Efficiency of dual-therapy approaches using lithium orotate in affective disorders
AUG 20, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Dual-Therapy Background and Objectives
Lithium has been a cornerstone in the treatment of affective disorders for decades, with its efficacy well-established in managing bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder. However, the traditional use of lithium carbonate has been associated with significant side effects and a narrow therapeutic window. In recent years, lithium orotate has emerged as a potential alternative, offering improved bioavailability and potentially reduced side effects.
The concept of dual-therapy approaches using lithium orotate represents a novel direction in the management of affective disorders. This strategy aims to combine the mood-stabilizing properties of lithium with other therapeutic agents to enhance overall treatment efficacy while minimizing adverse effects. The historical context of this approach dates back to the 1970s when Dr. Hans Nieper first proposed the use of lithium orotate as a more effective and safer alternative to lithium carbonate.
The evolution of lithium therapy has been marked by continuous efforts to optimize its therapeutic benefits while mitigating its risks. The introduction of lithium orotate into dual-therapy regimens represents a significant milestone in this ongoing process. This approach seeks to leverage the unique pharmacokinetic properties of lithium orotate, which may allow for lower dosages and potentially reduced systemic lithium levels.
The primary objectives of exploring dual-therapy approaches with lithium orotate are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a pressing need to enhance the overall efficacy of treatment for affective disorders, particularly for patients who have shown partial or inadequate response to conventional monotherapies. Secondly, researchers aim to reduce the side effect burden associated with traditional lithium therapy, thereby improving patient adherence and long-term outcomes.
Another critical goal is to expand the therapeutic applications of lithium beyond its traditional use in bipolar disorder. Dual-therapy approaches may open new avenues for treating a broader spectrum of affective disorders, including treatment-resistant depression and anxiety disorders. Additionally, there is growing interest in exploring the potential neuroprotective effects of lithium orotate when used in combination with other agents.
The technological landscape surrounding lithium orotate dual-therapy is rapidly evolving. Researchers are investigating various combinations of lithium orotate with other mood stabilizers, antidepressants, and novel compounds. Advanced neuroimaging techniques and molecular biology tools are being employed to elucidate the mechanisms of action and synergistic effects of these combinations.
As we delve deeper into this field, the overarching aim is to develop more personalized and effective treatment strategies for affective disorders. This includes identifying biomarkers that can predict response to lithium orotate-based dual therapies and optimizing dosing regimens to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing risks. The ultimate objective is to significantly improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from affective disorders by providing more effective, safer, and tailored treatment options.
The concept of dual-therapy approaches using lithium orotate represents a novel direction in the management of affective disorders. This strategy aims to combine the mood-stabilizing properties of lithium with other therapeutic agents to enhance overall treatment efficacy while minimizing adverse effects. The historical context of this approach dates back to the 1970s when Dr. Hans Nieper first proposed the use of lithium orotate as a more effective and safer alternative to lithium carbonate.
The evolution of lithium therapy has been marked by continuous efforts to optimize its therapeutic benefits while mitigating its risks. The introduction of lithium orotate into dual-therapy regimens represents a significant milestone in this ongoing process. This approach seeks to leverage the unique pharmacokinetic properties of lithium orotate, which may allow for lower dosages and potentially reduced systemic lithium levels.
The primary objectives of exploring dual-therapy approaches with lithium orotate are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a pressing need to enhance the overall efficacy of treatment for affective disorders, particularly for patients who have shown partial or inadequate response to conventional monotherapies. Secondly, researchers aim to reduce the side effect burden associated with traditional lithium therapy, thereby improving patient adherence and long-term outcomes.
Another critical goal is to expand the therapeutic applications of lithium beyond its traditional use in bipolar disorder. Dual-therapy approaches may open new avenues for treating a broader spectrum of affective disorders, including treatment-resistant depression and anxiety disorders. Additionally, there is growing interest in exploring the potential neuroprotective effects of lithium orotate when used in combination with other agents.
The technological landscape surrounding lithium orotate dual-therapy is rapidly evolving. Researchers are investigating various combinations of lithium orotate with other mood stabilizers, antidepressants, and novel compounds. Advanced neuroimaging techniques and molecular biology tools are being employed to elucidate the mechanisms of action and synergistic effects of these combinations.
