Evaluation of lithium orotate in ameliorating bipolar disorder cognitive deficits
AUG 20, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Background and Research Objectives
Lithium has been a cornerstone in the treatment of bipolar disorder for decades, with its mood-stabilizing properties well-established in clinical practice. However, the cognitive deficits associated with bipolar disorder have remained a significant challenge, often persisting even during periods of mood stability. In recent years, there has been growing interest in exploring alternative forms of lithium, such as lithium orotate, for their potential to address these cognitive impairments while maintaining mood stabilization.
The development of lithium orotate represents a significant evolution in the field of psychopharmacology. Unlike the more commonly prescribed lithium carbonate, lithium orotate is believed to have enhanced bioavailability and the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently. This characteristic has led researchers to hypothesize that lithium orotate may offer improved therapeutic effects, particularly in targeting cognitive symptoms, with potentially fewer side effects.
The primary objective of this research is to evaluate the efficacy of lithium orotate in ameliorating cognitive deficits associated with bipolar disorder. This investigation aims to address a critical gap in current treatment modalities, which often fail to adequately manage cognitive symptoms. By focusing on lithium orotate, we seek to explore whether this form of lithium can provide a more comprehensive treatment approach, addressing both mood stabilization and cognitive enhancement.
Our research goals encompass several key areas. Firstly, we aim to conduct a thorough assessment of lithium orotate's pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, particularly its distribution in brain tissues relevant to cognitive function. Secondly, we intend to evaluate its effects on specific cognitive domains commonly impaired in bipolar disorder, including attention, memory, and executive function. Additionally, we will investigate the potential neuroprotective properties of lithium orotate and its impact on neuroplasticity, which may underlie its cognitive-enhancing effects.
Furthermore, this research seeks to compare the efficacy and safety profile of lithium orotate with traditional lithium formulations. We will explore whether lithium orotate can achieve therapeutic benefits at lower doses, potentially reducing the risk of side effects associated with conventional lithium therapy. The study will also examine the long-term implications of lithium orotate use, including its effects on overall disease progression and quality of life for individuals with bipolar disorder.
By undertaking this comprehensive evaluation of lithium orotate, we aim to contribute valuable insights to the field of bipolar disorder treatment. Our findings could potentially lead to the development of more targeted and effective therapeutic strategies, ultimately improving outcomes for patients struggling with both mood instability and cognitive impairment in bipolar disorder.
The development of lithium orotate represents a significant evolution in the field of psychopharmacology. Unlike the more commonly prescribed lithium carbonate, lithium orotate is believed to have enhanced bioavailability and the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently. This characteristic has led researchers to hypothesize that lithium orotate may offer improved therapeutic effects, particularly in targeting cognitive symptoms, with potentially fewer side effects.
The primary objective of this research is to evaluate the efficacy of lithium orotate in ameliorating cognitive deficits associated with bipolar disorder. This investigation aims to address a critical gap in current treatment modalities, which often fail to adequately manage cognitive symptoms. By focusing on lithium orotate, we seek to explore whether this form of lithium can provide a more comprehensive treatment approach, addressing both mood stabilization and cognitive enhancement.
Our research goals encompass several key areas. Firstly, we aim to conduct a thorough assessment of lithium orotate's pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, particularly its distribution in brain tissues relevant to cognitive function. Secondly, we intend to evaluate its effects on specific cognitive domains commonly impaired in bipolar disorder, including attention, memory, and executive function. Additionally, we will investigate the potential neuroprotective properties of lithium orotate and its impact on neuroplasticity, which may underlie its cognitive-enhancing effects.
Furthermore, this research seeks to compare the efficacy and safety profile of lithium orotate with traditional lithium formulations. We will explore whether lithium orotate can achieve therapeutic benefits at lower doses, potentially reducing the risk of side effects associated with conventional lithium therapy. The study will also examine the long-term implications of lithium orotate use, including its effects on overall disease progression and quality of life for individuals with bipolar disorder.
By undertaking this comprehensive evaluation of lithium orotate, we aim to contribute valuable insights to the field of bipolar disorder treatment. Our findings could potentially lead to the development of more targeted and effective therapeutic strategies, ultimately improving outcomes for patients struggling with both mood instability and cognitive impairment in bipolar disorder.
