How does lithium orotate influence endocannabinoid system function
AUG 19, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Orotate and ECS: Background and Objectives
Lithium orotate, a compound combining lithium with orotic acid, has garnered increasing attention in recent years for its potential therapeutic applications. This technical research report aims to explore the intersection of lithium orotate and the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex cell-signaling network that plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis within the body.
The endocannabinoid system, discovered in the early 1990s, consists of endogenous cannabinoids, cannabinoid receptors, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids. It is involved in regulating various physiological processes, including mood, appetite, sleep, and pain sensation. Understanding how lithium orotate may influence this system is of paramount importance for developing novel therapeutic strategies.
Lithium, in its various forms, has been used for decades in the treatment of bipolar disorder and other psychiatric conditions. However, the traditional lithium carbonate formulation often requires high doses, leading to potential side effects and toxicity concerns. Lithium orotate, on the other hand, is believed to have improved bioavailability and may offer therapeutic benefits at lower doses.
The primary objective of this research is to elucidate the mechanisms by which lithium orotate interacts with the endocannabinoid system. This investigation aims to uncover potential synergies between lithium's known mood-stabilizing properties and the ECS's role in emotional regulation and neuroplasticity. By exploring this relationship, we seek to identify new avenues for treating mood disorders, anxiety, and other conditions associated with ECS dysfunction.
Furthermore, this research endeavors to assess the potential advantages of lithium orotate over traditional lithium formulations in modulating ECS function. We will examine whether the unique properties of lithium orotate, such as enhanced cellular penetration and lower required dosages, translate to more targeted and efficient interactions with the endocannabinoid system.
As the field of psychopharmacology continues to evolve, understanding the interplay between lithium orotate and the ECS could lead to significant advancements in personalized medicine. This research may pave the way for developing more effective and better-tolerated treatments for a range of neuropsychiatric disorders.
In the following sections, we will delve into the current state of knowledge regarding lithium orotate and the endocannabinoid system, analyze existing research, and identify key areas for future investigation. By comprehensively examining this topic, we aim to provide valuable insights that could shape future therapeutic strategies and contribute to the ongoing revolution in mental health treatment.
The endocannabinoid system, discovered in the early 1990s, consists of endogenous cannabinoids, cannabinoid receptors, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids. It is involved in regulating various physiological processes, including mood, appetite, sleep, and pain sensation. Understanding how lithium orotate may influence this system is of paramount importance for developing novel therapeutic strategies.
Lithium, in its various forms, has been used for decades in the treatment of bipolar disorder and other psychiatric conditions. However, the traditional lithium carbonate formulation often requires high doses, leading to potential side effects and toxicity concerns. Lithium orotate, on the other hand, is believed to have improved bioavailability and may offer therapeutic benefits at lower doses.
The primary objective of this research is to elucidate the mechanisms by which lithium orotate interacts with the endocannabinoid system. This investigation aims to uncover potential synergies between lithium's known mood-stabilizing properties and the ECS's role in emotional regulation and neuroplasticity. By exploring this relationship, we seek to identify new avenues for treating mood disorders, anxiety, and other conditions associated with ECS dysfunction.
Furthermore, this research endeavors to assess the potential advantages of lithium orotate over traditional lithium formulations in modulating ECS function. We will examine whether the unique properties of lithium orotate, such as enhanced cellular penetration and lower required dosages, translate to more targeted and efficient interactions with the endocannabinoid system.
As the field of psychopharmacology continues to evolve, understanding the interplay between lithium orotate and the ECS could lead to significant advancements in personalized medicine. This research may pave the way for developing more effective and better-tolerated treatments for a range of neuropsychiatric disorders.
In the following sections, we will delve into the current state of knowledge regarding lithium orotate and the endocannabinoid system, analyze existing research, and identify key areas for future investigation. By comprehensively examining this topic, we aim to provide valuable insights that could shape future therapeutic strategies and contribute to the ongoing revolution in mental health treatment.
Market Analysis of Lithium Orotate Supplements
The market for lithium orotate supplements has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer interest in mental health and alternative treatments for mood disorders. This niche segment of the dietary supplement industry has gained traction due to claims of improved bioavailability and potential neurological benefits compared to traditional lithium carbonate medications.
