Dodecane at the Forefront of Technological Progress
JUL 29, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dodecane Tech Evolution
Dodecane, a straight-chain alkane with twelve carbon atoms, has undergone significant technological evolution since its discovery. Initially recognized as a component of petroleum and natural gas, dodecane's journey from a simple hydrocarbon to a versatile compound at the forefront of technological progress is marked by several key milestones.
In the early 20th century, the primary focus was on isolating and characterizing dodecane as part of broader petroleum research. As analytical techniques improved, scientists gained a better understanding of its physical and chemical properties, laying the groundwork for future applications.
The 1950s and 1960s saw a surge in dodecane's industrial applications, particularly as a solvent in various chemical processes. Its low toxicity and high boiling point made it an attractive option for many industrial uses. This period also marked the beginning of dodecane's use in the fragrance industry, where its properties as a fixative became highly valued.
The 1970s and 1980s brought about a shift towards more specialized applications. Researchers began exploring dodecane's potential in energy storage and transfer, recognizing its favorable properties for phase change materials. This era also saw the first experiments with dodecane as a potential biofuel component, although practical applications were still limited.
The turn of the millennium heralded a new era for dodecane technology. Advancements in nanotechnology opened up novel applications, with dodecane being used in the synthesis of nanoparticles and as a component in advanced materials. Its role in energy storage solutions became more prominent, with research focusing on its use in thermal management systems for electronics and buildings.
In recent years, dodecane has found itself at the intersection of several cutting-edge fields. Its application in aerospace as a rocket propellant component has gained traction, while its potential in advanced battery technologies is being actively explored. The compound's role in sustainable chemistry has also expanded, with researchers investigating its production from renewable sources and its use in biodegradable materials.
The latest frontier in dodecane technology involves its application in quantum computing. Scientists are exploring its potential as a quantum fluid, opening up entirely new avenues for technological advancement. This development represents a significant leap from dodecane's traditional applications, showcasing its versatility and ongoing relevance in modern scientific research.
In the early 20th century, the primary focus was on isolating and characterizing dodecane as part of broader petroleum research. As analytical techniques improved, scientists gained a better understanding of its physical and chemical properties, laying the groundwork for future applications.
The 1950s and 1960s saw a surge in dodecane's industrial applications, particularly as a solvent in various chemical processes. Its low toxicity and high boiling point made it an attractive option for many industrial uses. This period also marked the beginning of dodecane's use in the fragrance industry, where its properties as a fixative became highly valued.
The 1970s and 1980s brought about a shift towards more specialized applications. Researchers began exploring dodecane's potential in energy storage and transfer, recognizing its favorable properties for phase change materials. This era also saw the first experiments with dodecane as a potential biofuel component, although practical applications were still limited.
The turn of the millennium heralded a new era for dodecane technology. Advancements in nanotechnology opened up novel applications, with dodecane being used in the synthesis of nanoparticles and as a component in advanced materials. Its role in energy storage solutions became more prominent, with research focusing on its use in thermal management systems for electronics and buildings.
In recent years, dodecane has found itself at the intersection of several cutting-edge fields. Its application in aerospace as a rocket propellant component has gained traction, while its potential in advanced battery technologies is being actively explored. The compound's role in sustainable chemistry has also expanded, with researchers investigating its production from renewable sources and its use in biodegradable materials.
The latest frontier in dodecane technology involves its application in quantum computing. Scientists are exploring its potential as a quantum fluid, opening up entirely new avenues for technological advancement. This development represents a significant leap from dodecane's traditional applications, showcasing its versatility and ongoing relevance in modern scientific research.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for dodecane has been steadily increasing across various industries, driven by its versatile applications and unique properties. In the petrochemical sector, dodecane serves as a crucial component in the production of diesel fuel and jet fuel, contributing to the growing demand for efficient and cleaner-burning transportation fuels. The aviation industry, in particular, has shown a significant interest in dodecane-based fuels due to their potential to reduce carbon emissions and improve engine performance.
