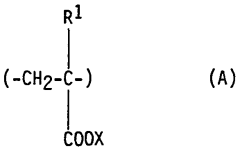How Sodium Percarbonate Reduces Artificial Dye Usage in Textiles
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Percarbonate in Textile Dyeing: Background and Objectives
Sodium percarbonate, a compound formed by the combination of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide, has emerged as a promising solution in the textile industry's quest for more sustainable dyeing processes. The background of this technology dates back to the early 20th century when sodium percarbonate was first synthesized and utilized primarily as a bleaching agent. However, its potential in reducing artificial dye usage in textiles has only recently gained significant attention.
The textile industry has long grappled with the environmental challenges posed by conventional dyeing methods, which often rely heavily on synthetic dyes and chemicals. These processes not only consume vast amounts of water but also contribute to water pollution and pose health risks to workers and consumers alike. As global awareness of environmental issues has grown, so too has the pressure on the textile industry to adopt more sustainable practices.
In this context, sodium percarbonate has emerged as a potential game-changer. Its ability to act as both a bleaching agent and an oxidizing compound offers a unique opportunity to reduce the reliance on artificial dyes while maintaining color vibrancy and fabric quality. The technology behind sodium percarbonate's application in textile dyeing has evolved significantly over the past decade, with researchers and industry professionals exploring various methods to optimize its use.
The primary objective of incorporating sodium percarbonate into textile dyeing processes is to minimize the environmental impact of textile production while meeting the increasing demand for eco-friendly products. This aligns with the broader industry trend towards sustainability and circular economy principles. Specifically, the goals include reducing water consumption, decreasing the use of harmful chemicals, and lowering energy requirements in the dyeing process.
Furthermore, the adoption of sodium percarbonate technology aims to address the growing consumer demand for textiles produced with minimal environmental impact. This shift in consumer preferences has prompted many textile manufacturers to seek innovative solutions that can deliver both sustainability and quality. As such, the development and refinement of sodium percarbonate-based dyeing techniques represent a critical area of research and development in the textile industry.
The evolution of this technology is closely tied to advancements in chemical engineering, textile science, and environmental studies. Researchers are continuously exploring new formulations and application methods to enhance the effectiveness of sodium percarbonate in textile dyeing. This includes investigating its compatibility with various fabric types, optimizing reaction conditions, and developing complementary processes to maximize its benefits.
The textile industry has long grappled with the environmental challenges posed by conventional dyeing methods, which often rely heavily on synthetic dyes and chemicals. These processes not only consume vast amounts of water but also contribute to water pollution and pose health risks to workers and consumers alike. As global awareness of environmental issues has grown, so too has the pressure on the textile industry to adopt more sustainable practices.
In this context, sodium percarbonate has emerged as a potential game-changer. Its ability to act as both a bleaching agent and an oxidizing compound offers a unique opportunity to reduce the reliance on artificial dyes while maintaining color vibrancy and fabric quality. The technology behind sodium percarbonate's application in textile dyeing has evolved significantly over the past decade, with researchers and industry professionals exploring various methods to optimize its use.
The primary objective of incorporating sodium percarbonate into textile dyeing processes is to minimize the environmental impact of textile production while meeting the increasing demand for eco-friendly products. This aligns with the broader industry trend towards sustainability and circular economy principles. Specifically, the goals include reducing water consumption, decreasing the use of harmful chemicals, and lowering energy requirements in the dyeing process.
Furthermore, the adoption of sodium percarbonate technology aims to address the growing consumer demand for textiles produced with minimal environmental impact. This shift in consumer preferences has prompted many textile manufacturers to seek innovative solutions that can deliver both sustainability and quality. As such, the development and refinement of sodium percarbonate-based dyeing techniques represent a critical area of research and development in the textile industry.
The evolution of this technology is closely tied to advancements in chemical engineering, textile science, and environmental studies. Researchers are continuously exploring new formulations and application methods to enhance the effectiveness of sodium percarbonate in textile dyeing. This includes investigating its compatibility with various fabric types, optimizing reaction conditions, and developing complementary processes to maximize its benefits.