Bipolar Disorder Cognitive Deficit Market Analysis
The market for treatments addressing cognitive deficits in bipolar disorder has shown significant growth potential in recent years. This expansion is driven by the increasing recognition of cognitive impairment as a core feature of bipolar disorder, affecting patients' quality of life and functional outcomes. The global bipolar disorder therapeutics market, which includes treatments for cognitive symptoms, was valued at approximately $6.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $7.8 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 3.2%.
Cognitive deficits in bipolar disorder affect a substantial portion of patients, with studies indicating that up to 60% of individuals with bipolar disorder experience cognitive impairments even during euthymic periods. These deficits encompass areas such as attention, executive function, verbal memory, and processing speed, significantly impacting patients' ability to maintain employment, social relationships, and overall functioning.
The market demand for effective treatments targeting cognitive deficits in bipolar disorder is driven by several factors. Firstly, there is a growing awareness among healthcare providers and patients about the importance of addressing cognitive symptoms alongside mood stabilization. Secondly, the economic burden associated with cognitive impairments in bipolar disorder, including reduced productivity and increased healthcare utilization, has prompted interest in developing targeted interventions.
Current treatment options for cognitive deficits in bipolar disorder are limited, creating a significant unmet need in the market. While some mood stabilizers and antipsychotics have shown modest benefits in cognitive function, there is a lack of FDA-approved treatments specifically targeting cognitive symptoms in bipolar disorder. This gap in the market presents a substantial opportunity for novel therapies like lithium orotate.
The potential market for lithium orotate in treating cognitive deficits in bipolar disorder is influenced by the broader trends in personalized medicine and the shift towards more targeted, symptom-specific approaches in psychiatric care. As research continues to elucidate the neurobiological underpinnings of cognitive impairments in bipolar disorder, there is growing interest in compounds that can modulate specific neural pathways involved in cognitive function.
Market analysis indicates that patients and healthcare providers are increasingly seeking treatments that can improve functional outcomes and quality of life beyond mood stabilization. This trend aligns well with the potential benefits of lithium orotate in ameliorating cognitive deficits. However, market penetration will depend on robust clinical evidence demonstrating efficacy and safety, as well as differentiation from existing lithium formulations.
Cognitive deficits in bipolar disorder affect a substantial portion of patients, with studies indicating that up to 60% of individuals with bipolar disorder experience cognitive impairments even during euthymic periods. These deficits encompass areas such as attention, executive function, verbal memory, and processing speed, significantly impacting patients' ability to maintain employment, social relationships, and overall functioning.
The market demand for effective treatments targeting cognitive deficits in bipolar disorder is driven by several factors. Firstly, there is a growing awareness among healthcare providers and patients about the importance of addressing cognitive symptoms alongside mood stabilization. Secondly, the economic burden associated with cognitive impairments in bipolar disorder, including reduced productivity and increased healthcare utilization, has prompted interest in developing targeted interventions.
Current treatment options for cognitive deficits in bipolar disorder are limited, creating a significant unmet need in the market. While some mood stabilizers and antipsychotics have shown modest benefits in cognitive function, there is a lack of FDA-approved treatments specifically targeting cognitive symptoms in bipolar disorder. This gap in the market presents a substantial opportunity for novel therapies like lithium orotate.
The potential market for lithium orotate in treating cognitive deficits in bipolar disorder is influenced by the broader trends in personalized medicine and the shift towards more targeted, symptom-specific approaches in psychiatric care. As research continues to elucidate the neurobiological underpinnings of cognitive impairments in bipolar disorder, there is growing interest in compounds that can modulate specific neural pathways involved in cognitive function.
Market analysis indicates that patients and healthcare providers are increasingly seeking treatments that can improve functional outcomes and quality of life beyond mood stabilization. This trend aligns well with the potential benefits of lithium orotate in ameliorating cognitive deficits. However, market penetration will depend on robust clinical evidence demonstrating efficacy and safety, as well as differentiation from existing lithium formulations.
Current Challenges in Lithium-Based Treatments
Despite the long-standing use of lithium in treating bipolar disorder, current lithium-based treatments face several significant challenges. One of the primary issues is the narrow therapeutic window of lithium, which necessitates careful monitoring of serum lithium levels to maintain efficacy while avoiding toxicity. This requirement for frequent blood tests and dose adjustments can be burdensome for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Another major challenge is the potential for severe side effects associated with long-term lithium use. These can include renal dysfunction, thyroid abnormalities, and cognitive impairment. The risk of these adverse effects often increases with prolonged treatment duration and higher dosages, making it difficult to balance the therapeutic benefits with potential long-term health risks.