The personal care and cosmetics industry has also embraced dodecane as a key ingredient in numerous products. Its excellent spreading properties and low viscosity make it an ideal choice for skincare formulations, hair care products, and makeup removers. The increasing consumer preference for natural and sustainable ingredients has further boosted the demand for dodecane in this sector, as it can be derived from renewable sources such as plant-based oils.
In the pharmaceutical industry, dodecane has found applications as a solvent and carrier for drug delivery systems. Its ability to enhance the bioavailability of certain medications has led to increased research and development efforts, potentially opening up new market opportunities in the coming years.
The electronics industry has also recognized the potential of dodecane in advanced manufacturing processes. Its use as a cleaning agent for precision components and as a heat transfer fluid in cooling systems has contributed to the growing demand in this sector. As the electronics industry continues to evolve with the development of more sophisticated devices, the demand for high-purity dodecane is expected to rise.
The global market for dodecane is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years, with Asia-Pacific emerging as a key region driving demand. The rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India have led to increased consumption of dodecane-based products across various sectors. Additionally, the shift towards sustainable and bio-based alternatives in developed economies is expected to create new opportunities for dodecane derived from renewable sources.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as price volatility of raw materials and environmental concerns related to fossil fuel-derived dodecane may impact market growth. However, ongoing research into sustainable production methods and the development of bio-based alternatives are expected to address these challenges and further expand the market potential for dodecane across diverse industries.
The personal care and cosmetics industry has also embraced dodecane as a key ingredient in numerous products. Its excellent spreading properties and low viscosity make it an ideal choice for skincare formulations, hair care products, and makeup removers. The increasing consumer preference for natural and sustainable ingredients has further boosted the demand for dodecane in this sector, as it can be derived from renewable sources such as plant-based oils.
In the pharmaceutical industry, dodecane has found applications as a solvent and carrier for drug delivery systems. Its ability to enhance the bioavailability of certain medications has led to increased research and development efforts, potentially opening up new market opportunities in the coming years.
The electronics industry has also recognized the potential of dodecane in advanced manufacturing processes. Its use as a cleaning agent for precision components and as a heat transfer fluid in cooling systems has contributed to the growing demand in this sector. As the electronics industry continues to evolve with the development of more sophisticated devices, the demand for high-purity dodecane is expected to rise.
The global market for dodecane is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years, with Asia-Pacific emerging as a key region driving demand. The rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India have led to increased consumption of dodecane-based products across various sectors. Additionally, the shift towards sustainable and bio-based alternatives in developed economies is expected to create new opportunities for dodecane derived from renewable sources.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as price volatility of raw materials and environmental concerns related to fossil fuel-derived dodecane may impact market growth. However, ongoing research into sustainable production methods and the development of bio-based alternatives are expected to address these challenges and further expand the market potential for dodecane across diverse industries.
Current Challenges
Despite its promising potential, dodecane faces several significant challenges in its journey towards technological advancement. One of the primary obstacles is the optimization of production processes to achieve cost-effective and scalable manufacturing. Current methods for synthesizing high-purity dodecane often involve complex and energy-intensive processes, limiting its widespread adoption in various industries.
Environmental concerns pose another substantial challenge. As a hydrocarbon, dodecane's production and use contribute to carbon emissions, raising questions about its long-term sustainability in an increasingly eco-conscious global market. Developing greener production methods and exploring bio-based alternatives are crucial steps in addressing these environmental issues.
The storage and transportation of dodecane present additional hurdles. Its relatively low flash point and potential for static accumulation require specialized handling and storage facilities, increasing operational costs and complexity for businesses looking to incorporate dodecane into their processes or products.
In the realm of applications, while dodecane shows promise in various fields, there is a need for further research to fully exploit its potential. For instance, in the aerospace industry, enhancing dodecane's performance as a rocket fuel additive requires overcoming issues related to combustion efficiency and stability under extreme conditions.
