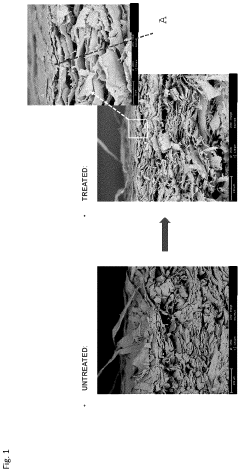
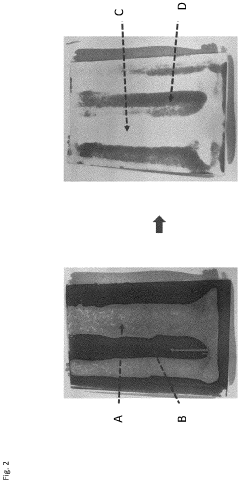
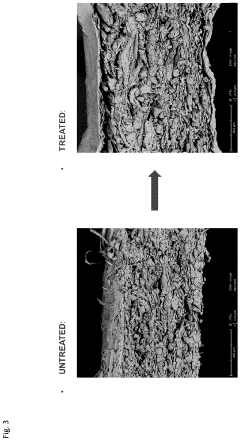
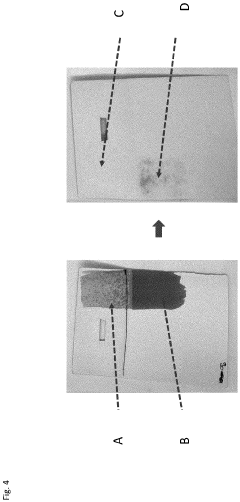
How to Enhance Recyclability of Cellophane Materials?
JUL 9, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Cellophane Recycling Background and Objectives
Cellophane, a transparent film made from regenerated cellulose, has been a staple in packaging and various industrial applications since its invention in the early 20th century. As environmental concerns grow, the focus on enhancing the recyclability of cellophane materials has become increasingly important. This technical research aims to explore the current state of cellophane recycling and identify potential avenues for improvement.
The development of cellophane technology has seen significant advancements over the years, from its initial creation as a moisture-proof coating to its widespread use in food packaging and other industries. However, the recyclability of cellophane has remained a challenge due to its unique chemical composition and manufacturing process.
The primary objective of this research is to investigate and propose innovative methods to enhance the recyclability of cellophane materials. This includes examining the current recycling processes, identifying bottlenecks, and exploring new technologies that could potentially revolutionize cellophane recycling.
One of the key areas of focus is the chemical structure of cellophane. Unlike traditional plastics, cellophane is derived from natural cellulose, which presents both advantages and challenges in terms of recycling. Understanding the molecular composition and how it affects recyclability is crucial for developing effective recycling strategies.
Another important aspect is the contamination of cellophane during its use. Many cellophane products are coated or combined with other materials to enhance their properties, which can complicate the recycling process. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach, combining chemical, mechanical, and biological methods.
The global push towards sustainable packaging solutions has created a renewed interest in cellophane as an eco-friendly alternative to petroleum-based plastics. However, to fully realize its potential as a sustainable material, significant improvements in its end-of-life management, particularly recycling, are necessary.
This research also aims to explore the economic viability of enhanced cellophane recycling. As with any recycling process, the cost-effectiveness and scalability of new technologies will play a crucial role in their adoption by the industry. Therefore, a comprehensive analysis of potential recycling methods must consider both technical feasibility and economic practicality.
By addressing these challenges and exploring innovative solutions, this research seeks to contribute to the development of more sustainable packaging materials and promote a circular economy approach to cellophane use and disposal.
The development of cellophane technology has seen significant advancements over the years, from its initial creation as a moisture-proof coating to its widespread use in food packaging and other industries. However, the recyclability of cellophane has remained a challenge due to its unique chemical composition and manufacturing process.
The primary objective of this research is to investigate and propose innovative methods to enhance the recyclability of cellophane materials. This includes examining the current recycling processes, identifying bottlenecks, and exploring new technologies that could potentially revolutionize cellophane recycling.