The variability in patient response to lithium treatment poses another significant challenge. While some individuals experience remarkable improvements in mood stability and cognitive function, others may show minimal response or intolerable side effects. This heterogeneity in treatment outcomes complicates clinical decision-making and highlights the need for more personalized approaches to lithium therapy.
Furthermore, the exact mechanisms by which lithium exerts its therapeutic effects in bipolar disorder, particularly in ameliorating cognitive deficits, remain incompletely understood. This knowledge gap hinders the development of more targeted and effective lithium-based treatments that could potentially offer improved efficacy and reduced side effects.
The limited formulations of lithium currently available also present challenges. Most lithium treatments are administered as carbonate or citrate salts, which can cause gastrointestinal disturbances in some patients. The exploration of alternative lithium compounds, such as lithium orotate, has been limited, leaving potential opportunities for improved formulations unexplored.
Lastly, the stigma associated with lithium use and the perception of it as an "old" medication can impact patient adherence and acceptance of treatment. This psychological barrier, combined with the practical challenges of managing lithium therapy, contributes to suboptimal treatment outcomes in some cases.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, including research into novel lithium formulations, improved understanding of lithium's mechanisms of action, development of biomarkers for treatment response, and strategies to mitigate long-term side effects. As the field progresses, overcoming these hurdles will be crucial in enhancing the efficacy and tolerability of lithium-based treatments for bipolar disorder and its associated cognitive deficits.
Another major challenge is the potential for severe side effects associated with long-term lithium use. These can include renal dysfunction, thyroid abnormalities, and cognitive impairment. The risk of these adverse effects often increases with prolonged treatment duration and higher dosages, making it difficult to balance the therapeutic benefits with potential long-term health risks.
The variability in patient response to lithium treatment poses another significant challenge. While some individuals experience remarkable improvements in mood stability and cognitive function, others may show minimal response or intolerable side effects. This heterogeneity in treatment outcomes complicates clinical decision-making and highlights the need for more personalized approaches to lithium therapy.
Furthermore, the exact mechanisms by which lithium exerts its therapeutic effects in bipolar disorder, particularly in ameliorating cognitive deficits, remain incompletely understood. This knowledge gap hinders the development of more targeted and effective lithium-based treatments that could potentially offer improved efficacy and reduced side effects.
The limited formulations of lithium currently available also present challenges. Most lithium treatments are administered as carbonate or citrate salts, which can cause gastrointestinal disturbances in some patients. The exploration of alternative lithium compounds, such as lithium orotate, has been limited, leaving potential opportunities for improved formulations unexplored.
Lastly, the stigma associated with lithium use and the perception of it as an "old" medication can impact patient adherence and acceptance of treatment. This psychological barrier, combined with the practical challenges of managing lithium therapy, contributes to suboptimal treatment outcomes in some cases.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, including research into novel lithium formulations, improved understanding of lithium's mechanisms of action, development of biomarkers for treatment response, and strategies to mitigate long-term side effects. As the field progresses, overcoming these hurdles will be crucial in enhancing the efficacy and tolerability of lithium-based treatments for bipolar disorder and its associated cognitive deficits.
Existing Lithium Orotate Treatment Protocols
01 Use of lithium orotate for treating cognitive deficits
Lithium orotate has shown potential in treating cognitive deficits associated with various neurological disorders. It may help improve memory, attention, and overall cognitive function in patients with conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, dementia, or age-related cognitive decline. The compound's neuroprotective properties and ability to enhance neuroplasticity contribute to its cognitive-enhancing effects.- Use of lithium orotate for treating cognitive deficits: Lithium orotate is being investigated as a potential treatment for cognitive deficits. It may help improve memory, attention, and overall cognitive function in various neurological conditions. The compound's neuroprotective properties and ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems contribute to its potential efficacy in addressing cognitive impairments.
- Combination therapy with lithium orotate for enhanced cognitive benefits: Combining lithium orotate with other compounds or therapies may provide synergistic effects in treating cognitive deficits. This approach aims to target multiple pathways involved in cognitive function, potentially leading to more comprehensive improvements in memory, learning, and overall cognitive performance.