Regulatory challenges also play a significant role in dodecane's technological progress. Varying international standards and regulations regarding the use and transport of hydrocarbons can complicate global supply chains and market expansion efforts. Harmonizing these regulations and ensuring compliance across different jurisdictions remains a complex task for industry stakeholders.
Furthermore, the competitive landscape poses challenges to dodecane's advancement. Alternative materials and technologies in various application areas, such as renewable energy storage solutions or advanced synthetic lubricants, are constantly evolving, potentially limiting dodecane's market penetration in certain sectors.
Lastly, there is a knowledge gap in understanding the long-term effects of dodecane exposure on human health and the environment. While generally considered low in toxicity, comprehensive studies on its bioaccumulation and potential ecological impacts are still needed to ensure its safe and responsible use across different applications.
Addressing these multifaceted challenges requires a concerted effort from researchers, industry players, and policymakers. Innovations in production technologies, environmental mitigation strategies, and application-specific enhancements will be crucial in positioning dodecane at the forefront of technological progress.
Environmental concerns pose another substantial challenge. As a hydrocarbon, dodecane's production and use contribute to carbon emissions, raising questions about its long-term sustainability in an increasingly eco-conscious global market. Developing greener production methods and exploring bio-based alternatives are crucial steps in addressing these environmental issues.
The storage and transportation of dodecane present additional hurdles. Its relatively low flash point and potential for static accumulation require specialized handling and storage facilities, increasing operational costs and complexity for businesses looking to incorporate dodecane into their processes or products.
In the realm of applications, while dodecane shows promise in various fields, there is a need for further research to fully exploit its potential. For instance, in the aerospace industry, enhancing dodecane's performance as a rocket fuel additive requires overcoming issues related to combustion efficiency and stability under extreme conditions.
Regulatory challenges also play a significant role in dodecane's technological progress. Varying international standards and regulations regarding the use and transport of hydrocarbons can complicate global supply chains and market expansion efforts. Harmonizing these regulations and ensuring compliance across different jurisdictions remains a complex task for industry stakeholders.
Furthermore, the competitive landscape poses challenges to dodecane's advancement. Alternative materials and technologies in various application areas, such as renewable energy storage solutions or advanced synthetic lubricants, are constantly evolving, potentially limiting dodecane's market penetration in certain sectors.
Lastly, there is a knowledge gap in understanding the long-term effects of dodecane exposure on human health and the environment. While generally considered low in toxicity, comprehensive studies on its bioaccumulation and potential ecological impacts are still needed to ensure its safe and responsible use across different applications.
Addressing these multifaceted challenges requires a concerted effort from researchers, industry players, and policymakers. Innovations in production technologies, environmental mitigation strategies, and application-specific enhancements will be crucial in positioning dodecane at the forefront of technological progress.
Existing Solutions
01 Synthesis and purification of dodecane
Various methods for synthesizing and purifying dodecane are described. These include catalytic processes, distillation techniques, and chemical reactions to produce high-purity dodecane for industrial applications.- Synthesis and production of dodecane: Various methods for synthesizing and producing dodecane are described, including catalytic processes, hydrogenation reactions, and chemical transformations of precursor molecules. These techniques aim to improve the efficiency and yield of dodecane production for industrial applications.
- Use of dodecane in cosmetic and personal care products: Dodecane is utilized as an ingredient in cosmetic and personal care formulations, serving as a solvent, emollient, or carrier for active ingredients. It can enhance the texture, spreadability, and overall performance of various beauty and skincare products.
- Application of dodecane in fuel and energy systems: Dodecane finds applications in fuel and energy systems, particularly as a component in jet fuels, diesel fuels, and other hydrocarbon-based energy sources. Its properties make it suitable for use in combustion engines and as a potential renewable fuel source.
- Dodecane as a solvent and extraction medium: The use of dodecane as a solvent and extraction medium in various industrial processes is explored. Its properties make it suitable for extracting organic compounds, separating mixtures, and as a reaction medium in chemical synthesis.
