Navigating Dodecane's Complex Journey in Modern Chemistry
JUL 29, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Dodecane Evolution
Dodecane, a straight-chain alkane with twelve carbon atoms, has undergone a remarkable evolution in modern chemistry. Its journey began in the early 20th century when it was first isolated and identified as a component of petroleum. Initially, dodecane was primarily viewed as a simple hydrocarbon with limited applications.
As analytical techniques improved in the mid-20th century, scientists gained a deeper understanding of dodecane's molecular structure and properties. This knowledge led to its increased use as a reference compound in chromatography and as a standard in various chemical analyses. The 1960s and 1970s saw a surge in research on dodecane's physical and chemical properties, establishing it as a model compound for studying alkane behavior.
The late 20th century marked a significant shift in dodecane's role in chemistry. With the growing focus on renewable energy sources, dodecane became a subject of interest in biofuel research. Its potential as a component in diesel fuel alternatives sparked numerous studies on its combustion properties and environmental impact. Concurrently, the petrochemical industry began exploring dodecane as a precursor for various chemical products.
In the early 21st century, nanotechnology opened new avenues for dodecane applications. Researchers discovered its utility in creating self-assembled monolayers and as a solvent in nanoparticle synthesis. This period also saw increased interest in dodecane's role in atmospheric chemistry, particularly its contribution to aerosol formation and climate effects.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in computational studies of dodecane, employing advanced molecular dynamics simulations to predict its behavior under various conditions. These studies have provided invaluable insights into dodecane's role in complex chemical systems, from fuel mixtures to biological membranes.
The evolution of dodecane in modern chemistry reflects broader trends in scientific advancement. From a simple hydrocarbon to a versatile compound with applications spanning energy, materials science, and environmental studies, dodecane's journey exemplifies the dynamic nature of chemical research. As technology continues to advance, dodecane's role in chemistry is likely to evolve further, potentially opening new frontiers in sustainable chemistry and advanced materials.
As analytical techniques improved in the mid-20th century, scientists gained a deeper understanding of dodecane's molecular structure and properties. This knowledge led to its increased use as a reference compound in chromatography and as a standard in various chemical analyses. The 1960s and 1970s saw a surge in research on dodecane's physical and chemical properties, establishing it as a model compound for studying alkane behavior.
The late 20th century marked a significant shift in dodecane's role in chemistry. With the growing focus on renewable energy sources, dodecane became a subject of interest in biofuel research. Its potential as a component in diesel fuel alternatives sparked numerous studies on its combustion properties and environmental impact. Concurrently, the petrochemical industry began exploring dodecane as a precursor for various chemical products.
In the early 21st century, nanotechnology opened new avenues for dodecane applications. Researchers discovered its utility in creating self-assembled monolayers and as a solvent in nanoparticle synthesis. This period also saw increased interest in dodecane's role in atmospheric chemistry, particularly its contribution to aerosol formation and climate effects.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in computational studies of dodecane, employing advanced molecular dynamics simulations to predict its behavior under various conditions. These studies have provided invaluable insights into dodecane's role in complex chemical systems, from fuel mixtures to biological membranes.
The evolution of dodecane in modern chemistry reflects broader trends in scientific advancement. From a simple hydrocarbon to a versatile compound with applications spanning energy, materials science, and environmental studies, dodecane's journey exemplifies the dynamic nature of chemical research. As technology continues to advance, dodecane's role in chemistry is likely to evolve further, potentially opening new frontiers in sustainable chemistry and advanced materials.
Market Applications
Dodecane, a versatile hydrocarbon compound, has found its way into numerous market applications across various industries. In the petroleum sector, dodecane serves as a crucial component in diesel fuel blends, enhancing combustion efficiency and reducing emissions. Its high energy density makes it an attractive option for improving fuel performance in automotive and industrial engines.