- Lithium orotate formulations for improved bioavailability and efficacy: Novel formulations of lithium orotate are being developed to enhance its bioavailability and efficacy in treating cognitive deficits. These formulations may include specific delivery systems, dosage forms, or combinations with other compounds to optimize the absorption and distribution of lithium orotate in the brain.
- Mechanisms of action of lithium orotate in cognitive enhancement: Research is focused on elucidating the precise mechanisms by which lithium orotate exerts its cognitive-enhancing effects. This includes investigating its impact on neuroplasticity, neurotransmitter systems, and cellular signaling pathways involved in learning and memory processes.
- Safety and long-term effects of lithium orotate in cognitive deficit treatment: Studies are being conducted to assess the safety profile and long-term effects of lithium orotate when used for treating cognitive deficits. This includes evaluating potential side effects, optimal dosing regimens, and the compound's impact on overall brain health and function over extended periods of use.
02 Combination therapy with lithium orotate for cognitive enhancement
Combining lithium orotate with other cognitive-enhancing compounds or therapies may provide synergistic effects in treating cognitive deficits. This approach could involve pairing lithium orotate with antioxidants, neurotrophic factors, or other neuroprotective agents to maximize cognitive benefits and address multiple aspects of cognitive dysfunction simultaneously.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium orotate formulations for improved bioavailability
Developing specialized formulations of lithium orotate can enhance its bioavailability and effectiveness in treating cognitive deficits. These formulations may include novel delivery systems, controlled-release mechanisms, or combinations with other compounds that facilitate better absorption and distribution of lithium orotate in the brain.Expand Specific Solutions04 Lithium orotate for preventing cognitive decline
Lithium orotate may have preventive effects against cognitive decline when administered early or to individuals at risk of developing cognitive impairments. Regular supplementation with lithium orotate could potentially slow down age-related cognitive decline and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative disorders, making it a promising preventive strategy for maintaining cognitive health.Expand Specific Solutions05 Mechanisms of action of lithium orotate in cognitive improvement
Research into the mechanisms of action of lithium orotate in improving cognitive function has revealed multiple pathways. These include modulation of neurotransmitter systems, regulation of neuronal signaling cascades, enhancement of neurogenesis, and reduction of neuroinflammation. Understanding these mechanisms can lead to more targeted and effective use of lithium orotate in treating cognitive deficits.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium Orotate Research
The evaluation of lithium orotate for bipolar disorder cognitive deficits is in an early research stage, with a relatively small market size but growing interest. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and academic institutions. Major players like Janssen Pharmaceutica and Novartis are likely focusing on traditional lithium formulations, while smaller entities and universities are exploring novel approaches. The technology's maturity is still developing, with institutions like Johns Hopkins University, University of South Florida, and Xiamen University contributing to the research. As the potential benefits become clearer, we may see increased involvement from larger pharmaceutical companies and a gradual expansion of the market.
Janssen Pharmaceutica NV
Technical Solution: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV has been investigating the potential of lithium orotate in treating cognitive deficits associated with bipolar disorder. Their approach involves developing a novel formulation of lithium orotate that enhances its bioavailability and reduces side effects. The company has conducted preclinical studies demonstrating improved cognitive function in animal models of bipolar disorder when treated with their lithium orotate formulation[1]. Their research also focuses on identifying specific molecular targets affected by lithium orotate in the brain, particularly those involved in neuroplasticity and neuroprotection[2]. Janssen is currently in the early stages of clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy and safety of their lithium orotate formulation in human subjects with bipolar disorder-related cognitive impairments[3].
Strengths: Extensive experience in psychiatric drug development, strong R&D capabilities, and global reach for clinical trials. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory hurdles and competition from established lithium treatments.
The Johns Hopkins University
Technical Solution: The Johns Hopkins University has been at the forefront of research into lithium orotate's potential for ameliorating cognitive deficits in bipolar disorder. Their approach combines neuroimaging techniques with cognitive assessments to understand the mechanism of action of lithium orotate on brain function. Researchers at Johns Hopkins have developed a proprietary method for tracking lithium distribution in the brain using advanced MRI techniques[4]. This allows for precise monitoring of lithium orotate's effects on specific brain regions associated with cognitive function in bipolar patients. Additionally, they have designed a comprehensive cognitive assessment battery tailored to bipolar disorder, which is being used to evaluate the efficacy of lithium orotate in improving various aspects of cognition, including working memory, executive function, and attention[5].