One of the key areas of focus is the chemical structure of cellophane. Unlike traditional plastics, cellophane is derived from natural cellulose, which presents both advantages and challenges in terms of recycling. Understanding the molecular composition and how it affects recyclability is crucial for developing effective recycling strategies.
Another important aspect is the contamination of cellophane during its use. Many cellophane products are coated or combined with other materials to enhance their properties, which can complicate the recycling process. Addressing these issues requires a multifaceted approach, combining chemical, mechanical, and biological methods.
The global push towards sustainable packaging solutions has created a renewed interest in cellophane as an eco-friendly alternative to petroleum-based plastics. However, to fully realize its potential as a sustainable material, significant improvements in its end-of-life management, particularly recycling, are necessary.
This research also aims to explore the economic viability of enhanced cellophane recycling. As with any recycling process, the cost-effectiveness and scalability of new technologies will play a crucial role in their adoption by the industry. Therefore, a comprehensive analysis of potential recycling methods must consider both technical feasibility and economic practicality.
By addressing these challenges and exploring innovative solutions, this research seeks to contribute to the development of more sustainable packaging materials and promote a circular economy approach to cellophane use and disposal.
Market Demand for Recyclable Packaging
The market demand for recyclable packaging has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. Cellophane, a biodegradable material derived from cellulose, has gained renewed interest as a potential solution for sustainable packaging. However, its recyclability remains a challenge that needs to be addressed to meet market expectations.
Consumer awareness of environmental issues has led to a significant shift in purchasing behavior, with many customers actively seeking eco-friendly packaging options. This trend has created a substantial market opportunity for recyclable cellophane materials. Major retailers and consumer goods companies have set ambitious targets to increase the use of recyclable packaging in their products, further driving demand for innovative solutions.
The food and beverage industry, in particular, has shown a strong interest in recyclable cellophane packaging. This sector accounts for a large portion of packaging waste and is under increasing pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. Cellophane's transparency, barrier properties, and potential for recyclability make it an attractive option for food packaging applications.
E-commerce growth has also contributed to the rising demand for recyclable packaging materials. As online shopping continues to expand, there is a pressing need for packaging solutions that can withstand shipping while still being environmentally friendly. Recyclable cellophane could potentially fill this gap in the market, offering both protection and sustainability.
Market research indicates that consumers are willing to pay a premium for products with recyclable packaging. This willingness to pay more has encouraged companies to invest in developing and implementing recyclable packaging solutions, including enhanced cellophane materials. The potential for brand differentiation and improved customer loyalty further incentivizes businesses to adopt recyclable packaging options.
Government regulations and initiatives aimed at reducing plastic waste have also played a crucial role in shaping market demand. Many countries have implemented or are considering policies that promote the use of recyclable and biodegradable packaging materials. These regulatory changes have created a favorable environment for the development and adoption of recyclable cellophane packaging.
Despite the growing demand, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of recyclable cellophane packaging. The current recycling infrastructure is not always equipped to handle cellophane materials effectively, which can limit their recyclability in practice. Addressing these infrastructure gaps and improving the recyclability of cellophane will be crucial to fully capitalize on the market potential.
In conclusion, the market demand for recyclable packaging, including enhanced cellophane materials, is robust and expected to continue growing. Meeting this demand will require ongoing innovation in material science and recycling technologies to overcome existing limitations and deliver truly recyclable cellophane packaging solutions.
Consumer awareness of environmental issues has led to a significant shift in purchasing behavior, with many customers actively seeking eco-friendly packaging options. This trend has created a substantial market opportunity for recyclable cellophane materials. Major retailers and consumer goods companies have set ambitious targets to increase the use of recyclable packaging in their products, further driving demand for innovative solutions.
The food and beverage industry, in particular, has shown a strong interest in recyclable cellophane packaging. This sector accounts for a large portion of packaging waste and is under increasing pressure to adopt more sustainable practices. Cellophane's transparency, barrier properties, and potential for recyclability make it an attractive option for food packaging applications.
