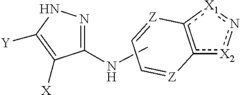
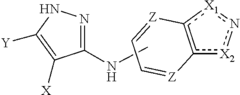
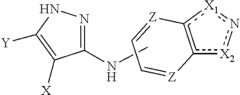
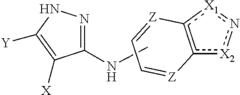
How does lithium orotate alter glutamate receptor signaling
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate and Glutamate Signaling: Background and Objectives
Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium bound to orotic acid, has garnered significant attention in the field of neuroscience and psychiatric research. This unique formulation has been proposed as an alternative to traditional lithium carbonate treatments, with potential implications for glutamate receptor signaling. The exploration of lithium orotate's effects on glutamatergic neurotransmission represents a critical area of investigation, given the pivotal role of glutamate in various neurological and psychiatric disorders.
The glutamatergic system, the primary excitatory neurotransmitter network in the mammalian central nervous system, plays a crucial role in synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. Dysregulation of glutamate signaling has been implicated in numerous neuropsychiatric conditions, including mood disorders, schizophrenia, and neurodegenerative diseases. Understanding how lithium orotate interacts with and potentially modulates glutamate receptor signaling could provide valuable insights into novel therapeutic approaches for these conditions.
Historically, lithium has been a cornerstone in the treatment of bipolar disorder and other mood-related conditions. However, the mechanisms underlying its therapeutic effects have remained elusive. Recent advances in neuroscience have shed light on lithium's potential influence on various neurotransmitter systems, including the glutamatergic pathway. The emergence of lithium orotate as a more bioavailable form of lithium has sparked renewed interest in exploring its specific effects on glutamate receptor signaling.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to elucidate the mechanisms by which lithium orotate alters glutamate receptor signaling. This investigation aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the current state of knowledge, identify key research findings, and highlight potential areas for future exploration. By examining the molecular interactions between lithium orotate and glutamate receptors, we seek to uncover novel insights that could inform the development of more targeted and effective therapeutic interventions.
Furthermore, this report will explore the potential advantages of lithium orotate over traditional lithium formulations in modulating glutamate signaling. We will examine the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of lithium orotate, with a particular focus on its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and its distribution within neural tissues. This analysis will help elucidate whether lithium orotate offers any unique benefits in terms of efficacy or reduced side effects compared to conventional lithium treatments.
As we delve into this complex interplay between lithium orotate and glutamate receptor signaling, we will also consider the broader implications for neuropsychiatric research and treatment paradigms. By synthesizing current knowledge and identifying key research questions, this report aims to provide a foundation for future investigations and potential clinical applications in the field of neuropsychopharmacology.
The glutamatergic system, the primary excitatory neurotransmitter network in the mammalian central nervous system, plays a crucial role in synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. Dysregulation of glutamate signaling has been implicated in numerous neuropsychiatric conditions, including mood disorders, schizophrenia, and neurodegenerative diseases. Understanding how lithium orotate interacts with and potentially modulates glutamate receptor signaling could provide valuable insights into novel therapeutic approaches for these conditions.
Historically, lithium has been a cornerstone in the treatment of bipolar disorder and other mood-related conditions. However, the mechanisms underlying its therapeutic effects have remained elusive. Recent advances in neuroscience have shed light on lithium's potential influence on various neurotransmitter systems, including the glutamatergic pathway. The emergence of lithium orotate as a more bioavailable form of lithium has sparked renewed interest in exploring its specific effects on glutamate receptor signaling.
The primary objective of this technical research report is to elucidate the mechanisms by which lithium orotate alters glutamate receptor signaling. This investigation aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the current state of knowledge, identify key research findings, and highlight potential areas for future exploration. By examining the molecular interactions between lithium orotate and glutamate receptors, we seek to uncover novel insights that could inform the development of more targeted and effective therapeutic interventions.
Furthermore, this report will explore the potential advantages of lithium orotate over traditional lithium formulations in modulating glutamate signaling. We will examine the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of lithium orotate, with a particular focus on its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and its distribution within neural tissues. This analysis will help elucidate whether lithium orotate offers any unique benefits in terms of efficacy or reduced side effects compared to conventional lithium treatments.
As we delve into this complex interplay between lithium orotate and glutamate receptor signaling, we will also consider the broader implications for neuropsychiatric research and treatment paradigms. By synthesizing current knowledge and identifying key research questions, this report aims to provide a foundation for future investigations and potential clinical applications in the field of neuropsychopharmacology.