Market research indicates that the global lithium orotate supplement market is expanding at a steady rate, with North America and Europe being the primary regions of consumption. The market is characterized by a mix of established supplement companies and newer, specialized brands focusing exclusively on lithium orotate products. Online retail channels have played a crucial role in the distribution and popularity of these supplements, allowing for direct-to-consumer sales and education.
Consumer demographics for lithium orotate supplements tend to skew towards adults aged 25-55, with a slightly higher representation of women. Many users report seeking these products for managing anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorder symptoms, as well as for general cognitive enhancement and mood stabilization. The growing trend of self-directed healthcare and interest in nootropics has further fueled market demand.
Despite the increasing popularity, the market faces challenges related to regulatory scrutiny and scientific validation. The FDA has not approved lithium orotate for any medical use, and the supplement exists in a gray area of regulation. This has led to some market fragmentation, with varying quality standards and dosage recommendations across different brands.
Pricing for lithium orotate supplements varies widely, reflecting the diverse range of product formulations and brand positioning. Premium products often emphasize purity, third-party testing, and additional supportive ingredients, commanding higher price points. The market also sees more affordable options, particularly from generic supplement manufacturers.
Looking ahead, the lithium orotate supplement market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, albeit with potential regulatory hurdles. Increased research into the endocannabinoid system and its interaction with lithium compounds may further influence market dynamics. As consumer awareness grows and more scientific studies emerge, the market is likely to see both consolidation among existing players and the entry of new competitors seeking to capitalize on the trend.
Market research indicates that the global lithium orotate supplement market is expanding at a steady rate, with North America and Europe being the primary regions of consumption. The market is characterized by a mix of established supplement companies and newer, specialized brands focusing exclusively on lithium orotate products. Online retail channels have played a crucial role in the distribution and popularity of these supplements, allowing for direct-to-consumer sales and education.
Consumer demographics for lithium orotate supplements tend to skew towards adults aged 25-55, with a slightly higher representation of women. Many users report seeking these products for managing anxiety, depression, and bipolar disorder symptoms, as well as for general cognitive enhancement and mood stabilization. The growing trend of self-directed healthcare and interest in nootropics has further fueled market demand.
Despite the increasing popularity, the market faces challenges related to regulatory scrutiny and scientific validation. The FDA has not approved lithium orotate for any medical use, and the supplement exists in a gray area of regulation. This has led to some market fragmentation, with varying quality standards and dosage recommendations across different brands.
Pricing for lithium orotate supplements varies widely, reflecting the diverse range of product formulations and brand positioning. Premium products often emphasize purity, third-party testing, and additional supportive ingredients, commanding higher price points. The market also sees more affordable options, particularly from generic supplement manufacturers.
Looking ahead, the lithium orotate supplement market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, albeit with potential regulatory hurdles. Increased research into the endocannabinoid system and its interaction with lithium compounds may further influence market dynamics. As consumer awareness grows and more scientific studies emerge, the market is likely to see both consolidation among existing players and the entry of new competitors seeking to capitalize on the trend.
Current Understanding of Lithium-ECS Interactions
The current understanding of lithium-ECS interactions is a complex and evolving field of research. Lithium, particularly in the form of lithium orotate, has been found to have potential influences on the endocannabinoid system (ECS), although the exact mechanisms are still being elucidated. Recent studies have shown that lithium may modulate the activity of key components of the ECS, including cannabinoid receptors and endocannabinoid-metabolizing enzymes.
One of the primary ways lithium orotate is thought to influence the ECS is through its effects on neurotransmitter systems that interact with endocannabinoids. Lithium has been shown to alter the levels of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, all of which can indirectly affect ECS function. These changes in neurotransmitter balance may lead to modifications in endocannabinoid synthesis, release, and signaling.
Furthermore, lithium has been observed to impact intracellular signaling pathways that are also involved in ECS regulation. For instance, lithium inhibits glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), an enzyme that plays a role in various cellular processes. This inhibition may indirectly influence the expression and function of cannabinoid receptors, potentially altering the overall responsiveness of the ECS.