E-commerce growth has also contributed to the rising demand for recyclable packaging materials. As online shopping continues to expand, there is a pressing need for packaging solutions that can withstand shipping while still being environmentally friendly. Recyclable cellophane could potentially fill this gap in the market, offering both protection and sustainability.
Market research indicates that consumers are willing to pay a premium for products with recyclable packaging. This willingness to pay more has encouraged companies to invest in developing and implementing recyclable packaging solutions, including enhanced cellophane materials. The potential for brand differentiation and improved customer loyalty further incentivizes businesses to adopt recyclable packaging options.
Government regulations and initiatives aimed at reducing plastic waste have also played a crucial role in shaping market demand. Many countries have implemented or are considering policies that promote the use of recyclable and biodegradable packaging materials. These regulatory changes have created a favorable environment for the development and adoption of recyclable cellophane packaging.
Despite the growing demand, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of recyclable cellophane packaging. The current recycling infrastructure is not always equipped to handle cellophane materials effectively, which can limit their recyclability in practice. Addressing these infrastructure gaps and improving the recyclability of cellophane will be crucial to fully capitalize on the market potential.
In conclusion, the market demand for recyclable packaging, including enhanced cellophane materials, is robust and expected to continue growing. Meeting this demand will require ongoing innovation in material science and recycling technologies to overcome existing limitations and deliver truly recyclable cellophane packaging solutions.
Current Challenges in Cellophane Recycling
Despite the widespread use of cellophane in packaging and various industries, its recyclability remains a significant challenge. The current recycling infrastructure is not well-equipped to handle cellophane materials effectively, leading to a substantial amount of waste ending up in landfills or incineration facilities.
One of the primary obstacles in cellophane recycling is its chemical composition. Cellophane is made from regenerated cellulose, which undergoes complex chemical processes during production. This results in a material that is difficult to break down and reprocess using conventional recycling methods. The presence of additives and coatings further complicates the recycling process, as these substances need to be separated from the base material.
The lack of established collection and sorting systems for cellophane waste poses another significant challenge. Unlike more common plastics, cellophane is often not included in standard recycling programs, leading to confusion among consumers and inefficient waste management. This absence of a dedicated recycling stream results in cellophane being mixed with other materials, making it harder to isolate and process effectively.
The economic viability of cellophane recycling is also a major hurdle. The costs associated with collecting, sorting, and processing cellophane often outweigh the potential value of the recycled material. This economic imbalance discourages investment in recycling infrastructure and technology specifically tailored for cellophane materials.
Furthermore, the quality of recycled cellophane is a concern for potential end-users. The degradation of cellulose fibers during the recycling process can lead to a loss of desirable properties, such as transparency and barrier characteristics. This reduction in quality limits the applications of recycled cellophane, making it less attractive for manufacturers and consumers alike.
The environmental impact of cellophane production and disposal is another critical issue. While cellophane is biodegradable under certain conditions, it often does not decompose efficiently in landfills or natural environments. This persistence contributes to long-term environmental pollution and underscores the need for more effective recycling solutions.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach involving technological innovation, policy changes, and consumer education. Developing new recycling technologies that can efficiently process cellophane without compromising its properties is crucial. Additionally, establishing dedicated collection and sorting systems for cellophane waste could significantly improve recycling rates. Implementing extended producer responsibility programs and incentives for using recycled cellophane could also drive positive change in the industry.
One of the primary obstacles in cellophane recycling is its chemical composition. Cellophane is made from regenerated cellulose, which undergoes complex chemical processes during production. This results in a material that is difficult to break down and reprocess using conventional recycling methods. The presence of additives and coatings further complicates the recycling process, as these substances need to be separated from the base material.
The lack of established collection and sorting systems for cellophane waste poses another significant challenge. Unlike more common plastics, cellophane is often not included in standard recycling programs, leading to confusion among consumers and inefficient waste management. This absence of a dedicated recycling stream results in cellophane being mixed with other materials, making it harder to isolate and process effectively.