Market Analysis for Lithium-Based Neuropsychiatric Treatments
The market for lithium-based neuropsychiatric treatments has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing prevalence of mental health disorders and the growing recognition of lithium's therapeutic potential. Lithium has long been established as a first-line treatment for bipolar disorder, but its applications are expanding to other neuropsychiatric conditions, including depression, schizophrenia, and neurodegenerative diseases.
The global market for lithium-based neuropsychiatric treatments is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate expected to remain strong over the next five years. This growth is attributed to several factors, including the rising incidence of mood disorders, increased awareness of mental health issues, and ongoing research into novel lithium formulations such as lithium orotate.
Lithium orotate, a specific form of lithium salt, has garnered attention in the market due to its potential for enhanced bioavailability and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate. This has opened up new opportunities for product development and market expansion, particularly in the nutraceutical and over-the-counter segments.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms focusing on innovative lithium-based therapies. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. However, developing regions are expected to witness faster growth rates due to improving healthcare infrastructure and increasing mental health awareness.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the stigma associated with mental health treatments and concerns over long-term lithium use. Regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials for new formulations also impact market dynamics. Nevertheless, ongoing research into lithium's mechanisms of action, including its effects on glutamate receptor signaling, is expected to drive innovation and market expansion.
The potential for lithium orotate to alter glutamate receptor signaling represents a significant area of interest for both researchers and pharmaceutical companies. This mechanism could lead to more targeted and effective treatments for various neuropsychiatric disorders, potentially expanding the market for lithium-based therapies beyond their traditional applications.
In conclusion, the market for lithium-based neuropsychiatric treatments, particularly those involving novel formulations like lithium orotate, shows promising growth potential. As research continues to uncover the intricate mechanisms of lithium's action on neurotransmitter systems, including glutamate signaling, the market is poised for further expansion and diversification in the coming years.
The global market for lithium-based neuropsychiatric treatments is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate expected to remain strong over the next five years. This growth is attributed to several factors, including the rising incidence of mood disorders, increased awareness of mental health issues, and ongoing research into novel lithium formulations such as lithium orotate.
Lithium orotate, a specific form of lithium salt, has garnered attention in the market due to its potential for enhanced bioavailability and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium carbonate. This has opened up new opportunities for product development and market expansion, particularly in the nutraceutical and over-the-counter segments.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms focusing on innovative lithium-based therapies. North America currently holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. However, developing regions are expected to witness faster growth rates due to improving healthcare infrastructure and increasing mental health awareness.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the stigma associated with mental health treatments and concerns over long-term lithium use. Regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials for new formulations also impact market dynamics. Nevertheless, ongoing research into lithium's mechanisms of action, including its effects on glutamate receptor signaling, is expected to drive innovation and market expansion.
The potential for lithium orotate to alter glutamate receptor signaling represents a significant area of interest for both researchers and pharmaceutical companies. This mechanism could lead to more targeted and effective treatments for various neuropsychiatric disorders, potentially expanding the market for lithium-based therapies beyond their traditional applications.
In conclusion, the market for lithium-based neuropsychiatric treatments, particularly those involving novel formulations like lithium orotate, shows promising growth potential. As research continues to uncover the intricate mechanisms of lithium's action on neurotransmitter systems, including glutamate signaling, the market is poised for further expansion and diversification in the coming years.
Current Understanding and Challenges in Glutamate Receptor Modulation
Glutamate receptor signaling plays a crucial role in neurotransmission and synaptic plasticity. Current understanding of glutamate receptor modulation has advanced significantly, revealing complex mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. However, several challenges remain in fully elucidating the intricate interactions between lithium orotate and glutamate receptor signaling.
Recent research has shed light on the modulatory effects of lithium orotate on glutamate receptors, particularly NMDA and AMPA receptors. Studies suggest that lithium orotate may alter receptor phosphorylation states, influencing their activation and desensitization kinetics. This modulation can potentially impact synaptic strength and neuroplasticity, which are critical for cognitive functions and mood regulation.
