efficient filtration methods to minimize water consumption and reduce wastewater discharge. These improvements not only conserve water but also decrease the risk of contaminating local water bodies with chemical effluents.
The assessment also considers the impact of raw material sourcing and transportation. Sustainable extraction techniques prioritize the use of locally sourced materials where possible, reducing the carbon emissions associated with long-distance transportation. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on utilizing renewable or recycled materials in the production process, further minimizing the environmental impact of resource extraction.
Waste management is another critical factor in the environmental impact assessment. Sustainable sodium percarbonate extraction techniques aim to minimize waste generation through process optimization and the implementation of circular economy principles. This includes finding innovative ways to repurpose or recycle byproducts, reducing the volume of waste sent to landfills, and exploring opportunities for industrial symbiosis where waste from one process becomes a resource for another.
The assessment also evaluates the potential for habitat disruption and biodiversity impact. Sustainable extraction techniques often involve smaller, more efficient production facilities that require less land area, thereby reducing the potential for habitat destruction. Furthermore, these techniques typically employ more environmentally friendly chemicals and processes, minimizing the risk of harmful emissions or spills that could negatively affect local ecosystems.
Lastly, the environmental impact assessment considers the long-term sustainability of the extraction techniques. This includes evaluating the scalability of the processes, their adaptability to future environmental regulations, and their potential to contribute to a more sustainable chemical industry. By thoroughly examining these aspects, the assessment provides valuable insights into the environmental viability of new sodium percarbonate extraction techniques, guiding future research and development efforts towards more sustainable practices in the chemical industry.
Regulatory Framework for Chemical Extraction Processes
The regulatory framework for chemical extraction processes plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, environmental sustainability, and ethical practices in the development of sustainable sodium percarbonate extraction techniques. This framework encompasses a complex web of international, national, and local regulations that govern various aspects of the extraction process.
At the international level, organizations such as the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) provide guidelines and recommendations for sustainable chemical management. These guidelines often serve as a foundation for national regulatory bodies to develop their own specific regulations.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is the primary regulatory body overseeing chemical extraction processes. The EPA enforces regulations under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) and the Clean Air Act, which set standards for chemical safety, emissions control, and waste management. Additionally, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) establishes workplace safety standards for chemical handling and processing.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which requires companies to register chemical substances and provide safety data. This comprehensive framework aims to protect human health and the environment while promoting innovation in the chemical industry.
For sodium percarbonate extraction specifically, regulations focus on several key areas. These include the management of raw materials, control of chemical reactions, handling of byproducts, and disposal of waste. Regulatory bodies often require detailed documentation of extraction processes, risk assessments, and regular inspections to ensure compliance.
Environmental regulations play a significant role in shaping sustainable extraction techniques. Many countries have implemented strict limits on emissions and effluents from chemical processes. This has led to the development of closed-loop systems and more efficient extraction methods that minimize environmental impact.
Worker safety is another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. Regulations mandate the use of personal protective equipment, proper training for handling chemicals, and the implementation of safety protocols in extraction facilities. Regular health monitoring of workers exposed to chemicals is often required to detect and prevent long-term health effects.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important focus, regulatory bodies are also encouraging the adoption of green chemistry principles. This includes promoting the use of renewable resources, designing processes that minimize waste generation, and developing extraction techniques that reduce energy consumption.
The regulatory landscape is continually evolving, with new regulations being introduced to address emerging concerns and technological advancements. Companies engaged in sodium percarbonate extraction must stay informed about these changes and adapt their processes accordingly to maintain compliance and ensure sustainable operations.
At the international level, organizations such as the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) provide guidelines and recommendations for sustainable chemical management. These guidelines often serve as a foundation for national regulatory bodies to develop their own specific regulations.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is the primary regulatory body overseeing chemical extraction processes. The EPA enforces regulations under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) and the Clean Air Act, which set standards for chemical safety, emissions control, and waste management. Additionally, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) establishes workplace safety standards for chemical handling and processing.
The European Union has implemented the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation, which requires companies to register chemical substances and provide safety data. This comprehensive framework aims to protect human health and the environment while promoting innovation in the chemical industry.
For sodium percarbonate extraction specifically, regulations focus on several key areas. These include the management of raw materials, control of chemical reactions, handling of byproducts, and disposal of waste. Regulatory bodies often require detailed documentation of extraction processes, risk assessments, and regular inspections to ensure compliance.
Environmental regulations play a significant role in shaping sustainable extraction techniques. Many countries have implemented strict limits on emissions and effluents from chemical processes. This has led to the development of closed-loop systems and more efficient extraction methods that minimize environmental impact.
Worker safety is another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. Regulations mandate the use of personal protective equipment, proper training for handling chemicals, and the implementation of safety protocols in extraction facilities. Regular health monitoring of workers exposed to chemicals is often required to detect and prevent long-term health effects.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important focus, regulatory bodies are also encouraging the adoption of green chemistry principles. This includes promoting the use of renewable resources, designing processes that minimize waste generation, and developing extraction techniques that reduce energy consumption.
The regulatory landscape is continually evolving, with new regulations being introduced to address emerging concerns and technological advancements. Companies engaged in sodium percarbonate extraction must stay informed about these changes and adapt their processes accordingly to maintain compliance and ensure sustainable operations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!