Environmental Considerations in Next-Gen Electrolytic Cell Designs
AUG 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Electrolytic Cell Evolution and Eco-Goals
Electrolytic cells have undergone significant evolution since their inception, driven by the need for improved efficiency and environmental sustainability. The journey began with simple designs focused primarily on production output, but has since progressed to incorporate sophisticated technologies aimed at minimizing environmental impact. This evolution reflects a growing awareness of the ecological consequences of industrial processes and a commitment to developing more sustainable solutions.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards creating next-generation electrolytic cells that not only maintain high production efficiency but also address critical environmental concerns. These eco-goals include reducing energy consumption, minimizing greenhouse gas emissions, and decreasing the overall carbon footprint of electrolytic processes. The industry has recognized the importance of aligning technological advancements with global sustainability objectives, such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
One of the key areas of development has been the improvement of electrode materials and designs. Researchers have explored novel materials that offer enhanced conductivity and durability while reducing the need for environmentally harmful substances. This has led to the development of electrodes with longer lifespans, reducing waste and the frequency of replacements. Additionally, advancements in membrane technology have resulted in more efficient ion exchange processes, further contributing to energy savings and reduced environmental impact.
Another significant trend in electrolytic cell evolution is the integration of renewable energy sources. Many next-generation designs are being optimized to work effectively with intermittent power supplies from solar and wind sources. This integration not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also helps to balance the grid by utilizing excess renewable energy during peak production periods.
Water management has also become a crucial aspect of eco-friendly electrolytic cell design. New systems incorporate advanced water recycling and purification technologies, significantly reducing freshwater consumption and minimizing the discharge of potentially harmful effluents. This not only conserves water resources but also helps to protect aquatic ecosystems from industrial pollution.
The pursuit of circular economy principles has led to innovations in byproduct utilization and waste reduction. Modern electrolytic cells are increasingly designed to capture and repurpose byproducts that were previously considered waste. This approach not only improves resource efficiency but also opens up new revenue streams for industries, creating a win-win situation for both economic and environmental interests.
As we look towards the future, the evolution of electrolytic cells continues to be guided by ambitious eco-goals. The industry is striving for designs that achieve near-zero emissions, complete water circularity, and full integration with renewable energy systems. These aspirations drive ongoing research and development efforts, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in sustainable industrial processes.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards creating next-generation electrolytic cells that not only maintain high production efficiency but also address critical environmental concerns. These eco-goals include reducing energy consumption, minimizing greenhouse gas emissions, and decreasing the overall carbon footprint of electrolytic processes. The industry has recognized the importance of aligning technological advancements with global sustainability objectives, such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
One of the key areas of development has been the improvement of electrode materials and designs. Researchers have explored novel materials that offer enhanced conductivity and durability while reducing the need for environmentally harmful substances. This has led to the development of electrodes with longer lifespans, reducing waste and the frequency of replacements. Additionally, advancements in membrane technology have resulted in more efficient ion exchange processes, further contributing to energy savings and reduced environmental impact.
Another significant trend in electrolytic cell evolution is the integration of renewable energy sources. Many next-generation designs are being optimized to work effectively with intermittent power supplies from solar and wind sources. This integration not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also helps to balance the grid by utilizing excess renewable energy during peak production periods.
Water management has also become a crucial aspect of eco-friendly electrolytic cell design. New systems incorporate advanced water recycling and purification technologies, significantly reducing freshwater consumption and minimizing the discharge of potentially harmful effluents. This not only conserves water resources but also helps to protect aquatic ecosystems from industrial pollution.
The pursuit of circular economy principles has led to innovations in byproduct utilization and waste reduction. Modern electrolytic cells are increasingly designed to capture and repurpose byproducts that were previously considered waste. This approach not only improves resource efficiency but also opens up new revenue streams for industries, creating a win-win situation for both economic and environmental interests.
As we look towards the future, the evolution of electrolytic cells continues to be guided by ambitious eco-goals. The industry is striving for designs that achieve near-zero emissions, complete water circularity, and full integration with renewable energy systems. These aspirations drive ongoing research and development efforts, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in sustainable industrial processes.
Green Electrolysis Market Analysis
The green electrolysis market is experiencing rapid growth driven by the increasing demand for clean hydrogen production and the global push towards decarbonization. As environmental considerations become paramount in next-generation electrolytic cell designs, the market for environmentally friendly electrolysis technologies is expanding significantly.
