How to Enhance Technological Applications with PTFE?
JUN 27, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PTFE Tech Evolution
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has undergone significant technological evolution since its accidental discovery in 1938. Initially developed as a byproduct of refrigerant research, PTFE's unique properties quickly garnered attention across various industries. The material's journey from a laboratory curiosity to a versatile industrial staple spans several decades, marked by continuous improvements in synthesis, processing, and application techniques.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the focus was primarily on refining PTFE production methods to enhance purity and consistency. This period saw the development of suspension polymerization techniques, which allowed for better control over particle size and distribution. The 1970s brought about advancements in PTFE modification, including the introduction of filled PTFE compounds that expanded its mechanical and thermal properties.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed a surge in PTFE's application diversity. Researchers explored ways to overcome its inherent limitations, such as poor wear resistance and difficulty in bonding. This led to the development of modified PTFE grades with improved mechanical properties and the introduction of etching techniques to enhance adhesion capabilities. Concurrently, the medical industry began to recognize PTFE's potential, leading to its widespread use in implants and surgical materials.
The turn of the millennium marked a new era in PTFE technology, characterized by nanotechnology integration and eco-friendly production methods. Researchers began exploring PTFE nanocomposites, which offered enhanced mechanical and thermal properties while maintaining the material's core benefits. Additionally, efforts to develop more sustainable production processes gained momentum, addressing environmental concerns associated with traditional PTFE manufacturing.
Recent years have seen a focus on expanding PTFE's functional capabilities. Innovations in surface modification techniques have opened up new possibilities for PTFE in areas such as self-cleaning surfaces and advanced filtration systems. The development of PTFE-based membranes with controlled porosity has revolutionized applications in water treatment and fuel cell technology.
Looking ahead, the evolution of PTFE technology is poised to continue its trajectory of innovation. Emerging trends include the development of bio-based PTFE alternatives, further advancements in nanocomposite formulations, and the exploration of PTFE's potential in cutting-edge fields such as quantum computing and space exploration. As researchers continue to push the boundaries of what's possible with this remarkable material, PTFE's role in technological applications is set to expand and diversify even further.
In the 1950s and 1960s, the focus was primarily on refining PTFE production methods to enhance purity and consistency. This period saw the development of suspension polymerization techniques, which allowed for better control over particle size and distribution. The 1970s brought about advancements in PTFE modification, including the introduction of filled PTFE compounds that expanded its mechanical and thermal properties.
The 1980s and 1990s witnessed a surge in PTFE's application diversity. Researchers explored ways to overcome its inherent limitations, such as poor wear resistance and difficulty in bonding. This led to the development of modified PTFE grades with improved mechanical properties and the introduction of etching techniques to enhance adhesion capabilities. Concurrently, the medical industry began to recognize PTFE's potential, leading to its widespread use in implants and surgical materials.
The turn of the millennium marked a new era in PTFE technology, characterized by nanotechnology integration and eco-friendly production methods. Researchers began exploring PTFE nanocomposites, which offered enhanced mechanical and thermal properties while maintaining the material's core benefits. Additionally, efforts to develop more sustainable production processes gained momentum, addressing environmental concerns associated with traditional PTFE manufacturing.
Recent years have seen a focus on expanding PTFE's functional capabilities. Innovations in surface modification techniques have opened up new possibilities for PTFE in areas such as self-cleaning surfaces and advanced filtration systems. The development of PTFE-based membranes with controlled porosity has revolutionized applications in water treatment and fuel cell technology.
Looking ahead, the evolution of PTFE technology is poised to continue its trajectory of innovation. Emerging trends include the development of bio-based PTFE alternatives, further advancements in nanocomposite formulations, and the exploration of PTFE's potential in cutting-edge fields such as quantum computing and space exploration. As researchers continue to push the boundaries of what's possible with this remarkable material, PTFE's role in technological applications is set to expand and diversify even further.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) applications has been steadily growing across various industries due to its unique properties and versatile nature. PTFE's exceptional chemical resistance, low friction coefficient, and high-temperature stability make it an attractive material for numerous technological applications.
In the automotive sector, there is a rising demand for PTFE-based components to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. PTFE coatings on engine parts help reduce friction, leading to improved performance and longevity. The aerospace industry also shows significant interest in PTFE applications, particularly for lightweight and durable components in aircraft and spacecraft.
The electronics industry has seen a surge in demand for PTFE-based materials in printed circuit boards and semiconductor manufacturing. PTFE's excellent dielectric properties and thermal stability make it ideal for high-frequency applications and miniaturization of electronic devices.
In the medical field, PTFE's biocompatibility and non-stick properties have led to increased adoption in implants, surgical instruments, and drug delivery systems. The growing emphasis on minimally invasive procedures and advanced medical technologies is driving the demand for PTFE-enhanced medical devices.
The chemical processing industry continues to be a major consumer of PTFE products, particularly in the form of linings for tanks, pipes, and valves. The material's resistance to corrosive chemicals and high temperatures makes it indispensable in harsh industrial environments.
The renewable energy sector, especially solar and wind power, is emerging as a new market for PTFE applications. PTFE-based materials are being used in photovoltaic panels and wind turbine components to improve efficiency and durability in challenging environmental conditions.
Consumer goods manufacturers are also exploring PTFE enhancements for products ranging from non-stick cookware to waterproof textiles. The growing consumer awareness of eco-friendly and durable products is driving innovation in PTFE-based consumer applications.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the global PTFE market in the range of 5-6% over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the expanding applications in emerging technologies and the continuous development of new PTFE grades with enhanced properties.
However, challenges such as the high cost of PTFE production and environmental concerns related to fluoropolymers may impact market growth. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to address these issues and explore more sustainable production methods.
In the automotive sector, there is a rising demand for PTFE-based components to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. PTFE coatings on engine parts help reduce friction, leading to improved performance and longevity. The aerospace industry also shows significant interest in PTFE applications, particularly for lightweight and durable components in aircraft and spacecraft.
