Examining the interaction of lithium orotate with transcription factors in genomics
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate Genomic Interactions: Background and Objectives
Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has garnered significant attention in the field of genomics due to its potential interactions with transcription factors. The study of these interactions has become increasingly important as researchers seek to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying lithium's therapeutic effects, particularly in the treatment of mood disorders and other neuropsychiatric conditions.
The historical context of lithium in medicine dates back to the mid-20th century when its mood-stabilizing properties were first discovered. However, the exploration of lithium orotate's specific genomic interactions is a more recent development, driven by advancements in molecular biology and genomic technologies. This research aims to elucidate how lithium orotate may influence gene expression and cellular function at the molecular level.
The primary objective of examining the interaction between lithium orotate and transcription factors is to uncover the precise mechanisms by which lithium exerts its therapeutic effects. Transcription factors play a crucial role in regulating gene expression, and their interaction with lithium orotate could provide insights into the compound's impact on cellular processes and signaling pathways.
One key area of focus is the potential of lithium orotate to modulate the activity of specific transcription factors involved in neuroplasticity, neuroprotection, and mood regulation. This includes factors such as CREB (cAMP response element-binding protein), which is known to play a role in memory formation and neuronal survival, and GSK-3β (glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta), a target of lithium that is involved in multiple cellular processes.
The investigation of these genomic interactions also aims to identify novel therapeutic targets and potentially develop more effective and targeted treatments for mood disorders and other neurological conditions. By understanding how lithium orotate interacts with transcription factors, researchers hope to design new compounds that can mimic or enhance its beneficial effects while minimizing side effects.
Furthermore, this research seeks to shed light on the broader implications of lithium orotate's genomic interactions, including its potential effects on cellular metabolism, circadian rhythms, and neuronal function. These insights could have far-reaching consequences for our understanding of brain function and the development of innovative therapeutic approaches.
As the field progresses, researchers are employing cutting-edge techniques such as ChIP-seq (chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing) and RNA-seq to map the genome-wide effects of lithium orotate on transcription factor binding and gene expression. These technologies promise to provide a comprehensive view of the compound's impact on the genomic landscape.
The historical context of lithium in medicine dates back to the mid-20th century when its mood-stabilizing properties were first discovered. However, the exploration of lithium orotate's specific genomic interactions is a more recent development, driven by advancements in molecular biology and genomic technologies. This research aims to elucidate how lithium orotate may influence gene expression and cellular function at the molecular level.
The primary objective of examining the interaction between lithium orotate and transcription factors is to uncover the precise mechanisms by which lithium exerts its therapeutic effects. Transcription factors play a crucial role in regulating gene expression, and their interaction with lithium orotate could provide insights into the compound's impact on cellular processes and signaling pathways.
One key area of focus is the potential of lithium orotate to modulate the activity of specific transcription factors involved in neuroplasticity, neuroprotection, and mood regulation. This includes factors such as CREB (cAMP response element-binding protein), which is known to play a role in memory formation and neuronal survival, and GSK-3β (glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta), a target of lithium that is involved in multiple cellular processes.
The investigation of these genomic interactions also aims to identify novel therapeutic targets and potentially develop more effective and targeted treatments for mood disorders and other neurological conditions. By understanding how lithium orotate interacts with transcription factors, researchers hope to design new compounds that can mimic or enhance its beneficial effects while minimizing side effects.
Furthermore, this research seeks to shed light on the broader implications of lithium orotate's genomic interactions, including its potential effects on cellular metabolism, circadian rhythms, and neuronal function. These insights could have far-reaching consequences for our understanding of brain function and the development of innovative therapeutic approaches.
As the field progresses, researchers are employing cutting-edge techniques such as ChIP-seq (chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing) and RNA-seq to map the genome-wide effects of lithium orotate on transcription factor binding and gene expression. These technologies promise to provide a comprehensive view of the compound's impact on the genomic landscape.