The market size for green electrolysis is projected to grow substantially in the coming years. This growth is fueled by government initiatives, corporate sustainability goals, and the declining costs of renewable energy sources. The European Union, in particular, has set ambitious targets for green hydrogen production, which is expected to drive significant investment in electrolysis technologies.
Key market segments for green electrolysis include power generation, transportation, and industrial applications. The power generation sector is increasingly looking to hydrogen as a means of energy storage and grid balancing, especially in regions with high renewable energy penetration. In the transportation sector, hydrogen fuel cells are gaining traction for long-haul trucking, shipping, and potentially aviation, creating demand for green hydrogen production through electrolysis.
Industrial applications represent another significant market opportunity. Industries such as steel production, chemical manufacturing, and refining are exploring green hydrogen as a means to reduce their carbon footprint. This shift is driven by both regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability commitments.
Geographically, Europe is currently leading the green electrolysis market, with countries like Germany, the Netherlands, and Denmark making substantial investments in hydrogen infrastructure. However, other regions are quickly catching up. Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, are emerging as key players in the market. North America is also seeing increased activity, with both the United States and Canada announcing hydrogen strategies.
The competitive landscape of the green electrolysis market is dynamic, with both established industrial players and innovative startups vying for market share. Major industrial companies are leveraging their expertise in traditional electrolysis to develop more environmentally friendly solutions. Meanwhile, startups are introducing novel technologies that promise higher efficiency and lower costs.
Key market drivers include the declining cost of renewable electricity, technological advancements in electrolysis efficiency, and supportive government policies. However, challenges remain, such as the need for significant infrastructure development and the current high costs compared to conventional hydrogen production methods.
As environmental considerations continue to shape the development of next-generation electrolytic cell designs, the green electrolysis market is poised for substantial growth. The integration of advanced materials, optimized cell architectures, and intelligent control systems will be crucial in addressing environmental concerns and driving market expansion.
The market size for green electrolysis is projected to grow substantially in the coming years. This growth is fueled by government initiatives, corporate sustainability goals, and the declining costs of renewable energy sources. The European Union, in particular, has set ambitious targets for green hydrogen production, which is expected to drive significant investment in electrolysis technologies.
Key market segments for green electrolysis include power generation, transportation, and industrial applications. The power generation sector is increasingly looking to hydrogen as a means of energy storage and grid balancing, especially in regions with high renewable energy penetration. In the transportation sector, hydrogen fuel cells are gaining traction for long-haul trucking, shipping, and potentially aviation, creating demand for green hydrogen production through electrolysis.
Industrial applications represent another significant market opportunity. Industries such as steel production, chemical manufacturing, and refining are exploring green hydrogen as a means to reduce their carbon footprint. This shift is driven by both regulatory pressures and corporate sustainability commitments.
Geographically, Europe is currently leading the green electrolysis market, with countries like Germany, the Netherlands, and Denmark making substantial investments in hydrogen infrastructure. However, other regions are quickly catching up. Asia-Pacific, particularly China, Japan, and South Korea, are emerging as key players in the market. North America is also seeing increased activity, with both the United States and Canada announcing hydrogen strategies.
The competitive landscape of the green electrolysis market is dynamic, with both established industrial players and innovative startups vying for market share. Major industrial companies are leveraging their expertise in traditional electrolysis to develop more environmentally friendly solutions. Meanwhile, startups are introducing novel technologies that promise higher efficiency and lower costs.
Key market drivers include the declining cost of renewable electricity, technological advancements in electrolysis efficiency, and supportive government policies. However, challenges remain, such as the need for significant infrastructure development and the current high costs compared to conventional hydrogen production methods.
As environmental considerations continue to shape the development of next-generation electrolytic cell designs, the green electrolysis market is poised for substantial growth. The integration of advanced materials, optimized cell architectures, and intelligent control systems will be crucial in addressing environmental concerns and driving market expansion.
Eco-Challenges in Current Electrolytic Cells
Current electrolytic cell designs face significant environmental challenges that necessitate urgent attention and innovative solutions. One of the primary concerns is the high energy consumption associated with traditional electrolytic processes. These cells often require substantial electrical input, contributing to increased carbon emissions and placing a considerable burden on power grids, particularly in regions still heavily reliant on fossil fuels for electricity generation.