The economic viability of cellophane recycling is also a major hurdle. The costs associated with collecting, sorting, and processing cellophane often outweigh the potential value of the recycled material. This economic imbalance discourages investment in recycling infrastructure and technology specifically tailored for cellophane materials.
Furthermore, the quality of recycled cellophane is a concern for potential end-users. The degradation of cellulose fibers during the recycling process can lead to a loss of desirable properties, such as transparency and barrier characteristics. This reduction in quality limits the applications of recycled cellophane, making it less attractive for manufacturers and consumers alike.
The environmental impact of cellophane production and disposal is another critical issue. While cellophane is biodegradable under certain conditions, it often does not decompose efficiently in landfills or natural environments. This persistence contributes to long-term environmental pollution and underscores the need for more effective recycling solutions.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach involving technological innovation, policy changes, and consumer education. Developing new recycling technologies that can efficiently process cellophane without compromising its properties is crucial. Additionally, establishing dedicated collection and sorting systems for cellophane waste could significantly improve recycling rates. Implementing extended producer responsibility programs and incentives for using recycled cellophane could also drive positive change in the industry.
Existing Cellophane Recycling Solutions
01 Biodegradable cellophane materials
Development of biodegradable cellophane materials that can be easily broken down in natural environments, reducing environmental impact and improving recyclability. These materials are designed to decompose into harmless substances, making them more eco-friendly alternatives to traditional cellophane.- Biodegradable cellophane materials: Development of biodegradable cellophane materials that can be easily recycled or composted. These materials are designed to break down naturally in the environment, reducing waste and environmental impact. The biodegradable properties are achieved through the use of specific additives or modifications to the cellulose structure.
- Chemical recycling of cellophane: Methods for chemically recycling cellophane materials by breaking them down into their constituent components. This process involves using solvents or chemical treatments to dissolve the cellophane, allowing for the recovery and reuse of cellulose. The recycled cellulose can then be used to produce new cellophane or other cellulose-based products.
- Mechanical recycling of cellophane: Techniques for mechanically recycling cellophane materials through processes such as shredding, grinding, and repulping. These methods aim to break down the cellophane into smaller particles or fibers that can be reprocessed into new products. The recycled material may be used in the production of packaging materials or other cellulose-based items.
- Cellophane-based composite materials: Development of composite materials that incorporate cellophane with other recyclable materials to enhance overall recyclability. These composites may combine cellophane with biodegradable plastics or other natural fibers to create materials with improved strength, flexibility, and recycling potential. The resulting products can be more easily separated and recycled at the end of their life cycle.
- Recycling systems for cellophane packaging: Design and implementation of recycling systems specifically tailored for cellophane packaging materials. These systems may include collection methods, sorting technologies, and processing facilities optimized for handling cellophane waste. The goal is to increase the efficiency of cellophane recycling and reduce the amount of material sent to landfills.
02 Chemical recycling processes for cellophane
Implementation of chemical recycling processes specifically designed for cellophane materials. These methods involve breaking down the cellophane into its chemical components, which can then be used to create new materials or products, effectively closing the recycling loop.Expand Specific Solutions03 Improved sorting and separation techniques
Development of advanced sorting and separation techniques to efficiently identify and isolate cellophane materials from mixed waste streams. This includes the use of optical sorting technologies and automated systems to enhance the recyclability of cellophane by ensuring its proper segregation from other materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cellophane-based composite materials
Creation of composite materials that incorporate cellophane with other recyclable substances, enhancing the overall recyclability of the final product. These composites are designed to maintain the desirable properties of cellophane while improving its ability to be recycled or repurposed.Expand Specific Solutions05 Eco-friendly additives for cellophane production
Incorporation of eco-friendly additives in cellophane production to enhance its recyclability without compromising its functional properties. These additives can improve the material's compatibility with existing recycling processes or facilitate its biodegradation when recycling is not feasible.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Cellophane and Recycling Industries
The recyclability of cellophane materials is a growing concern in the packaging industry, currently in its early development stage. The market for recyclable cellophane is expanding, driven by increasing environmental awareness and regulatory pressures. Technologically, the field is still evolving, with various companies exploring innovative solutions. Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd. and Seiko Epson Corp. are leveraging their expertise in materials science to develop more recyclable cellophane variants. Universities like Sichuan University and the University of Leeds are conducting research to improve the material's biodegradability. Specialized firms such as CelluComp Ltd. and Evrnu, Inc. are focusing on sustainable alternatives derived from waste streams. The collaboration between industry leaders and research institutions is accelerating progress towards enhancing cellophane recyclability.