The electronics industry has seen a surge in demand for PTFE-based materials in printed circuit boards and semiconductor manufacturing. PTFE's excellent dielectric properties and thermal stability make it ideal for high-frequency applications and miniaturization of electronic devices.
In the medical field, PTFE's biocompatibility and non-stick properties have led to increased adoption in implants, surgical instruments, and drug delivery systems. The growing emphasis on minimally invasive procedures and advanced medical technologies is driving the demand for PTFE-enhanced medical devices.
The chemical processing industry continues to be a major consumer of PTFE products, particularly in the form of linings for tanks, pipes, and valves. The material's resistance to corrosive chemicals and high temperatures makes it indispensable in harsh industrial environments.
The renewable energy sector, especially solar and wind power, is emerging as a new market for PTFE applications. PTFE-based materials are being used in photovoltaic panels and wind turbine components to improve efficiency and durability in challenging environmental conditions.
Consumer goods manufacturers are also exploring PTFE enhancements for products ranging from non-stick cookware to waterproof textiles. The growing consumer awareness of eco-friendly and durable products is driving innovation in PTFE-based consumer applications.
Market analysts project a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the global PTFE market in the range of 5-6% over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the expanding applications in emerging technologies and the continuous development of new PTFE grades with enhanced properties.
However, challenges such as the high cost of PTFE production and environmental concerns related to fluoropolymers may impact market growth. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to address these issues and explore more sustainable production methods.
PTFE Tech Challenges
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has been a revolutionary material in various technological applications due to its unique properties. However, as with any advanced material, PTFE faces several challenges that limit its full potential in certain applications. One of the primary challenges is its poor adhesion to other materials, which can restrict its use in composite structures or multi-layer systems. This inherent non-stick property, while beneficial in many scenarios, becomes a significant hurdle when bonding or coating is required.
Another major challenge lies in PTFE's relatively low mechanical strength and wear resistance compared to some other engineering plastics. This limitation can affect its long-term performance in high-stress or high-wear applications, necessitating frequent replacements or reinforcements. The material's creep behavior under sustained loads also poses challenges in applications requiring dimensional stability over extended periods.
The processing of PTFE presents its own set of challenges. Its high melting point and high melt viscosity make conventional thermoplastic processing methods ineffective. This necessitates specialized sintering processes, which can be energy-intensive and time-consuming, potentially increasing production costs and limiting mass production capabilities.
PTFE's thermal expansion characteristics, while advantageous in some applications, can be problematic in others. The material's relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion can lead to dimensional instability in precision components, especially in environments with significant temperature fluctuations. This challenge becomes particularly acute in applications where PTFE interfaces with materials having different thermal expansion properties.
From an environmental perspective, PTFE faces scrutiny due to concerns about the persistence of fluoropolymers in the environment and the potential health impacts of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), which was historically used in its production. While PFOA-free production methods have been developed, addressing these environmental concerns remains an ongoing challenge for the industry.
The electrical properties of PTFE, while excellent for many applications, can be a limitation in others. Its high dielectric strength and low dielectric constant, while ideal for insulation, can be problematic in applications requiring controlled electrical conductivity or electrostatic discharge properties. Modifying these properties without compromising other beneficial characteristics of PTFE remains a significant technical challenge.
Enhancing the performance of PTFE in extreme conditions, such as cryogenic temperatures or highly corrosive environments, presents another set of challenges. While PTFE generally performs well in these conditions, there is ongoing research to push its limits further, particularly in aerospace and chemical processing industries where material performance under extreme conditions is critical.
Another major challenge lies in PTFE's relatively low mechanical strength and wear resistance compared to some other engineering plastics. This limitation can affect its long-term performance in high-stress or high-wear applications, necessitating frequent replacements or reinforcements. The material's creep behavior under sustained loads also poses challenges in applications requiring dimensional stability over extended periods.
The processing of PTFE presents its own set of challenges. Its high melting point and high melt viscosity make conventional thermoplastic processing methods ineffective. This necessitates specialized sintering processes, which can be energy-intensive and time-consuming, potentially increasing production costs and limiting mass production capabilities.
PTFE's thermal expansion characteristics, while advantageous in some applications, can be problematic in others. The material's relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion can lead to dimensional instability in precision components, especially in environments with significant temperature fluctuations. This challenge becomes particularly acute in applications where PTFE interfaces with materials having different thermal expansion properties.
From an environmental perspective, PTFE faces scrutiny due to concerns about the persistence of fluoropolymers in the environment and the potential health impacts of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), which was historically used in its production. While PFOA-free production methods have been developed, addressing these environmental concerns remains an ongoing challenge for the industry.
The electrical properties of PTFE, while excellent for many applications, can be a limitation in others. Its high dielectric strength and low dielectric constant, while ideal for insulation, can be problematic in applications requiring controlled electrical conductivity or electrostatic discharge properties. Modifying these properties without compromising other beneficial characteristics of PTFE remains a significant technical challenge.
Enhancing the performance of PTFE in extreme conditions, such as cryogenic temperatures or highly corrosive environments, presents another set of challenges. While PTFE generally performs well in these conditions, there is ongoing research to push its limits further, particularly in aerospace and chemical processing industries where material performance under extreme conditions is critical.
Current PTFE Solutions
01 PTFE manufacturing processes
Various methods for producing PTFE are described, including polymerization techniques, extrusion processes, and molding methods. These processes aim to improve the quality, efficiency, and properties of the resulting PTFE materials.- PTFE manufacturing processes: Various methods for producing PTFE are described, including polymerization techniques, extrusion processes, and molding methods. These processes aim to improve the quality, consistency, and properties of PTFE products for different applications.
- PTFE composites and blends: The development of PTFE composites and blends with other materials to enhance specific properties such as wear resistance, thermal conductivity, or mechanical strength. These combinations create materials with improved performance for specialized applications.