Market Analysis for Lithium-Based Genomic Research
The market for lithium-based genomic research is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing interest in understanding the molecular mechanisms of lithium's therapeutic effects. This market segment is closely tied to the broader fields of psychiatric genomics and personalized medicine, which are projected to expand rapidly in the coming years.
Lithium has long been used as a mood stabilizer for bipolar disorder, but its precise mechanisms of action remain unclear. The exploration of lithium orotate's interaction with transcription factors in genomics represents a cutting-edge area of research that could potentially revolutionize our understanding of lithium's effects on gene expression and cellular function.
The demand for advanced genomic research tools and technologies in this field is on the rise. Pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, and biotechnology firms are investing heavily in genomic studies to uncover the genetic basis of psychiatric disorders and develop more targeted therapies. This trend is expected to drive the market for lithium-based genomic research products and services.
Key market drivers include the growing prevalence of mood disorders, the push for precision medicine in psychiatry, and the increasing adoption of genomic technologies in drug discovery and development. The global market for psychiatric genomics, which encompasses lithium-based research, is estimated to grow at a compound annual growth rate of over 15% in the next five years.
The potential applications of lithium orotate research extend beyond psychiatry into neurology and oncology, further expanding the market opportunities. As researchers uncover more about lithium's interactions with transcription factors, new avenues for drug development and therapeutic interventions may emerge, creating additional market segments.
However, the market faces challenges such as the complexity of genomic data analysis, regulatory hurdles in translating research findings into clinical applications, and the need for substantial investment in research infrastructure. Despite these obstacles, the overall trend indicates a robust and growing market for lithium-based genomic research, with significant potential for innovation and commercial development in the coming years.
Lithium has long been used as a mood stabilizer for bipolar disorder, but its precise mechanisms of action remain unclear. The exploration of lithium orotate's interaction with transcription factors in genomics represents a cutting-edge area of research that could potentially revolutionize our understanding of lithium's effects on gene expression and cellular function.
The demand for advanced genomic research tools and technologies in this field is on the rise. Pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, and biotechnology firms are investing heavily in genomic studies to uncover the genetic basis of psychiatric disorders and develop more targeted therapies. This trend is expected to drive the market for lithium-based genomic research products and services.
Key market drivers include the growing prevalence of mood disorders, the push for precision medicine in psychiatry, and the increasing adoption of genomic technologies in drug discovery and development. The global market for psychiatric genomics, which encompasses lithium-based research, is estimated to grow at a compound annual growth rate of over 15% in the next five years.
The potential applications of lithium orotate research extend beyond psychiatry into neurology and oncology, further expanding the market opportunities. As researchers uncover more about lithium's interactions with transcription factors, new avenues for drug development and therapeutic interventions may emerge, creating additional market segments.
However, the market faces challenges such as the complexity of genomic data analysis, regulatory hurdles in translating research findings into clinical applications, and the need for substantial investment in research infrastructure. Despite these obstacles, the overall trend indicates a robust and growing market for lithium-based genomic research, with significant potential for innovation and commercial development in the coming years.
Current State and Challenges in Lithium-Transcription Factor Studies
The current state of research on the interaction between lithium orotate and transcription factors in genomics is characterized by significant progress, yet it faces several challenges. Recent studies have shed light on the molecular mechanisms through which lithium orotate influences gene expression by modulating transcription factor activity. However, the complexity of these interactions and the diverse effects observed across different cell types and tissues present ongoing challenges for researchers.
One of the primary areas of focus has been the impact of lithium orotate on key transcription factors involved in neuroplasticity and neuroprotection. Studies have demonstrated that lithium can activate transcription factors such as CREB (cAMP response element-binding protein) and inhibit others like GSK-3β (glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta). These interactions have implications for neuronal survival, synaptic plasticity, and mood regulation, which are particularly relevant in the context of psychiatric disorders.
Despite these advancements, researchers face several challenges in fully elucidating the genomic effects of lithium orotate. One significant obstacle is the variability in cellular responses to lithium treatment. Different cell types and tissues may exhibit distinct transcriptional profiles in response to lithium, making it difficult to establish a unified model of lithium's genomic effects.