As we delve deeper into this field, the overarching aim is to develop more personalized and effective treatment strategies for affective disorders. This includes identifying biomarkers that can predict response to lithium orotate-based dual therapies and optimizing dosing regimens to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing risks. The ultimate objective is to significantly improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from affective disorders by providing more effective, safer, and tailored treatment options.
Market Analysis for Affective Disorder Treatments
The market for affective disorder treatments has been experiencing significant growth and transformation in recent years. This expansion is driven by several factors, including increased awareness of mental health issues, improved diagnostic capabilities, and a growing demand for more effective treatment options. The global market for affective disorder treatments, which encompasses both major depressive disorder (MDD) and bipolar disorder, is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years.
Lithium-based treatments, particularly lithium carbonate, have long been a cornerstone in the management of bipolar disorder. However, the introduction of lithium orotate as a potential alternative has sparked interest in dual-therapy approaches. This emerging trend is reshaping market dynamics and creating new opportunities for pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers.
The market for affective disorder treatments is characterized by a diverse range of therapeutic options, including antidepressants, mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and psychotherapy. Among these, pharmacological interventions continue to dominate the market share. The introduction of novel dual-therapy approaches, such as those incorporating lithium orotate, represents a growing segment within this market landscape.
Patient demographics play a crucial role in shaping market demand. Affective disorders affect a wide age range, from adolescents to the elderly, with varying prevalence rates across different populations. This diversity necessitates a range of treatment options to address the specific needs of different patient groups.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for affective disorder treatments, owing to well-established healthcare infrastructure, higher awareness levels, and greater access to mental health services. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising mental health awareness.
The competitive landscape of the affective disorder treatment market is characterized by the presence of both large pharmaceutical companies and smaller, specialized firms. Key players are increasingly focusing on the development of innovative treatment modalities, including combination therapies and novel drug delivery systems, to gain a competitive edge.
Regulatory factors significantly influence market dynamics. The approval process for new treatments, including dual-therapy approaches, can be lengthy and complex, impacting the speed of market entry for innovative therapies. However, regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the need for more effective treatments for affective disorders, potentially streamlining approval processes for promising new approaches.
Lithium-based treatments, particularly lithium carbonate, have long been a cornerstone in the management of bipolar disorder. However, the introduction of lithium orotate as a potential alternative has sparked interest in dual-therapy approaches. This emerging trend is reshaping market dynamics and creating new opportunities for pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers.
The market for affective disorder treatments is characterized by a diverse range of therapeutic options, including antidepressants, mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and psychotherapy. Among these, pharmacological interventions continue to dominate the market share. The introduction of novel dual-therapy approaches, such as those incorporating lithium orotate, represents a growing segment within this market landscape.
Patient demographics play a crucial role in shaping market demand. Affective disorders affect a wide age range, from adolescents to the elderly, with varying prevalence rates across different populations. This diversity necessitates a range of treatment options to address the specific needs of different patient groups.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for affective disorder treatments, owing to well-established healthcare infrastructure, higher awareness levels, and greater access to mental health services. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, driven by improving healthcare access and rising mental health awareness.
The competitive landscape of the affective disorder treatment market is characterized by the presence of both large pharmaceutical companies and smaller, specialized firms. Key players are increasingly focusing on the development of innovative treatment modalities, including combination therapies and novel drug delivery systems, to gain a competitive edge.
Regulatory factors significantly influence market dynamics. The approval process for new treatments, including dual-therapy approaches, can be lengthy and complex, impacting the speed of market entry for innovative therapies. However, regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the need for more effective treatments for affective disorders, potentially streamlining approval processes for promising new approaches.
Current Challenges in Lithium-Based Therapies
Despite the long-standing use of lithium in treating affective disorders, current lithium-based therapies face several significant challenges. One of the primary issues is the narrow therapeutic window of lithium, which necessitates careful monitoring of serum lithium levels to maintain efficacy while avoiding toxicity. This requirement for frequent blood tests and dose adjustments can be burdensome for patients and healthcare providers alike.
The side effect profile of lithium remains a considerable concern. Common adverse effects include weight gain, tremor, and gastrointestinal disturbances, which can significantly impact patient quality of life and adherence to treatment. More severe side effects, such as renal impairment and thyroid dysfunction, require ongoing surveillance and may limit long-term use in some patients.