The chemical industry utilizes dodecane as a solvent and intermediate in the production of various chemicals and materials. Its excellent solvency properties make it ideal for use in paints, coatings, and adhesives, where it aids in the dispersion of pigments and improves the overall product quality. Additionally, dodecane plays a role in the manufacturing of polymers and plastics, contributing to the development of durable and lightweight materials for consumer goods and industrial applications.
In the personal care and cosmetics industry, dodecane finds applications as an emollient and carrier oil in skincare products, hair care formulations, and fragrances. Its low viscosity and ability to spread easily on the skin make it a popular choice for creating smooth, non-greasy textures in lotions, creams, and other beauty products.
The agricultural sector benefits from dodecane's use in pesticide formulations, where it acts as a carrier for active ingredients, improving their efficacy and distribution. This application contributes to more efficient crop protection and increased agricultural yields.
In the field of energy storage, dodecane has shown promise as a potential hydrogen carrier in fuel cell technologies. Research is ongoing to explore its capacity to store and release hydrogen efficiently, potentially revolutionizing clean energy storage and transportation systems.
The electronics industry employs dodecane in the production of semiconductors and electronic components. Its low reactivity and ability to form thin, uniform films make it valuable in cleaning and coating processes during manufacturing.
As environmental concerns grow, the biodegradability of dodecane has led to its increased use in eco-friendly lubricants and hydraulic fluids. These applications cater to industries seeking more sustainable alternatives to traditional petroleum-based products.
The diverse market applications of dodecane highlight its significance in modern chemistry and industry. As research continues to uncover new properties and potential uses, dodecane's journey through various sectors is likely to expand, driving innovation and sustainability across multiple fields.
The chemical industry utilizes dodecane as a solvent and intermediate in the production of various chemicals and materials. Its excellent solvency properties make it ideal for use in paints, coatings, and adhesives, where it aids in the dispersion of pigments and improves the overall product quality. Additionally, dodecane plays a role in the manufacturing of polymers and plastics, contributing to the development of durable and lightweight materials for consumer goods and industrial applications.
In the personal care and cosmetics industry, dodecane finds applications as an emollient and carrier oil in skincare products, hair care formulations, and fragrances. Its low viscosity and ability to spread easily on the skin make it a popular choice for creating smooth, non-greasy textures in lotions, creams, and other beauty products.
The agricultural sector benefits from dodecane's use in pesticide formulations, where it acts as a carrier for active ingredients, improving their efficacy and distribution. This application contributes to more efficient crop protection and increased agricultural yields.
In the field of energy storage, dodecane has shown promise as a potential hydrogen carrier in fuel cell technologies. Research is ongoing to explore its capacity to store and release hydrogen efficiently, potentially revolutionizing clean energy storage and transportation systems.
The electronics industry employs dodecane in the production of semiconductors and electronic components. Its low reactivity and ability to form thin, uniform films make it valuable in cleaning and coating processes during manufacturing.
As environmental concerns grow, the biodegradability of dodecane has led to its increased use in eco-friendly lubricants and hydraulic fluids. These applications cater to industries seeking more sustainable alternatives to traditional petroleum-based products.
The diverse market applications of dodecane highlight its significance in modern chemistry and industry. As research continues to uncover new properties and potential uses, dodecane's journey through various sectors is likely to expand, driving innovation and sustainability across multiple fields.
Technical Challenges
Dodecane, a key player in modern chemistry, faces several technical challenges that hinder its full potential in various applications. One of the primary obstacles is its low solubility in water, which limits its use in aqueous systems. This hydrophobic nature makes it difficult to incorporate dodecane into water-based formulations, restricting its applications in areas such as drug delivery and environmental remediation.
Another significant challenge lies in the controlled functionalization of dodecane. While its long carbon chain provides opportunities for modification, achieving selective and precise functionalization at specific positions remains a complex task. This limitation impacts the development of tailored dodecane derivatives for specialized applications in industries such as pharmaceuticals and materials science.