Water usage and management present another critical eco-challenge. Many electrolytic processes demand large volumes of water, not only for the reaction itself but also for cooling and cleaning purposes. This intensive water consumption can strain local water resources, especially in water-scarce regions, and may lead to conflicts with other essential water needs such as agriculture and domestic use.
The production and disposal of electrodes pose additional environmental concerns. Many electrodes contain precious or rare earth metals, the mining and processing of which can result in significant ecological damage, including habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. Furthermore, the limited lifespan of these electrodes leads to frequent replacements, generating substantial waste that requires careful handling and disposal to prevent environmental contamination.
Electrolyte management is another area of environmental concern. The chemicals used as electrolytes can be highly corrosive and toxic. Improper handling, leaks, or spills can lead to soil and water pollution, potentially harming local ecosystems and posing risks to human health. The disposal of spent electrolytes also presents challenges, as they often require specialized treatment to neutralize harmful components before release into the environment.
Gaseous emissions from electrolytic cells, particularly in chlor-alkali processes, can contribute to air pollution if not properly managed. These emissions may include chlorine, hydrogen, and other potentially harmful gases that require sophisticated capture and treatment systems to mitigate their environmental impact.
The overall carbon footprint of electrolytic cell production and operation is a growing concern in the context of global climate change. From the manufacturing of cell components to the energy-intensive operation and maintenance processes, the cumulative environmental impact of these systems is substantial and requires a holistic approach to reduction and mitigation.
As industries strive for sustainability, addressing these eco-challenges in current electrolytic cell designs has become imperative. The development of next-generation cells must prioritize energy efficiency, water conservation, sustainable material use, and emission reduction to align with global environmental goals and ensure the long-term viability of electrolytic processes in various industrial applications.
Water usage and management present another critical eco-challenge. Many electrolytic processes demand large volumes of water, not only for the reaction itself but also for cooling and cleaning purposes. This intensive water consumption can strain local water resources, especially in water-scarce regions, and may lead to conflicts with other essential water needs such as agriculture and domestic use.
The production and disposal of electrodes pose additional environmental concerns. Many electrodes contain precious or rare earth metals, the mining and processing of which can result in significant ecological damage, including habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. Furthermore, the limited lifespan of these electrodes leads to frequent replacements, generating substantial waste that requires careful handling and disposal to prevent environmental contamination.
Electrolyte management is another area of environmental concern. The chemicals used as electrolytes can be highly corrosive and toxic. Improper handling, leaks, or spills can lead to soil and water pollution, potentially harming local ecosystems and posing risks to human health. The disposal of spent electrolytes also presents challenges, as they often require specialized treatment to neutralize harmful components before release into the environment.
Gaseous emissions from electrolytic cells, particularly in chlor-alkali processes, can contribute to air pollution if not properly managed. These emissions may include chlorine, hydrogen, and other potentially harmful gases that require sophisticated capture and treatment systems to mitigate their environmental impact.
The overall carbon footprint of electrolytic cell production and operation is a growing concern in the context of global climate change. From the manufacturing of cell components to the energy-intensive operation and maintenance processes, the cumulative environmental impact of these systems is substantial and requires a holistic approach to reduction and mitigation.
As industries strive for sustainability, addressing these eco-challenges in current electrolytic cell designs has become imperative. The development of next-generation cells must prioritize energy efficiency, water conservation, sustainable material use, and emission reduction to align with global environmental goals and ensure the long-term viability of electrolytic processes in various industrial applications.
Eco-Friendly Electrolytic Cell Solutions
01 Reduction of environmental impact in electrolytic processes
Electrolytic cells are being designed to minimize their environmental footprint. This includes developing more efficient processes that reduce energy consumption, implementing closed-loop systems to minimize waste, and using environmentally friendly materials in cell construction. These improvements aim to decrease greenhouse gas emissions and reduce the overall ecological impact of electrolytic operations.- Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: Electrolytic cells can be used to produce hydrogen and other clean fuels, potentially reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This technology can contribute to the development of more sustainable energy sources and help mitigate climate change impacts.
- Wastewater treatment and pollutant removal: Electrolytic cells can be employed in wastewater treatment processes to remove pollutants and contaminants. This application helps improve water quality and reduces the environmental impact of industrial and municipal wastewater discharge.
- Energy efficiency and resource conservation: Advancements in electrolytic cell technology focus on improving energy efficiency and reducing resource consumption. These improvements can lead to more sustainable industrial processes and lower overall environmental impact.