Circulose AB
Technical Solution: Circulose AB has developed a unique chemical recycling technology that can be applied to enhance the recyclability of cellophane materials. Their process involves dissolving cellulose-based waste, including cellophane, and removing non-cellulosic content to produce a pure, high-quality dissolving pulp[1]. This pulp can then be used to create new cellulose-based materials, including improved, more recyclable versions of cellophane. The company's technology allows for the recycling of mixed cellulosic waste streams, which is particularly valuable for cellophane that may be contaminated with other materials. Circulose's process can potentially recycle cellophane multiple times without significant degradation in quality, promoting a more circular economy for cellulose-based materials[2]. Additionally, their technology can be integrated into existing production facilities, making it easier for manufacturers to adopt more sustainable practices[3].
Strengths: Ability to handle mixed waste streams, potential for multiple recycling cycles. Weaknesses: Energy-intensive process, may require significant infrastructure investment.
CelluComp Ltd.
Technical Solution: CelluComp Ltd. has developed an innovative approach to enhance the recyclability of cellophane materials through their Curran® technology. While primarily focused on creating high-performance materials from plant-based sources, their technology can be adapted to improve cellophane recyclability. The process involves extracting nanocellulose fibers from root vegetables, which can be used to reinforce cellophane materials, making them stronger and more durable while maintaining their biodegradability[1]. This enhanced durability could potentially allow for multiple use cycles before recycling becomes necessary. CelluComp's technology also focuses on creating fully biodegradable materials, which could be applied to cellophane to ensure that any non-recycled waste would decompose naturally without environmental harm[2]. The company has also been exploring the use of their nanocellulose technology in creating barrier coatings for cellulose-based materials, which could improve the functionality of cellophane while maintaining its recyclability[3].
Strengths: Improved material durability, potential for biodegradability. Weaknesses: Technology not specifically developed for cellophane, may require significant adaptation.
Innovative Approaches to Enhance Cellophane Recyclability
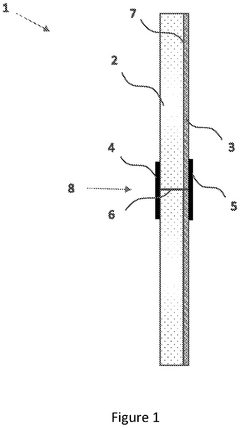
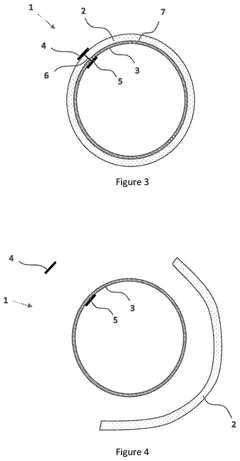
Recyclable cellulose-based substrate comprising cellulosic fibres and non-fibrous cellulosic material
PatentInactiveEP4389970A1
Innovation
- A cellulose-based substrate comprising native cellulosic fibers and non-fibrous cellulosic material is developed, where the substrate is treated with a gelatinizing agent to dissolve fibers and then subjected to a reprecipitation agent, allowing for at least 50 wt% recyclability by repulping, while maintaining properties like gas barrier and compostability.