- Dodecane in polymer and material science applications: Dodecane is employed in polymer and material science applications, including as a plasticizer, lubricant, or additive in various polymeric materials. It can modify the properties of plastics, rubbers, and other synthetic materials to enhance their performance characteristics.
02 Use of dodecane in cosmetic and personal care products
Dodecane is utilized as an ingredient in cosmetic and personal care formulations. It serves as an emollient, solvent, or carrier in products such as creams, lotions, and fragrances, contributing to improved texture and application properties.Expand Specific Solutions03 Dodecane in fuel and lubricant applications
Dodecane is employed in fuel and lubricant formulations. It is used as a component in diesel fuel, jet fuel, and various lubricating oils, contributing to improved performance and efficiency in engines and machinery.Expand Specific Solutions04 Dodecane as a solvent and extraction medium
The use of dodecane as a solvent and extraction medium in various industrial processes is described. It is employed in the extraction of natural products, separation of chemical compounds, and as a reaction medium in organic synthesis.Expand Specific Solutions05 Dodecane in polymer and material science applications
Dodecane finds applications in polymer and material science. It is used as a plasticizer, a component in polymer formulations, and in the production of specialty materials with specific properties for various industrial uses.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The development of dodecane technology is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market size and evolving applications across various industries. The global market for dodecane and related compounds is expanding, driven by demand in sectors such as petrochemicals, lubricants, and specialty chemicals. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Wanhua Chemical Group, BASF Corp., and Arkema France SA leading innovation in synthesis, purification, and application development. These industry leaders are investing in research and development to improve production efficiency and explore novel uses for dodecane. While the technology is relatively mature in traditional applications, emerging areas such as sustainable alternatives and advanced materials are pushing the boundaries of dodecane's potential, creating new competitive opportunities for companies like Shandong Guangtong New Materials and Sinopec Group Baling Petrochemical.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical Group has developed advanced catalytic processes for the production of high-purity dodecane. Their technology utilizes a novel zeolite-based catalyst system that enhances selectivity and yield. The process operates at lower temperatures and pressures compared to conventional methods, resulting in reduced energy consumption and improved process economics[1]. Additionally, Wanhua has implemented a proprietary purification technique that achieves dodecane purity levels exceeding 99.9%, meeting stringent requirements for high-performance applications in aerospace and electronics industries[2].
Strengths: High product purity, energy-efficient process, and versatile applications. Weaknesses: Potential high capital costs for specialized equipment and catalyst production.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has pioneered a bio-based route for dodecane production using renewable feedstocks. Their process employs genetically engineered microorganisms to convert plant-derived sugars into dodecane precursors, which are then catalytically upgraded to high-quality dodecane[3]. This approach significantly reduces the carbon footprint of dodecane production compared to traditional petroleum-based methods. BASF has also developed a continuous flow reactor system that improves process efficiency and allows for easier scale-up[4]. The company's technology integrates seamlessly with existing biorefinery infrastructure, promoting a circular economy approach to chemical manufacturing.
Strengths: Sustainable production method, reduced environmental impact, and integration with biorefinery systems. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs compared to petroleum-based routes and dependence on agricultural feedstocks.
Core Innovations
Carbon nanotube structures in sensor apparatuses for analyzing biomarkers in breath samples
PatentActiveUS20110098591A1
Innovation
- A system comprising an array of chemically sensitive sensors made from single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) coated with non-polar small organic molecules, in conjunction with learning and pattern recognition algorithms, is used to measure breath analytes. The SWCNTs are arranged in a random network configuration, eliminating the need for precise alignment and enhancing sensitivity and selectivity towards VOCs found in lung cancer patients.
