Enovix Approach to Cycle Life Optimization in Lithium-Ion Batteries
Enovix Li-ion Battery Evolution and Objectives
Lithium-ion batteries have undergone significant evolution since their commercial introduction in the early 1990s. The technology has seen continuous improvements in energy density, power output, and cycle life. Enovix, a pioneering company in the field, has been at the forefront of this evolution, particularly in addressing the critical aspect of cycle life optimization.
The primary objective of Enovix's approach to cycle life optimization is to develop lithium-ion batteries that can maintain their capacity over a greater number of charge-discharge cycles. This goal is driven by the increasing demand for long-lasting, high-performance batteries in various applications, from consumer electronics to electric vehicles and grid storage systems.
Enovix's evolutionary path in lithium-ion battery technology has focused on innovative electrode designs and advanced materials. Their proprietary 3D silicon anode technology represents a significant departure from traditional graphite anodes, aiming to increase energy density while simultaneously addressing cycle life challenges associated with silicon expansion during charging.
The company's objectives extend beyond merely increasing the number of cycles. Enovix aims to maintain a high percentage of initial capacity even after thousands of cycles, which is crucial for the longevity and reliability of battery-powered devices and systems. This approach aligns with the broader industry goal of reducing electronic waste and improving the sustainability of battery-powered technologies.
Another key objective in Enovix's cycle life optimization strategy is to achieve these improvements without compromising other critical battery parameters such as safety, charge rate, and operating temperature range. This holistic approach to battery development reflects the complex interplay between various performance metrics in lithium-ion technology.
Enovix's evolution in this field also encompasses the development of advanced manufacturing techniques. Their objective is to create scalable production methods that can maintain the integrity of their innovative battery architecture, ensuring that the benefits of their cycle life optimization approach can be realized in mass-produced batteries.
The company's research and development efforts are guided by the long-term objective of pushing the boundaries of what is possible with lithium-ion technology. By focusing on cycle life optimization, Enovix aims to address one of the most significant limitations of current battery technology, potentially extending the useful life of battery-powered devices and reducing the total cost of ownership for consumers and businesses alike.
Market Demand for Long-Lasting Li-ion Batteries
The demand for long-lasting lithium-ion batteries has been steadily increasing across various sectors, driven by the growing need for reliable and durable energy storage solutions. In the consumer electronics market, smartphones, laptops, and wearable devices require batteries that can maintain their capacity over extended periods, enhancing user experience and reducing the frequency of device replacements. This demand is further amplified by the rising trend of remote work and digital connectivity, which has intensified the reliance on portable electronic devices.
The electric vehicle (EV) industry represents a significant driver for advanced battery technologies. As the automotive sector transitions towards electrification, there is a critical need for batteries that can withstand thousands of charge cycles while maintaining high energy density. This requirement is essential for increasing the range of EVs and reducing the total cost of ownership, which are key factors in accelerating widespread EV adoption.
In the renewable energy sector, the integration of intermittent power sources such as solar and wind into the grid necessitates robust energy storage systems. Long-lasting batteries play a crucial role in grid stabilization, peak shaving, and load balancing. The ability to cycle frequently without significant degradation is paramount for ensuring the economic viability of large-scale energy storage projects.
The industrial and aerospace sectors also contribute to the demand for durable lithium-ion batteries. In industrial applications, batteries are used in robotics, automated guided vehicles, and backup power systems, where longevity and reliability are essential. The aerospace industry requires batteries that can withstand extreme conditions and maintain performance over extended periods, particularly for satellite and space exploration missions.
Market analysts project substantial growth in the advanced battery market, with a particular emphasis on technologies that enhance cycle life. This growth is underpinned by stringent environmental regulations, government incentives for clean energy adoption, and corporate sustainability initiatives. The push towards circular economy principles further accentuates the importance of long-lasting batteries, as they reduce waste and the environmental impact associated with battery production and disposal.
Innovations in battery chemistry, materials science, and manufacturing processes are key areas of focus for meeting this market demand. Companies investing in research and development of cycle life optimization techniques, such as Enovix, are well-positioned to capture significant market share. The ability to deliver batteries with extended lifespans not only addresses current market needs but also opens up new applications and use cases across various industries.
Current Challenges in Li-ion Battery Cycle Life
Lithium-ion batteries have become an integral part of modern technology, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. However, one of the most significant challenges facing these batteries is their cycle life - the number of charge-discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity significantly degrades. This issue is particularly critical in applications requiring long-term reliability and performance.
The primary factor affecting cycle life is the gradual degradation of battery components over time. The cathode material, typically composed of lithium metal oxides, can experience structural changes and dissolution during cycling. This leads to a loss of active material and a decrease in the battery's overall capacity. Similarly, the graphite anode can suffer from solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) growth and lithium plating, further reducing the battery's performance and lifespan.
Another major challenge is the mechanical stress induced during cycling. As lithium ions move in and out of the electrode materials, they cause volume changes that can lead to cracking and pulverization of the active particles. This not only reduces the amount of accessible active material but also creates new surfaces for unwanted side reactions, accelerating capacity fade.