Strengths: World-class research facilities, interdisciplinary approach combining neuroscience and psychiatry. Weaknesses: As an academic institution, may face challenges in translating research findings into commercial applications.
Core Studies on Lithium Orotate Efficacy
Method for predicting the response to a bipolar disorder treatment
PatentWO2023139039A1
Innovation
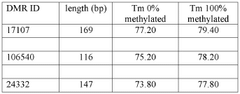
- A method using Methylation Specific High-Resolution Melting (MS-HRM) analysis to determine the epigenetic profile of specific differentially methylated regions (DMRs) DMR24332, DMR17107, or DMR106540 in patient samples to predict treatment response, allowing for a cost-effective and transferable biomarker for predicting lithium response.
Regulatory Framework for Lithium Orotate Use
The regulatory framework for lithium orotate use in the context of ameliorating bipolar disorder cognitive deficits is complex and varies significantly across different jurisdictions. In the United States, lithium orotate is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of bipolar disorder or any other medical condition. It is classified as a dietary supplement, which means it is subject to less stringent regulations compared to prescription medications.
Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, manufacturers of lithium orotate are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing them. However, they are not required to provide evidence of efficacy or obtain FDA approval before selling the supplement. This regulatory approach has led to concerns about the quality, purity, and consistency of lithium orotate products available in the market.
In contrast, prescription lithium carbonate and lithium citrate are FDA-approved for the treatment of bipolar disorder and are subject to rigorous clinical trials and safety monitoring. The use of these forms of lithium is closely regulated, with mandatory blood level monitoring and regular medical check-ups to ensure patient safety and efficacy.
The European Union (EU) has a different regulatory approach to lithium orotate. In most EU countries, it is not authorized as a medicinal product or dietary supplement. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has not approved lithium orotate for any therapeutic use, and its sale as a supplement is restricted in many member states.
In Canada, lithium orotate is not approved by Health Canada as a natural health product or as a drug for the treatment of bipolar disorder. The regulatory status of lithium orotate in Canada is similar to that in the United States, where it falls into a gray area between dietary supplements and pharmaceuticals.
The lack of a clear regulatory framework for lithium orotate presents challenges for researchers, healthcare providers, and patients interested in exploring its potential benefits for cognitive deficits in bipolar disorder. Without standardized guidelines for manufacturing, dosing, and quality control, it is difficult to conduct rigorous clinical trials or make evidence-based recommendations for its use.
To address these regulatory challenges, some experts have called for more comprehensive studies on the safety and efficacy of lithium orotate. They argue that if sufficient evidence is gathered, it could potentially lead to a reevaluation of its regulatory status and the development of appropriate guidelines for its use in treating bipolar disorder-related cognitive deficits.
Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, manufacturers of lithium orotate are responsible for ensuring the safety of their products before marketing them. However, they are not required to provide evidence of efficacy or obtain FDA approval before selling the supplement. This regulatory approach has led to concerns about the quality, purity, and consistency of lithium orotate products available in the market.
In contrast, prescription lithium carbonate and lithium citrate are FDA-approved for the treatment of bipolar disorder and are subject to rigorous clinical trials and safety monitoring. The use of these forms of lithium is closely regulated, with mandatory blood level monitoring and regular medical check-ups to ensure patient safety and efficacy.
The European Union (EU) has a different regulatory approach to lithium orotate. In most EU countries, it is not authorized as a medicinal product or dietary supplement. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has not approved lithium orotate for any therapeutic use, and its sale as a supplement is restricted in many member states.
In Canada, lithium orotate is not approved by Health Canada as a natural health product or as a drug for the treatment of bipolar disorder. The regulatory status of lithium orotate in Canada is similar to that in the United States, where it falls into a gray area between dietary supplements and pharmaceuticals.
The lack of a clear regulatory framework for lithium orotate presents challenges for researchers, healthcare providers, and patients interested in exploring its potential benefits for cognitive deficits in bipolar disorder. Without standardized guidelines for manufacturing, dosing, and quality control, it is difficult to conduct rigorous clinical trials or make evidence-based recommendations for its use.