The volatility of dodecane presents both advantages and challenges. Its relatively high vapor pressure makes it useful in certain applications but also poses difficulties in handling and storage. Controlling the evaporation rate of dodecane-based formulations is crucial for maintaining product stability and effectiveness, particularly in coatings and lubricants.
Dodecane's susceptibility to oxidation is another technical hurdle. When exposed to air and light, it can undergo auto-oxidation, leading to the formation of undesirable byproducts. This oxidative instability affects the long-term storage and use of dodecane-containing products, necessitating the development of effective stabilization strategies.
The purification and separation of dodecane from complex mixtures pose additional challenges. In petroleum refining and other industrial processes, efficiently isolating high-purity dodecane from similar hydrocarbons requires advanced separation techniques. The development of more selective and energy-efficient separation methods remains an ongoing area of research.
Environmental concerns associated with dodecane usage also present technical challenges. As a hydrocarbon, its potential environmental impact, particularly in cases of spills or improper disposal, necessitates the development of eco-friendly alternatives or improved biodegradation strategies. Balancing the industrial utility of dodecane with environmental sustainability is a critical challenge facing researchers and industry professionals.
Lastly, the scalability of dodecane-based processes and products presents technical hurdles. Translating laboratory-scale successes to industrial-scale production often encounters issues related to cost-effectiveness, process efficiency, and quality control. Overcoming these scaling challenges is essential for the widespread adoption of dodecane-based innovations in various sectors of the chemical industry.
Another significant challenge lies in the controlled functionalization of dodecane. While its long carbon chain provides opportunities for modification, achieving selective and precise functionalization at specific positions remains a complex task. This limitation impacts the development of tailored dodecane derivatives for specialized applications in industries such as pharmaceuticals and materials science.
The volatility of dodecane presents both advantages and challenges. Its relatively high vapor pressure makes it useful in certain applications but also poses difficulties in handling and storage. Controlling the evaporation rate of dodecane-based formulations is crucial for maintaining product stability and effectiveness, particularly in coatings and lubricants.
Dodecane's susceptibility to oxidation is another technical hurdle. When exposed to air and light, it can undergo auto-oxidation, leading to the formation of undesirable byproducts. This oxidative instability affects the long-term storage and use of dodecane-containing products, necessitating the development of effective stabilization strategies.
The purification and separation of dodecane from complex mixtures pose additional challenges. In petroleum refining and other industrial processes, efficiently isolating high-purity dodecane from similar hydrocarbons requires advanced separation techniques. The development of more selective and energy-efficient separation methods remains an ongoing area of research.
Environmental concerns associated with dodecane usage also present technical challenges. As a hydrocarbon, its potential environmental impact, particularly in cases of spills or improper disposal, necessitates the development of eco-friendly alternatives or improved biodegradation strategies. Balancing the industrial utility of dodecane with environmental sustainability is a critical challenge facing researchers and industry professionals.
Lastly, the scalability of dodecane-based processes and products presents technical hurdles. Translating laboratory-scale successes to industrial-scale production often encounters issues related to cost-effectiveness, process efficiency, and quality control. Overcoming these scaling challenges is essential for the widespread adoption of dodecane-based innovations in various sectors of the chemical industry.
Current Methodologies
01 Synthesis and production of dodecane
Dodecane can be synthesized through various chemical processes, including the hydrogenation of long-chain olefins or the Fischer-Tropsch process. It is also produced as a byproduct in petroleum refining. The synthesis methods often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to achieve high purity and yield.- Synthesis and production of dodecane: Various methods for synthesizing and producing dodecane are described, including catalytic processes, hydrogenation reactions, and chemical transformations. These techniques aim to efficiently produce high-purity dodecane for industrial applications.
- Applications of dodecane in fuel and energy: Dodecane is utilized in fuel and energy-related applications, such as jet fuel components, diesel fuel additives, and as a potential renewable energy source. Its properties make it suitable for improving fuel efficiency and performance in various combustion engines.
