How Chain Reactions Impact Electrolytic Cell Efficiency
AUG 1, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Electrolytic Cell Efficiency Background and Objectives
Electrolytic cell efficiency has been a critical focus in the field of electrochemistry since the early 19th century when the principles of electrolysis were first discovered. The evolution of this technology has been driven by the increasing demand for more efficient and sustainable energy production and storage solutions. As we delve into the impact of chain reactions on electrolytic cell efficiency, it is essential to understand the historical context and current objectives in this domain.
The primary goal of improving electrolytic cell efficiency is to maximize the conversion of electrical energy into desired chemical products while minimizing energy losses. This objective has become increasingly important in recent years due to the growing emphasis on renewable energy sources and the need for more efficient energy storage systems. The efficiency of electrolytic cells plays a crucial role in various industries, including hydrogen production, metal refining, and chlor-alkali processes.
Chain reactions in electrolytic cells refer to the series of interconnected chemical and electrochemical processes that occur at the electrode-electrolyte interface. These reactions can significantly influence the overall efficiency of the cell by affecting factors such as reaction kinetics, mass transport, and electrode surface properties. Understanding and optimizing these chain reactions is key to achieving higher electrolytic cell efficiencies.
Recent advancements in nanotechnology, materials science, and computational modeling have opened up new avenues for investigating and enhancing the efficiency of electrolytic cells. Researchers are now able to study the intricate details of electrode surfaces and electrolyte interactions at the molecular level, leading to the development of more efficient catalysts and electrode materials.
The current technological landscape presents both challenges and opportunities in the quest for improved electrolytic cell efficiency. One of the main challenges is the complex interplay between various factors affecting efficiency, including electrode material properties, electrolyte composition, operating conditions, and cell design. Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from electrochemistry, materials science, and engineering.
As we explore the impact of chain reactions on electrolytic cell efficiency, our objectives are twofold. First, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms by which chain reactions influence cell performance. This includes identifying key reaction pathways, rate-limiting steps, and potential side reactions that may hinder efficiency. Second, we seek to evaluate and propose innovative strategies for leveraging chain reactions to enhance overall cell efficiency, potentially leading to breakthroughs in energy conversion and storage technologies.
The primary goal of improving electrolytic cell efficiency is to maximize the conversion of electrical energy into desired chemical products while minimizing energy losses. This objective has become increasingly important in recent years due to the growing emphasis on renewable energy sources and the need for more efficient energy storage systems. The efficiency of electrolytic cells plays a crucial role in various industries, including hydrogen production, metal refining, and chlor-alkali processes.
Chain reactions in electrolytic cells refer to the series of interconnected chemical and electrochemical processes that occur at the electrode-electrolyte interface. These reactions can significantly influence the overall efficiency of the cell by affecting factors such as reaction kinetics, mass transport, and electrode surface properties. Understanding and optimizing these chain reactions is key to achieving higher electrolytic cell efficiencies.
Recent advancements in nanotechnology, materials science, and computational modeling have opened up new avenues for investigating and enhancing the efficiency of electrolytic cells. Researchers are now able to study the intricate details of electrode surfaces and electrolyte interactions at the molecular level, leading to the development of more efficient catalysts and electrode materials.
The current technological landscape presents both challenges and opportunities in the quest for improved electrolytic cell efficiency. One of the main challenges is the complex interplay between various factors affecting efficiency, including electrode material properties, electrolyte composition, operating conditions, and cell design. Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from electrochemistry, materials science, and engineering.
As we explore the impact of chain reactions on electrolytic cell efficiency, our objectives are twofold. First, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms by which chain reactions influence cell performance. This includes identifying key reaction pathways, rate-limiting steps, and potential side reactions that may hinder efficiency. Second, we seek to evaluate and propose innovative strategies for leveraging chain reactions to enhance overall cell efficiency, potentially leading to breakthroughs in energy conversion and storage technologies.
Market Analysis for High-Efficiency Electrolytic Cells
The market for high-efficiency electrolytic cells is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for clean energy solutions and the push towards decarbonization across various industries. As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental regulations and set ambitious carbon reduction targets, the adoption of electrolytic technologies, particularly in hydrogen production, is accelerating.
The global electrolytic cell market is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to exceed 5% between 2021 and 2026. This growth is primarily fueled by the rising interest in green hydrogen as a clean energy carrier and its potential applications in sectors such as transportation, power generation, and industrial processes.