- Recycling and material recovery: Electrolytic cells can be used in recycling processes to recover valuable materials from waste streams. This application helps conserve natural resources and reduces the environmental impact of mining and raw material extraction.
- Life cycle assessment and environmental monitoring: Implementing life cycle assessment and environmental monitoring systems for electrolytic cell technologies helps identify and mitigate potential environmental impacts throughout their production, use, and disposal phases.
02 Waste management and recycling in electrolytic cell operations
Advanced waste management techniques are being implemented in electrolytic cell facilities to reduce environmental impact. This includes the treatment and recycling of electrolytes, recovery of valuable byproducts, and proper disposal of hazardous materials. These practices help to minimize pollution and conserve resources, contributing to a more sustainable electrolytic industry.Expand Specific Solutions03 Green hydrogen production using electrolytic cells
Electrolytic cells are being utilized for the production of green hydrogen, a clean energy carrier. This process uses renewable electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuel-based hydrogen production. The environmental impact of this method is significantly lower, contributing to the reduction of carbon emissions in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Monitoring and control systems for environmental compliance
Advanced monitoring and control systems are being integrated into electrolytic cell operations to ensure environmental compliance. These systems track emissions, energy consumption, and waste production in real-time, allowing for immediate adjustments to minimize environmental impact. This technology helps facilities meet regulatory standards and optimize their processes for sustainability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Life cycle assessment of electrolytic cell technologies
Comprehensive life cycle assessments are being conducted on electrolytic cell technologies to evaluate their overall environmental impact. These studies consider factors such as raw material extraction, manufacturing processes, operational efficiency, and end-of-life disposal. The results inform the development of more sustainable electrolytic cell designs and operational practices, aiming to reduce the technology's ecological footprint throughout its entire lifecycle.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Green Electrolytic Industry
The environmental considerations in next-generation electrolytic cell designs are at a critical juncture, with the industry transitioning from early-stage research to commercial applications. The market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions. Technological maturity varies among key players, with companies like EnPower, Inc. and Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd. leading in innovative electrode architectures and battery systems. Established firms such as Siemens Energy Global GmbH & Co. KG and Toshiba Corp. are leveraging their expertise to advance electrolytic cell technologies. Research institutions like Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics and Ulsan National Institute of Science & Technology are contributing to fundamental breakthroughs, while startups like Power To Hydrogen LLC are focusing on specialized applications, collectively shaping the competitive landscape of this evolving field.
Siemens Energy Global GmbH & Co. KG
Technical Solution: Siemens Energy has developed advanced electrolytic cell designs that incorporate environmental considerations. Their approach focuses on improving energy efficiency and reducing the carbon footprint of electrolysis processes. The company has implemented a modular design for their electrolyzers, allowing for scalability and easier integration of renewable energy sources[1]. They have also developed proprietary electrode materials that enhance the overall efficiency of the electrolytic process while minimizing the use of rare earth elements[2]. Siemens Energy's next-generation electrolytic cells incorporate advanced membrane technology, which improves gas separation and reduces the need for additional purification steps, thereby lowering energy consumption and operational costs[3].
Strengths: High energy efficiency, scalable modular design, and integration with renewable energy sources. Weaknesses: Initial high capital costs and potential dependence on specific proprietary technologies.
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: CATL has focused on developing environmentally friendly electrolytic cell designs for battery production. Their approach includes the use of water-based electrode manufacturing processes, which significantly reduce the use of organic solvents and associated emissions[4]. CATL has also implemented a closed-loop recycling system for their electrolytic cells, recovering valuable materials and minimizing waste[5]. Their next-generation designs incorporate advanced thermal management systems that improve the overall efficiency and lifespan of the cells while reducing the risk of thermal runaway[6]. Additionally, CATL has invested in the development of solid-state electrolytes, which offer improved safety and energy density compared to traditional liquid electrolytes[7].
Strengths: Eco-friendly manufacturing processes, efficient material recycling, and advanced thermal management. Weaknesses: High research and development costs and potential challenges in scaling up new technologies.
Innovations in Sustainable Electrolysis
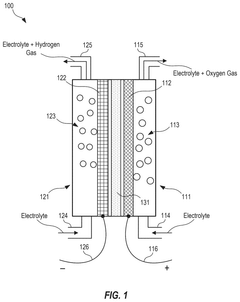
Electrolytic cell, method for operating a cell of this type and electrolyser
PatentWO2021239674A1
Innovation
- An electrolytic cell design with a permeable separator and a configuration where only one half-cell has an electrolyte inlet and the other has an outlet, allowing electrolyte to flow through the separator under overpressure, reducing stray currents and eliminating the need for multiple electrolyte circuits, while enhancing product gas separation and purity.