Recyclable packaging and manufacturing method
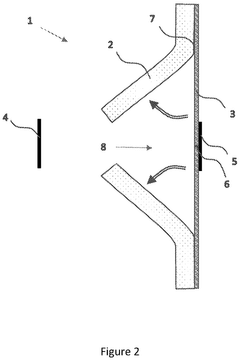
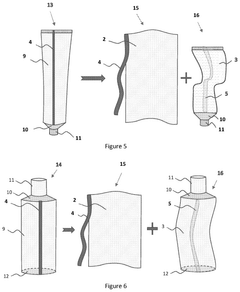
PatentPendingUS20250145337A1
Innovation
- The development of packaging with a peelable interface between structural and functional layers, allowing for easy separation and recycling. This involves using a structural layer based on cellulose and a functional layer based on recyclable plastics, with external and internal reinforcing strips to maintain packaging integrity and facilitate separation.
Environmental Impact of Cellophane Recycling
The environmental impact of cellophane recycling is a critical consideration in the quest to enhance the recyclability of cellophane materials. Cellophane, a biodegradable and compostable material derived from cellulose, presents both opportunities and challenges in terms of its environmental footprint during the recycling process.
One of the primary environmental benefits of cellophane recycling is the reduction of waste sent to landfills. By diverting cellophane from waste streams and reprocessing it, the volume of material occupying landfill space is significantly decreased. This not only conserves valuable land resources but also mitigates the release of greenhouse gases that occur during the decomposition of organic materials in landfills.
The recycling process itself, however, does have environmental implications. Energy consumption is a key factor, as the collection, sorting, and reprocessing of cellophane require substantial energy inputs. The transportation of recyclable cellophane to processing facilities contributes to carbon emissions, although this impact can be minimized through efficient logistics and the use of low-emission vehicles.
Water usage is another environmental consideration in cellophane recycling. The cleaning and decontamination of used cellophane often involve water-intensive processes. Implementing water-efficient technologies and closed-loop water systems can help mitigate this impact, ensuring responsible water management throughout the recycling chain.
Chemical treatments used in the recycling process may pose potential environmental risks if not properly managed. These chemicals, necessary for breaking down and reconstituting cellophane, must be carefully controlled to prevent soil and water pollution. Advanced treatment technologies and strict adherence to environmental regulations are essential to minimize the release of harmful substances into ecosystems.
On the positive side, recycling cellophane can lead to significant energy savings compared to the production of virgin cellophane. The reuse of cellulose fibers reduces the need for raw material extraction and processing, which are typically energy-intensive activities. This results in a lower overall carbon footprint for recycled cellophane products.
The biodegradability of cellophane presents a unique aspect in its environmental impact assessment. While this property is generally beneficial for end-of-life disposal, it can complicate recycling efforts. Ensuring that cellophane maintains its structural integrity throughout the recycling process is crucial to maximize material recovery and minimize waste.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of cellophane recycling is multifaceted, involving trade-offs between waste reduction, energy consumption, water usage, and chemical management. As technologies advance and recycling processes become more efficient, the net environmental benefit of cellophane recycling is likely to improve, contributing to more sustainable material management practices.
One of the primary environmental benefits of cellophane recycling is the reduction of waste sent to landfills. By diverting cellophane from waste streams and reprocessing it, the volume of material occupying landfill space is significantly decreased. This not only conserves valuable land resources but also mitigates the release of greenhouse gases that occur during the decomposition of organic materials in landfills.
The recycling process itself, however, does have environmental implications. Energy consumption is a key factor, as the collection, sorting, and reprocessing of cellophane require substantial energy inputs. The transportation of recyclable cellophane to processing facilities contributes to carbon emissions, although this impact can be minimized through efficient logistics and the use of low-emission vehicles.
Water usage is another environmental consideration in cellophane recycling. The cleaning and decontamination of used cellophane often involve water-intensive processes. Implementing water-efficient technologies and closed-loop water systems can help mitigate this impact, ensuring responsible water management throughout the recycling chain.
Chemical treatments used in the recycling process may pose potential environmental risks if not properly managed. These chemicals, necessary for breaking down and reconstituting cellophane, must be carefully controlled to prevent soil and water pollution. Advanced treatment technologies and strict adherence to environmental regulations are essential to minimize the release of harmful substances into ecosystems.