Key market segments for high-efficiency electrolytic cells include water electrolysis for hydrogen production, chlor-alkali production, and metal refining. The water electrolysis segment, in particular, is witnessing substantial growth due to the increasing focus on renewable hydrogen production. This segment is expected to dominate the market share, accounting for over 60% of the total electrolytic cell market by 2025.
Geographically, Europe and North America are currently leading the market for high-efficiency electrolytic cells, driven by strong government support and investments in clean energy infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to emerge as the fastest-growing market, with countries like China, Japan, and South Korea making significant strides in hydrogen technology development and deployment.
The market landscape is characterized by intense competition among established players and new entrants. Major companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve electrolytic cell efficiency and reduce production costs. Technological advancements, such as the development of proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolyzers and solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOEC), are expected to further drive market growth and expand application areas.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as high initial capital costs and the need for large-scale infrastructure development. However, ongoing technological improvements and economies of scale are expected to gradually reduce these barriers, making high-efficiency electrolytic cells more economically viable across various applications.
In conclusion, the market for high-efficiency electrolytic cells shows strong growth potential, driven by the global shift towards clean energy solutions and the increasing focus on hydrogen as a key component of future energy systems. As technology continues to advance and costs decrease, the adoption of high-efficiency electrolytic cells is expected to accelerate, opening up new opportunities across multiple industries and regions.
The global electrolytic cell market is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to exceed 5% between 2021 and 2026. This growth is primarily fueled by the rising interest in green hydrogen as a clean energy carrier and its potential applications in sectors such as transportation, power generation, and industrial processes.
Key market segments for high-efficiency electrolytic cells include water electrolysis for hydrogen production, chlor-alkali production, and metal refining. The water electrolysis segment, in particular, is witnessing substantial growth due to the increasing focus on renewable hydrogen production. This segment is expected to dominate the market share, accounting for over 60% of the total electrolytic cell market by 2025.
Geographically, Europe and North America are currently leading the market for high-efficiency electrolytic cells, driven by strong government support and investments in clean energy infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to emerge as the fastest-growing market, with countries like China, Japan, and South Korea making significant strides in hydrogen technology development and deployment.
The market landscape is characterized by intense competition among established players and new entrants. Major companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve electrolytic cell efficiency and reduce production costs. Technological advancements, such as the development of proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolyzers and solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOEC), are expected to further drive market growth and expand application areas.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as high initial capital costs and the need for large-scale infrastructure development. However, ongoing technological improvements and economies of scale are expected to gradually reduce these barriers, making high-efficiency electrolytic cells more economically viable across various applications.
In conclusion, the market for high-efficiency electrolytic cells shows strong growth potential, driven by the global shift towards clean energy solutions and the increasing focus on hydrogen as a key component of future energy systems. As technology continues to advance and costs decrease, the adoption of high-efficiency electrolytic cells is expected to accelerate, opening up new opportunities across multiple industries and regions.
Chain Reactions in Electrolytic Cells: Current Challenges
Electrolytic cells are fundamental to numerous industrial processes, yet their efficiency remains a critical challenge. Chain reactions within these cells significantly impact their performance, presenting both opportunities and obstacles for researchers and engineers. The current challenges in understanding and controlling chain reactions in electrolytic cells are multifaceted and complex.
One of the primary challenges is the intricate interplay between various chemical species within the electrolyte. As the primary reaction progresses, it often triggers a series of secondary reactions, forming a complex network of interdependent processes. These chain reactions can lead to unexpected byproducts, alter the local pH, and affect the overall cell potential, thereby influencing the efficiency of the desired electrochemical process.
The formation of gas bubbles at the electrode surface presents another significant challenge. In many electrolytic processes, such as water electrolysis, gas evolution is an integral part of the reaction. However, these bubbles can obstruct the electrode surface, reducing the active area for electron transfer and increasing the cell's internal resistance. The dynamics of bubble formation, growth, and detachment are closely linked to the chain reactions occurring in the electrolyte, making it a complex phenomenon to model and control.
Heat generation and dissipation within the cell also pose considerable challenges. Chain reactions often involve exothermic or endothermic processes, leading to temperature fluctuations that can affect reaction kinetics, mass transport, and even the stability of the electrodes. Managing this heat effectively while maintaining optimal reaction conditions is crucial for sustaining high efficiency in industrial-scale electrolytic cells.