- Use of dodecane in chemical processes and reactions: Dodecane serves as a reagent, solvent, or intermediate in various chemical processes and reactions. It is employed in organic synthesis, polymerization reactions, and as a starting material for producing other valuable chemicals.
- Dodecane in cosmetic and personal care products: Dodecane finds applications in cosmetic and personal care formulations due to its emollient properties and ability to enhance product texture. It is used in skincare products, hair care formulations, and as a carrier for active ingredients.
- Environmental and safety considerations of dodecane: Research and development efforts focus on addressing environmental and safety aspects of dodecane usage. This includes studying its biodegradability, potential environmental impacts, and developing safer handling and storage methods for industrial applications.
02 Applications in fuel and energy
Dodecane is widely used in the fuel and energy sector due to its high energy density and clean-burning properties. It is a component in jet fuels, diesel fuels, and other hydrocarbon-based energy sources. Research is ongoing to optimize its use in various energy applications, including as a potential hydrogen carrier for fuel cells.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in cosmetics and personal care products
Dodecane is utilized in cosmetics and personal care products as an emollient, solvent, and carrier for active ingredients. It has a light, non-greasy feel and is easily absorbed by the skin. Its properties make it suitable for use in various formulations, including moisturizers, sunscreens, and hair care products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Industrial and chemical applications
Dodecane finds applications in various industrial and chemical processes. It is used as a solvent in organic synthesis, as a standard in gas chromatography, and as a component in lubricants and cutting fluids. Its low reactivity and stability make it suitable for use in heat transfer fluids and as a diluent in chemical reactions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations
Research on dodecane also focuses on its environmental impact and safety aspects. Studies are conducted to assess its biodegradability, potential for bioaccumulation, and effects on aquatic ecosystems. Safety measures for handling and storage are developed, and efforts are made to minimize its release into the environment during production and use.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The competitive landscape for navigating dodecane's complex journey in modern chemistry is characterized by a mature market with established players and ongoing research. The global market for dodecane and related chemicals is substantial, driven by applications in various industries. Technologically, the field is well-developed, with companies like BASF, Arkema, and Wanhua Chemical Group leading in production and innovation. Research institutions such as the University of California and Rice University contribute to advancing the understanding and applications of dodecane. The involvement of pharmaceutical giants like Pfizer and specialty chemical companies like PharmaZell indicates the compound's importance in drug development and industrial processes, showcasing a diverse and competitive ecosystem.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed advanced catalytic processes for the efficient production and transformation of dodecane. Their approach involves using novel metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as catalysts, which offer high selectivity and yield in dodecane-related reactions[1]. The company has also implemented a green chemistry initiative, focusing on sustainable dodecane production from renewable feedstocks[2]. BASF's process integrates bio-based feedstocks with traditional petrochemical routes, resulting in a hybrid production method that reduces carbon footprint while maintaining product quality[3]. Additionally, they have invested in process intensification technologies, such as reactive distillation, to streamline dodecane purification and reduce energy consumption[4].
Strengths: Innovative catalytic processes, sustainable production methods, and process intensification. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs compared to traditional methods and reliance on specialized catalyst materials.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical has developed a proprietary technology for dodecane production and modification, focusing on its application in high-performance polymers and specialty chemicals. Their approach involves a novel hydrogenation process that yields ultra-high purity dodecane (>99.9%)[1]. The company has also implemented an integrated production system that combines dodecane synthesis with downstream product manufacturing, such as polyurethane precursors[2]. Wanhua's process utilizes advanced process control systems and machine learning algorithms to optimize reaction conditions and product quality[3]. Furthermore, they have developed eco-friendly formulations incorporating dodecane for various applications, including low-VOC coatings and biodegradable lubricants[4].
Strengths: High-purity product, integrated production system, and diverse application development. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in scaling up the novel hydrogenation process and dependency on specific raw material sources.