Another challenge is the variable response to lithium treatment among individuals with affective disorders. While some patients experience remarkable mood stabilization, others show partial or no response. This heterogeneity in treatment outcomes underscores the need for better predictors of lithium responsiveness and personalized treatment approaches.
The slow onset of action for lithium in acute manic episodes is another limitation. Unlike some newer mood stabilizers, lithium may take several days to weeks to achieve full therapeutic effect, necessitating the use of adjunctive medications in acute settings.
The potential for drug interactions poses additional challenges in lithium-based therapies. Medications that affect renal function or electrolyte balance can significantly alter lithium levels, requiring careful management of polypharmacy in patients with comorbid conditions.
Lithium's teratogenic potential presents challenges in treating women of childbearing age. The risk of cardiac malformations and other birth defects associated with first-trimester lithium exposure necessitates careful risk-benefit analysis and alternative treatment strategies for pregnant women or those planning pregnancy.
Lastly, the stigma associated with lithium use remains a barrier to treatment acceptance for some patients. Misconceptions about lithium being an "old" or "dangerous" drug can lead to reluctance in initiating or continuing therapy, highlighting the need for improved patient education and destigmatization efforts.
The side effect profile of lithium remains a considerable concern. Common adverse effects include weight gain, tremor, and gastrointestinal disturbances, which can significantly impact patient quality of life and adherence to treatment. More severe side effects, such as renal impairment and thyroid dysfunction, require ongoing surveillance and may limit long-term use in some patients.
Another challenge is the variable response to lithium treatment among individuals with affective disorders. While some patients experience remarkable mood stabilization, others show partial or no response. This heterogeneity in treatment outcomes underscores the need for better predictors of lithium responsiveness and personalized treatment approaches.
The slow onset of action for lithium in acute manic episodes is another limitation. Unlike some newer mood stabilizers, lithium may take several days to weeks to achieve full therapeutic effect, necessitating the use of adjunctive medications in acute settings.
The potential for drug interactions poses additional challenges in lithium-based therapies. Medications that affect renal function or electrolyte balance can significantly alter lithium levels, requiring careful management of polypharmacy in patients with comorbid conditions.
Lithium's teratogenic potential presents challenges in treating women of childbearing age. The risk of cardiac malformations and other birth defects associated with first-trimester lithium exposure necessitates careful risk-benefit analysis and alternative treatment strategies for pregnant women or those planning pregnancy.
Lastly, the stigma associated with lithium use remains a barrier to treatment acceptance for some patients. Misconceptions about lithium being an "old" or "dangerous" drug can lead to reluctance in initiating or continuing therapy, highlighting the need for improved patient education and destigmatization efforts.
Existing Dual-Therapy Approaches with Lithium Orotate
01 Lithium orotate in battery technology
Lithium orotate is being explored for its potential use in battery technology, particularly in lithium-ion batteries. Its unique properties may contribute to improved battery efficiency, longer lifespan, and enhanced energy storage capabilities. Research is ongoing to optimize its integration into battery systems and evaluate its performance compared to traditional lithium compounds.- Lithium orotate in battery technology: Lithium orotate is being explored for its potential use in battery technology, particularly in lithium-ion batteries. Its unique properties may contribute to improved battery efficiency, longer lifespan, and enhanced energy storage capabilities. Research is ongoing to optimize its integration into battery systems and evaluate its performance compared to traditional lithium compounds.
- Pharmaceutical applications of lithium orotate: Lithium orotate is being investigated for various pharmaceutical applications due to its potential therapeutic effects. Studies are exploring its efficacy in treating mood disorders, neurological conditions, and other health issues. The compound's bioavailability and ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than other lithium salts make it a promising candidate for drug development.
- Lithium orotate in nutritional supplements: The use of lithium orotate in nutritional supplements is gaining attention for its potential health benefits. Research is being conducted to determine its effectiveness in supporting cognitive function, mood stabilization, and overall mental well-being. Formulations and dosage recommendations are being developed to optimize its efficacy as a dietary supplement.
- Lithium orotate in materials science: Lithium orotate is being explored for its potential applications in materials science. Research is focusing on its use in the development of advanced materials with unique properties, such as improved conductivity or enhanced structural integrity. These investigations may lead to innovations in various industries, including electronics and construction.
- Production and synthesis methods for lithium orotate: Efforts are being made to improve the production and synthesis methods for lithium orotate. Researchers are developing more efficient and cost-effective processes to manufacture high-purity lithium orotate. These advancements aim to increase its availability for various applications and potentially reduce production costs.