The degradation of electrode materials is another pressing issue exacerbated by chain reactions. Secondary reactions can lead to the formation of species that corrode or passivate the electrode surface, gradually reducing its catalytic activity and longevity. This degradation not only affects the cell's efficiency but also increases maintenance costs and downtime in industrial applications.
Furthermore, the scaling up of laboratory findings to industrial processes introduces additional complexities. Chain reactions that may be manageable or even beneficial at small scales can become problematic in large-scale operations. Issues such as non-uniform current distribution, mass transport limitations, and heat management become more pronounced, requiring innovative engineering solutions to maintain efficiency at scale.
Lastly, the dynamic nature of chain reactions in electrolytic cells poses significant challenges for real-time monitoring and control. Traditional analytical techniques often provide only averaged or time-delayed information, making it difficult to capture the rapid and localized changes occurring at the electrode-electrolyte interface. Developing advanced in-situ monitoring techniques and predictive models capable of capturing these dynamics remains an active area of research and development in the field of electrochemistry.
One of the primary challenges is the intricate interplay between various chemical species within the electrolyte. As the primary reaction progresses, it often triggers a series of secondary reactions, forming a complex network of interdependent processes. These chain reactions can lead to unexpected byproducts, alter the local pH, and affect the overall cell potential, thereby influencing the efficiency of the desired electrochemical process.
The formation of gas bubbles at the electrode surface presents another significant challenge. In many electrolytic processes, such as water electrolysis, gas evolution is an integral part of the reaction. However, these bubbles can obstruct the electrode surface, reducing the active area for electron transfer and increasing the cell's internal resistance. The dynamics of bubble formation, growth, and detachment are closely linked to the chain reactions occurring in the electrolyte, making it a complex phenomenon to model and control.
Heat generation and dissipation within the cell also pose considerable challenges. Chain reactions often involve exothermic or endothermic processes, leading to temperature fluctuations that can affect reaction kinetics, mass transport, and even the stability of the electrodes. Managing this heat effectively while maintaining optimal reaction conditions is crucial for sustaining high efficiency in industrial-scale electrolytic cells.
The degradation of electrode materials is another pressing issue exacerbated by chain reactions. Secondary reactions can lead to the formation of species that corrode or passivate the electrode surface, gradually reducing its catalytic activity and longevity. This degradation not only affects the cell's efficiency but also increases maintenance costs and downtime in industrial applications.
Furthermore, the scaling up of laboratory findings to industrial processes introduces additional complexities. Chain reactions that may be manageable or even beneficial at small scales can become problematic in large-scale operations. Issues such as non-uniform current distribution, mass transport limitations, and heat management become more pronounced, requiring innovative engineering solutions to maintain efficiency at scale.
Lastly, the dynamic nature of chain reactions in electrolytic cells poses significant challenges for real-time monitoring and control. Traditional analytical techniques often provide only averaged or time-delayed information, making it difficult to capture the rapid and localized changes occurring at the electrode-electrolyte interface. Developing advanced in-situ monitoring techniques and predictive models capable of capturing these dynamics remains an active area of research and development in the field of electrochemistry.
Current Solutions for Enhancing Cell Efficiency
01 Electrode material optimization
Improving the efficiency of electrolytic cells by optimizing electrode materials. This includes using advanced materials with higher conductivity, catalytic activity, and durability to enhance the overall performance of the cell. Such materials can reduce energy losses and increase the rate of desired reactions.- Electrode material optimization: Improving the efficiency of electrolytic cells by optimizing electrode materials. This includes using advanced materials with higher conductivity, catalytic activity, and durability. Such improvements can lead to reduced energy consumption and increased product yield in electrolysis processes.
- Membrane technology advancements: Enhancing electrolytic cell efficiency through improved membrane technologies. This involves developing membranes with better ion selectivity, lower resistance, and higher stability. Advanced membranes can significantly reduce energy losses and increase overall system performance.
- Cell design and configuration optimization: Optimizing the design and configuration of electrolytic cells to improve efficiency. This includes innovations in cell geometry, flow patterns, and component arrangements to enhance mass transfer, reduce ohmic losses, and improve current distribution.