Key Innovations
Host cells and methods for producing diacid compounds
PatentWO2012071439A1
Innovation
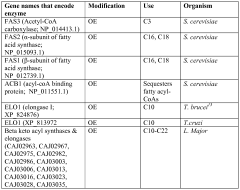
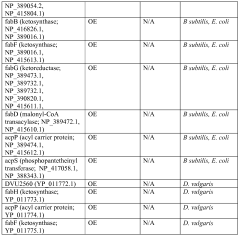
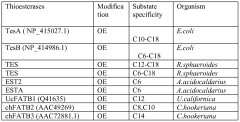
- Genetically engineered host cells using recombinant vectors and pathways such as Type I, II, and III fatty acid synthases, Type I polyketide synthases, and 2-ketoacid biosynthesis to produce specific chain length fatty acids and diacids from fermentable carbon sources, enabling controlled production and secretion of α,ω-dicarboxylic acids and ω-hydroxy fatty acids.
Process for producing long chain amino acids and dibasic acids
PatentActiveUS20190292134A1
Innovation
- A process utilizing commercially available hydroxy fatty acids as starting materials to produce long chain amino acids and dibasic acids through oxidation, oximation, esterification or amidation, and Beckmann rearrangement, followed by hydrolysis, which provides high yields and mild reaction conditions, and uses stable and renewable materials like castor oil.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of dodecane, a key component in modern chemistry, is a critical consideration in its production, use, and disposal. As a hydrocarbon, dodecane poses significant environmental challenges, particularly in terms of air and water pollution, as well as its contribution to climate change.
In the atmosphere, dodecane can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog when it reacts with other pollutants in the presence of sunlight. This photochemical reaction can lead to respiratory issues in humans and damage to vegetation. Moreover, as a volatile organic compound (VOC), dodecane can directly impact air quality, potentially causing short-term health effects such as eye and respiratory tract irritation.
Water contamination is another major concern associated with dodecane. Accidental spills or improper disposal can lead to the introduction of this hydrocarbon into aquatic ecosystems. Due to its low water solubility and tendency to form a surface film, dodecane can have detrimental effects on aquatic life, disrupting oxygen transfer and potentially causing toxicity to various organisms.
The production and use of dodecane also contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily through the energy-intensive processes involved in its manufacture and the potential for fugitive emissions during handling and storage. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, the carbon footprint associated with dodecane and similar hydrocarbons is coming under increased scrutiny.
In response to these environmental concerns, there is a growing focus on developing more sustainable alternatives and improving the lifecycle management of dodecane. This includes exploring bio-based alternatives, enhancing production efficiency to reduce emissions, and implementing stricter regulations on its use and disposal. Additionally, research is being conducted on more effective remediation techniques for dodecane contamination in soil and water.
The chemical industry is also investing in green chemistry principles to mitigate the environmental impact of dodecane and similar compounds. This involves designing chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. Efforts are being made to develop catalysts that can enable more environmentally friendly synthesis routes for dodecane and its derivatives.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, companies working with dodecane are increasingly required to implement comprehensive environmental management systems. These systems aim to monitor and minimize the environmental footprint of dodecane throughout its lifecycle, from production to end-use and disposal.
In the atmosphere, dodecane can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and smog when it reacts with other pollutants in the presence of sunlight. This photochemical reaction can lead to respiratory issues in humans and damage to vegetation. Moreover, as a volatile organic compound (VOC), dodecane can directly impact air quality, potentially causing short-term health effects such as eye and respiratory tract irritation.
Water contamination is another major concern associated with dodecane. Accidental spills or improper disposal can lead to the introduction of this hydrocarbon into aquatic ecosystems. Due to its low water solubility and tendency to form a surface film, dodecane can have detrimental effects on aquatic life, disrupting oxygen transfer and potentially causing toxicity to various organisms.