- Surface modification of PTFE: Techniques for modifying the surface of PTFE to improve its adhesion, wettability, or compatibility with other materials. These modifications can include chemical treatments, plasma treatments, or the application of coatings to enhance PTFE's functionality in various applications.
- PTFE in membrane technology: The use of PTFE in the development of high-performance membranes for filtration, separation, and other applications. These membranes leverage PTFE's unique properties such as chemical resistance and hydrophobicity to create efficient and durable filtration systems.
- PTFE recycling and sustainability: Methods for recycling and reprocessing PTFE materials to improve sustainability and reduce waste. These processes aim to recover and reuse PTFE from end-of-life products or manufacturing scrap, contributing to a more circular economy for fluoropolymers.
02 PTFE composites and blends
The development of PTFE composites and blends with other materials to enhance specific properties such as wear resistance, thermal conductivity, or mechanical strength. These combinations aim to create materials with improved performance for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Surface modification of PTFE
Techniques for modifying the surface of PTFE to improve its adhesion, wettability, or compatibility with other materials. These modifications can include chemical treatments, plasma treatments, or the application of coatings to enhance PTFE's functionality in specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 PTFE in membrane and filtration applications
The use of PTFE in the development of membranes and filtration systems, leveraging its non-stick and chemical-resistant properties. These applications can include water treatment, gas separation, or industrial filtration processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 PTFE in electronic and electrical applications