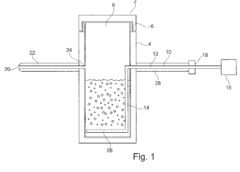
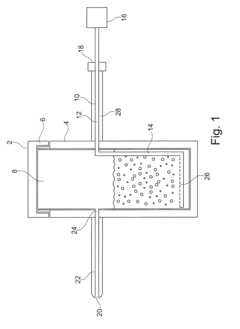
Application device for applying at least one sublimatable condensable compound, in particular of condensable cyclododecane, on surfaces of solid substrates or construction parts and device for determining the quality, in particular of the surface of a solid substrate or component
PatentInactiveEP2829328A1
Innovation
- A device with a heatable material container, gas inlet system, and application line allows for the controlled liquefaction and sublimation of cyclododecane onto surfaces, ensuring a homogeneous coating without crystallization or flocculation, using a heatable cover, flexible gas inlet sections, and a nozzle for precise application.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of dodecane, a key component in various industrial applications, is a critical consideration as technological progress advances. As a hydrocarbon, dodecane's production and use have significant implications for the environment, particularly in terms of carbon emissions and potential pollution risks.
In the context of fuel applications, dodecane's combustion contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide. However, its higher energy density compared to shorter-chain hydrocarbons can lead to improved fuel efficiency in certain applications, potentially offsetting some environmental concerns. This balance between energy efficiency and emissions is a key focus area for ongoing research and development efforts.
The production of dodecane, typically derived from petroleum sources, also carries environmental considerations. The extraction and refining processes associated with fossil fuels have well-documented environmental impacts, including habitat disruption, water pollution, and air quality degradation. As such, there is growing interest in developing more sustainable production methods for dodecane and similar hydrocarbons.
One promising avenue for mitigating the environmental impact of dodecane is the exploration of bio-based production methods. Researchers are investigating the potential of using renewable biomass feedstocks to synthesize dodecane and other long-chain hydrocarbons. This approach could significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with dodecane production, aligning with global efforts to transition towards more sustainable chemical manufacturing processes.
In industrial applications, the use of dodecane as a solvent or intermediate in chemical processes presents both opportunities and challenges from an environmental perspective. While its relatively low volatility can reduce air emissions compared to more volatile solvents, proper handling and disposal practices are crucial to prevent soil and water contamination. Advanced containment and recycling technologies are being developed to minimize the risk of environmental release and maximize resource efficiency.
The marine environment is particularly sensitive to the potential impacts of dodecane, especially in the context of fuel spills or leaks. Research into the behavior and fate of dodecane in aquatic ecosystems is ongoing, with a focus on developing more effective remediation strategies and environmentally friendly alternatives for marine applications.
As technological progress continues, the environmental impact of dodecane remains a key consideration for researchers, industry leaders, and policymakers. Efforts to balance its valuable properties with environmental sustainability are driving innovation in production methods, application technologies, and end-of-life management strategies. The future of dodecane in technological applications will likely be shaped by these ongoing efforts to minimize its environmental footprint while maximizing its utility across various sectors.
In the context of fuel applications, dodecane's combustion contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide. However, its higher energy density compared to shorter-chain hydrocarbons can lead to improved fuel efficiency in certain applications, potentially offsetting some environmental concerns. This balance between energy efficiency and emissions is a key focus area for ongoing research and development efforts.
The production of dodecane, typically derived from petroleum sources, also carries environmental considerations. The extraction and refining processes associated with fossil fuels have well-documented environmental impacts, including habitat disruption, water pollution, and air quality degradation. As such, there is growing interest in developing more sustainable production methods for dodecane and similar hydrocarbons.
One promising avenue for mitigating the environmental impact of dodecane is the exploration of bio-based production methods. Researchers are investigating the potential of using renewable biomass feedstocks to synthesize dodecane and other long-chain hydrocarbons. This approach could significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with dodecane production, aligning with global efforts to transition towards more sustainable chemical manufacturing processes.
In industrial applications, the use of dodecane as a solvent or intermediate in chemical processes presents both opportunities and challenges from an environmental perspective. While its relatively low volatility can reduce air emissions compared to more volatile solvents, proper handling and disposal practices are crucial to prevent soil and water contamination. Advanced containment and recycling technologies are being developed to minimize the risk of environmental release and maximize resource efficiency.