Electrolyte decomposition is another critical issue affecting cycle life. The high voltages and reactive species present in lithium-ion batteries can cause the electrolyte to break down over time, forming resistive layers on electrode surfaces and consuming active lithium. This process not only increases internal resistance but also depletes the limited supply of lithium ions, further diminishing capacity.
Temperature management presents an additional hurdle in optimizing cycle life. High temperatures accelerate side reactions and degradation processes, while low temperatures can lead to lithium plating and reduced kinetics. Maintaining optimal operating temperatures across various usage scenarios and environments remains a significant engineering challenge.
Balancing performance with longevity is yet another obstacle. Strategies that enhance cycle life, such as limiting the depth of discharge or using more stable but less energy-dense materials, often come at the cost of reduced energy density or power capability. Finding the right trade-off between these competing factors is crucial for different applications.
Lastly, the variability in usage patterns and environmental conditions makes it difficult to predict and optimize cycle life across all scenarios. Batteries in different applications may experience vastly different cycling profiles, charge rates, and environmental stresses, necessitating tailored solutions for each use case.
Enovix's Cycle Life Optimization Techniques
01 Electrode material optimization
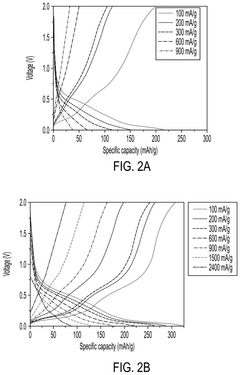
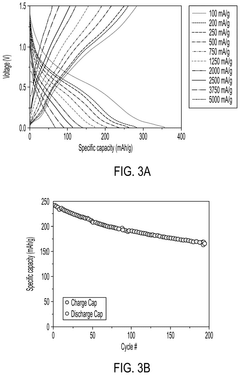
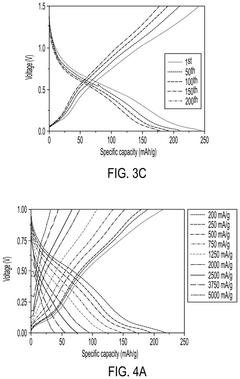
Improving the composition and structure of electrode materials can significantly enhance the cycle life of lithium-ion batteries. This includes developing novel cathode and anode materials with higher stability, better conductivity, and improved capacity retention. Techniques such as doping, surface modification, and nanostructuring are employed to achieve these improvements.- Electrode material optimization: Improving the composition and structure of electrode materials can significantly enhance the cycle life of lithium-ion batteries. This includes developing novel cathode and anode materials with higher stability, better conductivity, and improved capacity retention over multiple charge-discharge cycles.
- Electrolyte formulation: Advanced electrolyte formulations play a crucial role in extending battery cycle life. This involves developing new electrolyte additives, optimizing electrolyte composition, and creating novel electrolyte systems that minimize side reactions, reduce electrode degradation, and enhance overall battery performance.
- Battery management systems: Implementing sophisticated battery management systems can significantly improve cycle life. These systems monitor and control various parameters such as temperature, charge-discharge rates, and voltage levels to optimize battery performance and prevent degradation over time.
- Nanostructured materials: Incorporating nanostructured materials in battery components can enhance cycle life by improving mechanical stability, increasing active surface area, and facilitating faster ion transport. This approach can lead to batteries with higher capacity retention and longer lifespan.
- Protective coatings and interfaces: Developing protective coatings and engineered interfaces for electrode materials can significantly improve cycle life. These coatings and interfaces help prevent unwanted side reactions, reduce electrode degradation, and maintain structural integrity over multiple charge-discharge cycles.
02 Electrolyte formulation
Advanced electrolyte formulations play a crucial role in extending the cycle life of lithium-ion batteries. This involves developing new electrolyte additives, optimizing electrolyte composition, and creating novel electrolyte systems that enhance the stability of the electrode-electrolyte interface, reduce side reactions, and improve overall battery performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Battery management systems
Implementing sophisticated battery management systems can significantly improve the cycle life of lithium-ion batteries. These systems monitor and control various parameters such as charging/discharging rates, temperature, and state of charge to optimize battery performance and prevent degradation. Advanced algorithms and sensing technologies are utilized to achieve precise control and extend battery lifespan.Expand Specific Solutions04 Structural design and packaging
Innovative structural designs and packaging techniques can enhance the cycle life of lithium-ion batteries. This includes developing new cell architectures, improving thermal management systems, and optimizing the overall battery pack design to minimize stress on individual cells and ensure uniform performance across the battery system.Expand Specific Solutions05 Advanced manufacturing processes
Implementing advanced manufacturing processes can lead to improved cycle life in lithium-ion batteries. This involves developing precision manufacturing techniques, enhancing quality control measures, and utilizing novel production methods to ensure consistent and high-quality battery components. These processes aim to minimize defects and optimize the overall battery structure for extended cycle life.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Advanced Li-ion Battery Technology
The Enovix approach to cycle life optimization in lithium-ion batteries is situated within a highly competitive and rapidly evolving industry. The market for advanced battery technologies is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for electric vehicles and energy storage solutions. Key players like Contemporary Amperex Technology, LG Energy Solution, and Samsung SDI are investing heavily in research and development to improve battery performance and longevity. The technology is still maturing, with companies like StoreDot and Qnovo focusing on innovative charging and management solutions. Established automotive manufacturers such as Tesla and Renault are also actively involved in battery development, indicating the strategic importance of this technology across multiple sectors.