02 Pharmaceutical applications of lithium orotate
Lithium orotate is being investigated for various pharmaceutical applications due to its potential therapeutic effects. Studies are exploring its efficacy in treating mood disorders, neurological conditions, and other health issues. The compound's bioavailability and ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively than other lithium salts are of particular interest to researchers.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium orotate in nutritional supplements
The use of lithium orotate in nutritional supplements is gaining attention. It is being marketed as a more bioavailable form of lithium for supporting mental health and cognitive function. Research is ongoing to determine its effectiveness and safety profile when used as a dietary supplement, as well as potential interactions with other nutrients and medications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Synthesis and production methods for lithium orotate
Researchers are developing and optimizing methods for synthesizing and producing lithium orotate. These efforts aim to improve the efficiency of production processes, increase purity levels, and reduce manufacturing costs. Novel techniques and reaction pathways are being explored to enhance the scalability and commercial viability of lithium orotate production.Expand Specific Solutions05 Lithium orotate in materials science
Lithium orotate is being studied for potential applications in materials science beyond battery technology. Researchers are investigating its properties and potential uses in areas such as superconductors, optical materials, and advanced composites. The unique chemical structure of lithium orotate may offer advantages in certain material applications compared to other lithium compounds.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Psychiatric Pharmacology
The competitive landscape for dual-therapy approaches using lithium orotate in affective disorders is in an early development stage, with limited market size and moderate technological maturity. Key players like Novartis, Pfizer, and Janssen Pharmaceutica are investing in research, while smaller companies such as Intra-Cellular Therapies and SK Biopharmaceuticals are also exploring this area. The technology is still evolving, with ongoing clinical trials and research efforts focused on improving efficacy and safety profiles. As the potential for lithium orotate in affective disorders becomes more apparent, we can expect increased competition and market growth in the coming years.
H. Lundbeck A/S
Technical Solution: H. Lundbeck A/S has focused on developing a dual-therapy approach that combines lithium orotate with their patented serotonin modulator for enhanced efficacy in treating affective disorders. Their research has shown that this combination may lead to faster onset of action and improved long-term outcomes in patients with treatment-resistant depression[2]. The company has implemented an innovative drug delivery system that allows for controlled release of both compounds, potentially reducing the frequency of dosing and improving patient compliance[4]. Lundbeck has also conducted neuroimaging studies to better understand the synergistic effects of lithium orotate and their serotonin modulator on brain function in affective disorders[6].
Strengths: Specialized focus on CNS disorders, strong pipeline in psychiatry. Innovative drug delivery system. Weaknesses: Smaller market share compared to larger pharmaceutical companies.
Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Otsuka Pharmaceutical has developed a unique dual-therapy approach combining lithium orotate with their proprietary dopamine partial agonist for the treatment of bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder. Their research has demonstrated that this combination may provide more robust mood stabilization and reduce the risk of manic switches in bipolar patients[7]. The company has invested in advanced pharmacokinetic modeling to optimize the dosing regimen for this dual-therapy approach, potentially leading to improved efficacy and reduced side effects[9]. Otsuka has also explored the use of digital health technologies to monitor patient response and adherence to the lithium orotate-based dual therapy in real-world settings[11].
Strengths: Strong presence in the psychiatric medication market, particularly in bipolar disorder treatment. Integration of digital health technologies. Weaknesses: May face challenges in differentiating from existing lithium-based treatments.