One of the primary challenges in understanding lithium orotate's effects on glutamate receptor signaling lies in the complexity of the signaling cascades involved. The glutamatergic system interacts with numerous other neurotransmitter systems and intracellular signaling pathways, making it difficult to isolate the specific effects of lithium orotate. Additionally, the dose-dependent nature of lithium's actions further complicates the interpretation of experimental results.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the long-term consequences of lithium orotate-induced alterations in glutamate receptor signaling. While acute effects have been observed, the chronic impact on receptor expression, synaptic plasticity, and overall brain function remains unclear. This gap in knowledge is particularly relevant for potential therapeutic applications, as many psychiatric disorders require long-term treatment.
The heterogeneity of glutamate receptor subunit compositions across different brain regions presents an additional layer of complexity. Lithium orotate may have differential effects on various receptor subtypes, leading to region-specific alterations in glutamatergic transmission. Elucidating these nuanced effects requires sophisticated experimental approaches and advanced imaging techniques.
Furthermore, the precise mechanisms by which lithium orotate crosses the blood-brain barrier and accumulates in neural tissues are not fully understood. This knowledge gap hinders the development of targeted delivery methods and optimal dosing strategies for modulating glutamate receptor signaling effectively.
Lastly, translating findings from preclinical models to human subjects remains a significant challenge. The complexity of the human brain and the ethical constraints on invasive studies limit our ability to directly observe lithium orotate's effects on glutamate receptor signaling in vivo. Developing non-invasive biomarkers and advanced neuroimaging techniques to assess glutamatergic function in humans is crucial for bridging this translational gap.
Recent research has shed light on the modulatory effects of lithium orotate on glutamate receptors, particularly NMDA and AMPA receptors. Studies suggest that lithium orotate may alter receptor phosphorylation states, influencing their activation and desensitization kinetics. This modulation can potentially impact synaptic strength and neuroplasticity, which are critical for cognitive functions and mood regulation.
One of the primary challenges in understanding lithium orotate's effects on glutamate receptor signaling lies in the complexity of the signaling cascades involved. The glutamatergic system interacts with numerous other neurotransmitter systems and intracellular signaling pathways, making it difficult to isolate the specific effects of lithium orotate. Additionally, the dose-dependent nature of lithium's actions further complicates the interpretation of experimental results.
Another significant challenge is the limited understanding of the long-term consequences of lithium orotate-induced alterations in glutamate receptor signaling. While acute effects have been observed, the chronic impact on receptor expression, synaptic plasticity, and overall brain function remains unclear. This gap in knowledge is particularly relevant for potential therapeutic applications, as many psychiatric disorders require long-term treatment.
The heterogeneity of glutamate receptor subunit compositions across different brain regions presents an additional layer of complexity. Lithium orotate may have differential effects on various receptor subtypes, leading to region-specific alterations in glutamatergic transmission. Elucidating these nuanced effects requires sophisticated experimental approaches and advanced imaging techniques.
Furthermore, the precise mechanisms by which lithium orotate crosses the blood-brain barrier and accumulates in neural tissues are not fully understood. This knowledge gap hinders the development of targeted delivery methods and optimal dosing strategies for modulating glutamate receptor signaling effectively.
Lastly, translating findings from preclinical models to human subjects remains a significant challenge. The complexity of the human brain and the ethical constraints on invasive studies limit our ability to directly observe lithium orotate's effects on glutamate receptor signaling in vivo. Developing non-invasive biomarkers and advanced neuroimaging techniques to assess glutamatergic function in humans is crucial for bridging this translational gap.
Existing Mechanisms of Lithium's Effect on Glutamate Signaling
01 Lithium orotate's effect on glutamate receptor signaling
Lithium orotate has been found to modulate glutamate receptor signaling pathways in the brain. This compound may influence the activity of various glutamate receptors, potentially leading to neuroprotective effects and improved cognitive function. The interaction between lithium orotate and glutamate receptors could have implications for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders.- Lithium orotate's effect on glutamate receptor signaling: Lithium orotate has been found to modulate glutamate receptor signaling pathways in the brain. This compound may influence the activity of various glutamate receptors, potentially affecting neurotransmission and synaptic plasticity. The interaction between lithium orotate and glutamate receptors could have implications for neurological and psychiatric disorders.
- Therapeutic applications of lithium orotate in neurological disorders: Lithium orotate has shown potential therapeutic benefits in treating various neurological disorders related to glutamate signaling dysfunction. Its ability to modulate glutamate receptor activity may help in managing conditions such as bipolar disorder, depression, and neurodegenerative diseases. Research suggests that lithium orotate could offer neuroprotective effects and improve cognitive function.