Another challenge lies in distinguishing the direct effects of lithium on transcription factors from its indirect effects mediated through complex signaling cascades. Lithium is known to influence multiple cellular pathways, and teasing apart these interconnected mechanisms requires sophisticated experimental designs and analytical approaches.
The dose-dependent nature of lithium's effects adds another layer of complexity to the research. Therapeutic concentrations of lithium that are effective for mood stabilization may have different genomic impacts compared to higher or lower doses, necessitating careful consideration of dosage in experimental designs.
Furthermore, the long-term effects of lithium on gene expression and transcription factor activity remain poorly understood. While acute effects have been well-documented, the chronic impact of lithium treatment on genomic regulation, particularly in the context of long-term psychiatric treatment, requires further investigation.
Technological limitations also pose challenges in this field. While high-throughput sequencing and proteomics have greatly advanced our understanding of lithium's genomic effects, integrating these diverse data sets to form a coherent picture of lithium-transcription factor interactions remains a significant challenge.
In conclusion, while substantial progress has been made in understanding the interaction of lithium orotate with transcription factors in genomics, researchers continue to grapple with the complexity of cellular responses, the interconnectedness of signaling pathways, dosage effects, long-term impacts, and technological limitations. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for advancing our understanding of lithium's therapeutic mechanisms and potentially developing more targeted and effective treatments for psychiatric disorders.
One of the primary areas of focus has been the impact of lithium orotate on key transcription factors involved in neuroplasticity and neuroprotection. Studies have demonstrated that lithium can activate transcription factors such as CREB (cAMP response element-binding protein) and inhibit others like GSK-3β (glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta). These interactions have implications for neuronal survival, synaptic plasticity, and mood regulation, which are particularly relevant in the context of psychiatric disorders.
Despite these advancements, researchers face several challenges in fully elucidating the genomic effects of lithium orotate. One significant obstacle is the variability in cellular responses to lithium treatment. Different cell types and tissues may exhibit distinct transcriptional profiles in response to lithium, making it difficult to establish a unified model of lithium's genomic effects.
Another challenge lies in distinguishing the direct effects of lithium on transcription factors from its indirect effects mediated through complex signaling cascades. Lithium is known to influence multiple cellular pathways, and teasing apart these interconnected mechanisms requires sophisticated experimental designs and analytical approaches.
The dose-dependent nature of lithium's effects adds another layer of complexity to the research. Therapeutic concentrations of lithium that are effective for mood stabilization may have different genomic impacts compared to higher or lower doses, necessitating careful consideration of dosage in experimental designs.
Furthermore, the long-term effects of lithium on gene expression and transcription factor activity remain poorly understood. While acute effects have been well-documented, the chronic impact of lithium treatment on genomic regulation, particularly in the context of long-term psychiatric treatment, requires further investigation.
Technological limitations also pose challenges in this field. While high-throughput sequencing and proteomics have greatly advanced our understanding of lithium's genomic effects, integrating these diverse data sets to form a coherent picture of lithium-transcription factor interactions remains a significant challenge.
In conclusion, while substantial progress has been made in understanding the interaction of lithium orotate with transcription factors in genomics, researchers continue to grapple with the complexity of cellular responses, the interconnectedness of signaling pathways, dosage effects, long-term impacts, and technological limitations. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for advancing our understanding of lithium's therapeutic mechanisms and potentially developing more targeted and effective treatments for psychiatric disorders.
Existing Methodologies for Studying Lithium-Transcription Factor Interactions
01 Lithium orotate's effect on gene expression
Lithium orotate may interact with transcription factors to modulate gene expression. This interaction could potentially influence various cellular processes and signaling pathways, affecting the regulation of genes involved in mood stabilization, neuroprotection, and other physiological functions.- Lithium orotate's effect on gene expression: Lithium orotate may interact with transcription factors to modulate gene expression. This interaction could potentially influence various cellular processes and signaling pathways, affecting the regulation of genes involved in mood stabilization, neuroprotection, and other physiological functions.