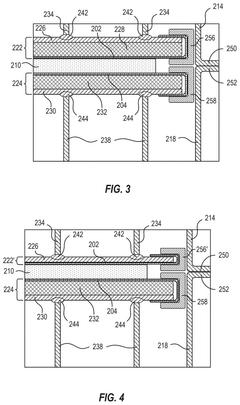
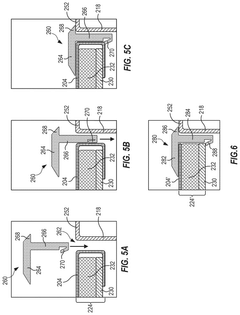
Electrolyzer cell and methods of using and manufacturing the same
PatentPendingUS20250230560A1
Innovation
- An electrolyzer cell design featuring non-welded electrodes and a zero-gap configuration with elastic elements and conductive meshes to minimize resistive losses, allowing for easy electrode replacement without welding, thereby enhancing efficiency and reducing maintenance complexity.
Environmental Regulations Impact
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in shaping the design and implementation of next-generation electrolytic cell technologies. As global concerns about climate change and environmental protection intensify, regulatory bodies worldwide are imposing stricter guidelines on industrial processes, including electrolysis.
The impact of these regulations is multifaceted, affecting various aspects of electrolytic cell design and operation. One primary focus is on reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with the electrolysis process. Many jurisdictions have implemented carbon pricing mechanisms or cap-and-trade systems, which incentivize companies to adopt more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly technologies.
Water management is another critical area influenced by environmental regulations. Electrolytic processes often require significant water inputs, and regulations increasingly mandate the implementation of water recycling and conservation measures. This has led to innovations in cell designs that minimize water consumption and improve overall process efficiency.
Waste management and disposal regulations also significantly impact electrolytic cell designs. Stringent rules governing the handling and disposal of hazardous materials have prompted researchers and engineers to develop novel approaches to reduce waste generation and improve the recyclability of cell components.
The push for circular economy principles in industrial processes has further influenced electrolytic cell designs. Regulations encouraging the use of recycled materials and the design of easily recyclable products are driving innovations in material selection and cell architecture.
Energy efficiency standards are becoming increasingly stringent, affecting the power consumption aspects of electrolytic cells. This has led to a focus on developing more efficient electrode materials, optimizing cell geometries, and improving overall system designs to reduce energy losses.
Noise pollution regulations have also impacted cell designs, particularly in urban or densely populated areas. Engineers must now consider acoustic insulation and vibration reduction techniques in their designs to comply with local noise ordinances.
The regulatory landscape is not static, and anticipating future environmental regulations is crucial for long-term success in electrolytic cell development. This includes preparing for potential restrictions on certain materials, stricter emissions limits, and more comprehensive life cycle assessment requirements.
Compliance with these evolving regulations often necessitates significant investments in research and development, as well as potential retrofitting of existing facilities. However, it also drives innovation and can lead to competitive advantages for companies that successfully develop compliant, high-performance electrolytic cell technologies.
The impact of these regulations is multifaceted, affecting various aspects of electrolytic cell design and operation. One primary focus is on reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with the electrolysis process. Many jurisdictions have implemented carbon pricing mechanisms or cap-and-trade systems, which incentivize companies to adopt more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly technologies.
Water management is another critical area influenced by environmental regulations. Electrolytic processes often require significant water inputs, and regulations increasingly mandate the implementation of water recycling and conservation measures. This has led to innovations in cell designs that minimize water consumption and improve overall process efficiency.
Waste management and disposal regulations also significantly impact electrolytic cell designs. Stringent rules governing the handling and disposal of hazardous materials have prompted researchers and engineers to develop novel approaches to reduce waste generation and improve the recyclability of cell components.
The push for circular economy principles in industrial processes has further influenced electrolytic cell designs. Regulations encouraging the use of recycled materials and the design of easily recyclable products are driving innovations in material selection and cell architecture.
Energy efficiency standards are becoming increasingly stringent, affecting the power consumption aspects of electrolytic cells. This has led to a focus on developing more efficient electrode materials, optimizing cell geometries, and improving overall system designs to reduce energy losses.