- Process control and monitoring systems: Implementing advanced process control and monitoring systems to optimize electrolytic cell performance. This involves using sensors, data analytics, and intelligent control algorithms to maintain optimal operating conditions and quickly respond to process variations.
- Electrolyte composition and additives: Improving electrolytic cell efficiency through optimized electrolyte compositions and additives. This includes developing electrolyte formulations that enhance conductivity, reduce side reactions, and improve the stability of electrodes and membranes.
02 Membrane and separator enhancements
Developing and implementing improved membranes and separators in electrolytic cells to increase efficiency. These components play a crucial role in ion transport and preventing unwanted reactions, thereby improving the overall cell performance and reducing energy consumption.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrolyte composition optimization
Enhancing electrolytic cell efficiency through the optimization of electrolyte composition. This involves adjusting the concentration, pH, and additives in the electrolyte to improve conductivity, reduce side reactions, and enhance the desired electrochemical processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cell design and configuration improvements
Improving the efficiency of electrolytic cells through innovative design and configuration. This includes optimizing cell geometry, electrode spacing, and flow patterns to enhance mass transfer, reduce ohmic losses, and improve overall cell performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Process control and monitoring systems
Implementing advanced process control and monitoring systems to optimize electrolytic cell efficiency. This involves using sensors, data analytics, and intelligent control algorithms to maintain optimal operating conditions, detect and address inefficiencies, and maximize overall cell performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Electrolytic Cell Industry
The competitive landscape for chain reactions impacting electrolytic cell efficiency is characterized by a rapidly evolving market in its early growth stage. The global market size for advanced electrolysis technologies is expanding, driven by increasing demand for clean hydrogen production. Companies like Electric Hydrogen Co. and Elchemtech Co., Ltd. are at the forefront of developing innovative electrolysis solutions. Established players such as Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. and Robert Bosch GmbH are also investing in this space, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities. The technology is progressing towards maturity, with ongoing research focused on improving efficiency and scalability. Research institutions like Indian Institute of Technology Delhi and Commissariat à l´énergie atomique et aux énergies Alternatives are contributing to fundamental advancements in the field.
Ningde Amperex Technology Ltd.
Technical Solution: Ningde Amperex Technology Ltd. (CATL) has developed advanced electrolyte formulations to enhance chain reactions in lithium-ion batteries. Their electrolyte additives promote the formation of a stable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer, which improves the efficiency of charge transfer at the electrode-electrolyte interface[1]. CATL's electrolytes also incorporate flame-retardant compounds to mitigate thermal runaway risks associated with chain reactions[2]. The company has implemented nano-engineered separators that facilitate controlled ion transport while preventing dendrite formation, thus maintaining high coulombic efficiency over extended cycling[3].
Strengths: Improved safety and longevity of batteries, enhanced energy density. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs, complexity in large-scale manufacturing.
Uchicago Argonne LLC
Technical Solution: Argonne National Laboratory, operated by UChicago Argonne LLC, has conducted extensive research on improving electrolytic cell efficiency through the optimization of chain reactions. Their work includes the development of advanced electrocatalysts using atomic layer deposition techniques, which allow for precise control over catalyst composition and structure[13]. Argonne has also pioneered the use of in-situ characterization techniques to study reaction mechanisms and identify rate-limiting steps in electrolytic processes[14]. Their research on electrolyte additives has led to the discovery of novel compounds that enhance the stability of electrode-electrolyte interfaces, reducing side reactions and improving overall cell efficiency[15].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research capabilities, access to advanced characterization techniques, and potential for breakthrough discoveries. Weaknesses: Challenges in translating laboratory-scale results to industrial applications, longer timelines for commercialization.
Innovations in Chain Reaction Management
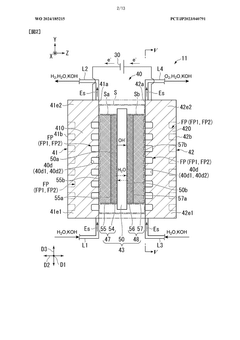
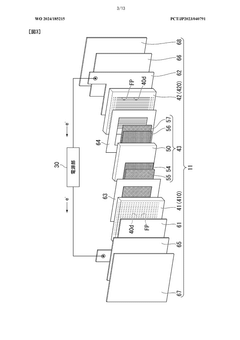
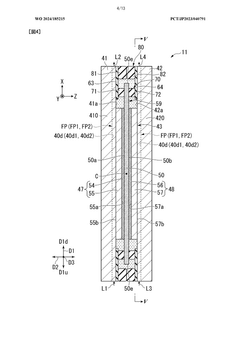
Electrolytic cell and electrolytic apparatus
PatentWO2024185215A1
Innovation
- The electrolytic cell design includes a flow direction changing unit that alters the flow direction of the electrolytic solution, intersecting the original flow direction at multiple positions, and a configuration where the ion exchange membrane is positioned between separators with power supply bodies, reducing the retention of electrolytic solution near the catalyst layers and minimizing hydroxide ion concentration gradients.