The incorporation of PTFE in electronic and electrical components due to its excellent dielectric properties and thermal stability. This can include its use in insulation, printed circuit boards, or high-frequency applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key PTFE Players
The technological applications of PTFE are in a mature stage, with a well-established market and significant industry players. The global PTFE market size is substantial, estimated to reach over $4 billion by 2027, driven by increasing demand in various sectors such as automotive, electronics, and industrial applications. Key companies like W. L. Gore & Associates, DAIKIN INDUSTRIES, and AGC, Inc. are at the forefront of PTFE innovation, focusing on enhancing its properties and expanding its applications. Research institutions such as Zhejiang University and Ghent University are contributing to advancements in PTFE technology, particularly in areas like membrane development and surface modification, indicating ongoing efforts to improve and diversify PTFE applications.
W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc.
Technical Solution: W. L. Gore & Associates has developed advanced PTFE-based technologies to enhance various applications. Their ePTFE (expanded PTFE) technology offers a microporous structure with high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent chemical resistance[1]. They have applied this in diverse fields, including medical devices, fabrics, and industrial components. For instance, their GORE-TEX fabrics utilize ePTFE membranes to create waterproof yet breathable materials[2]. In electronics, Gore's PTFE-based cable and wire insulation provides high-frequency signal transmission with minimal loss[3]. They've also developed PTFE-based filtration membranes for industrial processes, offering superior chemical resistance and durability[4].