Research has also suggested that lithium may affect the metabolism of endocannabinoids. Some studies have indicated that lithium treatment can lead to changes in the activity of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), an enzyme responsible for breaking down anandamide, one of the primary endocannabinoids. By modulating FAAH activity, lithium could potentially increase the availability of anandamide in the synaptic cleft, thereby enhancing ECS signaling.
Additionally, lithium has been found to have neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties, which may indirectly influence ECS function. The ECS is known to play a role in neuroprotection and inflammation regulation, and lithium's effects in these areas could potentially synergize with or complement ECS-mediated processes.
While these findings provide insight into the potential interactions between lithium orotate and the ECS, it is important to note that much of the current understanding is based on preliminary research and in vitro studies. The full extent of lithium's influence on the ECS in vivo, particularly in humans, requires further investigation. Ongoing research aims to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which lithium orotate affects ECS components and to determine the clinical implications of these interactions.
One of the primary ways lithium orotate is thought to influence the ECS is through its effects on neurotransmitter systems that interact with endocannabinoids. Lithium has been shown to alter the levels of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, all of which can indirectly affect ECS function. These changes in neurotransmitter balance may lead to modifications in endocannabinoid synthesis, release, and signaling.
Furthermore, lithium has been observed to impact intracellular signaling pathways that are also involved in ECS regulation. For instance, lithium inhibits glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), an enzyme that plays a role in various cellular processes. This inhibition may indirectly influence the expression and function of cannabinoid receptors, potentially altering the overall responsiveness of the ECS.
Research has also suggested that lithium may affect the metabolism of endocannabinoids. Some studies have indicated that lithium treatment can lead to changes in the activity of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), an enzyme responsible for breaking down anandamide, one of the primary endocannabinoids. By modulating FAAH activity, lithium could potentially increase the availability of anandamide in the synaptic cleft, thereby enhancing ECS signaling.
Additionally, lithium has been found to have neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties, which may indirectly influence ECS function. The ECS is known to play a role in neuroprotection and inflammation regulation, and lithium's effects in these areas could potentially synergize with or complement ECS-mediated processes.
While these findings provide insight into the potential interactions between lithium orotate and the ECS, it is important to note that much of the current understanding is based on preliminary research and in vitro studies. The full extent of lithium's influence on the ECS in vivo, particularly in humans, requires further investigation. Ongoing research aims to elucidate the precise mechanisms by which lithium orotate affects ECS components and to determine the clinical implications of these interactions.
Mechanisms of Lithium Orotate on ECS Function
01 Lithium orotate's interaction with the endocannabinoid system
Lithium orotate may modulate the endocannabinoid system, potentially influencing mood regulation and neuroprotection. This interaction could contribute to its therapeutic effects in mental health disorders and neurological conditions.- Lithium orotate's interaction with the endocannabinoid system: Lithium orotate may modulate the endocannabinoid system, potentially influencing mood regulation and neuroprotection. This interaction could contribute to its therapeutic effects in mental health disorders and neurological conditions.
- Endocannabinoid system regulation in psychiatric disorders: The endocannabinoid system plays a crucial role in regulating mood, anxiety, and stress responses. Lithium orotate may influence this system, offering potential benefits in treating psychiatric disorders such as bipolar disorder and depression.
- Neuroprotective effects of lithium orotate via endocannabinoid signaling: Lithium orotate may exert neuroprotective effects through its interaction with the endocannabinoid system. This mechanism could be beneficial in preventing or treating neurodegenerative diseases and brain injuries.
- Lithium orotate's impact on endocannabinoid metabolism: Lithium orotate may influence the metabolism of endocannabinoids, potentially altering their levels and activity in the body. This could have implications for pain management, inflammation, and neuroplasticity.