- Mechanisms of lithium orotate's action on glutamate receptors: Studies have investigated the molecular mechanisms by which lithium orotate interacts with glutamate receptors. This compound may influence receptor phosphorylation, trafficking, or expression levels. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing targeted therapies and optimizing treatment strategies for disorders involving glutamate signaling abnormalities.
- Comparative analysis of lithium orotate and other lithium compounds: Research has compared the effects of lithium orotate to other lithium compounds, such as lithium carbonate, on glutamate receptor signaling. These studies aim to determine if lithium orotate offers any advantages in terms of bioavailability, efficacy, or reduced side effects. Understanding the unique properties of lithium orotate could lead to improved treatment options for patients with glutamate-related disorders.
- Development of novel lithium orotate formulations: Efforts have been made to develop new formulations and delivery methods for lithium orotate to enhance its effects on glutamate receptor signaling. These innovations may include controlled-release formulations, combination therapies, or targeted delivery systems. Improved formulations could potentially increase the efficacy and safety of lithium orotate in treating glutamate-related disorders.
02 Glutamate receptor signaling in neurological disorders
Research has focused on the role of glutamate receptor signaling in various neurological disorders. Abnormalities in glutamate signaling have been implicated in conditions such as depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. Understanding these signaling pathways may lead to the development of novel therapeutic approaches targeting glutamate receptors.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium compounds and neuroprotection
Lithium compounds, including lithium orotate, have demonstrated neuroprotective properties. These compounds may help prevent neuronal damage and promote neuroplasticity through various mechanisms, including the modulation of glutamate receptor signaling. The neuroprotective effects of lithium compounds could have potential applications in treating neurodegenerative diseases.Expand Specific Solutions04 Glutamate receptor subtypes and their functions
Research has identified various subtypes of glutamate receptors, each with distinct functions in neurotransmission and synaptic plasticity. Understanding the specific roles of these receptor subtypes in glutamate signaling is crucial for developing targeted therapies. The interaction between lithium orotate and specific glutamate receptor subtypes may contribute to its therapeutic effects.Expand Specific Solutions05 Lithium orotate as a potential alternative to other lithium formulations
Lithium orotate has been investigated as a potential alternative to more commonly used lithium formulations, such as lithium carbonate. Its unique properties and potential effects on glutamate receptor signaling may offer advantages in terms of bioavailability and reduced side effects. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the benefits and mechanisms of action of lithium orotate compared to other lithium compounds.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium Research and Pharmaceutical Industry
The competitive landscape for research on lithium orotate's effects on glutamate receptor signaling is in an early developmental stage, with a relatively small market size due to its niche focus. The technology is still emerging, with varying levels of maturity across different players. Key companies like Merck & Co., Bristol Myers Squibb, and Novartis are likely at the forefront, leveraging their extensive pharmaceutical R&D capabilities. Academic institutions such as Vanderbilt University and The Scripps Research Institute are also contributing significantly to the field. Smaller biotechnology firms like Addex Pharma SA may be developing specialized approaches, while larger pharmaceutical companies are exploring broader applications in neurological disorders.
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.
Technical Solution: Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. has developed a novel approach to modulate glutamate receptor signaling using lithium orotate. Their research focuses on the interaction between lithium orotate and NMDA receptors, a type of glutamate receptor. The company's studies have shown that lithium orotate can act as a partial antagonist of NMDA receptors, potentially reducing excessive glutamatergic signaling without completely blocking it[1]. This mechanism may provide neuroprotective effects and improve cognitive function in various neurological disorders. Merck's researchers have also investigated the impact of lithium orotate on AMPA receptors, another crucial glutamate receptor subtype, finding that it may enhance AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity[3].
Strengths: Targeted approach to glutamate modulation, potential for neuroprotection and cognitive enhancement. Weaknesses: Possible side effects due to broad impact on glutamate signaling, need for careful dosing to avoid lithium toxicity.
Addex Pharma SA
Technical Solution: Addex Pharma SA has developed a unique allosteric modulation approach to alter glutamate receptor signaling using lithium orotate. Their technology focuses on positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) and negative allosteric modulators (NAMs) of metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs). In the context of lithium orotate, Addex has investigated its potential as a PAM for specific mGluR subtypes, particularly mGluR2 and mGluR3[2]. This approach aims to enhance the natural signaling of these receptors without directly activating them, potentially leading to a more subtle and physiologically relevant modulation of glutamate signaling. Addex's research has shown that lithium orotate, when combined with their proprietary allosteric modulators, can fine-tune glutamate receptor activity, potentially offering therapeutic benefits in conditions such as anxiety, depression, and schizophrenia[4].