Strengths: Versatile applications across multiple industries, proprietary ePTFE technology, high-performance products. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to traditional materials, potential environmental concerns due to PFAS content.
DAIKIN INDUSTRIES Ltd.
Technical Solution: Daikin has developed innovative PTFE-based solutions to enhance technological applications. Their NEOFLON PTFE series offers high thermal stability, excellent chemical resistance, and low friction properties[1]. Daikin has applied this technology in various fields, including automotive, electronics, and industrial coatings. For semiconductor manufacturing, they've created PTFE-based materials that provide contamination-free environments crucial for chip production[2]. In the automotive sector, Daikin's PTFE compounds are used in fuel system components, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions[3]. They've also developed water-repellent coatings using PTFE technology for electronic devices, enhancing durability and performance[4].
Strengths: Wide range of PTFE grades for specific applications, strong presence in Asian markets, continuous innovation in PTFE technology. Weaknesses: Potential regulatory challenges due to environmental concerns about fluoropolymers, competition from alternative materials.
PTFE Core Innovations
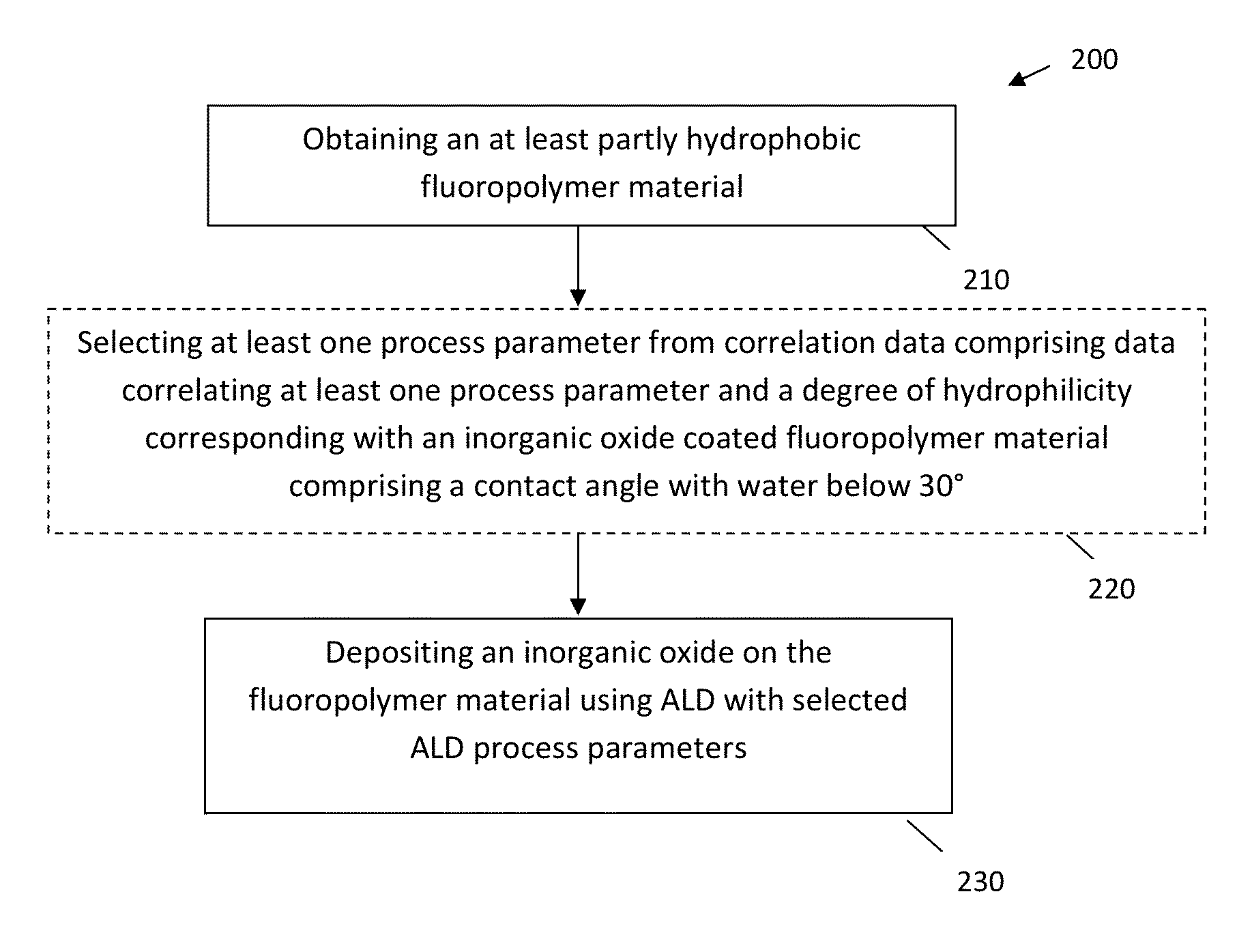
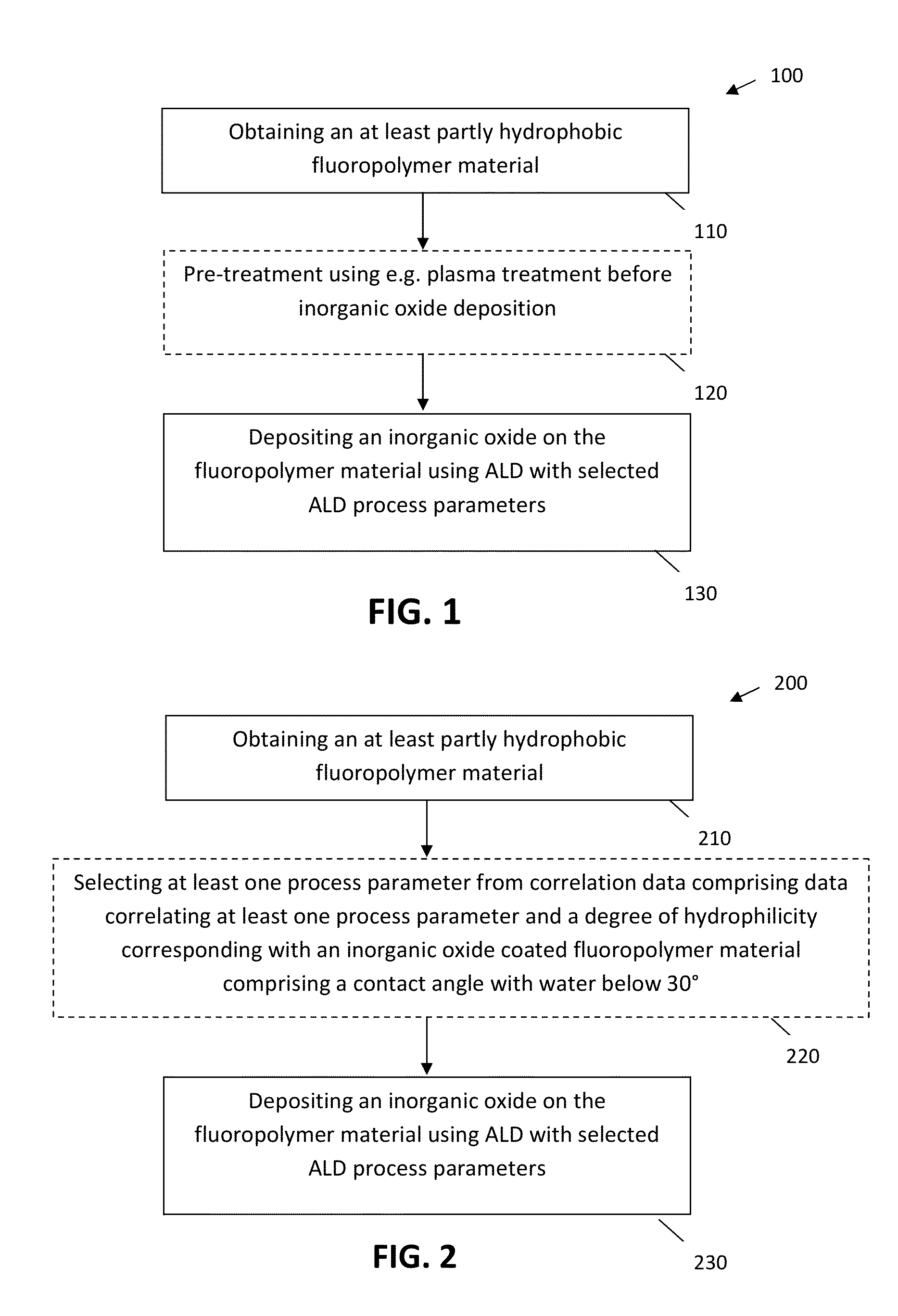
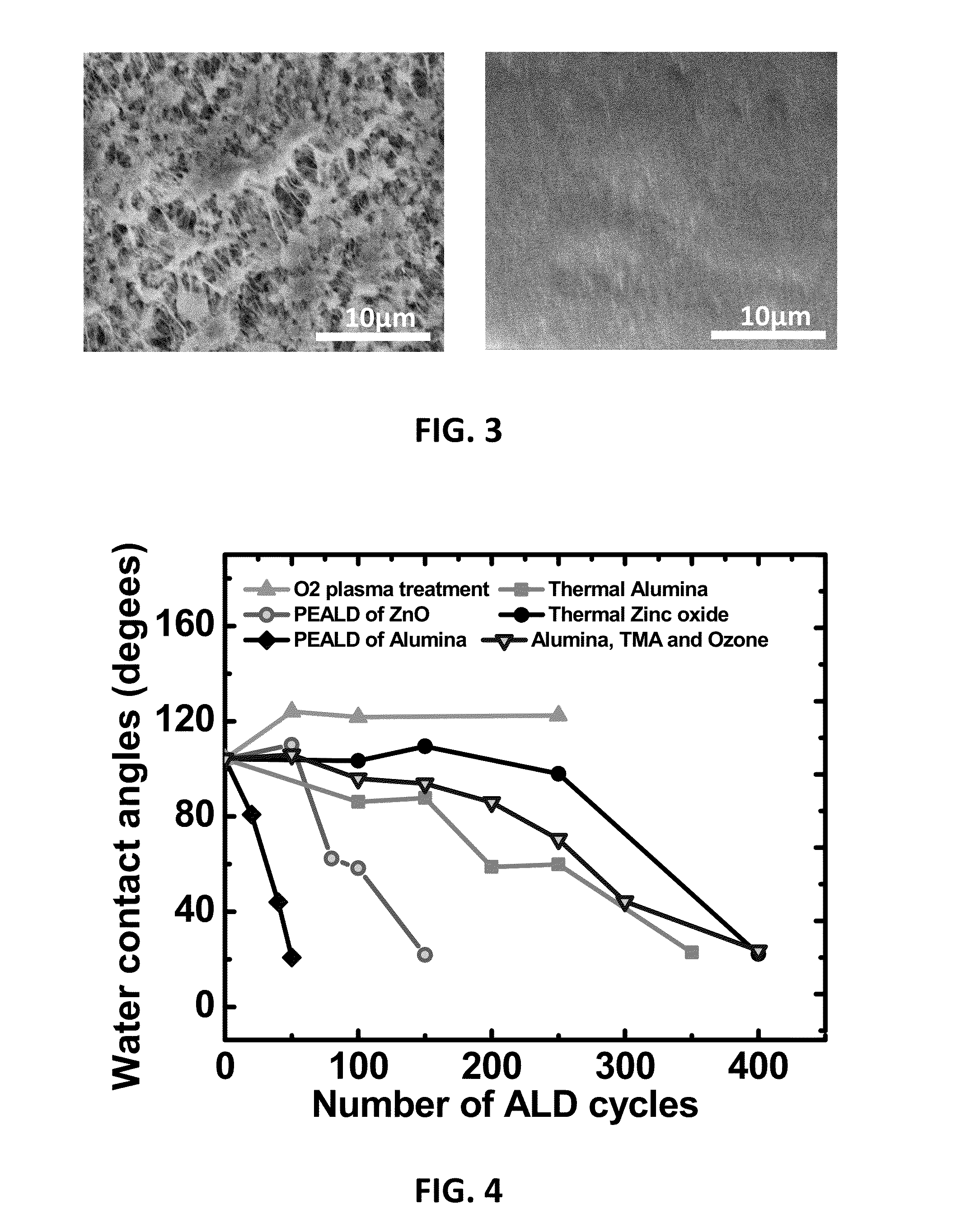
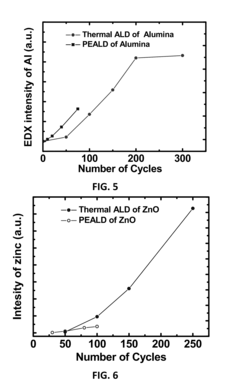
Methods for Obtaining Hydrophilic Fluoropolymers
PatentInactiveUS20150345018A1
Innovation
- A method involving plasma and/or ozon activation followed by atomic layer deposition of an inorganic coating, such as Al2O3 or ZnO, to achieve a water contact angle below 30°, allowing for selective hydrophilic tuning of fluoropolymer substrates without additional processing steps like UV irradiation, and ensuring good adhesion properties.