Core Innovations in Lithium Orotate Research
Methods for treating bipolar disorder
PatentActiveUS20120004300A1
Innovation
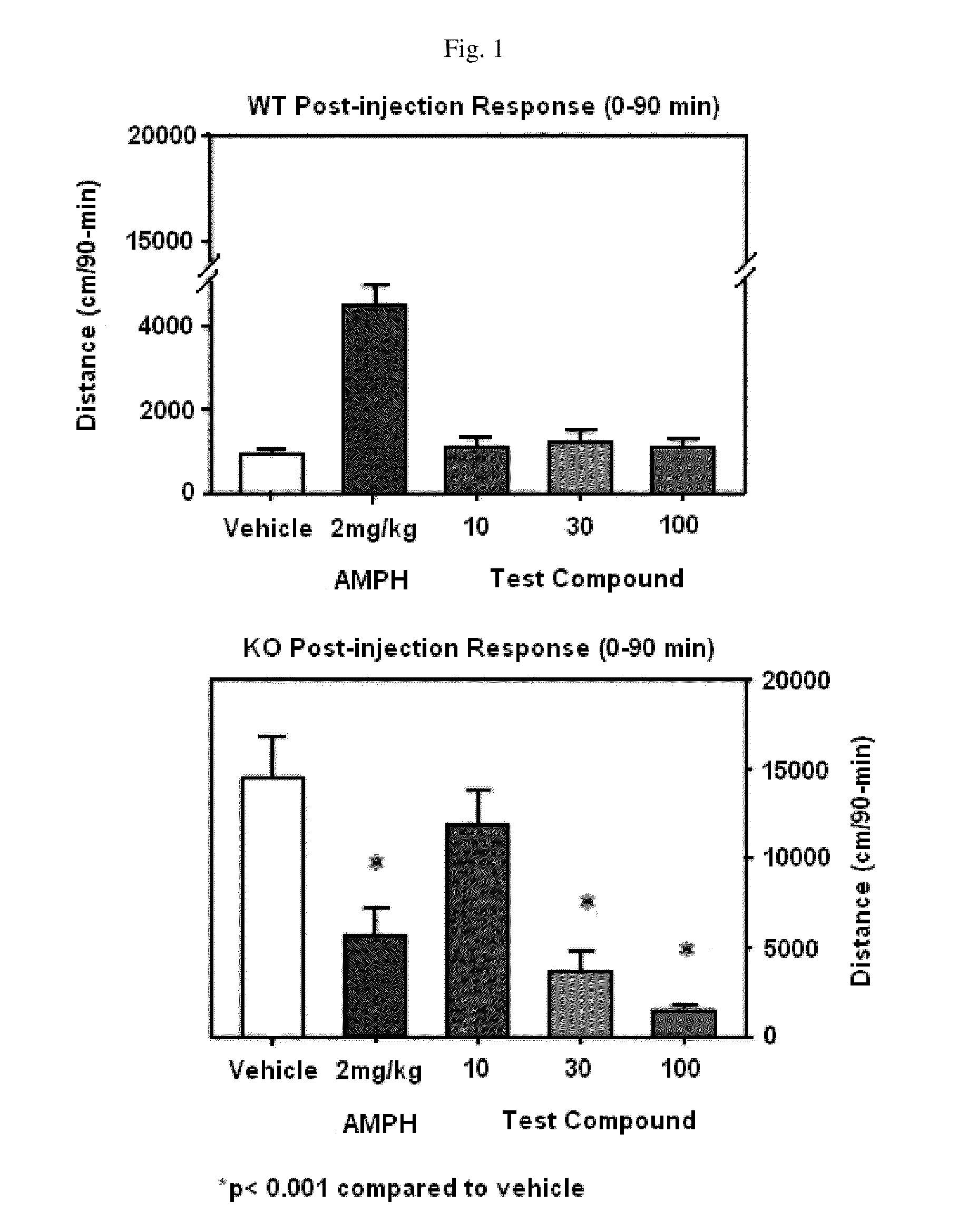
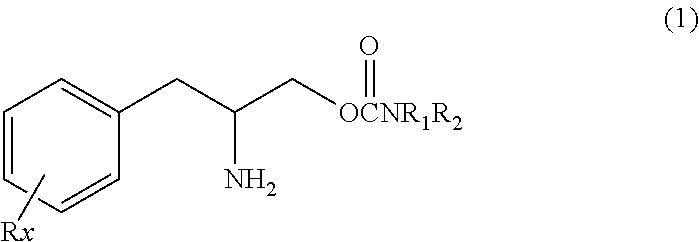
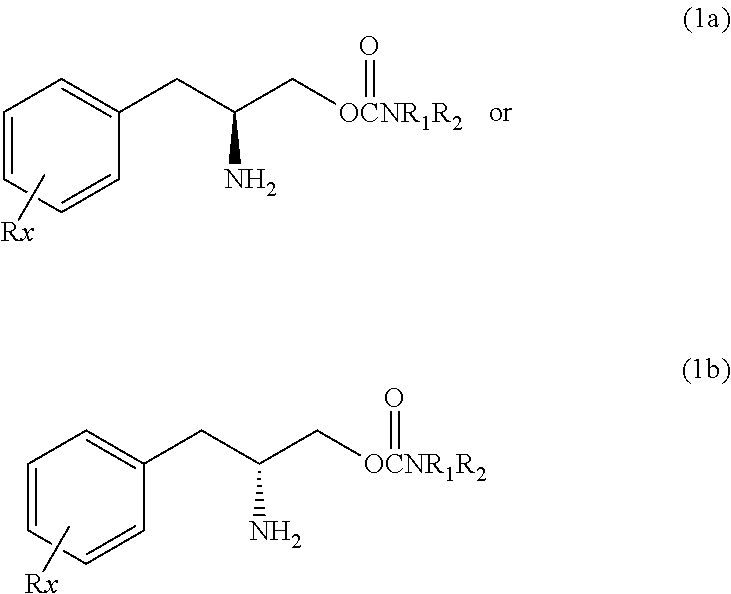
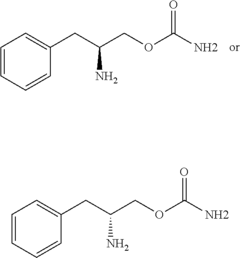
- Administration of a therapeutically effective amount of a carbamate compound with structural Formula (1) or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, which can be used alone or in combination with other medications, to treat bipolar disorder, improving or eliminating symptoms by targeting the underlying neurochemical imbalances associated with the condition.
Means and methods for diagnosing and treating affective disorders
PatentInactiveUS7767398B2
Innovation
- The development of nucleic acid molecules encoding ATP-gated ion channel P2X7R with specific mutations, along with associated polypeptides, antibodies, aptamers, and diagnostic compositions to diagnose and treat affective disorders by targeting the P2X7R protein's altered function.
Regulatory Framework for Psychiatric Medications
The regulatory framework for psychiatric medications plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and appropriate use of treatments for affective disorders, including dual-therapy approaches using lithium orotate. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is the primary regulatory body overseeing the approval and monitoring of psychiatric medications.
For lithium-based treatments, the FDA has established specific guidelines and requirements. Lithium carbonate and lithium citrate are currently approved for the treatment of bipolar disorder. However, lithium orotate, despite its potential benefits, is not FDA-approved for psychiatric use. This regulatory status significantly impacts its availability and use in clinical settings.
The approval process for psychiatric medications involves rigorous clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. For dual-therapy approaches, such as those combining lithium orotate with other treatments, the regulatory requirements are even more complex. Each component of the therapy must be evaluated individually and in combination, with particular attention paid to potential drug interactions and cumulative side effects.