Strengths: Highly targeted approach, potential for reduced side effects compared to direct receptor agonists/antagonists. Weaknesses: Complexity in developing specific modulators, potential for unexpected interactions with other signaling pathways.
Innovative Studies on Lithium Orotate and Glutamate Receptors
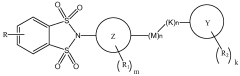
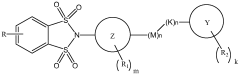
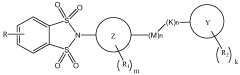
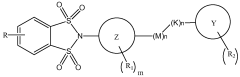
Substituted 1,1,3,3-tetraoxidobenzo[d][1,3,2]dithiazoles as mglur4 allosteric potentiators, compositions, and methods of treating neurological dysfunction
PatentWO2010088406A1
Innovation
- Development of substituted 1,1,3,3-tetraoxido benzo[d]isothiazoles as allosteric modulators of mGluR4 receptors, which can affect the sensitivity of mGluR4 receptors to agonists without binding to the orthosteric agonist binding site, and are administered in specific dosages to treat various disorders.
Benzothiazole and benzisothiazole-substituted compounds as mglur4 allosteric potentiators, compositions, and methods of treating neurological dysfunction
PatentActiveUS20180022744A1
Innovation
- Development of compounds with a specific structure represented by formula (I) that act as allosteric modulators of mGluR4 receptors, potentiating their activity without binding to the orthosteric agonist site, thereby enhancing their sensitivity to agonists and providing therapeutic benefits for neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Safety and Efficacy Profiles of Lithium Orotate
Lithium orotate, a compound consisting of lithium and orotic acid, has gained attention in recent years as a potential alternative to traditional lithium carbonate in the treatment of various neurological and psychiatric disorders. The safety and efficacy profiles of lithium orotate are of particular interest due to its purported ability to cross the blood-brain barrier more efficiently than other lithium formulations.
In terms of safety, lithium orotate is generally considered to have a lower risk of toxicity compared to lithium carbonate. This is primarily due to the lower dosage required to achieve therapeutic effects, which reduces the likelihood of adverse reactions. However, it is important to note that long-term studies on the safety of lithium orotate are limited, and more research is needed to fully understand its potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
The efficacy of lithium orotate has been reported in several studies, particularly in the treatment of mood disorders such as bipolar disorder and depression. Some research suggests that lithium orotate may be more effective than lithium carbonate in managing these conditions, with patients experiencing fewer side effects and requiring lower doses to achieve therapeutic benefits. Additionally, there is emerging evidence that lithium orotate may have neuroprotective properties, potentially offering benefits in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders.
One of the key advantages of lithium orotate is its improved bioavailability. The orotate ion is believed to act as a carrier, facilitating the transport of lithium across cell membranes and the blood-brain barrier. This enhanced delivery mechanism may contribute to its reported efficacy at lower doses compared to other lithium formulations.
Despite these promising findings, it is crucial to acknowledge that the body of research on lithium orotate is still relatively small compared to the extensive studies conducted on lithium carbonate. Many of the claims regarding its superior efficacy and safety profile are based on limited clinical trials and anecdotal evidence. As such, more rigorous, large-scale studies are necessary to definitively establish the comparative benefits and risks of lithium orotate.
In clinical practice, the use of lithium orotate remains controversial. While some healthcare providers advocate for its use, particularly in cases where patients have not responded well to traditional lithium treatments, others are more cautious due to the lack of standardized dosing guidelines and long-term safety data. The regulatory status of lithium orotate also varies across different countries, with some classifying it as a dietary supplement rather than a pharmaceutical drug.
In terms of safety, lithium orotate is generally considered to have a lower risk of toxicity compared to lithium carbonate. This is primarily due to the lower dosage required to achieve therapeutic effects, which reduces the likelihood of adverse reactions. However, it is important to note that long-term studies on the safety of lithium orotate are limited, and more research is needed to fully understand its potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
The efficacy of lithium orotate has been reported in several studies, particularly in the treatment of mood disorders such as bipolar disorder and depression. Some research suggests that lithium orotate may be more effective than lithium carbonate in managing these conditions, with patients experiencing fewer side effects and requiring lower doses to achieve therapeutic benefits. Additionally, there is emerging evidence that lithium orotate may have neuroprotective properties, potentially offering benefits in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders.