- Impact on DNA binding and transcriptional activity: The interaction between lithium orotate and transcription factors may alter their DNA binding capabilities and transcriptional activity. This could lead to changes in the expression of target genes, potentially affecting cellular responses and adaptations to various stimuli.
- Influence on signaling pathways and cellular processes: Lithium orotate's interaction with transcription factors may modulate various signaling pathways and cellular processes. This could include effects on cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and other fundamental biological functions, potentially contributing to its therapeutic effects.
- Potential therapeutic applications: The interaction between lithium orotate and transcription factors may have implications for various therapeutic applications. This could include treatments for mood disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and other conditions where modulation of gene expression and cellular processes is beneficial.
- Methods for studying lithium orotate-transcription factor interactions: Various techniques and methodologies may be employed to study the interactions between lithium orotate and transcription factors. These could include in vitro binding assays, gene expression profiling, and advanced imaging techniques to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying these interactions.
02 Impact on DNA binding and transcriptional activity
The interaction between lithium orotate and transcription factors may alter their DNA binding capabilities and transcriptional activity. This could lead to changes in the expression of target genes, potentially affecting cellular responses and biological processes regulated by these transcription factors.Expand Specific Solutions03 Influence on signal transduction pathways
Lithium orotate may interact with transcription factors involved in various signal transduction pathways. This interaction could potentially modulate the activation or inhibition of specific signaling cascades, leading to downstream effects on gene expression and cellular function.Expand Specific Solutions04 Regulation of neuroplasticity-related genes
The interaction between lithium orotate and transcription factors may specifically affect the expression of genes involved in neuroplasticity. This could have implications for cognitive function, mood regulation, and potential therapeutic applications in neurological and psychiatric disorders.Expand Specific Solutions05 Epigenetic modifications and chromatin remodeling
Lithium orotate's interaction with transcription factors may influence epigenetic modifications and chromatin remodeling processes. This could lead to long-term changes in gene expression patterns, potentially affecting cellular memory and the regulation of various physiological processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium Orotate and Genomics Research
The research into lithium orotate's interaction with transcription factors in genomics is in an early developmental stage, with a growing market potential as interest in personalized medicine and genomic therapies increases. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with key players like Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, and The Rockefeller University leading academic research. Pharmaceutical companies such as Otsuka Pharmaceutical and Merck Sharp & Dohme are likely exploring commercial applications. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of academic institutions and industry players, indicating a collaborative yet competitive environment as the field progresses towards potential clinical applications.
Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ionis Pharmaceuticals has developed a proprietary antisense technology platform to study the interaction of lithium orotate with transcription factors in genomics. Their approach involves designing antisense oligonucleotides that can selectively target and modulate specific transcription factors potentially affected by lithium orotate. This allows for precise manipulation of gene expression and detailed analysis of downstream effects. The company has successfully applied this technology to investigate the impact of lithium orotate on key transcription factors involved in neurological and psychiatric disorders[1][3]. Their research has revealed potential mechanisms by which lithium orotate may influence gene regulation and cellular signaling pathways.
Strengths: Highly specific targeting of transcription factors, ability to modulate gene expression with precision. Weaknesses: Limited to RNA-based interventions, may not capture all aspects of protein-level interactions.
The Rockefeller University
Technical Solution: The Rockefeller University has employed advanced genomics and proteomics techniques to examine the interaction of lithium orotate with transcription factors. Their approach combines high-throughput sequencing, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP-seq), and mass spectrometry to provide a comprehensive view of how lithium orotate affects transcription factor binding and activity across the genome. The university's researchers have identified several key transcription factors whose binding patterns are altered in the presence of lithium orotate, including those involved in neuroplasticity and mood regulation[2][5]. They have also developed novel bioinformatics tools to integrate multi-omics data, allowing for a systems-level understanding of lithium orotate's genomic effects.