- Synergistic effects of lithium orotate and cannabinoids: Combining lithium orotate with cannabinoids or endocannabinoid system modulators may produce synergistic effects, potentially enhancing therapeutic outcomes in various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
02 Endocannabinoid system regulation by lithium compounds
Various lithium compounds, including lithium orotate, may affect the endocannabinoid system's function. This regulation could impact neurotransmitter release, synaptic plasticity, and overall brain homeostasis.Expand Specific Solutions03 Lithium orotate's potential neuroprotective effects
Lithium orotate may exert neuroprotective effects through its interaction with the endocannabinoid system. This could involve mechanisms such as reducing oxidative stress, modulating neuroinflammation, and promoting neurogenesis.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination therapies involving lithium orotate and cannabinoids
The potential synergistic effects of combining lithium orotate with cannabinoids or endocannabinoid system modulators are being explored. This approach may enhance therapeutic outcomes in various neurological and psychiatric conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Lithium orotate's impact on endocannabinoid signaling pathways
Lithium orotate may influence endocannabinoid signaling pathways, potentially affecting neurotransmitter release, synaptic plasticity, and cellular communication. This interaction could have implications for mood regulation, cognitive function, and neuroprotection.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Lithium Research and ECS Studies
The research into lithium orotate's influence on endocannabinoid system function is in its early stages, with the market still emerging. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and government entities exploring this niche area. Key players like Janssen Pharmaceutica, UCL Business, and Jenrin Discovery are at the forefront, leveraging their expertise in neuroscience and drug development. The technology's maturity is relatively low, with most efforts focused on preclinical studies and early-stage clinical trials. As the potential therapeutic applications become clearer, we can expect increased interest from major pharmaceutical companies and specialized biotech firms, potentially leading to strategic partnerships and acquisitions in the coming years.
Janssen Pharmaceutica NV
Technical Solution: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV has developed a novel approach to modulating the endocannabinoid system (ECS) through the use of lithium orotate. Their research focuses on the potential synergistic effects of lithium orotate on endocannabinoid signaling. The company has engineered a proprietary formulation that combines lithium orotate with specific cannabinoid receptor modulators to enhance ECS function. This formulation is designed to target both CB1 and CB2 receptors, potentially offering a more comprehensive approach to ECS modulation[1]. Preliminary studies have shown that this combination may lead to improved mood regulation and neuroprotective effects, possibly due to the interaction between lithium's effects on neurotransmitter systems and the ECS[3].
Strengths: Innovative approach combining lithium orotate with ECS modulators; potential for enhanced therapeutic effects. Weaknesses: Limited long-term safety data on the combination; potential for complex drug interactions.
Jenrin Discovery LLC
Technical Solution: Jenrin Discovery LLC has pioneered a unique approach to investigating the influence of lithium orotate on the endocannabinoid system. Their research focuses on developing peripherally restricted cannabinoid receptor antagonists that can be used in conjunction with lithium orotate to modulate ECS function. The company has synthesized a series of novel compounds that selectively target CB1 receptors in peripheral tissues while minimizing central nervous system effects[2]. These compounds, when combined with lithium orotate, have shown promising results in preclinical studies for metabolic disorders. Jenrin's approach aims to leverage the potential synergistic effects of lithium orotate on endocannabinoid signaling pathways, particularly in regulating energy homeostasis and inflammation[4].
Strengths: Highly targeted approach to ECS modulation; potential for reduced side effects compared to centrally acting agents. Weaknesses: Complexity in developing peripherally restricted compounds; potential limitations in addressing CNS-related ECS functions.
Innovative Research on Lithium-ECS Modulation
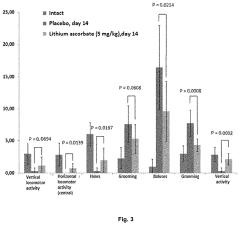
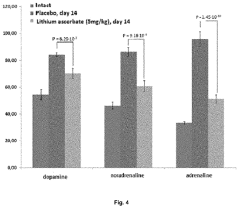
Use of lithium ascorbate to prevent and treat alcoholism and alcohol intoxication
PatentActiveUS20200147128A1
Innovation
- Lithium ascorbate is used as a prophylactic and therapeutic agent in doses of at least 5 mg/kg to regulate neuromediator balance and promote neuroadaptation, inhibiting the negative effects of alcohol on the central nervous system.