One of the key advantages of lithium orotate is its improved bioavailability. The orotate ion is believed to act as a carrier, facilitating the transport of lithium across cell membranes and the blood-brain barrier. This enhanced delivery mechanism may contribute to its reported efficacy at lower doses compared to other lithium formulations.
Despite these promising findings, it is crucial to acknowledge that the body of research on lithium orotate is still relatively small compared to the extensive studies conducted on lithium carbonate. Many of the claims regarding its superior efficacy and safety profile are based on limited clinical trials and anecdotal evidence. As such, more rigorous, large-scale studies are necessary to definitively establish the comparative benefits and risks of lithium orotate.
In clinical practice, the use of lithium orotate remains controversial. While some healthcare providers advocate for its use, particularly in cases where patients have not responded well to traditional lithium treatments, others are more cautious due to the lack of standardized dosing guidelines and long-term safety data. The regulatory status of lithium orotate also varies across different countries, with some classifying it as a dietary supplement rather than a pharmaceutical drug.
Regulatory Landscape for Novel Lithium Formulations
The regulatory landscape for novel lithium formulations, such as lithium orotate, is complex and evolving. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved lithium orotate for medical use, classifying it as a dietary supplement rather than a pharmaceutical drug. This classification means that lithium orotate is subject to less stringent regulations compared to prescription lithium medications.
Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, manufacturers of lithium orotate are not required to demonstrate safety or efficacy before marketing their products. However, they must ensure that their products are safe and that any claims made about them are not false or misleading. The FDA can take action against manufacturers if safety issues arise or if unsubstantiated health claims are made.
In contrast, prescription lithium medications, such as lithium carbonate and lithium citrate, are regulated as pharmaceutical drugs. These formulations have undergone rigorous clinical trials and have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of bipolar disorder. They are subject to strict manufacturing standards, dosage guidelines, and ongoing safety monitoring.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) and other international regulatory bodies have similar approaches, generally not recognizing lithium orotate as an approved medication. In many countries, it falls under the category of food supplements or alternative medicines, with varying degrees of regulation.
Despite the lack of formal approval, some healthcare practitioners and patients have shown interest in lithium orotate due to claims of improved bioavailability and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium formulations. However, the absence of comprehensive clinical studies and regulatory oversight raises concerns about its safety and efficacy.
Regulatory agencies worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing the dietary supplement market, including novel lithium formulations. There is growing pressure for more stringent regulations to ensure consumer safety and product quality. This may lead to future changes in the regulatory landscape for lithium orotate and similar compounds.
As research into the mechanisms of lithium's action on glutamate receptor signaling progresses, regulatory bodies may reassess their stance on novel lithium formulations. Future regulatory decisions will likely depend on the outcomes of rigorous scientific studies examining the safety, efficacy, and long-term effects of these alternative lithium compounds.
Under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994, manufacturers of lithium orotate are not required to demonstrate safety or efficacy before marketing their products. However, they must ensure that their products are safe and that any claims made about them are not false or misleading. The FDA can take action against manufacturers if safety issues arise or if unsubstantiated health claims are made.
In contrast, prescription lithium medications, such as lithium carbonate and lithium citrate, are regulated as pharmaceutical drugs. These formulations have undergone rigorous clinical trials and have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of bipolar disorder. They are subject to strict manufacturing standards, dosage guidelines, and ongoing safety monitoring.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) and other international regulatory bodies have similar approaches, generally not recognizing lithium orotate as an approved medication. In many countries, it falls under the category of food supplements or alternative medicines, with varying degrees of regulation.
Despite the lack of formal approval, some healthcare practitioners and patients have shown interest in lithium orotate due to claims of improved bioavailability and reduced side effects compared to traditional lithium formulations. However, the absence of comprehensive clinical studies and regulatory oversight raises concerns about its safety and efficacy.
Regulatory agencies worldwide are increasingly scrutinizing the dietary supplement market, including novel lithium formulations. There is growing pressure for more stringent regulations to ensure consumer safety and product quality. This may lead to future changes in the regulatory landscape for lithium orotate and similar compounds.
As research into the mechanisms of lithium's action on glutamate receptor signaling progresses, regulatory bodies may reassess their stance on novel lithium formulations. Future regulatory decisions will likely depend on the outcomes of rigorous scientific studies examining the safety, efficacy, and long-term effects of these alternative lithium compounds.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!