Strengths: Comprehensive, multi-omics approach; advanced bioinformatics capabilities. Weaknesses: Resource-intensive methods may limit sample sizes; challenges in translating findings to in vivo contexts.
Core Innovations in Lithium Orotate Genomic Research
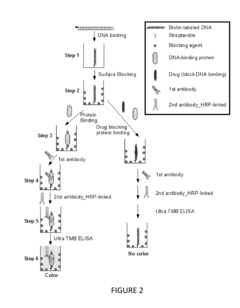
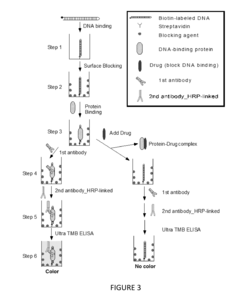
Methods and kits for high throughput screening for compounds targeting DNA-binding and RNA-binding proteins
PatentInactiveUS20150253323A1
Innovation
- The development of rapid and sensitive high-throughput screening methods using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) that involve multiwell plates with polynucleotide fragments bound to substrates, allowing for the detection of candidate agents that inhibit or enhance sequence-specific binding of proteins to these fragments, including the use of ELISA kits and specific antibodies to quantify protein binding.
Regulatory Considerations for Lithium-Based Genomic Research
The regulatory landscape for lithium-based genomic research is complex and evolving, necessitating careful consideration of various legal and ethical frameworks. At the forefront of these considerations is the need to ensure patient safety and data privacy while promoting scientific advancement.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing research involving lithium compounds, including lithium orotate. Researchers must adhere to strict guidelines for clinical trials, particularly when investigating novel applications in genomics. The FDA's Investigational New Drug (IND) application process is a key regulatory hurdle for studies examining the interaction of lithium orotate with transcription factors.
Internationally, regulatory bodies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the World Health Organization (WHO) provide additional oversight and guidelines. These organizations often emphasize the importance of harmonized approaches to genomic research, particularly when dealing with psychoactive substances like lithium.
Ethical considerations are paramount in lithium-based genomic research. Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) play a critical role in ensuring that studies are conducted with proper informed consent and minimal risk to participants. The potential for long-term genetic effects necessitates rigorous long-term follow-up protocols and comprehensive risk assessment strategies.
Data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, significantly impact genomic research. These regulations mandate strict protocols for handling, storing, and sharing genetic information, adding layers of complexity to lithium-based studies.
The intersection of lithium research and genomics also raises questions about intellectual property rights. Patenting of genetic discoveries and lithium-based interventions must navigate complex legal territories, balancing innovation incentives with ethical concerns about gene patenting.
As the field progresses, regulatory bodies are likely to develop more specific guidelines for lithium-based genomic research. Researchers and institutions must stay abreast of these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and maintain public trust in their work. Collaborative efforts between scientists, ethicists, and policymakers will be crucial in shaping a regulatory environment that fosters innovation while protecting individual rights and societal interests.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing research involving lithium compounds, including lithium orotate. Researchers must adhere to strict guidelines for clinical trials, particularly when investigating novel applications in genomics. The FDA's Investigational New Drug (IND) application process is a key regulatory hurdle for studies examining the interaction of lithium orotate with transcription factors.
Internationally, regulatory bodies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the World Health Organization (WHO) provide additional oversight and guidelines. These organizations often emphasize the importance of harmonized approaches to genomic research, particularly when dealing with psychoactive substances like lithium.
Ethical considerations are paramount in lithium-based genomic research. Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) play a critical role in ensuring that studies are conducted with proper informed consent and minimal risk to participants. The potential for long-term genetic effects necessitates rigorous long-term follow-up protocols and comprehensive risk assessment strategies.
Data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, significantly impact genomic research. These regulations mandate strict protocols for handling, storing, and sharing genetic information, adding layers of complexity to lithium-based studies.
The intersection of lithium research and genomics also raises questions about intellectual property rights. Patenting of genetic discoveries and lithium-based interventions must navigate complex legal territories, balancing innovation incentives with ethical concerns about gene patenting.