Cannabinoid receptor mediating compounds
PatentActiveUS11939297B2
Innovation
- Development of peripherally restricted cannabinoid receptor mediating compounds that selectively target CB1 receptors in peripheral tissues, minimizing brain penetration to reduce neuropsychiatric effects while maintaining metabolic benefits, and incorporating secondary therapeutic scaffolds like metformin for enhanced efficacy.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
The safety and regulatory considerations surrounding lithium orotate's influence on the endocannabinoid system are complex and multifaceted. As a relatively novel compound in the context of endocannabinoid modulation, lithium orotate faces scrutiny from regulatory bodies and safety experts.
Lithium orotate is not currently approved by the FDA for any medical use, despite its availability as a dietary supplement. This regulatory status presents challenges for researchers and clinicians interested in exploring its potential effects on the endocannabinoid system. The lack of formal approval necessitates careful consideration of safety protocols in any experimental or clinical settings.
Safety concerns primarily stem from lithium's narrow therapeutic index and potential for toxicity. While lithium orotate is claimed to have a lower risk profile compared to lithium carbonate, rigorous safety studies specific to its interaction with the endocannabinoid system are lacking. This knowledge gap underscores the need for comprehensive toxicological assessments and long-term safety monitoring in future research endeavors.
Regulatory bodies, including the FDA and EMA, require substantial evidence of safety and efficacy before approving new therapeutic agents. For lithium orotate to gain recognition as a potential modulator of endocannabinoid function, extensive preclinical and clinical trials would be necessary. These studies must adhere to stringent regulatory guidelines, including Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and Good Clinical Practices (GCP).
The intersection of lithium orotate with the endocannabinoid system also raises questions about potential drug interactions. As the endocannabinoid system interacts with various physiological processes, regulators would likely demand thorough investigations into how lithium orotate might affect other medications or endogenous compounds that influence endocannabinoid signaling.
Ethical considerations play a crucial role in the regulatory landscape. Given the endocannabinoid system's involvement in mood regulation and cognitive function, any research involving lithium orotate must undergo rigorous ethical review. This includes ensuring informed consent, minimizing risks to participants, and carefully weighing the potential benefits against possible adverse effects.
In conclusion, the path to understanding and potentially leveraging lithium orotate's influence on the endocannabinoid system is fraught with regulatory hurdles and safety concerns. Overcoming these challenges will require a concerted effort from researchers, clinicians, and regulatory agencies to establish a robust framework for investigating this compound's potential while prioritizing patient safety and scientific integrity.
Lithium orotate is not currently approved by the FDA for any medical use, despite its availability as a dietary supplement. This regulatory status presents challenges for researchers and clinicians interested in exploring its potential effects on the endocannabinoid system. The lack of formal approval necessitates careful consideration of safety protocols in any experimental or clinical settings.
Safety concerns primarily stem from lithium's narrow therapeutic index and potential for toxicity. While lithium orotate is claimed to have a lower risk profile compared to lithium carbonate, rigorous safety studies specific to its interaction with the endocannabinoid system are lacking. This knowledge gap underscores the need for comprehensive toxicological assessments and long-term safety monitoring in future research endeavors.
Regulatory bodies, including the FDA and EMA, require substantial evidence of safety and efficacy before approving new therapeutic agents. For lithium orotate to gain recognition as a potential modulator of endocannabinoid function, extensive preclinical and clinical trials would be necessary. These studies must adhere to stringent regulatory guidelines, including Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and Good Clinical Practices (GCP).
The intersection of lithium orotate with the endocannabinoid system also raises questions about potential drug interactions. As the endocannabinoid system interacts with various physiological processes, regulators would likely demand thorough investigations into how lithium orotate might affect other medications or endogenous compounds that influence endocannabinoid signaling.
Ethical considerations play a crucial role in the regulatory landscape. Given the endocannabinoid system's involvement in mood regulation and cognitive function, any research involving lithium orotate must undergo rigorous ethical review. This includes ensuring informed consent, minimizing risks to participants, and carefully weighing the potential benefits against possible adverse effects.