On the positive side, recycling cellophane can lead to significant energy savings compared to the production of virgin cellophane. The reuse of cellulose fibers reduces the need for raw material extraction and processing, which are typically energy-intensive activities. This results in a lower overall carbon footprint for recycled cellophane products.
The biodegradability of cellophane presents a unique aspect in its environmental impact assessment. While this property is generally beneficial for end-of-life disposal, it can complicate recycling efforts. Ensuring that cellophane maintains its structural integrity throughout the recycling process is crucial to maximize material recovery and minimize waste.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of cellophane recycling is multifaceted, involving trade-offs between waste reduction, energy consumption, water usage, and chemical management. As technologies advance and recycling processes become more efficient, the net environmental benefit of cellophane recycling is likely to improve, contributing to more sustainable material management practices.
Regulatory Framework for Packaging Recycling
The regulatory framework for packaging recycling plays a crucial role in enhancing the recyclability of cellophane materials. Governments worldwide are implementing increasingly stringent regulations to address the environmental impact of packaging waste, including cellophane.
In the European Union, the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (PPWD) sets targets for recycling and recovery of packaging materials. The directive requires member states to achieve specific recycling rates for different packaging materials, including plastics. This has led to the development of extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, where manufacturers are responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling.
The United States lacks a comprehensive federal framework for packaging recycling, resulting in a patchwork of state and local regulations. However, several states have implemented bottle deposit schemes and mandatory recycling programs. California's Rigid Plastic Packaging Container (RPPC) law requires manufacturers to meet specific recycling rates or use a certain percentage of recycled content in their packaging.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have implemented advanced recycling systems. Japan's Container and Packaging Recycling Law mandates that businesses and consumers share the responsibility for recycling packaging materials. South Korea's Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) system has led to significant improvements in recycling rates for various packaging materials.
Many countries are also introducing bans or taxes on single-use plastics, which indirectly affects cellophane packaging. These regulations encourage the development of more recyclable alternatives and push manufacturers to improve the recyclability of existing materials.
The regulatory landscape is evolving rapidly, with a growing focus on circular economy principles. The European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan, for instance, aims to make all packaging reusable or recyclable by 2030. This ambitious target is driving innovation in packaging design and recycling technologies.
To enhance the recyclability of cellophane materials, manufacturers must stay informed about these regulatory developments and proactively adapt their products and processes. This may involve redesigning packaging to improve recyclability, investing in new recycling technologies, or exploring alternative materials that meet regulatory requirements while maintaining the desired properties of cellophane.
In the European Union, the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive (PPWD) sets targets for recycling and recovery of packaging materials. The directive requires member states to achieve specific recycling rates for different packaging materials, including plastics. This has led to the development of extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, where manufacturers are responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling.
The United States lacks a comprehensive federal framework for packaging recycling, resulting in a patchwork of state and local regulations. However, several states have implemented bottle deposit schemes and mandatory recycling programs. California's Rigid Plastic Packaging Container (RPPC) law requires manufacturers to meet specific recycling rates or use a certain percentage of recycled content in their packaging.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have implemented advanced recycling systems. Japan's Container and Packaging Recycling Law mandates that businesses and consumers share the responsibility for recycling packaging materials. South Korea's Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) system has led to significant improvements in recycling rates for various packaging materials.
Many countries are also introducing bans or taxes on single-use plastics, which indirectly affects cellophane packaging. These regulations encourage the development of more recyclable alternatives and push manufacturers to improve the recyclability of existing materials.
The regulatory landscape is evolving rapidly, with a growing focus on circular economy principles. The European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan, for instance, aims to make all packaging reusable or recyclable by 2030. This ambitious target is driving innovation in packaging design and recycling technologies.
To enhance the recyclability of cellophane materials, manufacturers must stay informed about these regulatory developments and proactively adapt their products and processes. This may involve redesigning packaging to improve recyclability, investing in new recycling technologies, or exploring alternative materials that meet regulatory requirements while maintaining the desired properties of cellophane.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!