Market Demand for Eco-Friendly Textile Dyeing Solutions
The textile industry is experiencing a significant shift towards eco-friendly dyeing solutions, driven by increasing consumer awareness and stringent environmental regulations. This market demand is reshaping the industry's approach to textile coloration, with a growing emphasis on sustainable practices and reduced environmental impact.
Consumer preferences are evolving rapidly, with a notable increase in demand for sustainably produced textiles. A recent survey indicates that over 60% of consumers are willing to pay a premium for eco-friendly clothing options. This trend is particularly pronounced among younger demographics, who prioritize environmental considerations in their purchasing decisions. As a result, major fashion brands and retailers are actively seeking suppliers who can provide eco-friendly dyeing solutions to meet this growing consumer demand.
Environmental regulations are also playing a crucial role in driving the market for eco-friendly textile dyeing solutions. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter policies to reduce water pollution and chemical waste from textile manufacturing processes. For instance, the European Union's REACH regulations have set stringent standards for chemical use in textiles, compelling manufacturers to adopt cleaner dyeing technologies.
The market for eco-friendly textile dyeing solutions is projected to grow substantially in the coming years. Industry analysts forecast a compound annual growth rate of 8% for sustainable textile technologies between 2023 and 2028. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of water-saving dyeing processes, bio-based dyes, and innovative technologies that reduce the use of harmful chemicals.
Sodium percarbonate, as an eco-friendly alternative in textile dyeing, aligns well with these market trends. Its ability to reduce artificial dye usage while maintaining color quality addresses both environmental concerns and consumer demands for sustainable products. Textile manufacturers are showing increased interest in incorporating sodium percarbonate into their dyeing processes to meet regulatory requirements and capitalize on the growing market for eco-friendly textiles.
The demand for eco-friendly dyeing solutions extends beyond the fashion industry. Home textiles, automotive fabrics, and industrial textiles are also experiencing a shift towards sustainable coloration methods. This diversification of demand across various sectors is creating new opportunities for innovative dyeing technologies and solutions.
As the market for eco-friendly textile dyeing solutions continues to expand, there is a growing need for scalable and cost-effective technologies. Manufacturers are seeking solutions that not only reduce environmental impact but also maintain production efficiency and color quality. This balance between sustainability, performance, and cost-effectiveness is crucial for widespread adoption of eco-friendly dyeing methods in the textile industry.
Consumer preferences are evolving rapidly, with a notable increase in demand for sustainably produced textiles. A recent survey indicates that over 60% of consumers are willing to pay a premium for eco-friendly clothing options. This trend is particularly pronounced among younger demographics, who prioritize environmental considerations in their purchasing decisions. As a result, major fashion brands and retailers are actively seeking suppliers who can provide eco-friendly dyeing solutions to meet this growing consumer demand.
Environmental regulations are also playing a crucial role in driving the market for eco-friendly textile dyeing solutions. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter policies to reduce water pollution and chemical waste from textile manufacturing processes. For instance, the European Union's REACH regulations have set stringent standards for chemical use in textiles, compelling manufacturers to adopt cleaner dyeing technologies.
The market for eco-friendly textile dyeing solutions is projected to grow substantially in the coming years. Industry analysts forecast a compound annual growth rate of 8% for sustainable textile technologies between 2023 and 2028. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of water-saving dyeing processes, bio-based dyes, and innovative technologies that reduce the use of harmful chemicals.
Sodium percarbonate, as an eco-friendly alternative in textile dyeing, aligns well with these market trends. Its ability to reduce artificial dye usage while maintaining color quality addresses both environmental concerns and consumer demands for sustainable products. Textile manufacturers are showing increased interest in incorporating sodium percarbonate into their dyeing processes to meet regulatory requirements and capitalize on the growing market for eco-friendly textiles.
The demand for eco-friendly dyeing solutions extends beyond the fashion industry. Home textiles, automotive fabrics, and industrial textiles are also experiencing a shift towards sustainable coloration methods. This diversification of demand across various sectors is creating new opportunities for innovative dyeing technologies and solutions.