Expandable Functional TFE Copolymer Fine Powder, the Expandable Functional Products Obtained Therefrom and Reaction of the Expanded Products
PatentActiveUS20100248324A1
Innovation
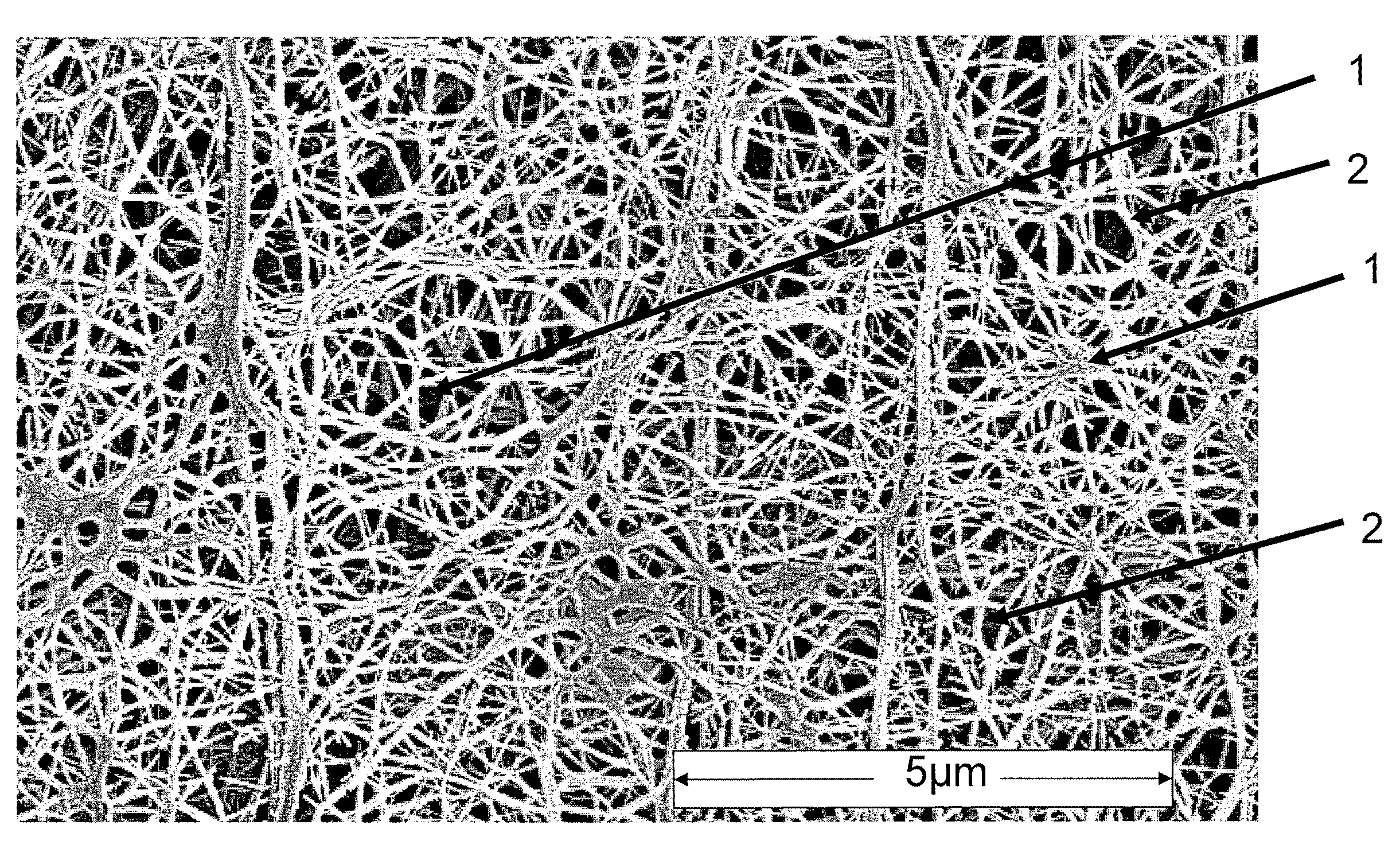
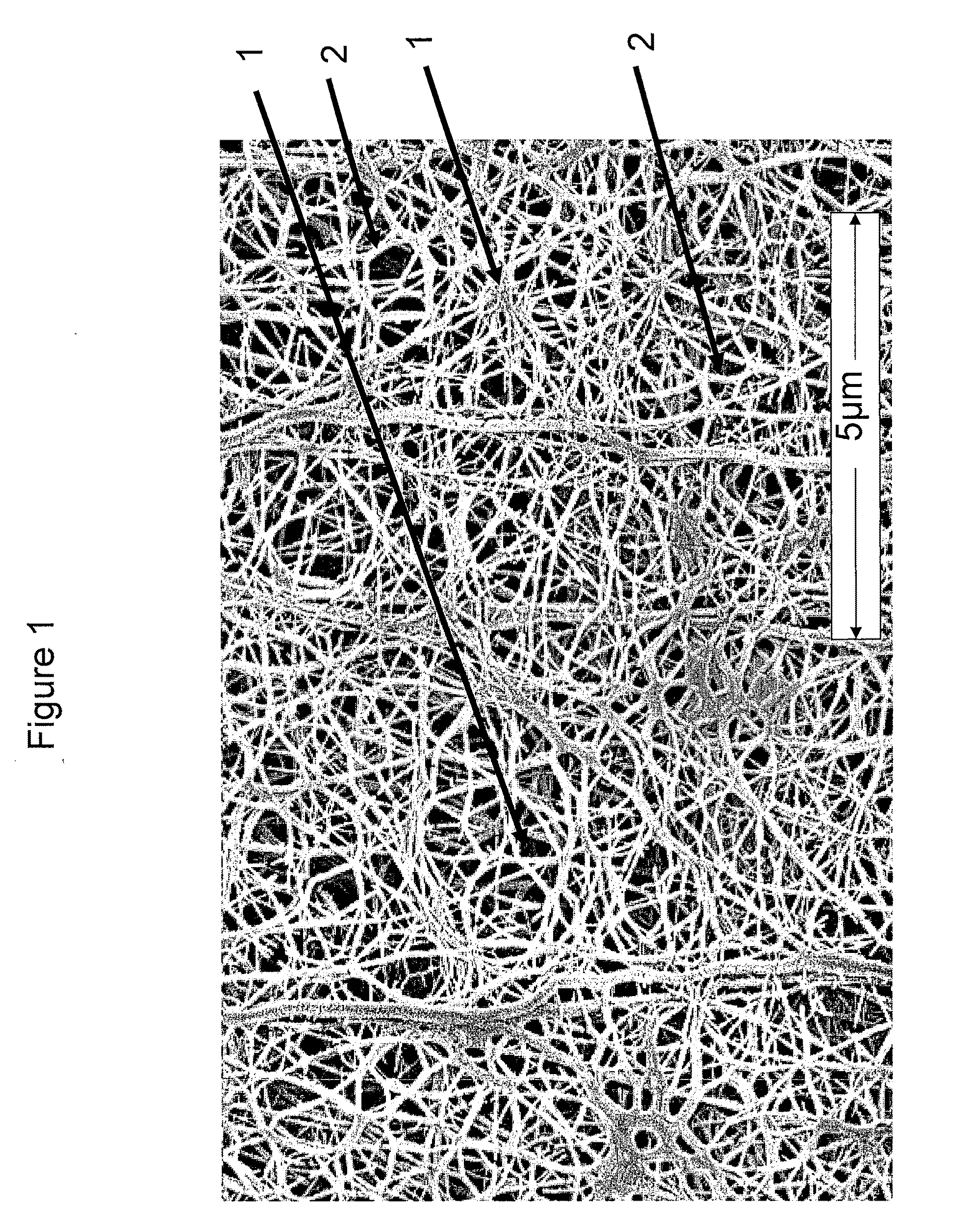
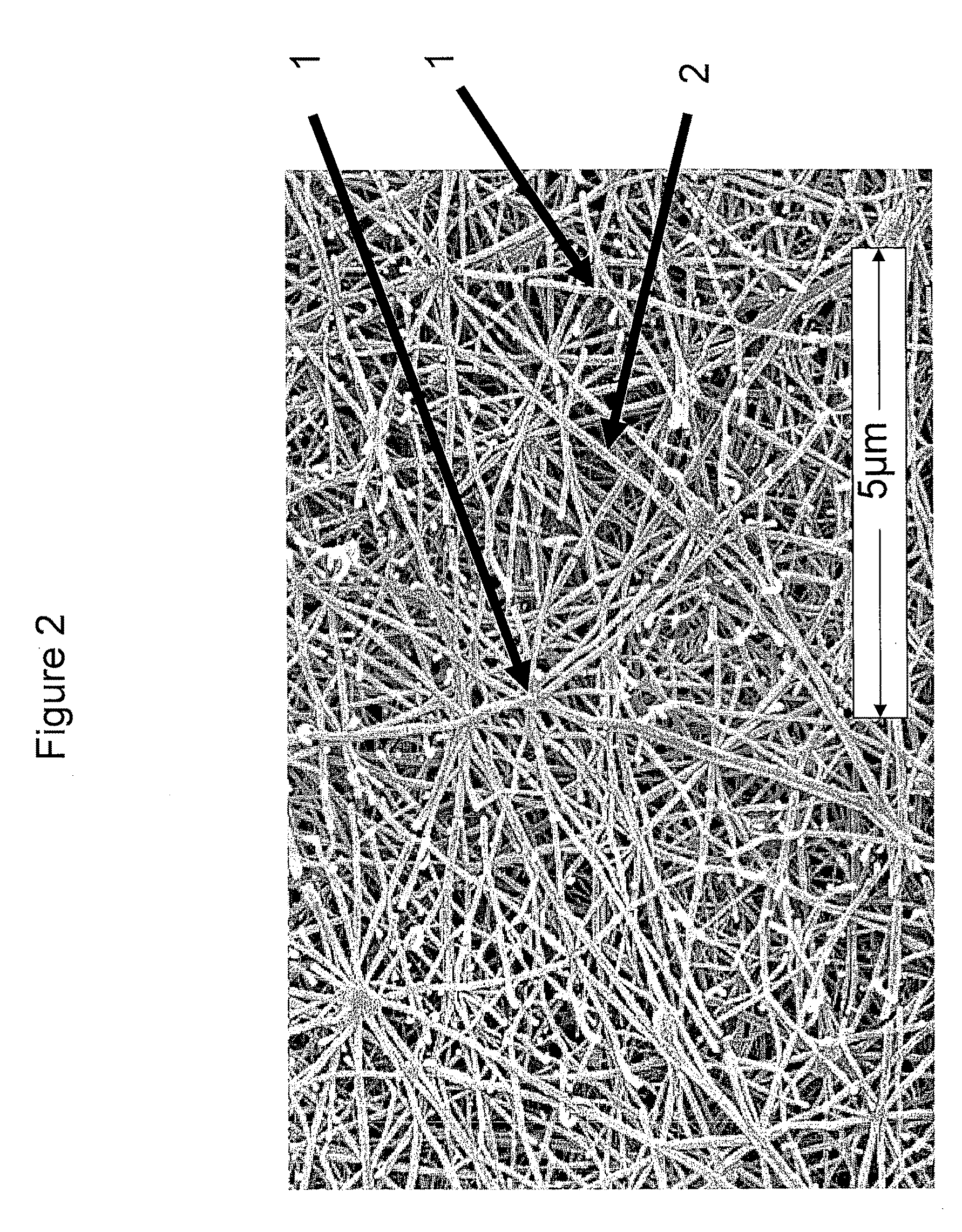
- Functional TFE copolymers are produced through an aqueous dispersion polymerization process, incorporating comonomers with pendant functional groups that are integrated into the polymer chain, enabling expansion into microporous structures with nodes interconnected by fibrils, and subsequent chemical reactions to modify properties.
PTFE Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a critical consideration in its technological applications. While PTFE offers numerous benefits in various industries, its production and disposal processes raise significant environmental concerns.
PTFE manufacturing involves the use of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), a persistent organic pollutant. PFOA has been linked to various health issues and environmental contamination. It can persist in the environment for extended periods, accumulating in living organisms and potentially causing long-term ecological damage. Efforts to phase out PFOA in PTFE production have led to the development of alternative manufacturing processes, but these alternatives may still have environmental implications that require further study.
The durability and chemical resistance of PTFE, while advantageous in many applications, contribute to its environmental persistence. PTFE products do not biodegrade easily, leading to accumulation in landfills and potential leaching of harmful compounds into soil and water systems. This persistence raises concerns about long-term environmental impacts and the potential for microplastic pollution.
Incineration of PTFE waste can release harmful substances, including hydrogen fluoride and other toxic gases. These emissions can contribute to air pollution and pose health risks to nearby communities. Proper disposal and recycling of PTFE products are essential to mitigate these environmental hazards, but current recycling technologies for PTFE are limited and often energy-intensive.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research aims to improve the environmental profile of PTFE. Efforts include developing more eco-friendly production methods, exploring biodegradable alternatives, and enhancing recycling technologies. Some manufacturers are investigating the use of renewable resources in PTFE production to reduce its carbon footprint.