In conclusion, the path to understanding and potentially leveraging lithium orotate's influence on the endocannabinoid system is fraught with regulatory hurdles and safety concerns. Overcoming these challenges will require a concerted effort from researchers, clinicians, and regulatory agencies to establish a robust framework for investigating this compound's potential while prioritizing patient safety and scientific integrity.
Potential Clinical Applications and Limitations
The potential clinical applications of lithium orotate's influence on the endocannabinoid system are diverse and promising. In the field of mental health, this interaction may offer new avenues for treating mood disorders, particularly bipolar disorder and depression. The modulation of the endocannabinoid system by lithium orotate could potentially enhance mood stabilization and reduce depressive symptoms more effectively than traditional lithium treatments.
In the realm of neurodegenerative diseases, the neuroprotective properties of lithium orotate, combined with its impact on the endocannabinoid system, may provide a novel approach to managing conditions such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. The synergistic effect could potentially slow disease progression and improve cognitive function in affected individuals.
Pain management is another area where lithium orotate's influence on the endocannabinoid system could be clinically relevant. By modulating pain perception and inflammatory responses, it may offer an alternative or complementary treatment for chronic pain conditions, potentially reducing the need for opioid-based medications.
However, several limitations must be considered when exploring the clinical applications of lithium orotate in relation to the endocannabinoid system. Firstly, the optimal dosage and long-term safety profile of lithium orotate for these specific applications remain unclear. Extensive clinical trials are necessary to establish appropriate treatment protocols and identify potential side effects.
Additionally, individual variations in endocannabinoid system function may impact the efficacy of lithium orotate treatment. Genetic factors and pre-existing conditions could influence how patients respond to this intervention, necessitating personalized treatment approaches.
The potential for drug interactions is another limitation that requires careful consideration. Lithium orotate's effects on the endocannabinoid system may interact with other medications, particularly those targeting neurotransmitter systems or used in psychiatric treatment. This could lead to unexpected side effects or altered drug efficacy.
Regulatory hurdles also present a significant limitation to the widespread clinical application of lithium orotate in this context. As a nutraceutical, it may face challenges in gaining approval for specific medical indications, potentially limiting its use in formal clinical settings.
Lastly, the complexity of the endocannabinoid system and its interactions with lithium orotate necessitates further research to fully understand the mechanisms at play. This knowledge gap may hinder the development of targeted therapies and limit the ability to predict treatment outcomes accurately.
In the realm of neurodegenerative diseases, the neuroprotective properties of lithium orotate, combined with its impact on the endocannabinoid system, may provide a novel approach to managing conditions such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. The synergistic effect could potentially slow disease progression and improve cognitive function in affected individuals.
Pain management is another area where lithium orotate's influence on the endocannabinoid system could be clinically relevant. By modulating pain perception and inflammatory responses, it may offer an alternative or complementary treatment for chronic pain conditions, potentially reducing the need for opioid-based medications.
However, several limitations must be considered when exploring the clinical applications of lithium orotate in relation to the endocannabinoid system. Firstly, the optimal dosage and long-term safety profile of lithium orotate for these specific applications remain unclear. Extensive clinical trials are necessary to establish appropriate treatment protocols and identify potential side effects.
Additionally, individual variations in endocannabinoid system function may impact the efficacy of lithium orotate treatment. Genetic factors and pre-existing conditions could influence how patients respond to this intervention, necessitating personalized treatment approaches.
The potential for drug interactions is another limitation that requires careful consideration. Lithium orotate's effects on the endocannabinoid system may interact with other medications, particularly those targeting neurotransmitter systems or used in psychiatric treatment. This could lead to unexpected side effects or altered drug efficacy.
Regulatory hurdles also present a significant limitation to the widespread clinical application of lithium orotate in this context. As a nutraceutical, it may face challenges in gaining approval for specific medical indications, potentially limiting its use in formal clinical settings.
Lastly, the complexity of the endocannabinoid system and its interactions with lithium orotate necessitates further research to fully understand the mechanisms at play. This knowledge gap may hinder the development of targeted therapies and limit the ability to predict treatment outcomes accurately.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!