The marine environment is particularly sensitive to the potential impacts of dodecane, especially in the context of fuel spills or leaks. Research into the behavior and fate of dodecane in aquatic ecosystems is ongoing, with a focus on developing more effective remediation strategies and environmentally friendly alternatives for marine applications.
As technological progress continues, the environmental impact of dodecane remains a key consideration for researchers, industry leaders, and policymakers. Efforts to balance its valuable properties with environmental sustainability are driving innovation in production methods, application technologies, and end-of-life management strategies. The future of dodecane in technological applications will likely be shaped by these ongoing efforts to minimize its environmental footprint while maximizing its utility across various sectors.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding dodecane and its applications is a critical aspect of its technological progress. As a key component in various industries, including aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and energy, dodecane is subject to a complex web of regulations that govern its production, transportation, and use.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a significant role in regulating dodecane under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The TSCA requires manufacturers and importers to report new chemical substances, including dodecane derivatives, before they are introduced into commerce. This ensures that potential environmental and health risks are assessed and mitigated.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established exposure limits for dodecane in workplace environments. These regulations aim to protect workers from potential health hazards associated with long-term exposure to the chemical. Employers are required to implement safety measures, provide personal protective equipment, and conduct regular air quality monitoring in facilities where dodecane is used or produced.
Internationally, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation in the European Union impacts the use and distribution of dodecane. Companies must register substances manufactured or imported in quantities over one tonne per year, providing detailed information on their properties, uses, and potential risks.
The transportation of dodecane is regulated by various agencies, including the Department of Transportation (DOT) in the United States and the International Maritime Organization (IMO) for global shipping. These regulations cover aspects such as packaging, labeling, and handling procedures to ensure safe transport and prevent environmental contamination.
In the aerospace industry, the use of dodecane as a rocket propellant is subject to stringent regulations set by agencies like NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA). These guidelines cover aspects such as purity standards, storage conditions, and safety protocols during launch operations.
As research into new applications of dodecane progresses, regulatory bodies are likely to adapt their frameworks to address emerging concerns. For instance, the potential use of dodecane in advanced energy storage systems may lead to new regulations focused on fire safety and environmental impact.
The evolving regulatory landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for technological advancement. While compliance requirements may initially slow innovation, they also drive the development of safer and more efficient processes. Companies at the forefront of dodecane technology must stay abreast of these regulatory changes and actively engage with policymakers to shape future guidelines that balance innovation with safety and environmental protection.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a significant role in regulating dodecane under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The TSCA requires manufacturers and importers to report new chemical substances, including dodecane derivatives, before they are introduced into commerce. This ensures that potential environmental and health risks are assessed and mitigated.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established exposure limits for dodecane in workplace environments. These regulations aim to protect workers from potential health hazards associated with long-term exposure to the chemical. Employers are required to implement safety measures, provide personal protective equipment, and conduct regular air quality monitoring in facilities where dodecane is used or produced.
Internationally, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation in the European Union impacts the use and distribution of dodecane. Companies must register substances manufactured or imported in quantities over one tonne per year, providing detailed information on their properties, uses, and potential risks.
The transportation of dodecane is regulated by various agencies, including the Department of Transportation (DOT) in the United States and the International Maritime Organization (IMO) for global shipping. These regulations cover aspects such as packaging, labeling, and handling procedures to ensure safe transport and prevent environmental contamination.
In the aerospace industry, the use of dodecane as a rocket propellant is subject to stringent regulations set by agencies like NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA). These guidelines cover aspects such as purity standards, storage conditions, and safety protocols during launch operations.
As research into new applications of dodecane progresses, regulatory bodies are likely to adapt their frameworks to address emerging concerns. For instance, the potential use of dodecane in advanced energy storage systems may lead to new regulations focused on fire safety and environmental impact.
The evolving regulatory landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for technological advancement. While compliance requirements may initially slow innovation, they also drive the development of safer and more efficient processes. Companies at the forefront of dodecane technology must stay abreast of these regulatory changes and actively engage with policymakers to shape future guidelines that balance innovation with safety and environmental protection.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!