The application of PTFE in certain technologies can indirectly contribute to environmental protection. For instance, its use in fuel-efficient engines and renewable energy systems can help reduce overall carbon emissions. Additionally, PTFE's non-stick properties can reduce the need for harmful cleaning chemicals in various industrial processes.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, the PTFE industry faces pressure to innovate and adapt. This has led to increased investment in research and development focused on sustainable PTFE alternatives and improved lifecycle management. The future of PTFE in technological applications will likely depend on balancing its unique properties with enhanced environmental performance.
PTFE manufacturing involves the use of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), a persistent organic pollutant. PFOA has been linked to various health issues and environmental contamination. It can persist in the environment for extended periods, accumulating in living organisms and potentially causing long-term ecological damage. Efforts to phase out PFOA in PTFE production have led to the development of alternative manufacturing processes, but these alternatives may still have environmental implications that require further study.
The durability and chemical resistance of PTFE, while advantageous in many applications, contribute to its environmental persistence. PTFE products do not biodegrade easily, leading to accumulation in landfills and potential leaching of harmful compounds into soil and water systems. This persistence raises concerns about long-term environmental impacts and the potential for microplastic pollution.
Incineration of PTFE waste can release harmful substances, including hydrogen fluoride and other toxic gases. These emissions can contribute to air pollution and pose health risks to nearby communities. Proper disposal and recycling of PTFE products are essential to mitigate these environmental hazards, but current recycling technologies for PTFE are limited and often energy-intensive.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research aims to improve the environmental profile of PTFE. Efforts include developing more eco-friendly production methods, exploring biodegradable alternatives, and enhancing recycling technologies. Some manufacturers are investigating the use of renewable resources in PTFE production to reduce its carbon footprint.
The application of PTFE in certain technologies can indirectly contribute to environmental protection. For instance, its use in fuel-efficient engines and renewable energy systems can help reduce overall carbon emissions. Additionally, PTFE's non-stick properties can reduce the need for harmful cleaning chemicals in various industrial processes.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, the PTFE industry faces pressure to innovate and adapt. This has led to increased investment in research and development focused on sustainable PTFE alternatives and improved lifecycle management. The future of PTFE in technological applications will likely depend on balancing its unique properties with enhanced environmental performance.
PTFE Industry Standards
PTFE industry standards play a crucial role in ensuring the quality, safety, and consistency of PTFE products across various applications. These standards are developed and maintained by international organizations such as ASTM International, ISO, and DIN, as well as regional bodies like JIS in Japan and GB in China.
ASTM International has established several key standards for PTFE, including ASTM D4894 for molding and extrusion materials, and ASTM D4895 for compression molding materials. These standards define specific requirements for physical properties, chemical composition, and performance characteristics of PTFE resins and products.
ISO standards also provide comprehensive guidelines for PTFE materials and products. ISO 13000 series, particularly ISO 13000-1 and ISO 13000-2, cover the classification and specifications of PTFE sheets, rods, and tubes. These standards ensure that PTFE products meet specific dimensional tolerances, mechanical properties, and thermal stability requirements.
In the European market, DIN standards are widely recognized. DIN EN ISO 12086 focuses on the determination of tensile properties of PTFE materials, while DIN EN ISO 4589 addresses the oxygen index test method for flammability assessment of PTFE products.
Industry standards also extend to specific PTFE applications. For instance, FDA regulations in the United States provide guidelines for the use of PTFE in food contact materials, ensuring safety and compliance in the food processing industry. Similarly, standards like SAE AS8049 govern the use of PTFE in aerospace applications, specifying requirements for seals and gaskets.
To enhance technological applications with PTFE, adherence to these industry standards is essential. Manufacturers and researchers must consider these standards during product development, quality control, and performance testing. By aligning with established standards, PTFE products can achieve consistent quality, improved reliability, and broader market acceptance.
Furthermore, ongoing research and development efforts in PTFE technology often lead to the revision and creation of new standards. This continuous evolution ensures that industry standards keep pace with technological advancements, enabling the development of innovative PTFE applications while maintaining high quality and safety standards.
ASTM International has established several key standards for PTFE, including ASTM D4894 for molding and extrusion materials, and ASTM D4895 for compression molding materials. These standards define specific requirements for physical properties, chemical composition, and performance characteristics of PTFE resins and products.
ISO standards also provide comprehensive guidelines for PTFE materials and products. ISO 13000 series, particularly ISO 13000-1 and ISO 13000-2, cover the classification and specifications of PTFE sheets, rods, and tubes. These standards ensure that PTFE products meet specific dimensional tolerances, mechanical properties, and thermal stability requirements.
In the European market, DIN standards are widely recognized. DIN EN ISO 12086 focuses on the determination of tensile properties of PTFE materials, while DIN EN ISO 4589 addresses the oxygen index test method for flammability assessment of PTFE products.
Industry standards also extend to specific PTFE applications. For instance, FDA regulations in the United States provide guidelines for the use of PTFE in food contact materials, ensuring safety and compliance in the food processing industry. Similarly, standards like SAE AS8049 govern the use of PTFE in aerospace applications, specifying requirements for seals and gaskets.
To enhance technological applications with PTFE, adherence to these industry standards is essential. Manufacturers and researchers must consider these standards during product development, quality control, and performance testing. By aligning with established standards, PTFE products can achieve consistent quality, improved reliability, and broader market acceptance.
Furthermore, ongoing research and development efforts in PTFE technology often lead to the revision and creation of new standards. This continuous evolution ensures that industry standards keep pace with technological advancements, enabling the development of innovative PTFE applications while maintaining high quality and safety standards.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!