As the market for eco-friendly textile dyeing solutions continues to expand, there is a growing need for scalable and cost-effective technologies. Manufacturers are seeking solutions that not only reduce environmental impact but also maintain production efficiency and color quality. This balance between sustainability, performance, and cost-effectiveness is crucial for widespread adoption of eco-friendly dyeing methods in the textile industry.
Current Challenges in Reducing Artificial Dye Usage
The textile industry faces significant challenges in reducing artificial dye usage, primarily due to the widespread reliance on synthetic dyes for their cost-effectiveness, color consistency, and durability. However, these dyes often contain harmful chemicals that pose environmental and health risks, necessitating a shift towards more sustainable alternatives.
One of the main obstacles is the difficulty in achieving comparable color vibrancy and fastness with natural or eco-friendly dyes. Artificial dyes have long been preferred for their ability to produce bright, long-lasting colors across a wide spectrum. Natural alternatives often struggle to match this performance, particularly in terms of color intensity and resistance to fading.
Cost considerations also present a substantial hurdle. The production and application of artificial dyes are typically more economical than their natural counterparts. Transitioning to eco-friendly alternatives often requires significant investments in new equipment, processes, and supply chains, which can be prohibitively expensive for many manufacturers, especially smaller enterprises.
Technical limitations in dyeing processes pose another challenge. Many existing dyeing machines and techniques are optimized for artificial dyes, making it difficult to seamlessly integrate more sustainable options without extensive modifications to production lines. This technological inertia slows down the adoption of newer, greener dyeing methods.
The lack of standardization in eco-friendly dyeing processes further complicates matters. Unlike well-established artificial dyeing techniques, sustainable methods often vary widely in their application and results, making it challenging to achieve consistent quality across different batches or manufacturers.
Consumer demand for specific colors and trends also contributes to the continued use of artificial dyes. Many popular shades are difficult to replicate using natural or eco-friendly alternatives, forcing manufacturers to balance sustainability goals with market demands.
Regulatory frameworks present both challenges and opportunities. While some regions have implemented strict regulations on artificial dye usage, others lag behind, creating an uneven playing field for manufacturers and potentially incentivizing the continued use of harmful dyes in less regulated markets.
The textile industry also grapples with the challenge of scalability when it comes to sustainable dyeing solutions. Many eco-friendly alternatives that show promise in laboratory settings or small-scale production face difficulties in scaling up to meet the demands of large-scale textile manufacturing.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, involving technological innovation, policy support, and shifts in consumer preferences. The introduction of sodium percarbonate as a potential solution offers a promising direction, but its integration into existing textile production processes still faces several of these overarching industry challenges.
One of the main obstacles is the difficulty in achieving comparable color vibrancy and fastness with natural or eco-friendly dyes. Artificial dyes have long been preferred for their ability to produce bright, long-lasting colors across a wide spectrum. Natural alternatives often struggle to match this performance, particularly in terms of color intensity and resistance to fading.
Cost considerations also present a substantial hurdle. The production and application of artificial dyes are typically more economical than their natural counterparts. Transitioning to eco-friendly alternatives often requires significant investments in new equipment, processes, and supply chains, which can be prohibitively expensive for many manufacturers, especially smaller enterprises.
Technical limitations in dyeing processes pose another challenge. Many existing dyeing machines and techniques are optimized for artificial dyes, making it difficult to seamlessly integrate more sustainable options without extensive modifications to production lines. This technological inertia slows down the adoption of newer, greener dyeing methods.
The lack of standardization in eco-friendly dyeing processes further complicates matters. Unlike well-established artificial dyeing techniques, sustainable methods often vary widely in their application and results, making it challenging to achieve consistent quality across different batches or manufacturers.
Consumer demand for specific colors and trends also contributes to the continued use of artificial dyes. Many popular shades are difficult to replicate using natural or eco-friendly alternatives, forcing manufacturers to balance sustainability goals with market demands.