As the field progresses, regulatory bodies are likely to develop more specific guidelines for lithium-based genomic research. Researchers and institutions must stay abreast of these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and maintain public trust in their work. Collaborative efforts between scientists, ethicists, and policymakers will be crucial in shaping a regulatory environment that fosters innovation while protecting individual rights and societal interests.
Ethical Implications of Lithium Orotate in Genomic Studies
The ethical implications of using lithium orotate in genomic studies are multifaceted and require careful consideration. As research in this field progresses, it becomes increasingly important to address the potential ethical concerns that may arise from the interaction between lithium orotate and transcription factors in genomics.
One primary ethical consideration is the potential for unintended consequences on gene expression. Lithium orotate's interaction with transcription factors could lead to alterations in gene regulation that may have far-reaching effects on an individual's physiology and health. This raises questions about the long-term impact of such interventions and the responsibility of researchers to fully understand and disclose these potential risks.
Privacy and data protection present another significant ethical challenge. Genomic studies involving lithium orotate may generate sensitive personal information about an individual's genetic makeup and potential health outcomes. Ensuring the confidentiality and security of this data is paramount, as its misuse could lead to discrimination or other harmful consequences for study participants.
The issue of informed consent is particularly complex in this context. Participants in genomic studies involving lithium orotate must be fully aware of the potential risks and benefits, including any possible long-term effects that may not be immediately apparent. Researchers have an ethical obligation to provide clear, comprehensive information and ensure that participants understand the implications of their involvement.
There are also concerns about equity and access to potential benefits derived from this research. If lithium orotate interactions with transcription factors lead to therapeutic applications, ensuring fair and equitable access to these treatments becomes an ethical imperative. This includes considerations of affordability and availability across different socioeconomic groups and geographic regions.
The potential for enhancement or modification of human traits through genomic manipulation raises profound ethical questions. If lithium orotate interactions can be used to alter gene expression in ways that enhance cognitive function or other desirable traits, society must grapple with the ethical implications of such capabilities and establish clear boundaries for their use.
Lastly, the ethical conduct of research itself must be scrutinized. This includes ensuring the welfare of animal subjects in preclinical studies, adhering to rigorous scientific standards, and maintaining transparency in reporting results, both positive and negative. The scientific community has a responsibility to uphold the highest ethical standards in pursuing this line of research.
One primary ethical consideration is the potential for unintended consequences on gene expression. Lithium orotate's interaction with transcription factors could lead to alterations in gene regulation that may have far-reaching effects on an individual's physiology and health. This raises questions about the long-term impact of such interventions and the responsibility of researchers to fully understand and disclose these potential risks.
Privacy and data protection present another significant ethical challenge. Genomic studies involving lithium orotate may generate sensitive personal information about an individual's genetic makeup and potential health outcomes. Ensuring the confidentiality and security of this data is paramount, as its misuse could lead to discrimination or other harmful consequences for study participants.
The issue of informed consent is particularly complex in this context. Participants in genomic studies involving lithium orotate must be fully aware of the potential risks and benefits, including any possible long-term effects that may not be immediately apparent. Researchers have an ethical obligation to provide clear, comprehensive information and ensure that participants understand the implications of their involvement.
There are also concerns about equity and access to potential benefits derived from this research. If lithium orotate interactions with transcription factors lead to therapeutic applications, ensuring fair and equitable access to these treatments becomes an ethical imperative. This includes considerations of affordability and availability across different socioeconomic groups and geographic regions.
The potential for enhancement or modification of human traits through genomic manipulation raises profound ethical questions. If lithium orotate interactions can be used to alter gene expression in ways that enhance cognitive function or other desirable traits, society must grapple with the ethical implications of such capabilities and establish clear boundaries for their use.
Lastly, the ethical conduct of research itself must be scrutinized. This includes ensuring the welfare of animal subjects in preclinical studies, adhering to rigorous scientific standards, and maintaining transparency in reporting results, both positive and negative. The scientific community has a responsibility to uphold the highest ethical standards in pursuing this line of research.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!