Electrolytic cell for electrochemically depositing one of the following metals: copper, zinc, lead, nickel or cobalt
PatentWO2000015874A1
Innovation
- The electrolytic cell design incorporates numerous openings in the container base for electrolyte passage, a distribution chamber under the base, and a return chamber on the side walls to facilitate electrolyte recirculation, leveraging gas evolution to drive electrolyte circulation and eliminate the need for external pumps.
Energy Consumption and Sustainability Aspects
The energy consumption and sustainability aspects of electrolytic cell efficiency are critical considerations in the context of chain reactions. Electrolytic cells are widely used in various industrial processes, particularly in the production of chemicals and metals. However, these processes often require significant energy input, which can have substantial environmental and economic implications.
Chain reactions in electrolytic cells can significantly impact energy consumption. When properly controlled, these reactions can enhance the overall efficiency of the process, reducing the amount of energy required per unit of product. For instance, in chlor-alkali production, the chain reaction involving chlorine and hydrogen can be harnessed to improve the energy efficiency of the electrolysis process. By optimizing these chain reactions, industries can potentially reduce their energy consumption by 10-15%, leading to substantial cost savings and reduced carbon footprints.
However, uncontrolled chain reactions can also lead to increased energy consumption and reduced sustainability. Exothermic side reactions may generate excess heat, requiring additional cooling systems and energy expenditure. Moreover, unwanted chain reactions can produce byproducts that necessitate further processing or disposal, increasing the overall energy demand of the system.
The sustainability aspects of electrolytic cell efficiency are closely tied to energy consumption. As global efforts to combat climate change intensify, industries are under increasing pressure to reduce their carbon emissions. Improving the energy efficiency of electrolytic cells through better management of chain reactions can significantly contribute to these sustainability goals. For example, in the aluminum industry, which relies heavily on electrolytic processes, even small improvements in cell efficiency can translate to substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, the sustainability of electrolytic processes extends beyond energy consumption to resource utilization. Chain reactions can influence the selectivity of the electrolytic process, potentially improving the yield of desired products while minimizing waste. This not only reduces the energy required for subsequent separation and purification steps but also conserves raw materials, contributing to overall resource efficiency.
Advancements in electrode materials and cell designs that leverage beneficial chain reactions while suppressing detrimental ones are key areas of research for improving sustainability. These innovations aim to increase the lifespan of electrolytic cells, reduce maintenance requirements, and minimize the need for replacement of components, all of which contribute to reduced resource consumption and improved long-term sustainability.
Chain reactions in electrolytic cells can significantly impact energy consumption. When properly controlled, these reactions can enhance the overall efficiency of the process, reducing the amount of energy required per unit of product. For instance, in chlor-alkali production, the chain reaction involving chlorine and hydrogen can be harnessed to improve the energy efficiency of the electrolysis process. By optimizing these chain reactions, industries can potentially reduce their energy consumption by 10-15%, leading to substantial cost savings and reduced carbon footprints.
However, uncontrolled chain reactions can also lead to increased energy consumption and reduced sustainability. Exothermic side reactions may generate excess heat, requiring additional cooling systems and energy expenditure. Moreover, unwanted chain reactions can produce byproducts that necessitate further processing or disposal, increasing the overall energy demand of the system.
The sustainability aspects of electrolytic cell efficiency are closely tied to energy consumption. As global efforts to combat climate change intensify, industries are under increasing pressure to reduce their carbon emissions. Improving the energy efficiency of electrolytic cells through better management of chain reactions can significantly contribute to these sustainability goals. For example, in the aluminum industry, which relies heavily on electrolytic processes, even small improvements in cell efficiency can translate to substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, the sustainability of electrolytic processes extends beyond energy consumption to resource utilization. Chain reactions can influence the selectivity of the electrolytic process, potentially improving the yield of desired products while minimizing waste. This not only reduces the energy required for subsequent separation and purification steps but also conserves raw materials, contributing to overall resource efficiency.