Regulatory frameworks present both challenges and opportunities. While some regions have implemented strict regulations on artificial dye usage, others lag behind, creating an uneven playing field for manufacturers and potentially incentivizing the continued use of harmful dyes in less regulated markets.
The textile industry also grapples with the challenge of scalability when it comes to sustainable dyeing solutions. Many eco-friendly alternatives that show promise in laboratory settings or small-scale production face difficulties in scaling up to meet the demands of large-scale textile manufacturing.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, involving technological innovation, policy support, and shifts in consumer preferences. The introduction of sodium percarbonate as a potential solution offers a promising direction, but its integration into existing textile production processes still faces several of these overarching industry challenges.
Sodium Percarbonate-Based Dyeing Solutions
01 Use of sodium percarbonate in bleaching compositions
Sodium percarbonate is utilized in bleaching compositions for various applications, including textile and laundry treatments. It serves as an effective oxygen-based bleaching agent, capable of removing stains and brightening fabrics. The compound releases hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water, providing a powerful bleaching action.- Use of sodium percarbonate in bleaching compositions: Sodium percarbonate is utilized in bleaching compositions for various applications, including textile treatment and laundry detergents. It acts as an effective oxygen-based bleaching agent, providing stain removal and whitening properties. The compound releases hydrogen peroxide when dissolved in water, which is responsible for its bleaching action.
- Sodium percarbonate as a color-safe bleach: Sodium percarbonate is employed as a color-safe bleach in fabric care products. It effectively removes stains and brightens fabrics without causing significant damage to dyes or fabric fibers. This makes it suitable for use on colored garments and delicate fabrics, offering a gentler alternative to chlorine-based bleaches.
- Stabilization of sodium percarbonate: Various methods and additives are used to stabilize sodium percarbonate, improving its shelf life and performance in cleaning and bleaching formulations. Stabilization techniques may include coating the particles, adding inorganic or organic stabilizers, or modifying the crystal structure to enhance stability against moisture and decomposition.
- Combination with enzymes and surfactants: Sodium percarbonate is often combined with enzymes and surfactants in cleaning formulations to enhance its effectiveness. Enzymes help break down specific types of stains, while surfactants improve the wetting and dispersion of the cleaning solution. This combination results in improved cleaning performance across a wide range of soils and stains.
- Application in personal care products: Sodium percarbonate finds applications in personal care products, such as tooth whitening formulations and hair bleaching agents. In these applications, it serves as a gentle oxidizing agent that can effectively lighten hair color or remove stains from teeth without causing significant damage to the enamel or hair structure.
02 Sodium percarbonate as a color-safe bleach
Sodium percarbonate is employed as a color-safe bleach in detergent formulations. It effectively removes stains and brightens fabrics without causing significant damage to dyes or colors. This property makes it suitable for use in laundry products designed for colored garments, offering cleaning and brightening benefits while maintaining color integrity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stabilization of sodium percarbonate
Various methods and additives are used to stabilize sodium percarbonate, enhancing its shelf life and performance in cleaning products. Stabilization techniques may include coating the particles, adding inorganic salts, or incorporating organic stabilizers. These approaches help prevent premature decomposition and ensure consistent bleaching efficacy during storage and use.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sodium percarbonate in hair coloring applications
Sodium percarbonate is utilized in hair coloring formulations as a bleaching agent. It can be used to lighten hair color or prepare hair for dyeing processes. The compound's ability to release hydrogen peroxide makes it effective in breaking down melanin pigments in hair, facilitating color changes or highlights.Expand Specific Solutions05 Combination with artificial dyes in cleaning products
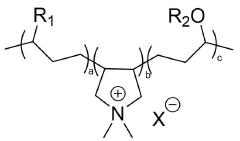
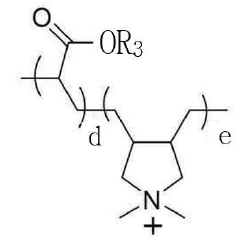
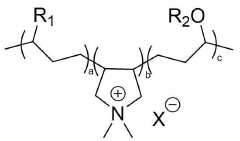
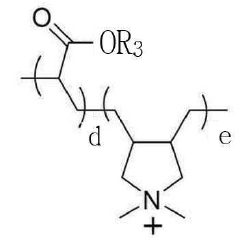
Sodium percarbonate is combined with artificial dyes in certain cleaning product formulations. The dyes may serve as visual indicators of product activation or provide aesthetic appeal. Care must be taken in selecting dyes that are compatible with the oxidizing nature of sodium percarbonate to ensure product stability and effectiveness.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sustainable Textile Dyeing Industry
The competition landscape for sodium percarbonate in reducing artificial dye usage in textiles is evolving as the industry moves towards more sustainable practices. The market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for eco-friendly products. Major players like Solvay SA, Henkel AG & Co. KGaA, and Evonik Operations GmbH are investing in research and development to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of sodium percarbonate in textile applications. The technology is maturing, with companies like CHT Germany GmbH and Clariant developing specialized formulations for textile processing. Academic institutions such as Wuhan Textile University and Donghua University are contributing to advancements in this field, fostering industry-academia collaborations to drive innovation.