To address these regulatory challenges, some experts have called for more comprehensive studies on the safety and efficacy of lithium orotate. They argue that if sufficient evidence is gathered, it could potentially lead to a reevaluation of its regulatory status and the development of appropriate guidelines for its use in treating bipolar disorder-related cognitive deficits.
Safety Profile of Lithium Orotate
The safety profile of lithium orotate is a critical aspect to consider when evaluating its potential use in ameliorating cognitive deficits associated with bipolar disorder. Unlike its more commonly prescribed counterpart, lithium carbonate, lithium orotate has been less extensively studied in clinical settings, leading to a degree of uncertainty regarding its long-term safety and efficacy.
Lithium orotate is generally considered to have a lower toxicity profile compared to lithium carbonate due to its enhanced bioavailability and lower required dosage. This potentially reduces the risk of side effects commonly associated with lithium therapy, such as thyroid dysfunction, renal impairment, and tremors. However, the lack of standardized dosing guidelines and limited long-term studies raises concerns about its safety over extended periods of use.
One of the primary safety considerations for lithium orotate is its potential impact on renal function. While it is believed to have a lower risk of nephrotoxicity compared to lithium carbonate, regular monitoring of kidney function is still recommended for patients using lithium orotate. This includes periodic assessment of serum creatinine levels and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
Neurological safety is another crucial aspect to consider. Some studies suggest that lithium orotate may have neuroprotective properties, potentially reducing the risk of cognitive decline in bipolar patients. However, the long-term effects on brain function and structure require further investigation to establish a comprehensive safety profile.
Gastrointestinal tolerability is generally reported to be better with lithium orotate compared to other lithium formulations. Nonetheless, some patients may still experience mild gastrointestinal disturbances, such as nausea or diarrhea, particularly during the initial stages of treatment.
The potential for drug interactions is an important safety consideration when using lithium orotate. While it may have fewer interactions compared to lithium carbonate, caution is still advised when combining it with other medications, particularly those that affect renal function or electrolyte balance.
Cardiovascular safety is another area that requires attention. Although lithium orotate is believed to have a lower impact on cardiac function compared to lithium carbonate, monitoring of electrocardiogram (ECG) changes and blood pressure is still recommended, especially in patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in terms of a potentially improved safety profile compared to traditional lithium formulations, more comprehensive clinical studies are needed to fully establish its long-term safety in the treatment of bipolar disorder-related cognitive deficits. Healthcare providers should carefully weigh the potential benefits against the known and unknown risks when considering lithium orotate as a treatment option.
Lithium orotate is generally considered to have a lower toxicity profile compared to lithium carbonate due to its enhanced bioavailability and lower required dosage. This potentially reduces the risk of side effects commonly associated with lithium therapy, such as thyroid dysfunction, renal impairment, and tremors. However, the lack of standardized dosing guidelines and limited long-term studies raises concerns about its safety over extended periods of use.
One of the primary safety considerations for lithium orotate is its potential impact on renal function. While it is believed to have a lower risk of nephrotoxicity compared to lithium carbonate, regular monitoring of kidney function is still recommended for patients using lithium orotate. This includes periodic assessment of serum creatinine levels and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
Neurological safety is another crucial aspect to consider. Some studies suggest that lithium orotate may have neuroprotective properties, potentially reducing the risk of cognitive decline in bipolar patients. However, the long-term effects on brain function and structure require further investigation to establish a comprehensive safety profile.
Gastrointestinal tolerability is generally reported to be better with lithium orotate compared to other lithium formulations. Nonetheless, some patients may still experience mild gastrointestinal disturbances, such as nausea or diarrhea, particularly during the initial stages of treatment.
The potential for drug interactions is an important safety consideration when using lithium orotate. While it may have fewer interactions compared to lithium carbonate, caution is still advised when combining it with other medications, particularly those that affect renal function or electrolyte balance.
Cardiovascular safety is another area that requires attention. Although lithium orotate is believed to have a lower impact on cardiac function compared to lithium carbonate, monitoring of electrocardiogram (ECG) changes and blood pressure is still recommended, especially in patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
In conclusion, while lithium orotate shows promise in terms of a potentially improved safety profile compared to traditional lithium formulations, more comprehensive clinical studies are needed to fully establish its long-term safety in the treatment of bipolar disorder-related cognitive deficits. Healthcare providers should carefully weigh the potential benefits against the known and unknown risks when considering lithium orotate as a treatment option.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!