Ningde Amperex Technology Ltd.
StoreDot Ltd.
Core Innovations in Enovix Battery Design
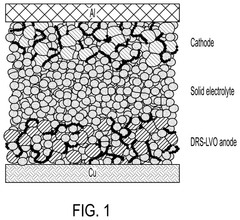
- A solid-state lithium-ion battery design featuring a lithium vanadium oxide anode with a disordered rocksalt structure, paired with a solid electrolyte and a nickel-rich cathode, enabling ultrafast charging and maintaining high energy density and cycle stability.
- Ultrafast electroplating of carbon as a coating agent for anode and cathode materials, specifically optimizing the carbon coating process to enhance cycle life, energy, and power densities, including the use of pulse waveform deposition and specific counter electrode configurations.
Environmental Impact of Extended Battery Life
The environmental impact of extended battery life in lithium-ion batteries, particularly through Enovix's approach to cycle life optimization, is a critical consideration in the broader context of sustainable energy solutions. By significantly increasing the number of charge-discharge cycles a battery can undergo before degradation, Enovix's technology has the potential to substantially reduce electronic waste and the frequency of battery replacements.
This extended lifespan directly translates to a reduction in raw material extraction and processing required for battery production. The mining of lithium, cobalt, and other essential battery materials often involves significant environmental disruption, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. By prolonging battery life, the demand for these materials per unit of energy storage over time is effectively decreased, leading to a lower overall environmental footprint.
Furthermore, the improved cycle life addresses one of the key challenges in renewable energy storage systems. With batteries capable of withstanding more charge-discharge cycles, renewable energy sources like solar and wind become more viable for long-term, large-scale energy storage. This enhancement could accelerate the transition away from fossil fuels, contributing to reduced carbon emissions and mitigating climate change impacts.
The extended battery life also has implications for consumer electronics and electric vehicles. Longer-lasting batteries in these applications mean fewer replacements, reducing the volume of electronic waste generated. This is particularly significant given the challenges associated with recycling lithium-ion batteries and the potential environmental hazards posed by improper disposal.
However, it's important to consider potential trade-offs. The manufacturing process for these advanced batteries may initially require more energy or resources. A comprehensive life cycle assessment would be necessary to quantify the net environmental benefit, considering factors such as production energy, material sourcing, and end-of-life management.
In the context of circular economy principles, Enovix's approach aligns well with the goal of maximizing resource efficiency. By extending the useful life of batteries, it promotes a more sustainable use of resources and potentially reduces the overall environmental impact of energy storage solutions. This could lead to a paradigm shift in how we approach battery technology and energy storage systems, prioritizing longevity and sustainability alongside performance metrics.
Safety Considerations in High-Cycle Li-ion Batteries
Safety considerations are paramount in the development and implementation of high-cycle lithium-ion batteries, particularly in the context of Enovix's approach to cycle life optimization. As these batteries are designed to withstand a greater number of charge-discharge cycles, the potential for safety issues increases, necessitating robust safety measures and protocols.
One of the primary safety concerns in high-cycle Li-ion batteries is thermal runaway, which can occur due to overcharging, physical damage, or manufacturing defects. Enovix's 3D silicon anode technology, while offering improved energy density and cycle life, requires careful thermal management to prevent excessive heat generation during rapid charging and discharging cycles.
The increased energy density of Enovix's batteries also raises concerns about the potential for more severe consequences in the event of a failure. To address this, advanced battery management systems (BMS) are crucial. These systems continuously monitor battery temperature, voltage, and current, implementing safeguards to prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits.
Mechanical integrity is another critical safety aspect, especially given the unique 3D structure of Enovix's batteries. The design must withstand physical stresses associated with repeated cycling without compromising the internal structure, which could lead to internal short circuits or electrolyte leakage.
Electrolyte stability is a key factor in ensuring long-term safety of high-cycle batteries. Enovix's approach likely involves the use of advanced electrolyte formulations that remain stable over extended cycling, reducing the risk of decomposition and gas generation that could lead to battery swelling or rupture.
Safety testing protocols for high-cycle Li-ion batteries must be more rigorous than those for conventional batteries. This includes extended cycle life testing under various environmental conditions, abuse testing to simulate extreme scenarios, and accelerated aging tests to predict long-term safety performance.
The manufacturing process itself must incorporate stringent quality control measures to ensure consistency and eliminate defects that could compromise safety. This is particularly important for Enovix's 3D silicon anode technology, which requires precise fabrication techniques.
Lastly, end-of-life considerations and safe disposal methods must be developed for high-cycle Li-ion batteries. As these batteries are designed to last longer, they may accumulate more wear and potential safety risks over time, necessitating clear guidelines for when and how to safely retire and recycle them.