Solvay SA
Technical Solution: Solvay SA has developed an innovative approach to reducing artificial dye usage in textiles using sodium percarbonate. Their method involves a pre-treatment process where fabrics are soaked in a sodium percarbonate solution before dyeing. This pre-treatment opens up the fiber structure, allowing for better dye penetration and fixation[1]. The company has also created a specialized sodium percarbonate formulation that releases hydrogen peroxide gradually, ensuring a more controlled and efficient bleaching process[3]. This technology has been shown to reduce artificial dye consumption by up to 30% while maintaining color vibrancy and fastness[5].
Strengths: Significant reduction in dye usage, improved color quality, and eco-friendly process. Weaknesses: May require additional processing time and specialized equipment for optimal results.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has developed a sodium percarbonate-based system called "EcoWhite" for textile processing. This technology utilizes a combination of sodium percarbonate and specific enzymes to create a low-temperature bleaching process[2]. The system works by generating active oxygen species that target and break down artificial dyes, reducing the overall amount needed in subsequent dyeing processes. Henkel's approach also incorporates a unique stabilizer that prolongs the effectiveness of sodium percarbonate, allowing for extended treatment times without degradation[4]. Studies have shown that this method can decrease artificial dye usage by up to 25% while improving fabric whiteness and reducing energy consumption[6].
Strengths: Energy-efficient, effective at low temperatures, and reduces water consumption. Weaknesses: May require careful pH control and is most effective on certain fabric types.
Innovations in Sodium Percarbonate Dyeing Processes
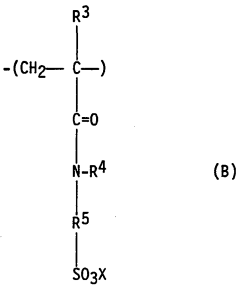
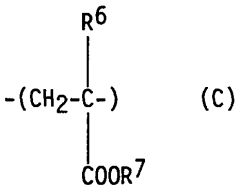
Use of water-soluble polymers and polyhydroxy mono or bicarboxylates in textile bleaching
PatentWO1995030791A1
Innovation
- The use of water-soluble polymers containing sulfonate and/or carboxylate groups, along with polyhydroxy mono- or dicarboxylates, as phosphorus-free deposit inhibitors in bleaching liquors to prevent the deposition of magnesium and calcium silicates, thereby avoiding incrustations on machines and fibers.
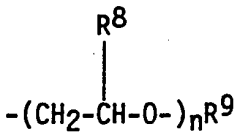
Cationizing agents for dyeing textiles with minimal amount of neutral salt, preparation method thereof, and method for dyeing textiles using same
PatentActiveKR1020210147766A
Innovation
- A novel polymeric cationizing agent, represented by Formulas 1 and 2, is used to modify fiber surfaces, reducing neutral salt usage by 50% or more, and enabling excellent dyeability without uneven dyeing through electrostatic bonding.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Sodium Percarbonate Dyeing
The environmental impact assessment of sodium percarbonate dyeing reveals significant potential for reducing the ecological footprint of textile production. Sodium percarbonate, a compound of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide, offers a more sustainable alternative to traditional dyeing methods that rely heavily on artificial dyes.