Noise pollution regulations have also impacted cell designs, particularly in urban or densely populated areas. Engineers must now consider acoustic insulation and vibration reduction techniques in their designs to comply with local noise ordinances.
The regulatory landscape is not static, and anticipating future environmental regulations is crucial for long-term success in electrolytic cell development. This includes preparing for potential restrictions on certain materials, stricter emissions limits, and more comprehensive life cycle assessment requirements.
Compliance with these evolving regulations often necessitates significant investments in research and development, as well as potential retrofitting of existing facilities. However, it also drives innovation and can lead to competitive advantages for companies that successfully develop compliant, high-performance electrolytic cell technologies.
Life Cycle Assessment of Electrolytic Cells
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of electrolytic cells is a crucial component in evaluating the environmental impact of next-generation designs. This comprehensive approach examines the entire lifecycle of electrolytic cells, from raw material extraction to manufacturing, use, and end-of-life disposal or recycling. By conducting a thorough LCA, researchers and engineers can identify key areas for improvement in environmental performance and sustainability.
The assessment typically begins with the extraction and processing of raw materials used in electrolytic cell construction. This includes the environmental impacts associated with mining and refining metals, such as platinum, iridium, or nickel, which are commonly used as catalysts or electrode materials. The production of other components, like membranes and electrolytes, is also considered in this stage.
Manufacturing processes are then evaluated, focusing on energy consumption, emissions, and waste generation during cell assembly. This stage often reveals opportunities for optimization, such as implementing more efficient production techniques or utilizing renewable energy sources in manufacturing facilities.
The use phase of electrolytic cells is particularly significant in the LCA. This stage examines the energy efficiency of the cells during operation, the consumption of resources like water and electrolytes, and the production of any by-products or emissions. For next-generation designs, improvements in energy efficiency and reduced resource consumption are key factors in minimizing environmental impact.
End-of-life considerations are increasingly important in the LCA of electrolytic cells. This includes assessing the recyclability of materials, the potential for refurbishment or reuse of components, and the environmental implications of disposal methods. Advanced designs may incorporate materials that are more easily recycled or biodegradable, reducing the long-term environmental footprint.
Throughout the LCA, various environmental impact categories are evaluated, including global warming potential, resource depletion, water usage, and toxicity. These assessments help in identifying trade-offs between different design choices and their environmental consequences. For instance, a design that reduces energy consumption during use might require more energy-intensive manufacturing processes or less recyclable materials.
The results of the LCA provide valuable insights for guiding the development of more sustainable electrolytic cell designs. They can inform decisions on material selection, manufacturing processes, and operational parameters to minimize overall environmental impact. Additionally, LCA findings can be used to compare different cell designs and technologies, supporting evidence-based decision-making in research and development efforts.
The assessment typically begins with the extraction and processing of raw materials used in electrolytic cell construction. This includes the environmental impacts associated with mining and refining metals, such as platinum, iridium, or nickel, which are commonly used as catalysts or electrode materials. The production of other components, like membranes and electrolytes, is also considered in this stage.
Manufacturing processes are then evaluated, focusing on energy consumption, emissions, and waste generation during cell assembly. This stage often reveals opportunities for optimization, such as implementing more efficient production techniques or utilizing renewable energy sources in manufacturing facilities.
The use phase of electrolytic cells is particularly significant in the LCA. This stage examines the energy efficiency of the cells during operation, the consumption of resources like water and electrolytes, and the production of any by-products or emissions. For next-generation designs, improvements in energy efficiency and reduced resource consumption are key factors in minimizing environmental impact.
End-of-life considerations are increasingly important in the LCA of electrolytic cells. This includes assessing the recyclability of materials, the potential for refurbishment or reuse of components, and the environmental implications of disposal methods. Advanced designs may incorporate materials that are more easily recycled or biodegradable, reducing the long-term environmental footprint.
Throughout the LCA, various environmental impact categories are evaluated, including global warming potential, resource depletion, water usage, and toxicity. These assessments help in identifying trade-offs between different design choices and their environmental consequences. For instance, a design that reduces energy consumption during use might require more energy-intensive manufacturing processes or less recyclable materials.
The results of the LCA provide valuable insights for guiding the development of more sustainable electrolytic cell designs. They can inform decisions on material selection, manufacturing processes, and operational parameters to minimize overall environmental impact. Additionally, LCA findings can be used to compare different cell designs and technologies, supporting evidence-based decision-making in research and development efforts.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!