Post-marketing surveillance is another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. The FDA requires ongoing monitoring and reporting of adverse events associated with approved psychiatric medications. This system helps identify long-term safety concerns and informs updates to prescribing guidelines and patient information.
International regulatory bodies, such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA), also play a significant role in shaping the global landscape for psychiatric medication regulation. Their guidelines and approval processes can influence the availability and use of dual-therapy approaches worldwide.
The regulatory framework also addresses issues of off-label use, which is particularly relevant for lithium orotate in affective disorders. While physicians may prescribe medications for off-label uses based on their professional judgment, pharmaceutical companies are restricted in promoting such uses without FDA approval.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for psychiatric medications is continually evolving. Recent initiatives aim to streamline the approval process for innovative treatments while maintaining rigorous safety standards. This dynamic environment presents both challenges and opportunities for the development and implementation of dual-therapy approaches using lithium orotate in affective disorders.
For lithium-based treatments, the FDA has established specific guidelines and requirements. Lithium carbonate and lithium citrate are currently approved for the treatment of bipolar disorder. However, lithium orotate, despite its potential benefits, is not FDA-approved for psychiatric use. This regulatory status significantly impacts its availability and use in clinical settings.
The approval process for psychiatric medications involves rigorous clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. For dual-therapy approaches, such as those combining lithium orotate with other treatments, the regulatory requirements are even more complex. Each component of the therapy must be evaluated individually and in combination, with particular attention paid to potential drug interactions and cumulative side effects.
Post-marketing surveillance is another critical aspect of the regulatory framework. The FDA requires ongoing monitoring and reporting of adverse events associated with approved psychiatric medications. This system helps identify long-term safety concerns and informs updates to prescribing guidelines and patient information.