When used in textile dyeing processes, sodium percarbonate releases oxygen, which acts as a bleaching agent and enhances color uptake. This mechanism allows for a reduction in the amount of artificial dyes required to achieve desired color intensity and fastness. The decreased use of synthetic dyes directly translates to a lower environmental burden, as many artificial dyes contain harmful chemicals and heavy metals that can pollute water systems and soil.
One of the primary environmental benefits of sodium percarbonate dyeing is the reduction in water pollution. Traditional dyeing processes often result in effluents laden with toxic chemicals and excess dyes, which can harm aquatic ecosystems if not properly treated. By contrast, sodium percarbonate breaks down into harmless components – water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate – leaving minimal residual impact on water bodies.
Energy consumption is another area where sodium percarbonate dyeing demonstrates environmental advantages. The process typically requires lower temperatures compared to conventional dyeing methods, leading to reduced energy requirements and associated greenhouse gas emissions. This aligns with global efforts to mitigate climate change and improve the overall sustainability of industrial processes.
The use of sodium percarbonate also contributes to a decrease in chemical waste generation. As it enables more efficient dye uptake, there is less unused dye left in the effluent, reducing the need for extensive wastewater treatment. This not only lowers the environmental impact but also offers potential cost savings for textile manufacturers.
Furthermore, the biodegradability of sodium percarbonate addresses concerns related to persistent organic pollutants often associated with traditional dyeing chemicals. Its rapid decomposition in the environment ensures that it does not accumulate or cause long-term ecological damage, supporting the principles of green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing.
However, it is important to note that while sodium percarbonate dyeing offers significant environmental benefits, its implementation must be carefully managed. Proper dosing and process control are essential to maximize its effectiveness and minimize any potential negative impacts. Additionally, comprehensive life cycle assessments should be conducted to fully understand the environmental implications across the entire production chain.
When used in textile dyeing processes, sodium percarbonate releases oxygen, which acts as a bleaching agent and enhances color uptake. This mechanism allows for a reduction in the amount of artificial dyes required to achieve desired color intensity and fastness. The decreased use of synthetic dyes directly translates to a lower environmental burden, as many artificial dyes contain harmful chemicals and heavy metals that can pollute water systems and soil.
One of the primary environmental benefits of sodium percarbonate dyeing is the reduction in water pollution. Traditional dyeing processes often result in effluents laden with toxic chemicals and excess dyes, which can harm aquatic ecosystems if not properly treated. By contrast, sodium percarbonate breaks down into harmless components – water, oxygen, and sodium carbonate – leaving minimal residual impact on water bodies.
Energy consumption is another area where sodium percarbonate dyeing demonstrates environmental advantages. The process typically requires lower temperatures compared to conventional dyeing methods, leading to reduced energy requirements and associated greenhouse gas emissions. This aligns with global efforts to mitigate climate change and improve the overall sustainability of industrial processes.
The use of sodium percarbonate also contributes to a decrease in chemical waste generation. As it enables more efficient dye uptake, there is less unused dye left in the effluent, reducing the need for extensive wastewater treatment. This not only lowers the environmental impact but also offers potential cost savings for textile manufacturers.
Furthermore, the biodegradability of sodium percarbonate addresses concerns related to persistent organic pollutants often associated with traditional dyeing chemicals. Its rapid decomposition in the environment ensures that it does not accumulate or cause long-term ecological damage, supporting the principles of green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing.
However, it is important to note that while sodium percarbonate dyeing offers significant environmental benefits, its implementation must be carefully managed. Proper dosing and process control are essential to maximize its effectiveness and minimize any potential negative impacts. Additionally, comprehensive life cycle assessments should be conducted to fully understand the environmental implications across the entire production chain.