The production and use of dodecane also contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily through the energy-intensive processes involved in its manufacture and the potential for fugitive emissions during handling and storage. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, the carbon footprint associated with dodecane and similar hydrocarbons is coming under increased scrutiny.
In response to these environmental concerns, there is a growing focus on developing more sustainable alternatives and improving the lifecycle management of dodecane. This includes exploring bio-based alternatives, enhancing production efficiency to reduce emissions, and implementing stricter regulations on its use and disposal. Additionally, research is being conducted on more effective remediation techniques for dodecane contamination in soil and water.
The chemical industry is also investing in green chemistry principles to mitigate the environmental impact of dodecane and similar compounds. This involves designing chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. Efforts are being made to develop catalysts that can enable more environmentally friendly synthesis routes for dodecane and its derivatives.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, companies working with dodecane are increasingly required to implement comprehensive environmental management systems. These systems aim to monitor and minimize the environmental footprint of dodecane throughout its lifecycle, from production to end-use and disposal.
Safety Regulations
The handling and transportation of dodecane are subject to stringent safety regulations due to its flammable nature and potential environmental impact. These regulations are designed to protect workers, the public, and the environment from the risks associated with this hydrocarbon compound.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established specific guidelines for the handling of dodecane in industrial settings. These include requirements for proper ventilation, personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response procedures. Workers must be trained in the safe handling of dodecane and be provided with appropriate safety data sheets (SDS) that detail its hazards and proper handling procedures.
The transportation of dodecane is regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT) in the US and similar agencies in other countries. It is classified as a Class 3 flammable liquid, which necessitates specific packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements. Containers must be properly sealed and labeled with appropriate hazard warnings. Vehicles transporting dodecane must display proper placards and follow designated routes to minimize risks to populated areas.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in dodecane management. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the US and equivalent agencies worldwide have established guidelines for the storage, disposal, and accidental release of dodecane. These regulations aim to prevent soil and water contamination, which could have severe ecological consequences.
International maritime transport of dodecane is governed by the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code, which provides detailed instructions for safe shipment by sea. This includes specifications for container types, stowage requirements, and emergency procedures in case of spills or fires at sea.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation applies to dodecane. This comprehensive framework requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals and provide safety information, ensuring that potential risks are identified and managed throughout the supply chain.
As the chemical industry continues to evolve, safety regulations for dodecane are regularly reviewed and updated. Recent trends include increased focus on sustainable practices, such as developing safer alternatives and improving recycling processes. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on harmonizing international regulations to facilitate global trade while maintaining high safety standards.
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established specific guidelines for the handling of dodecane in industrial settings. These include requirements for proper ventilation, personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response procedures. Workers must be trained in the safe handling of dodecane and be provided with appropriate safety data sheets (SDS) that detail its hazards and proper handling procedures.
The transportation of dodecane is regulated by the Department of Transportation (DOT) in the US and similar agencies in other countries. It is classified as a Class 3 flammable liquid, which necessitates specific packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements. Containers must be properly sealed and labeled with appropriate hazard warnings. Vehicles transporting dodecane must display proper placards and follow designated routes to minimize risks to populated areas.
Environmental regulations also play a crucial role in dodecane management. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the US and equivalent agencies worldwide have established guidelines for the storage, disposal, and accidental release of dodecane. These regulations aim to prevent soil and water contamination, which could have severe ecological consequences.
International maritime transport of dodecane is governed by the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code, which provides detailed instructions for safe shipment by sea. This includes specifications for container types, stowage requirements, and emergency procedures in case of spills or fires at sea.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation applies to dodecane. This comprehensive framework requires manufacturers and importers to register chemicals and provide safety information, ensuring that potential risks are identified and managed throughout the supply chain.
As the chemical industry continues to evolve, safety regulations for dodecane are regularly reviewed and updated. Recent trends include increased focus on sustainable practices, such as developing safer alternatives and improving recycling processes. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on harmonizing international regulations to facilitate global trade while maintaining high safety standards.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!