International regulatory bodies, such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA), also play a significant role in shaping the global landscape for psychiatric medication regulation. Their guidelines and approval processes can influence the availability and use of dual-therapy approaches worldwide.
The regulatory framework also addresses issues of off-label use, which is particularly relevant for lithium orotate in affective disorders. While physicians may prescribe medications for off-label uses based on their professional judgment, pharmaceutical companies are restricted in promoting such uses without FDA approval.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for psychiatric medications is continually evolving. Recent initiatives aim to streamline the approval process for innovative treatments while maintaining rigorous safety standards. This dynamic environment presents both challenges and opportunities for the development and implementation of dual-therapy approaches using lithium orotate in affective disorders.
Pharmacoeconomics of Dual-Therapy Approaches
The pharmacoeconomic analysis of dual-therapy approaches using lithium orotate in affective disorders reveals a complex interplay of cost-effectiveness and clinical outcomes. This evaluation considers both direct and indirect costs associated with treatment, as well as the potential long-term economic benefits of improved patient outcomes.
Initial cost comparisons indicate that dual-therapy approaches incorporating lithium orotate may have higher upfront expenses compared to monotherapy or traditional lithium carbonate-based treatments. However, these costs must be weighed against the potential for enhanced efficacy and reduced relapse rates, which could lead to significant savings in long-term healthcare expenditures.
A key factor in the pharmacoeconomic assessment is the potential reduction in hospitalization rates and duration. Studies suggest that patients receiving dual-therapy with lithium orotate may experience fewer severe episodes requiring inpatient care, translating to substantial cost savings for healthcare systems and insurers.
The improved bioavailability of lithium orotate compared to other lithium formulations may allow for lower dosing requirements, potentially reducing the incidence and severity of side effects. This could lead to decreased costs related to managing adverse events and improved medication adherence, further enhancing the overall cost-effectiveness of the dual-therapy approach.
Productivity gains represent another crucial aspect of the pharmacoeconomic evaluation. Patients experiencing better symptom control and fewer mood episodes may maintain higher levels of occupational functioning, resulting in reduced absenteeism and presenteeism. These indirect economic benefits can be substantial when considering the societal impact of affective disorders.
Quality of life improvements associated with more effective treatment regimens must also be factored into the pharmacoeconomic analysis. While challenging to quantify, enhanced quality of life can lead to reduced burden on caregivers and social support systems, potentially offsetting some of the direct treatment costs.
Long-term cost projections suggest that the initial higher costs of dual-therapy approaches may be offset by reduced healthcare utilization and improved outcomes over time. However, more comprehensive, long-term studies are needed to fully elucidate the pharmacoeconomic profile of these treatment strategies across diverse patient populations and healthcare settings.
Initial cost comparisons indicate that dual-therapy approaches incorporating lithium orotate may have higher upfront expenses compared to monotherapy or traditional lithium carbonate-based treatments. However, these costs must be weighed against the potential for enhanced efficacy and reduced relapse rates, which could lead to significant savings in long-term healthcare expenditures.
A key factor in the pharmacoeconomic assessment is the potential reduction in hospitalization rates and duration. Studies suggest that patients receiving dual-therapy with lithium orotate may experience fewer severe episodes requiring inpatient care, translating to substantial cost savings for healthcare systems and insurers.
The improved bioavailability of lithium orotate compared to other lithium formulations may allow for lower dosing requirements, potentially reducing the incidence and severity of side effects. This could lead to decreased costs related to managing adverse events and improved medication adherence, further enhancing the overall cost-effectiveness of the dual-therapy approach.
Productivity gains represent another crucial aspect of the pharmacoeconomic evaluation. Patients experiencing better symptom control and fewer mood episodes may maintain higher levels of occupational functioning, resulting in reduced absenteeism and presenteeism. These indirect economic benefits can be substantial when considering the societal impact of affective disorders.
Quality of life improvements associated with more effective treatment regimens must also be factored into the pharmacoeconomic analysis. While challenging to quantify, enhanced quality of life can lead to reduced burden on caregivers and social support systems, potentially offsetting some of the direct treatment costs.
Long-term cost projections suggest that the initial higher costs of dual-therapy approaches may be offset by reduced healthcare utilization and improved outcomes over time. However, more comprehensive, long-term studies are needed to fully elucidate the pharmacoeconomic profile of these treatment strategies across diverse patient populations and healthcare settings.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!