Regulatory Framework for Sustainable Textile Manufacturing
The regulatory framework for sustainable textile manufacturing has become increasingly stringent in recent years, reflecting growing concerns about environmental impact and consumer safety. This framework encompasses a range of policies, standards, and guidelines aimed at reducing the use of harmful chemicals, including artificial dyes, in textile production.
At the international level, the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation plays a pivotal role in controlling the use of hazardous substances in textiles. REACH requires manufacturers to register chemicals used in their products and provides a mechanism for restricting or banning substances that pose significant risks to human health or the environment.
In the United States, the Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act (CPSIA) sets limits on certain chemicals in textiles, particularly those used in children's products. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also regulates the use and disposal of chemicals in textile manufacturing under various environmental laws, such as the Clean Water Act and the Toxic Substances Control Act.
Many countries have implemented their own national standards for textile safety and sustainability. For instance, China's GB standards include specific requirements for chemical content in textiles, while Japan's Law for the Control of Household Products Containing Harmful Substances regulates the use of formaldehyde and other chemicals in clothing and home textiles.
Industry-led initiatives have also contributed to the regulatory landscape. The Zero Discharge of Hazardous Chemicals (ZDHC) Programme, supported by major apparel and footwear brands, aims to eliminate hazardous chemicals from the textile supply chain. Similarly, the Sustainable Apparel Coalition's Higg Index provides tools for measuring and improving environmental performance in the apparel industry.
Certification schemes such as OEKO-TEX Standard 100 and the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) have gained prominence, offering consumers assurance that certified products meet specific environmental and safety criteria. These standards often go beyond legal requirements, setting more stringent limits on chemical usage and promoting sustainable practices.
The regulatory framework also increasingly emphasizes transparency and traceability in the textile supply chain. The EU's upcoming Strategy for Sustainable Textiles, expected to be implemented in the near future, aims to establish a comprehensive set of measures to ensure textiles are designed for longevity, repairability, and recyclability, with a focus on reducing the environmental footprint of the industry.
As awareness of the environmental impact of textile manufacturing grows, regulators are likely to continue tightening restrictions on chemical usage, including artificial dyes. This evolving regulatory landscape creates both challenges and opportunities for the industry, driving innovation in sustainable textile production methods and alternative dyeing technologies.
At the international level, the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation plays a pivotal role in controlling the use of hazardous substances in textiles. REACH requires manufacturers to register chemicals used in their products and provides a mechanism for restricting or banning substances that pose significant risks to human health or the environment.
In the United States, the Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act (CPSIA) sets limits on certain chemicals in textiles, particularly those used in children's products. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also regulates the use and disposal of chemicals in textile manufacturing under various environmental laws, such as the Clean Water Act and the Toxic Substances Control Act.
Many countries have implemented their own national standards for textile safety and sustainability. For instance, China's GB standards include specific requirements for chemical content in textiles, while Japan's Law for the Control of Household Products Containing Harmful Substances regulates the use of formaldehyde and other chemicals in clothing and home textiles.
Industry-led initiatives have also contributed to the regulatory landscape. The Zero Discharge of Hazardous Chemicals (ZDHC) Programme, supported by major apparel and footwear brands, aims to eliminate hazardous chemicals from the textile supply chain. Similarly, the Sustainable Apparel Coalition's Higg Index provides tools for measuring and improving environmental performance in the apparel industry.
Certification schemes such as OEKO-TEX Standard 100 and the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) have gained prominence, offering consumers assurance that certified products meet specific environmental and safety criteria. These standards often go beyond legal requirements, setting more stringent limits on chemical usage and promoting sustainable practices.
The regulatory framework also increasingly emphasizes transparency and traceability in the textile supply chain. The EU's upcoming Strategy for Sustainable Textiles, expected to be implemented in the near future, aims to establish a comprehensive set of measures to ensure textiles are designed for longevity, repairability, and recyclability, with a focus on reducing the environmental footprint of the industry.
As awareness of the environmental impact of textile manufacturing grows, regulators are likely to continue tightening restrictions on chemical usage, including artificial dyes. This evolving regulatory landscape creates both challenges and opportunities for the industry, driving innovation in sustainable textile production methods and alternative dyeing technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!