Advancements in electrode materials and cell designs that leverage beneficial chain reactions while suppressing detrimental ones are key areas of research for improving sustainability. These innovations aim to increase the lifespan of electrolytic cells, reduce maintenance requirements, and minimize the need for replacement of components, all of which contribute to reduced resource consumption and improved long-term sustainability.
Safety Considerations in Electrolytic Processes
Safety considerations in electrolytic processes are paramount to ensure the efficient and secure operation of electrolytic cells. The chain reactions occurring within these cells can significantly impact their efficiency and pose potential hazards if not properly managed. One of the primary safety concerns is the production of hydrogen gas as a byproduct of electrolysis. This highly flammable gas can accumulate in confined spaces, creating an explosion risk if ignited.
To mitigate this danger, proper ventilation systems must be implemented to disperse hydrogen gas safely. Additionally, the use of hydrogen detectors and alarm systems is crucial for early detection of any leaks or dangerous concentrations. Regular maintenance and inspection of these safety systems are essential to ensure their reliability and effectiveness.
Another critical safety aspect is the handling and storage of electrolytes, which are often corrosive and toxic. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) must be worn by operators, including chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, and appropriate clothing. Spill containment measures and emergency shower stations should be readily available in case of accidental exposure.
The electrical components of electrolytic cells also present safety challenges. High currents and voltages used in these processes can lead to electrical shock hazards. Proper insulation, grounding, and the use of residual current devices (RCDs) are necessary to protect workers from electrical accidents. Regular electrical safety audits and maintenance of power supply systems are crucial to prevent malfunctions that could lead to safety incidents.
Temperature control is another vital safety consideration in electrolytic processes. Overheating can lead to rapid chain reactions, potentially causing electrolyte decomposition or cell damage. Implementing robust temperature monitoring and control systems, including automatic shutoffs in case of overheating, is essential to maintain safe operating conditions.
The management of waste products and spent electrolytes requires careful attention to environmental and safety regulations. Proper disposal procedures must be followed to prevent contamination and ensure compliance with environmental standards. This may include neutralization processes, filtration, or specialized waste treatment facilities.
Training and education of personnel are fundamental to maintaining a safe working environment in electrolytic processes. Operators must be well-versed in emergency procedures, the proper use of safety equipment, and the potential hazards associated with the chemicals and processes involved. Regular safety drills and refresher courses should be conducted to reinforce best practices and keep safety protocols at the forefront of daily operations.
To mitigate this danger, proper ventilation systems must be implemented to disperse hydrogen gas safely. Additionally, the use of hydrogen detectors and alarm systems is crucial for early detection of any leaks or dangerous concentrations. Regular maintenance and inspection of these safety systems are essential to ensure their reliability and effectiveness.
Another critical safety aspect is the handling and storage of electrolytes, which are often corrosive and toxic. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) must be worn by operators, including chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, and appropriate clothing. Spill containment measures and emergency shower stations should be readily available in case of accidental exposure.
The electrical components of electrolytic cells also present safety challenges. High currents and voltages used in these processes can lead to electrical shock hazards. Proper insulation, grounding, and the use of residual current devices (RCDs) are necessary to protect workers from electrical accidents. Regular electrical safety audits and maintenance of power supply systems are crucial to prevent malfunctions that could lead to safety incidents.
Temperature control is another vital safety consideration in electrolytic processes. Overheating can lead to rapid chain reactions, potentially causing electrolyte decomposition or cell damage. Implementing robust temperature monitoring and control systems, including automatic shutoffs in case of overheating, is essential to maintain safe operating conditions.
The management of waste products and spent electrolytes requires careful attention to environmental and safety regulations. Proper disposal procedures must be followed to prevent contamination and ensure compliance with environmental standards. This may include neutralization processes, filtration, or specialized waste treatment facilities.
Training and education of personnel are fundamental to maintaining a safe working environment in electrolytic processes. Operators must be well-versed in emergency procedures, the proper use of safety equipment, and the potential hazards associated with the chemicals and processes involved. Regular safety drills and refresher courses should be conducted to reinforce best practices and keep safety protocols at the forefront of daily operations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!